unit 11 - bioenergetics
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
bioenergetics is what kind of study
quantitative
bioenergetics definition
energy that is used when substates are transformed into products in biochemical reactions
biochemical reactions - mean?
catalysed by enzymes
the energy transferred from substrate to products is controlled by (2)
enthalpy
entropy
Enthalpy (H) measures what
stability
Entropy (S) measures what
organisation (of bonds)
Enthalpy - what letter and what letter when it is balanced
H
triangle(delta) H (balance)
Entropy - what letter and when it is balance
S
triangle(delta) S (balance)
Enthalpy - depends on the valve of 2 types of reactions
exothermic
endothermic
Enthalpy, exothermic - what is the reaction
NEGATIVE
delta H-
Enthalpy, endothermic - what is the reaction
POSITIVE
delta H+
Entropy, what result can entropy have
positive or negative
entropy
if the result is positive or negative is it called something different or still called entropy
still called entropy (not classified into 2 types) (single reaction)
what is Gibbs free energy
expresses the amount of energy capable of doing work during a reaction at constant temperature and pressure
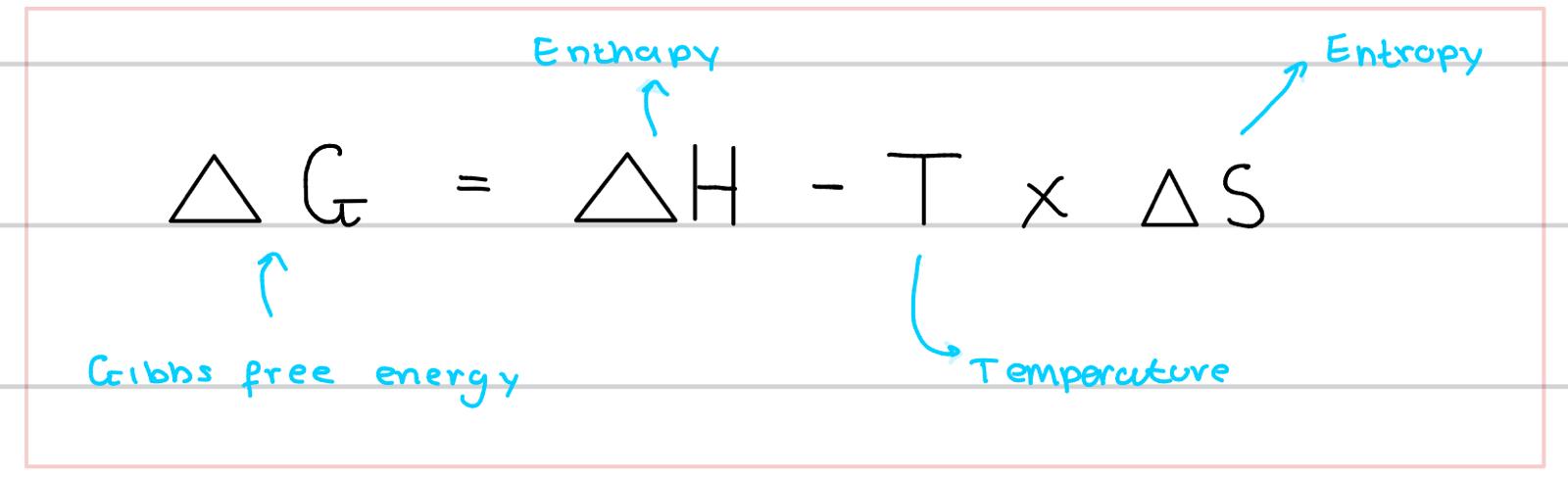
what is the Gibbs free energy equation
(delta G) = (delta H) - (T) x (delta S)
the result of the Gibbs free energy equation gives how many different types of results
3
what are the 3 results from Gibbs free energy equation
delta G = 0
delta G = greater than 0
delta G = less than 0
Gibbs free energy equation
delta G = 0 means what
not frequent
reaction is at equilibrium
Gibbs free energy equation
delta G = > 0 means what
positive reaction
frequent
Gibbs free energy equation
delta G = < 0 means
negative reaction
frequent
when Delta G is positive the reaction is called what
Endergonic
when Delta G is negative the reaction is called what
Exogonic
are exothermic, endothermic and Exogonic and Endergonic the same
no
exogonic and endogonic are related to Gibbs free energy
exothermic and endothermic are related to Enthalpy
endergonic (+) means what
process consumes energy especially ATP
is endergonic (+) spontaneous
NON-SPONTANEOUS PROCESS
exogonic (-) means what
process/reaction that produces energy
exogonic (-) is it spontaneous + what does that mean
yes
it is easy for us to perform
spontaneous
exogonic vs endogonic
endogonic (+) = non-spontaneous
exogonic (-) = spontaneous
which reactions is better for are metabolic processes
exogonic reactions
are all are metabolic reactions exogonic
no
what do we need to do if some of are metaobic reactions are endergonic
we need to transform endergonic reactions into exogonic reactions
we need to transform endergonic reactions into exogonic reactions - HOW?
