Circulatory System Review
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to the circulatory system, facilitating focused review and study.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Circulatory System
A system that transports nutrients, gases, waste products, and more throughout the body.
Purpose of circulatory system
Transports
Blood clotting factors
chemical messengers
antibodies
temperature balance
Animals without a circulatory system
sponge
Hydra
Flatworms
Animals without a circulatory system (sponge)
have the simplest form of a circulatory system, water currents bring in nutrients and release waste
Animals without a circulatory system (hydra)
Have the simplest form of a circulatory system, water currents bring in nutrients and release waste
Animals without a circulatory system (Flatworms)
Have a very thin body, dont have circulatory system as they are very thin and can easily do gas diffusion
Diffusion
The process by which substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Open Circulatory System
A system where blood is pumped by a heart and empties into an open fluid space, mixing with interstitial fluid to form hemolymph.
Closed Circulatory System
A system where blood circulates in a continuous loop through a network of vessels.
Hemolymph
A fluid in invertebrates, comparable to blood, that transports nutrients and waste. blood + intestitial fluid = hemolymph
Is a major O2 transporter in invertebrates
Not bout to blood cells
Oxygenation causes color changes
Color of deoxygenated blood
Colorless Cu (I)
Color of oxygenated blood
Blue Cu(II)
Functions of insect hemolymph
transports nutrient, hormones, waste products and immune molecules
works in heat transfer
Hydraulic skeleton especially in larvae
Common elements of a closed circulatory system
a fluid
A pump
Vessels
Systolic Pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart beats and pumps blood.
Diastolic Pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Who uses a closed circulatory system?
All vertebrates and some invertebrates
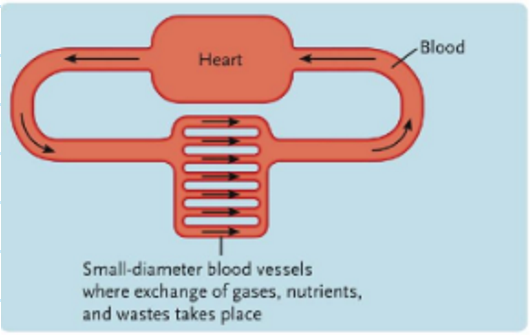
What kind of circulatory system is this?
Closed circulatory system
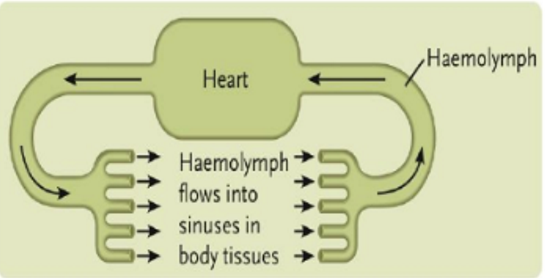
What kind of circulatory system is this?
Open circulatory system
Single circulation
A type of circulatory system where blood flows in one loop, typically found in fish, where blood passes through the heart once for each complete circuit.
Parallel circulation
A circulatory system where blood is distributed through multiple circuits, allowing for different oxygenation levels and pressures. Common in some amphibians and most mammals.
Double circulation
A type of circulatory system in which blood flows through two separate circuits: one for oxygenating blood in the lungs and the other for delivering oxygenated blood to the body. This system is found in birds and mammals.
Fish circulatory system
Undivided, blood is oxygenated before entering the body. Has a higher blood pressure than in an open system. Two chambered heart (bottom ventricle and top atrium)
What are the two parts of a fish circulatory system
Bottom ventricle and top atrium
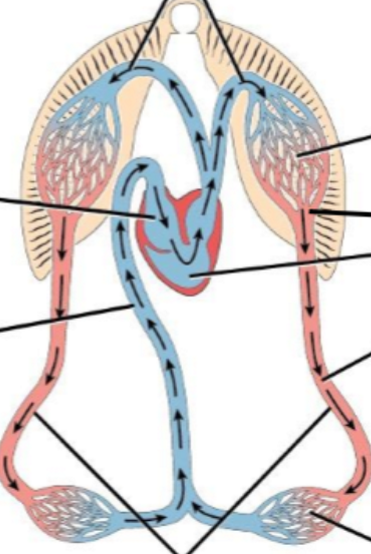
What animal uses this kind of circulatory system
Fish
Amphibian and reptile circulatory system
partially divided, blood is oxygenated before going to the body.
