Transport in plants
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what does the xylem transport
water and minerals
what does phloem transport
sugars and sucrose
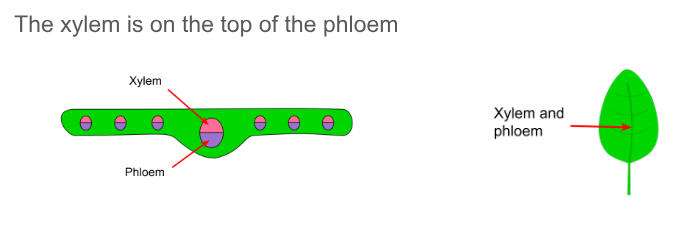
describe the position of the xylem and phloem in the leaf
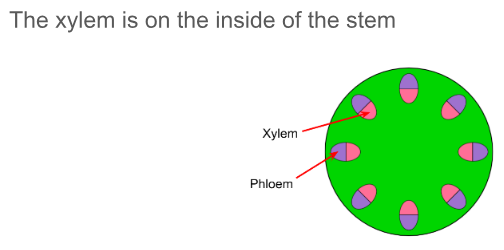
describe the position of the xylem and phloem in the stem
describe the position of the xylem and phloem in the root

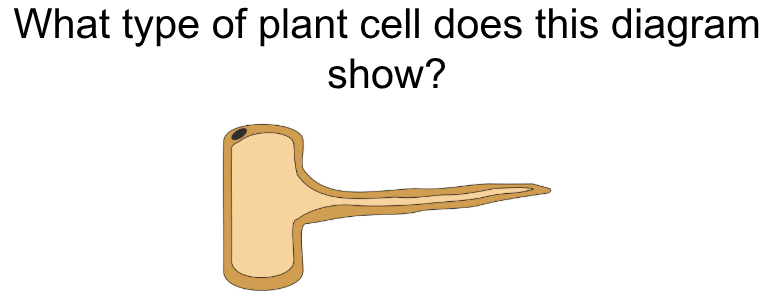
root hair cell
describe the pathway of water through a plant
root hair cell→root cortex cells→xylem→mesophyll cells
how do you investigate the pathway of water through a plant

describe the process of transpiration
water is lost through the stomata
more water is drawn up to replace the lost water
what is the transpiration stream
the transpiration stream is the flow of water through a plant
define transpiration
the evaporation of water from the aerial parts of a plant on the surface of the mesophyll cells which is followed by diffusion of water vapour through the stomata
why is water lost from plants
plants have large air spaces in them
plants have stomata in the leaves which allows water to diffuse out of the plant
plants have a large surface area for evaporation to occur
how do the interconnecting air spaces affect the water vapour loss
the interconnecting air spaces between the mesophyll cells create a large internal surface area
this increases the amount of water which can evaporate from the leaf
how does the shape and size of the stomata affect water loss
a greater number of stomata leads to more evaporation of water vapour from the leaves, increasing rate of transpiration
a larger size of stomata also leads to more evaporation and increases the rate of transpiration
explain the movement of water through a plant
water evaporation from the leaves creating a negative pressure in the xylem (transpiration pull)
water is drawn up the xylem in a column that is held together by cohesion
how does temperature affect the rate transpiration
as the temperature increasing, so does the transpiration rate
how does the wind speed affect the rate of transpiration
the faster the wind speed, the faster the water is moved away from the plant, creating a steeper gradient and increasing the transpiration rate
what causes wilting
a lack of water which means the plant cells are not turgid and so the plant is not supported
describe translocation
translocation is the movement of sugars and amino acids up or down the phloem from source to sink (with the use of energy)