energy coupling

we want to form sucrose, what is the Gibbs free energy, spontaneous or not and why
+27 is greater than 0 so it is endergonic reaction and Non-spontaneous

what do we need to do because it is endergonic
transform it via energy coupling into an exergoinc reaction
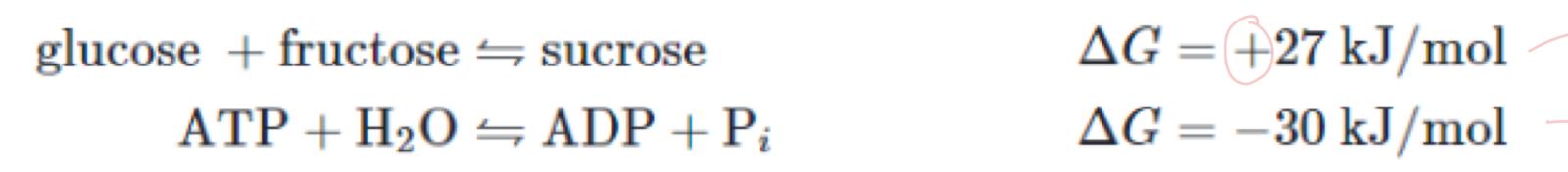
what is this second reaction called
hydrolysis
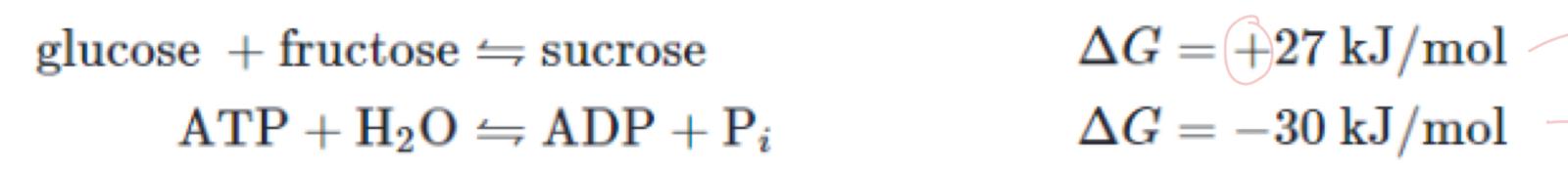