One pump means that there is one blood pressure
Three chambers
left atrium
right atrium
ventricle
What are the three chambers of the amphibian and reptile circulatory system
Left atrium, right atrium, ventricle
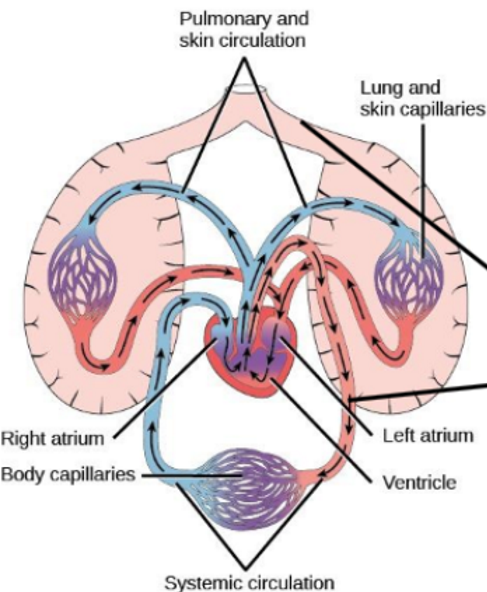
What animal uses this kind of circulatory system
Amphibians and most reptiles
Crocodiles, birds and mammals circulatory system
Completely divided (double circuit)
Blood is oxygenated first
there is two pump meaning that there is two blood pressures
There four chambers
The left side of the heart always deals with the oxygenated blood (the pulmonary circuit)
What are the two circuits of the mammalian heart
Pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit
Pulmonary circuit
The right heart, regulates between the heart and the lung
Systemic circuit
Left heart, regulates the blood flow between the heart and the rest of the body.
Valves
Valves work based on pressure. When pressure is greater behind the valve it opens, when pressure is greater in front of the valve it closes. Left side of the septum is thicker in the muscles as it requires more force for contraction.
Cardiac Cycle
The sequence of events in one heartbeat, including contraction and relaxation phases.
Neurogenic hearts
In some crustaceans, beats under the control of the nervous system
Myogenic hearts
All other animals (not crustaceans) contractions are initiated within the heart
Systolic pressure
The contraction of ventricles pushes blood into the arteries at peak pressure. contraction
Diastolic pressure
Between contractions when the blood pressure in the arteries falls to a minimum pressure. Relaxation
Order of contraction
Both atria go first followed by both ventricles
Cardiac conduction
Heart has a rhythmical electrical activity. The source of the electrical activity is a network of specialized cardiac muscle fibers called auto-rhythmic fibers
auto-rhythmic fibers
generate electrical impulses to regulate heartbeats. They are self excitable, generate action potentials act as a pacemaker setting the rhythm of the heart, and transmits electric signals through the heart
Cardiac muscle action potential
A stimulation opens the Na gates and Na enters the cell. This causes the cell depolarization. This causes the Na concentration goes down and K channels to open, allowing K to exit the cell, leading to repolarization. Causing the K concentration to increase
Pacemaker
A specialized cardiac muscle fiber that initiates and regulates heart contractions.
Electrocardiography
is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on the skin. It helps diagnose various heart conditions and is essential in monitoring heart health.
Order of a ECG reading
P wave
Atrial depolarization
Atrial contraction
QRS complex
Ventricular depolarization
Ventricular contraction
T wave
ventricle repolarization
amount of blood pumped by each ventricle
7560000 ml per day
Autonomic Regulation
The process by which the autonomic nervous system controls heart rate through sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. Controlled by the medulla oblongata
Medulla oblongata
part of the hind brain or the brain stem. Controls heart rate. Blood pressure changes are monitored by baroreceptors which is monitored by medulla oblongata
Role of the sympathetic division in circulatory system
Increases the heart rate
Role of the parasympathetic division
Decrease the heart rate
Break down of blood
Plasma portion
Water
Proteins
ions, sugars, lipids, amino acids
Cellular portions
Leukocytes
platelets
Components
red blood cells - enythrocytes
Plasma portion of the blood
Water
Plasma proteins
Ions, sugars, lipids, amino acids, hormones
Cellular portion of blood
Leukocytes
Platelets
Components of blood
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Arterioles
Small branches of arteries that deliver blood to capillaries.
Capillaries
Microscopic blood vessels where the exchange of materials occurs between blood and tissues.
Veins
Blood vessels that return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Venules
Collect blood from the capillaries
Arteries and arterioles
have thick walls, blood flows under high pressures and acts as pressure reservoirs
Veins and venules
Have thinner walls, blood flows under lower pressure. Work as blood reservoirs
Features of a capillary
Walls are single endothelia cells, and are very near the body cells they are the most numerous vessels in the body
Lymphatic System
A system that collects and returns interstitial fluid to the bloodstream and plays a role in the immune response.
Components of the lymph system
lymph
lymphatic vessels
lymphatic tissues
lymphatic nodules
lymphatic nodes
tonsils
spleen
thymus
Functions of the lymphatic system
helps maintain fluid homeostasis, fat absorption and defends the microorganisms
Cardiac Output
The volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, calculated as stroke volume multiplied by heart rate.
Bradycardia
A slower than normal heart rate.
Tachycardia
A faster than normal heart rate.