EXAM 5 SECTION D
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
individual risk rating
Prospective
Experience Rating
Schedule Rating
Composite Rating
Retrospective
same renewal between single no cred experience credit
Retrospective vs Prospective Rating
Responsiveness
Retrospective → more responsive
Losses during policy period impact prem of _____ period
Prospective → less responsive
Chg prem only on _____
Stability of Prem
Retrospective → less stable
Prem chg not only _____ periods but also within same period
Uses _____ year data & _____ _____
Prospective → more stable
Prem don’t change within policy period
Sched rating → mod determined at start of policy term & doesn't change
Exp rating → uses multiple yrs of _____ & applies cred
Incentive for Risk Control
Retrospective → more immediate incentive
Reduced loss result in lower prem for same term
Prospective → less incentive
Exp rating → takes time before reduced loss impacts prem
Sched rating → uncertain if will be given sched _____
standard prem
= Manual Prem x Exp Mod Factor x Sched Mod Factor
experience history
______ Rating: gives credit or debit based on insured’s claims _____ on prior terms
Mod = % debit or credit
ISO CGL → pos is debit, neg is credit
+1 to get factor
NCCI → already in factor form!
stability responsiveness recent stable
Experience Rating → length of Experience Period
Balance ______ vs ______
Short period → more responsive to _____ losses
But less cred, less _____ mod factors
prem detrended CSLC EER LDF basic msl
ISO CGL Experience Rating
**CSLC = Expected Ult Basic Lim Loss&ALAE NOT limited by MSL
If no MSL, EER = 1!
STEPS
For each subline, calculate Basic Lim Expected Loss
BLEL = Expected LR x Basic Lim _____
For each subline & year, calculate CSLC
CSLC = BLEL _____ back to each year
Total CSLC → sum across all sublines & years
For each subline & year, calculated Expected Dev
Expected Dev = _____ x _____ x _____
***This LDF is more like % unreported
Sum to get Total Expected Dev (for AER num)
Actual Basic Lim Loss&ALAE limited by MSL
Cap each individual actual loss at _____ lim
Add ALAE and cap Loss&ALAE at _____ (Max Single Loss)
Sum to get part of AER num
Mod = Z x (AER - EER)/EER
Add 1 to get factor
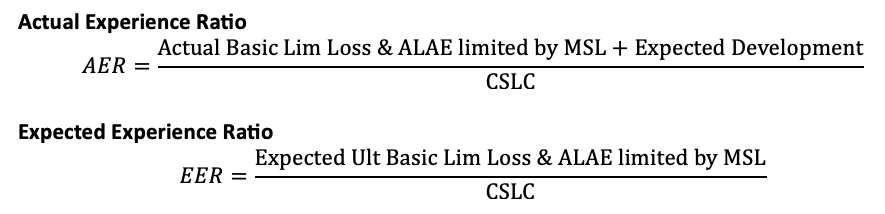
z eer
ISO CGL Experience Mod
Mod = _____ x (AER - EER)/_____
*Add 1 to get factor
overly influencing freq sev expected impact cred
ISO CGL Experience Rating
Why cap losses at basic lim & MSL?
Prevent large individ claims from _____ _____ experience mod
Make plan more responsive to _____ than _____
Why does MSL inc as size of risk inc?
Larger risk = larger _____ loss
So less _____ loss of a given size will have on mod
MSL inc to allow for more _____
primary excess
NCCI Experience Rating
Only use loss (no ALAE)
Split into 2 portions:
_____ → capped at C
_____
Cred-weigh each separately
A = actual loss
E = expected loss
Ze = W x Zp
*Sometimes will be given a stabilizing value
Add to both num & denom!
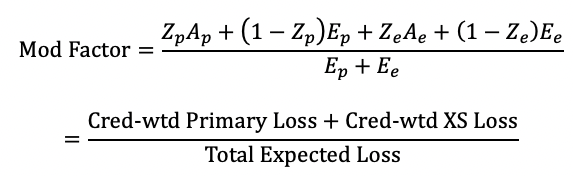
weighting ballast payroll capped payroll elr
NCCI Experience Rating (another formula)
W = _____ Value
B = _____ Value → stabilizing value
For each class i:
Di = D-Ratio
ELRi = Expected Loss Rate
Expected Loss per $100 _____
STEPS:
Calculate Ap = actual loss _____ at C
Ae = A - Ap
Expected Loss for class i
Ei = (_____i/100) x _____i
Sum to get E = Expected Total Loss
Expected Primary Loss
Ep = sum(Di x Ei)
Expected XS Loss
Ee = E - Ep
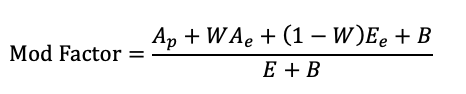
subjectively experience
Schedule Rating: UW _____ assign credit/debit to individual risks
Based on risk chars NOT already reflected in _____ rating
composite rating
rating a policy w/ multiple coverages using a single exposure base
large ded policies
large employers purchase policies w/ large ded
insured retain more loss/risk
Calculations:
Use standard PP formula
Num → only use expected loss XS of ded!
XS Ratio = 1 - LER
Expected XS Loss = XS Ratio x Expected Ground-Up Loss
**PAY ATTENTION TO WHAT RATIOS APPLY TO!
Ground up, XS, loss below ded
incl/excl ALAE
incentive ulae reimbursement credit profit
Considerations of Large Deductible:
Claims Handling: who’ll be responsible for adjusting claims below ded
Insured → usually hire a TPA, less _____ to keep loss below ded
Insurer → higher _____
Application of Ded: loss only or loss+ALAE?
Ded Processing: if insurer pays all loss first, then seek _____ for below ded
Extra FE:
Cost to bill & process these amts
_____ risk in case insured unable to pay
Risk Margin: losses above large ded are difficult to est
Inc _____ margin to reflect higher risk
(b+ca)t lae taxes
NCCI Retrospective Premium
R = _____ H ≤ R ≤ G
R = Retro Prem → capped between H, G
b = Basic Prem
Profit & Expenses (excluding _____, _____)
Net insurance charge
A = Rept Loss (may or not incl ALAE)
May be capped by Per Occurrence Limit
C = Loss Conversion Factor
CA = converted loss
T = Tax Multiplier
e - (c-1)e(a) + ci
NCCI Retrospective Basic Prem
b = ______
e = Expense & Profits (excl Taxes)
CI = Converted Net Insurance Charge
**Often given as a ratio to STANDARD PREM!
expenses profits lae taxes net insurance charge
NCCI Retro Rating Basic Prem
Total _____ & _____
Excluding _____ & _____
_____ _____ _____ for limiting prem by max&min
e(a) c
Converted Net Insurance Charge: charge for limiting prem by max & min
CI = (Insurance Charge - Savings) x _____ x _____

downwards rept loss
How could retrospective prem change between adjustments?
Ex: At first adjustment, retro prem capped @ max prem
Can only develop _____
Will only dec if _____ _____ dec
Case reserve dec
Settled for less than current case reserves