what happens when ATP is hydrolysed
phosphate group is released
releases -30kj/mol

what is the maths
+27 - 30 = -3
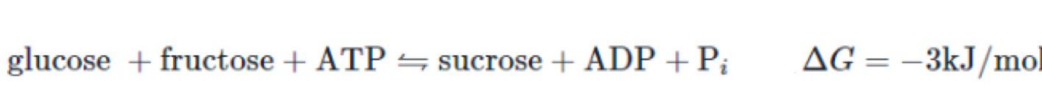
now the reaction is what
exogonic = spontaneous
the hydrolysis of ATP always releases about
-30kj/mol
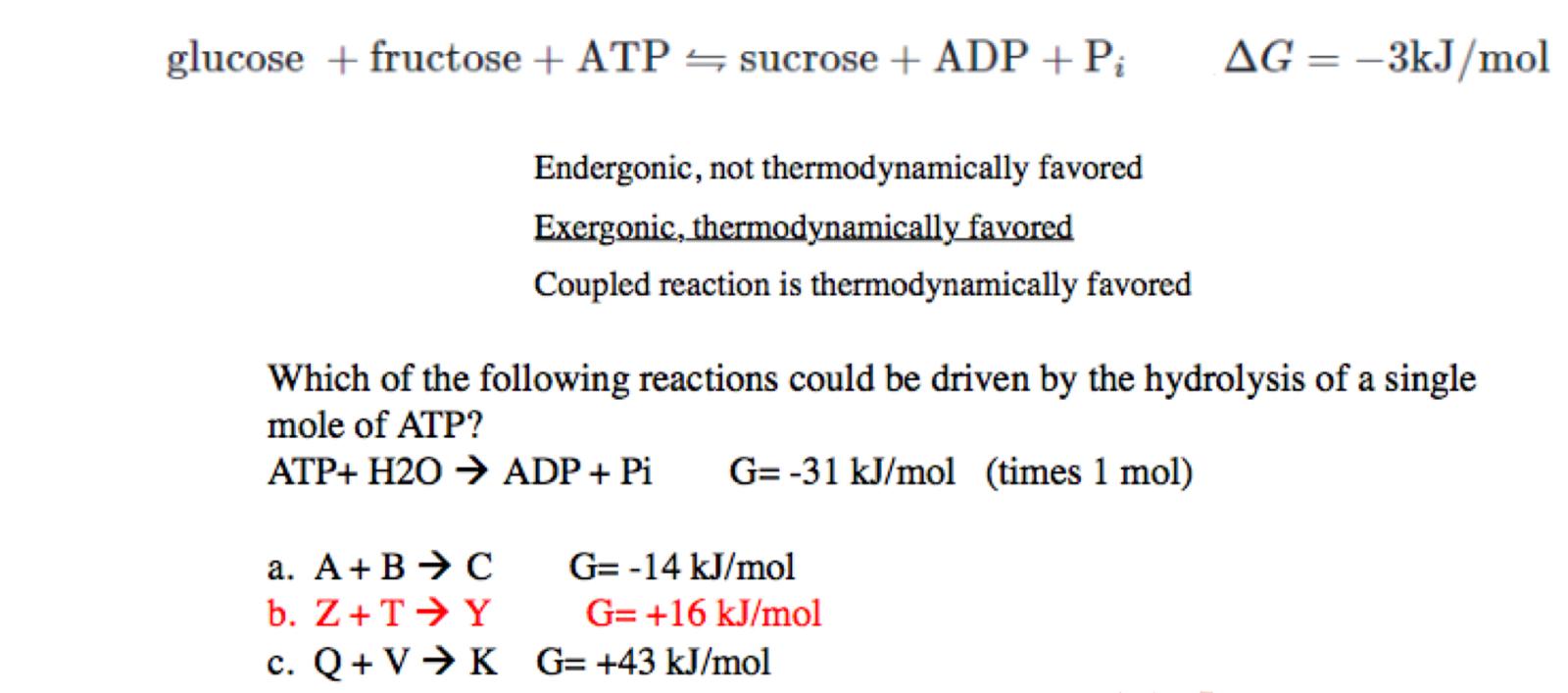
explanation for option A
the result is already - (exogonic + spontaneous) so no need for hydrolysis of ATP
