Integumentary Screening
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Where are some common pressure sore areas?
bony prominences: back of head, shoulder, elbow, hip, heel
Stage 1 pressure ulcer
skin is still intact
Stage 2 pressure ulcer
dermis is exposed, partial thickness skin loss
Stage 3 pressure ulcer
fat/adipose tissue visible, slough /eschar present
Stage 4 pressure ulcer
bone is exposed
True or false: pitting edema only occurs with serious health conditions
false: mild pitting edema can occur with acute injuries such as ankle sprains
What does bilateral pitting edema indicate?
heart conditions such as congestive heart failure
What does unilateral pitting edema indicate?
venous obstruction or lymphatic blockage
Pitting edema scale: 0
no pitting edema
Pitting edema scale: 1+
mild pitting edema, 2mm depression that disappears rapidly
Pitting edema scale: 2 +
moderate pitting edema, 4mm depression that disappears in 10-15 seconds
Pitting edema scale: 3+
moderate severe pitting edema, 6mm depression that lasts >1 min
Pitting edema scale: 4+
severe pitting edema, 8mm depression that lasts >2 min
What is hemosiderin staining?
rusty brown darkening of skin due to venous valve failure
Where is hemosiderin staining most common?
distal lower extremities
What is lipodermatosclerosis?
inflammation of subcutenous fat, skin hardening
What is an indication of peripheral artery disease?
dependent rubor: limb appears red on feet/lower legs in a dependent position
What are some signs of cellulitis?
hot, acutely painful, edema, induration, spreading redness
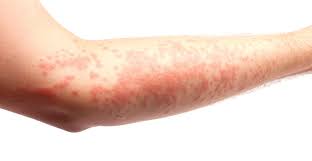
What is a reactive erythema?
acute onset rash from non-infectious causes such as bug bite,mild allergic reactions
What is precancerous growths called?
actinic keratoses
How is melanoma different from other skin cancer types?
malignant form of skin cancer, specifically out of control melanocyte growthT
True or false: melanoma has a low survival rate
false: melanoma has one of the higher survival rates in the early stages
What are some risk factors for Melanoma?
UV exposure, repeated sunburns, weak immune system, family hx
Which of the following is NOT a normal characteristic of a mole
> ¼ diameter
How is nodular melanoma different from regular melanoma?
most aggressive form, typically occurs in men >60 and occurs in any part of the body
Why do we assess nail beds?
can indicate several other disorders
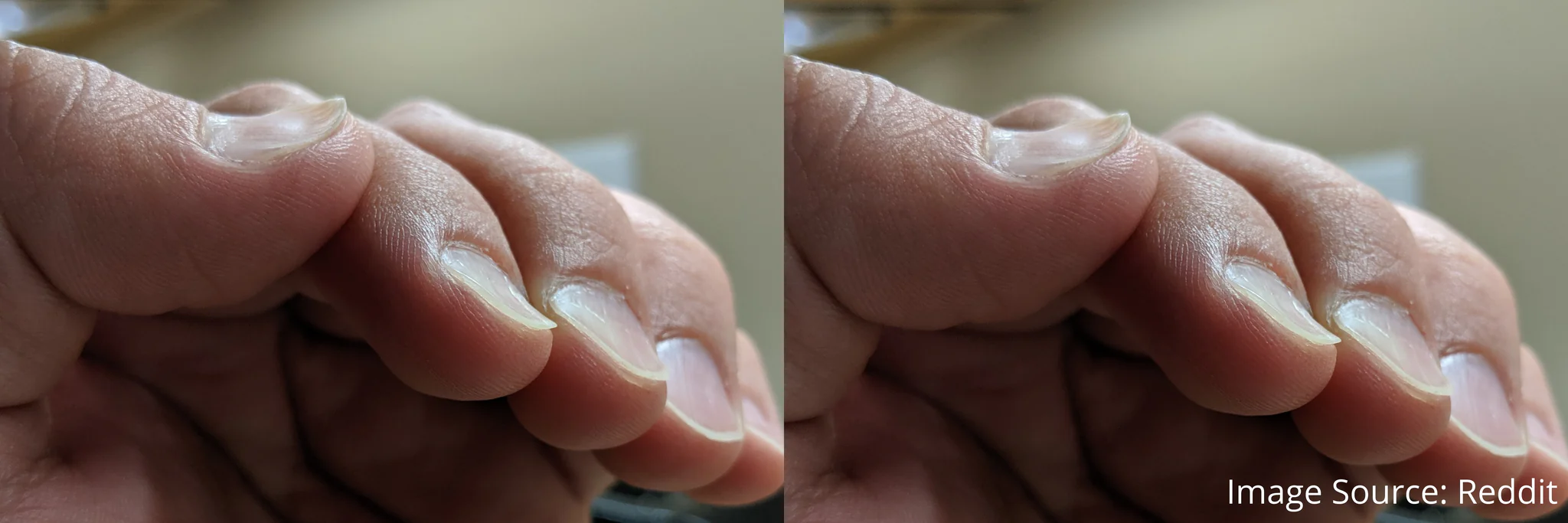
What is koilonychia indicate?
anemia, thyroid disorder, syphilis
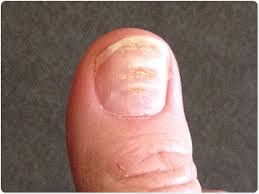
What does Beau’s lines indicate?
alcohol abuse, nutrition, MI
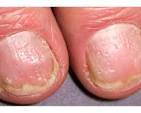
What does nail pitting indicate?
psorasis
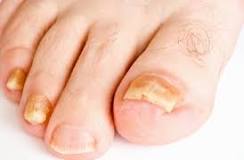
What does Onycholysis indicate?
fungus/psorasisW
What does a dark brown line on the nail indicate?
melanoma, malignant cancerW
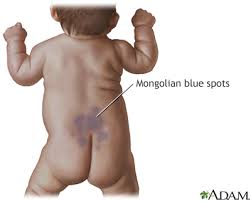
What is a mongolian spot?
Congenital birthmarks found on babies that typically fade but can stay