Suture, Needles, and Staples
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Suture
any material that holds tissue together
Multifilament suture
very strong, reactions, can harbor bacteria
Monofilament suture
Prevents wicking, lower infection; poor knotting, significant memory
Sizes of sutures
11-0 is smallest, increases as the #-0 decreases, size increases as whole numbers go up
What is 0-4-0 suture used most for?
Routine type surgeries
What is 5-0 to 7-0 suture used most for?
Delicate Vascular work
What is 8-0 to 10-0 suture used most for?
Ophthalmic surgery
Chromic Gut suture
Absorbable suture; absorbs in 10-15 days; easy to work with and inexpensive
Synthetic Absorbable Suture Options
PDS, Polyglecaprone-Monocryl, PLA (Vicryl), PGA (Dexon), Polyglyconate-Maxon, Polysorb, GLycomer 631-Biosyn
How is synthetic absorbable suture material broken down?
Hydrolysis
How long does synthetic absorbable suture material take to absorb?
40-60 days
Organic Nonabsorbable Suture
Silk is most common
Silk suture use
Cardiovascular, ophthalmic, GI, vessel ligation, PU
Silk Suture
twisted or braided; wicking, avoid in contaminated sites; can cause inflammation;
Synthetic Nonabsorbable Materials
less irritating than silk; very strong; not inclined to harbor bacterial growth
Metallic Sutures
Usually stainless steel; monofilament wire or twisted multifilament wire; minimal tissue reaction; knot ends evoke an inflammatory reaction; stable in contaminated wounds
Swaged Needle
atraumatic; suture already attached to the needle
Eyed needle
reusable; suture must be threaded through eye, have to drag not through
Tapered needles
atraumatic; suited to soft tissue; dilates rather than cuts
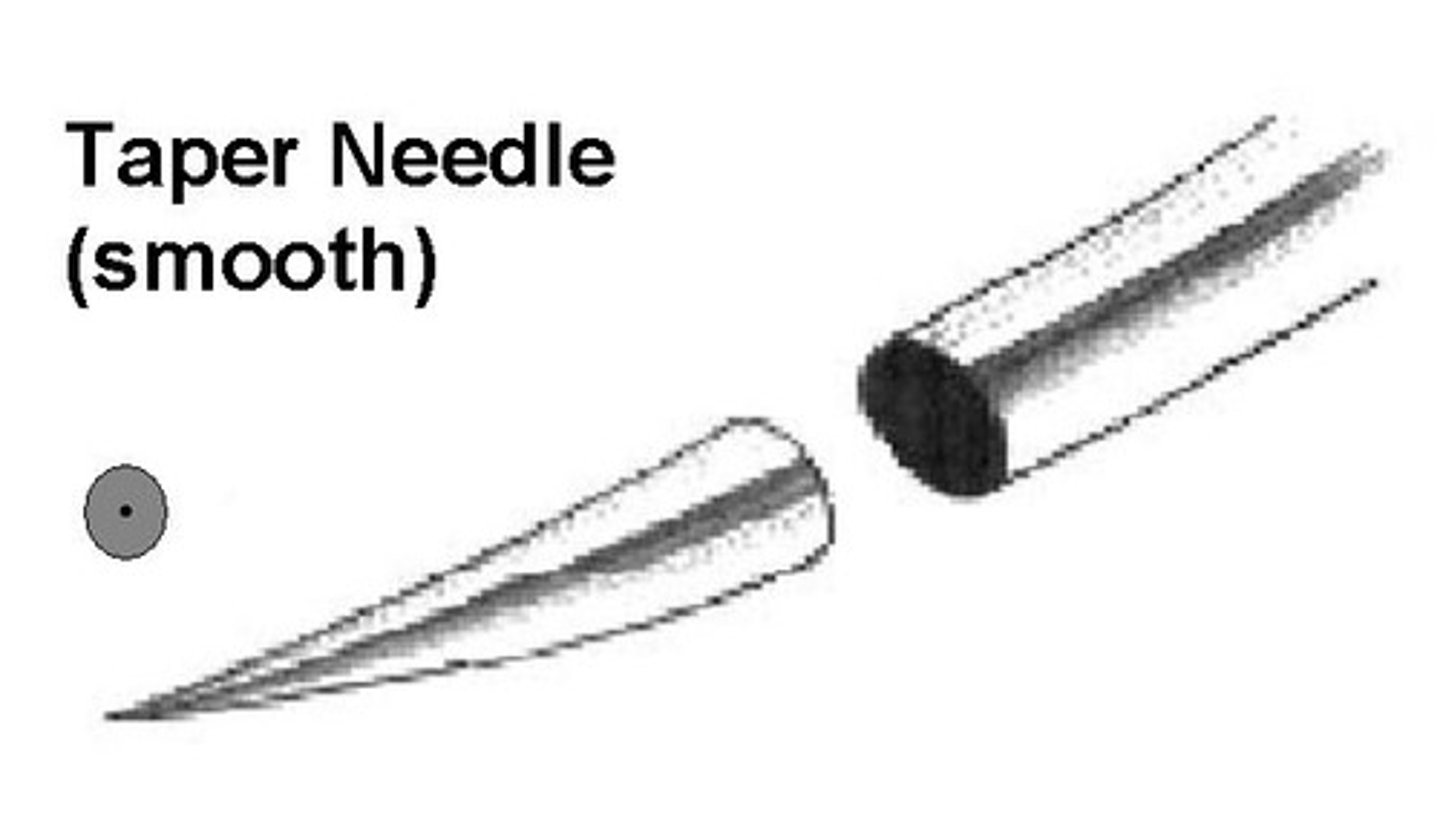
What are taper needles used for?