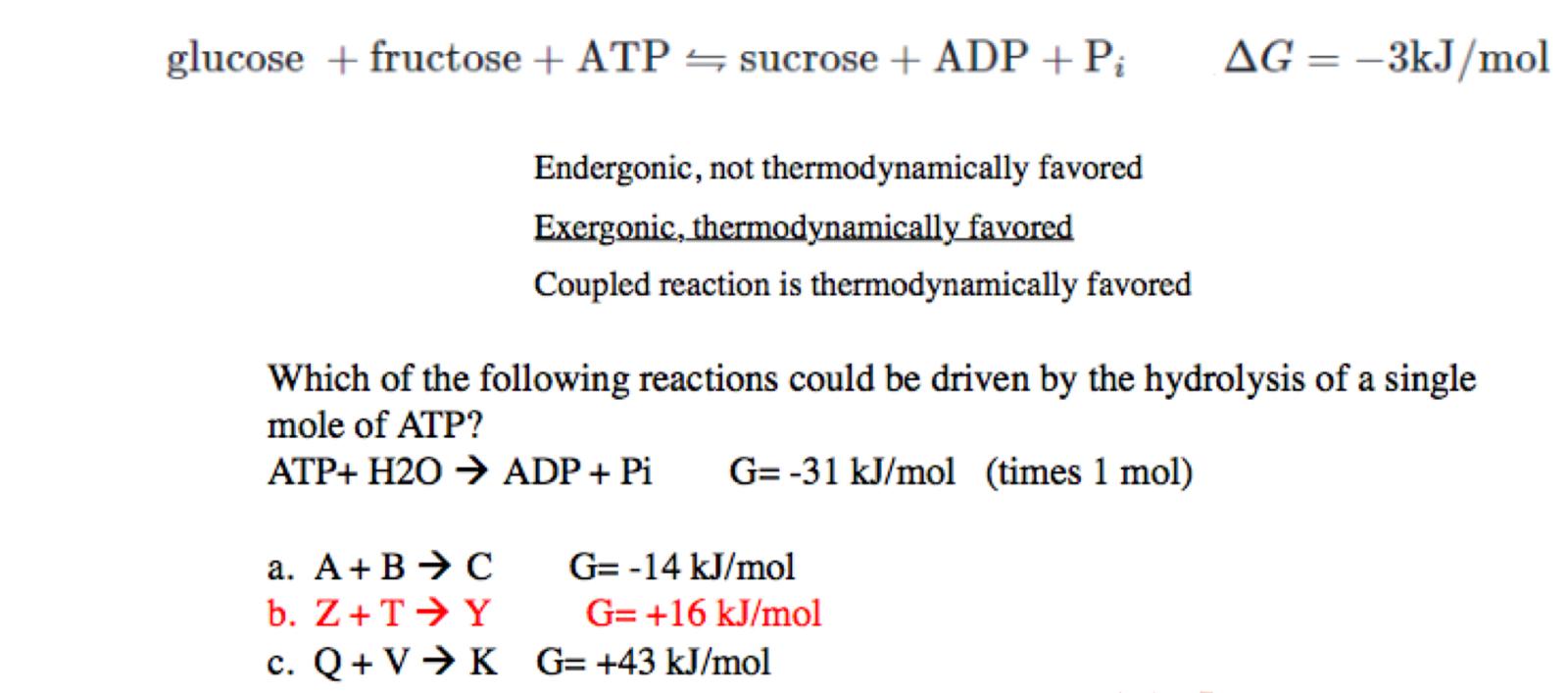
explanation of option B
+16 - 31 = -15
making it an exogonic and spontaneous reaction
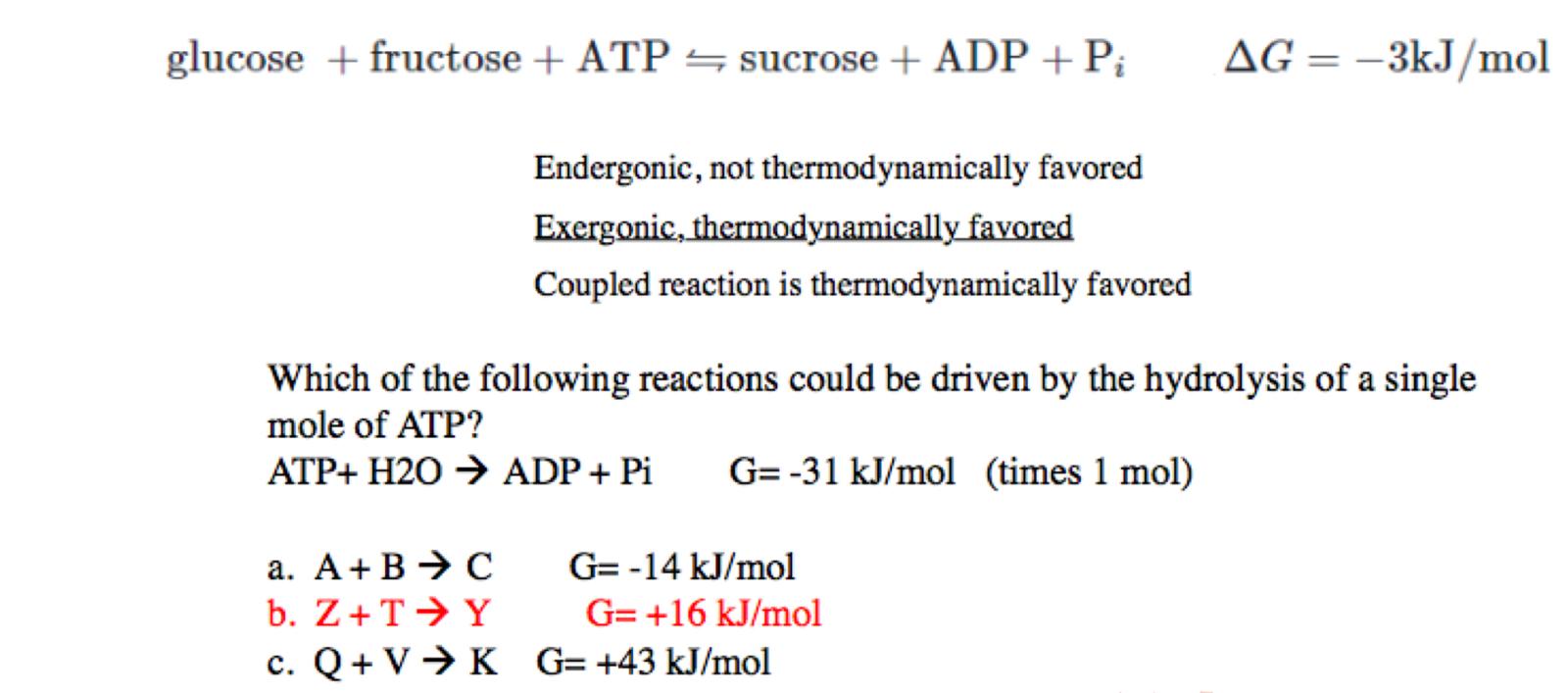
explanation for C
+43 -31 = 12
its still endogonic
the hydrolysis of 1 mole of ATP is not enough
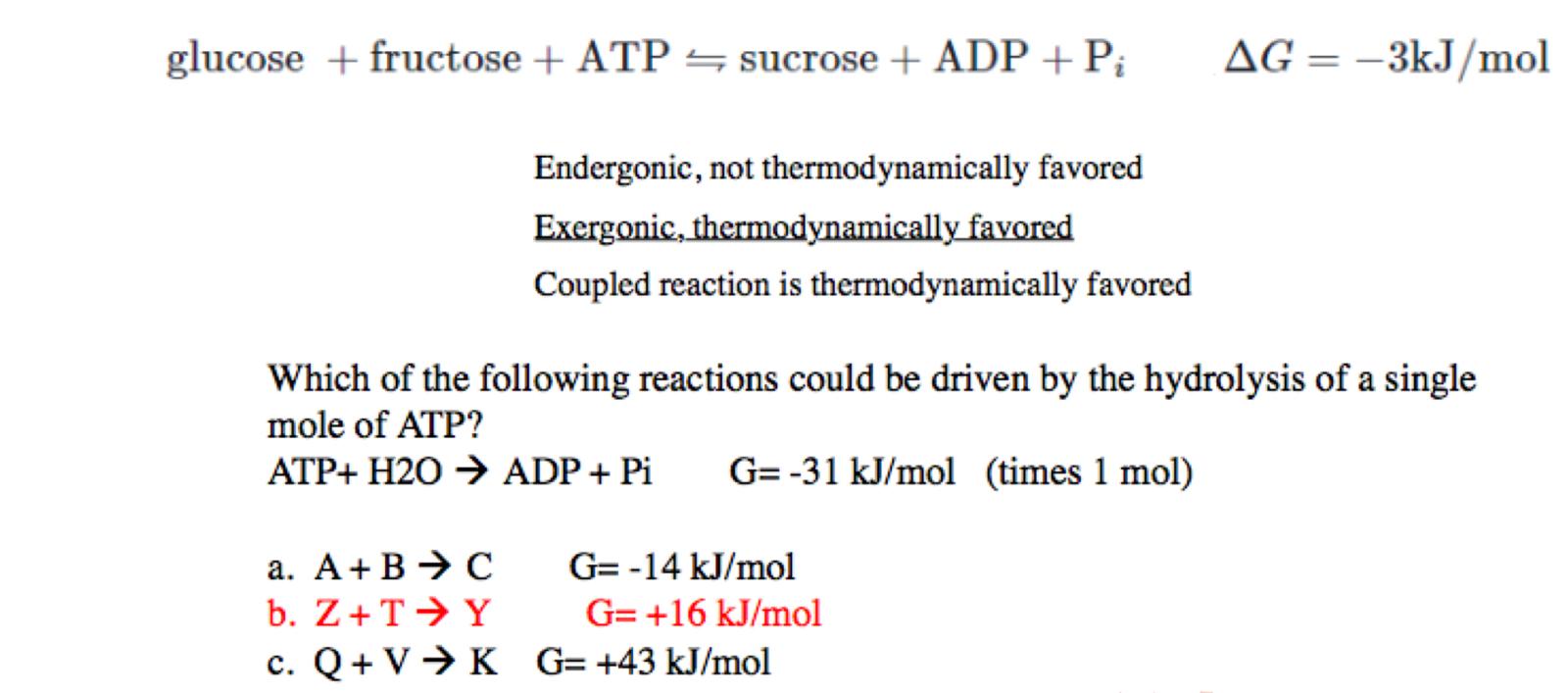
for option C what would need to happen to make the reaction Exogonic and spontaneous
a double-dephosphorylation
what is the flow diagram for a double dephosphorylation and how much energy does it release
ATP→ ADP → AMP = -60kj/mol
what are the energy rich compounds (4)
ATP
GTP
CTP
UTP
what is the relevance of these 4 energy rich compounds
they mediate the coupling of the endergonic and exergonic reactions
how do
ATP
GTP
CTP
UTP
release energy ?
through hydrolysis(+water) and group transfer
ATP
GTP
CTP
UTP
they transfer energy in a …..
single reaction
(ATP + H20 = ADP + Pi)
ATP
GTP
CTP
UTP
they release how much energy per mol
-30kj/mol
structure of ATP
atp is composed of 3 things - what are they
nitrogen base = ADENINE
sugar = RIBOSE
3 x phosphate
what happens if we have
nitrogen base = adenine
sugar = ribose
2 X PHOSPHATE
ADP
what happens if we have
nitrogen base = adenine
sugar = ribose
1 X PHOSPHATE
AMP
whats the difference between
ATP
GTP
CTP
UTP
the nitrogen base
ATP = ADENINE
GTP =
GUANINE
ATP = ADENINE
CTP =
CYTOSINE
ATP = ADENINE
UTP =
URACIL
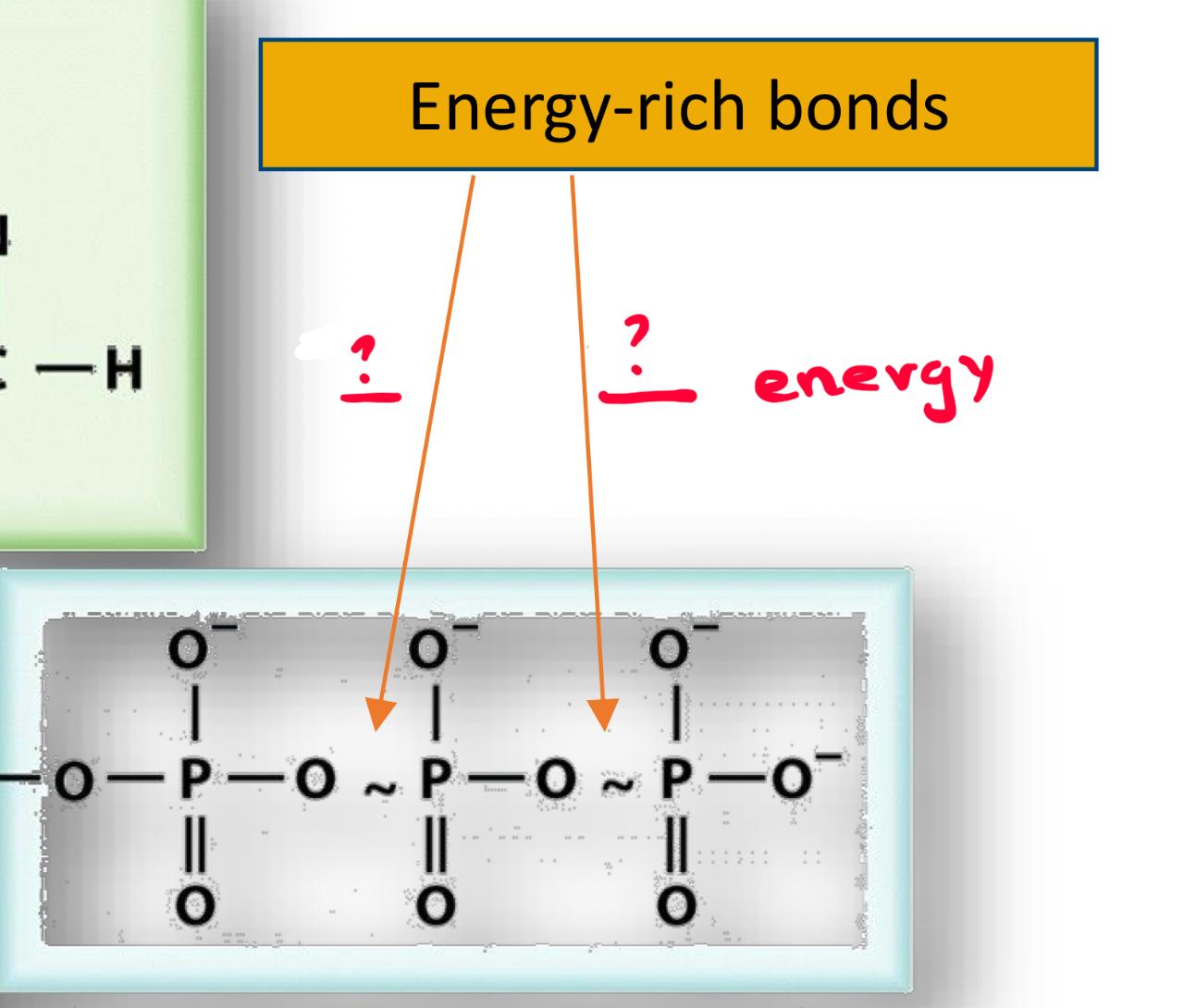
this is ATP, if we break 1 of the enery rich bonds how much energy is relased
-30
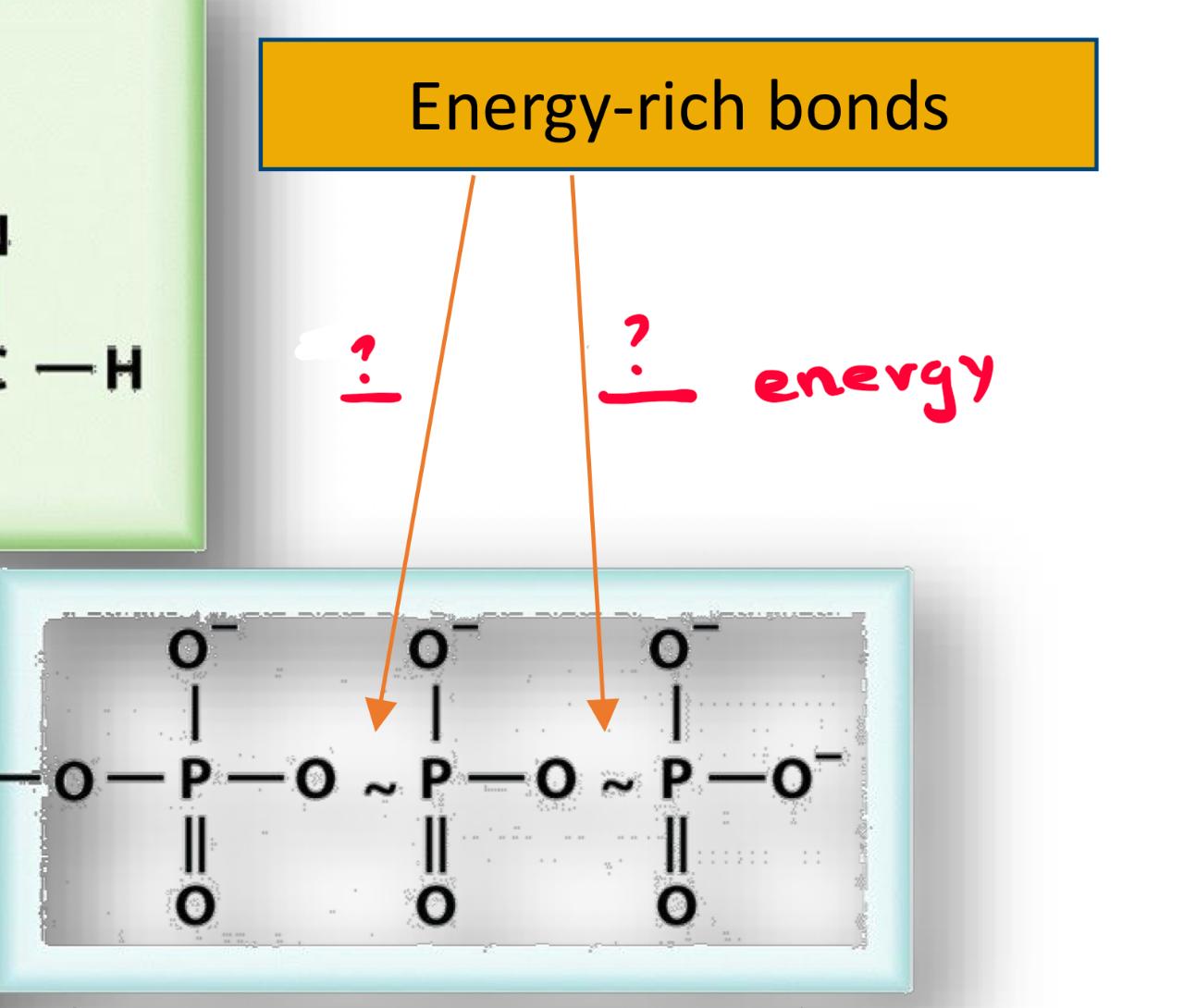
if we break both of the energy rich bonds = hydrolyse the whole ATP molecule we get
-60
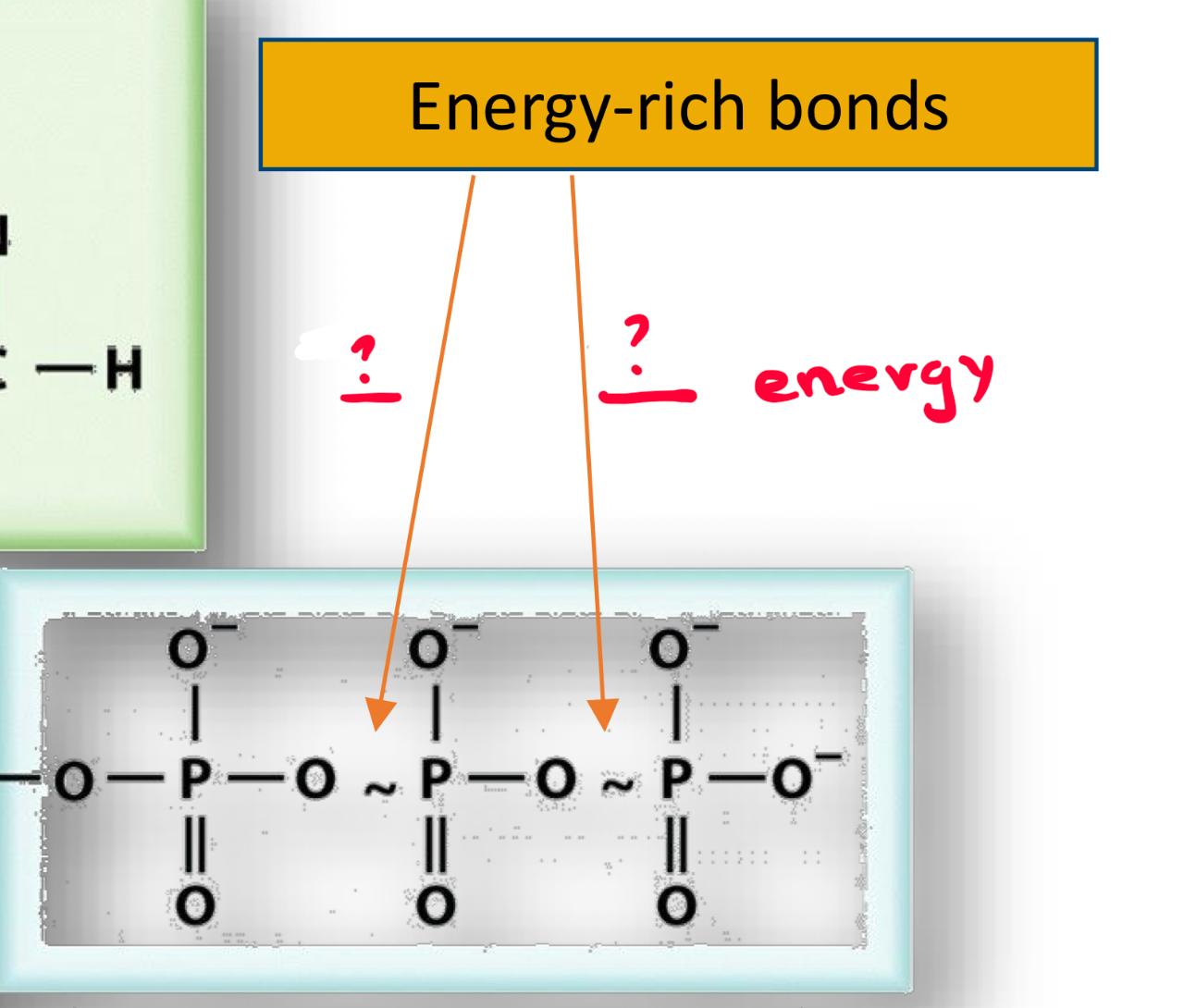
ATP double phosphorylation reasles -60 and what is it
AMP
from
ATP
GTP
CTP
UTP
what are the most frequent energetic molecules
atp
gtp
CTP is used in a process called
Glycosylation
what is Glycosylation process
the addition of carbohydrates to proteins = makes Glycoproteins
UTP is a compound used in the ..
synthesis of glycogen
phosphocreatine system , located where
in muscles