Intestine, SQ tissues, fascia
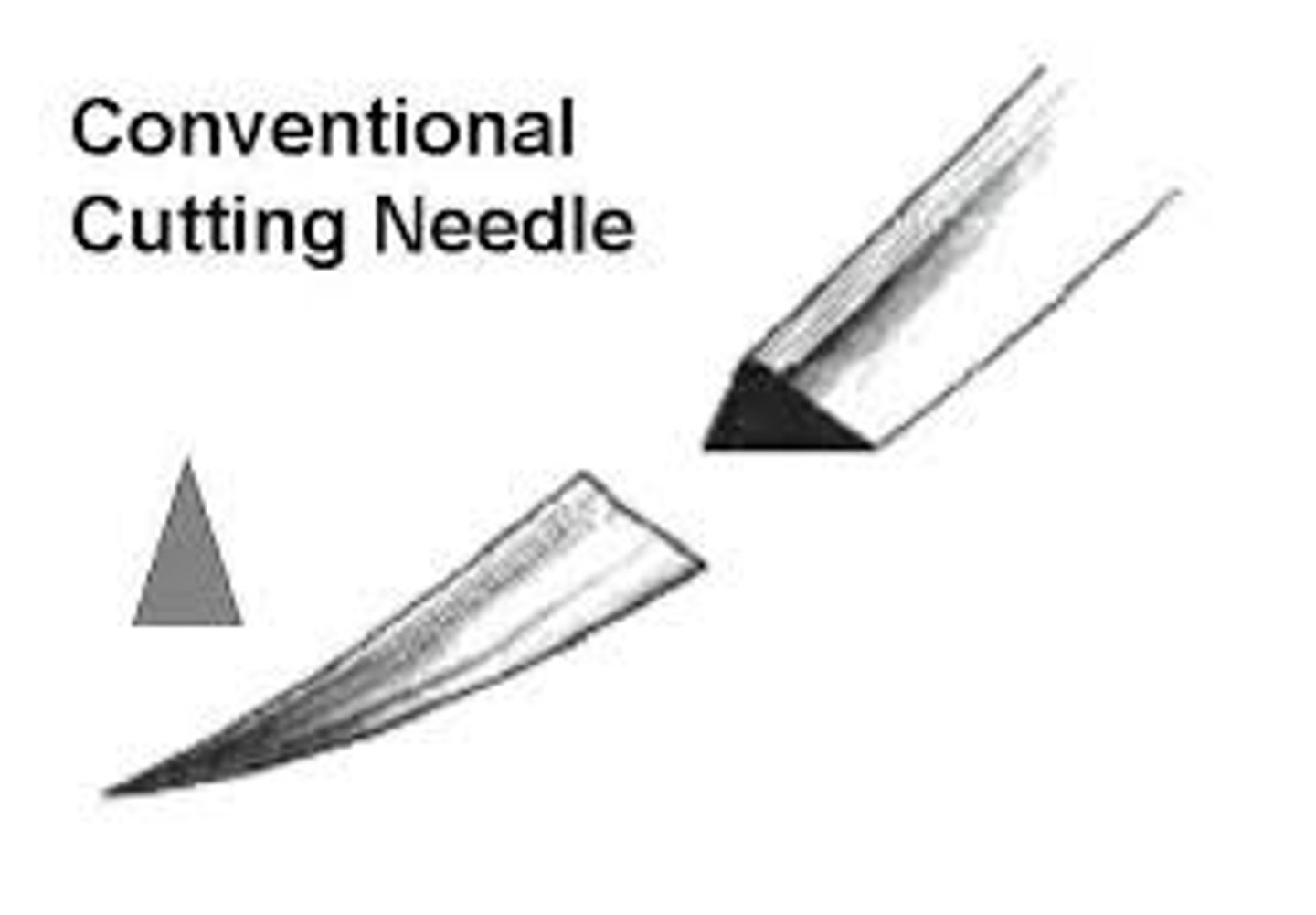
Cutting needle
very sharp, cuts rather than dilates, creates weakness allowing suture to tear out; end triangle in shape (three cutting edges)
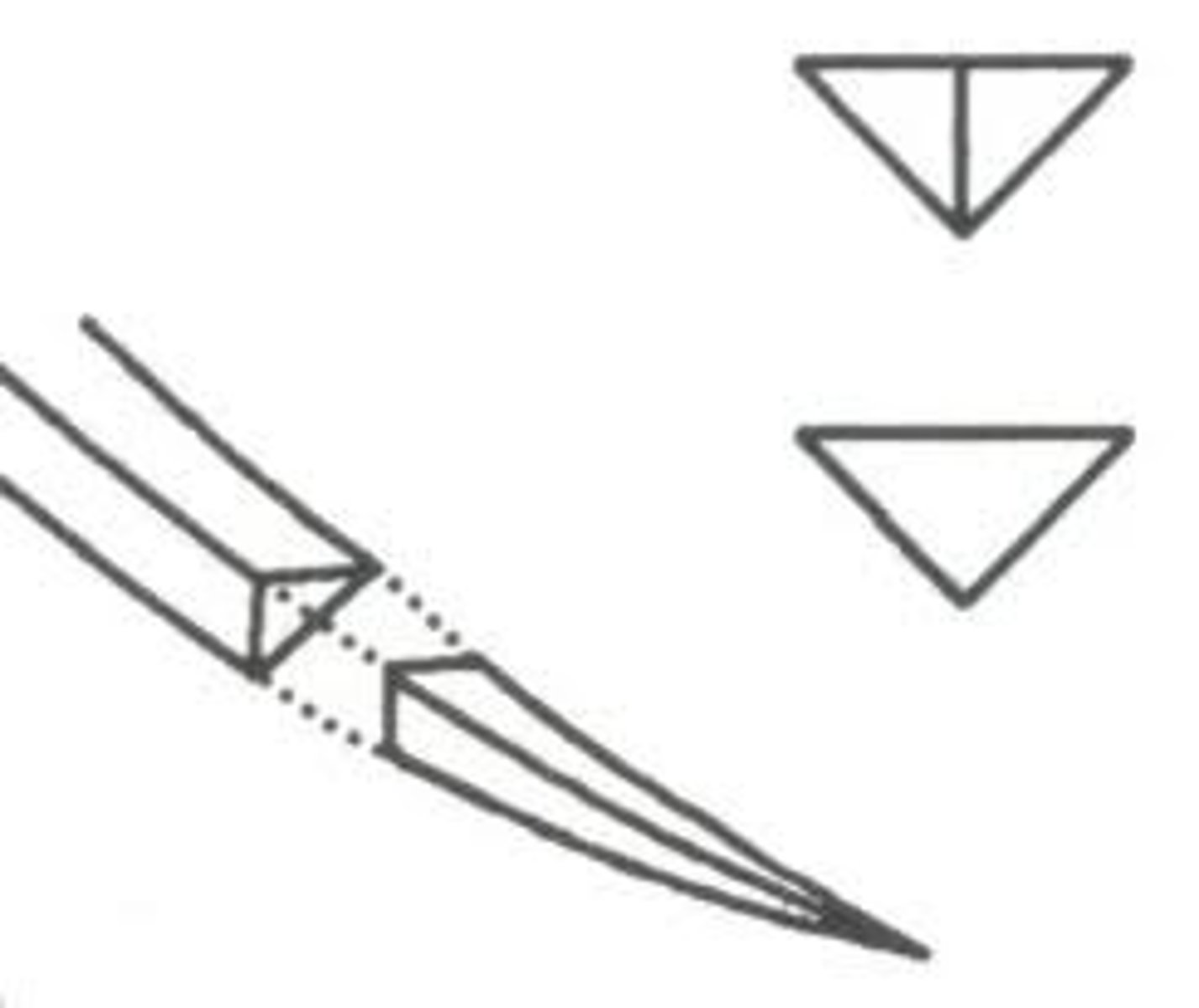
Reverse cutting needle
Very sharp, ideal for skin, cuts rather than dilates; Upside-down triangle
What is a cutting needle used for?
skin, eye tissues and facial tissue; not for areas needling seel
What are reverse cutting needles used for?
suturing most hollow organs
Taper-cutting
ideal in tough or calcified tissues
Metal Clips and Staples
used to ligate small blood vessels, pull wound edges together