phosphocreatine system is the fastest way to
produce a single ATP
what is phosphocreatine made from
creatine bound to a phosphate
what happens if we split phosphocreatine into
phosphate
creatine
and we combine this phosphate with what ….
ADP
what happens if we split phosphocreatine into
phosphate
creatine
and we combine this phosphate with ADP ?
we get ATP
how many reactions in the phosphocreatine system to get ATP (and what are they)
2
1 = splitting of phosphocreatine
1 = ADP + Pi
the processes of producing 1 ATP from phosphocreatine is catalysed by ….
creatine-kinase
so the first process to produce energy in muscles is
phosphocreatine system
what is the second one ?
glycolysis and kerb cycle
what are we using in glycolysis and kreb cycle to make ATP
carbohydrates
what is the process of getting ATP from Lipids
Beta oxidation
we can combine beta oxidation of fatty acids with what
kreb cycle
in carbohydrates we have ……?
in lipid we have ……? ……
glycolysis + kreb cycle
beta oxidation + kreb cycle
we change the biomolecule that we use
in glycolysis we use ….1…..
in beta oxidation we use ……2…
glucose
fatty acids
electron transporters
NAD+ , FAD and FMN are what type of enzymes
Catabolic Coenzymes
electron transporters
NADP+ is what type of enzyme
Anabolic enzyme

summary - read
done

electron transport summary - read
done
metabolism is what
the chemical changes in living cells by which energy is provided for vital processes and activities and new material is assimilated
metabolism are reactions that happened where
cytoplasm
different organelles in the cells
metabolic reactions can be split into 2 types
catabolic reactions
anabolic reactions
catabolism means
degradation
(set of reactions by which the cell degrades nutrients)
catabolism is the same as degradation which is the
production of energy (ATP)
anabolism is the same as
synthesis (makes new compounds)
(set of reactions by which the cell synthesis its biomolecules)
anabolism does what with energy (ATP)
consumes energy
catabolism vs anabolism - energy
catabolism - produces energy
anabolism - consumes energy
catabolism step 1
starch is degraded into glucose
catabolism step 2
glucose is degraded into Acetyl-CoA
Step 3 catabolism
when Acetyl-CoA is in high enough levels it is transformed in the Kreb cycle
fill out the blanks
….1…. → ….2….. → …..3….→ high levels reached —→ …..4…. → = …. 5
starch
glucose
Acetly-CoA
kreb cycle
ATP

catabolism - read
done
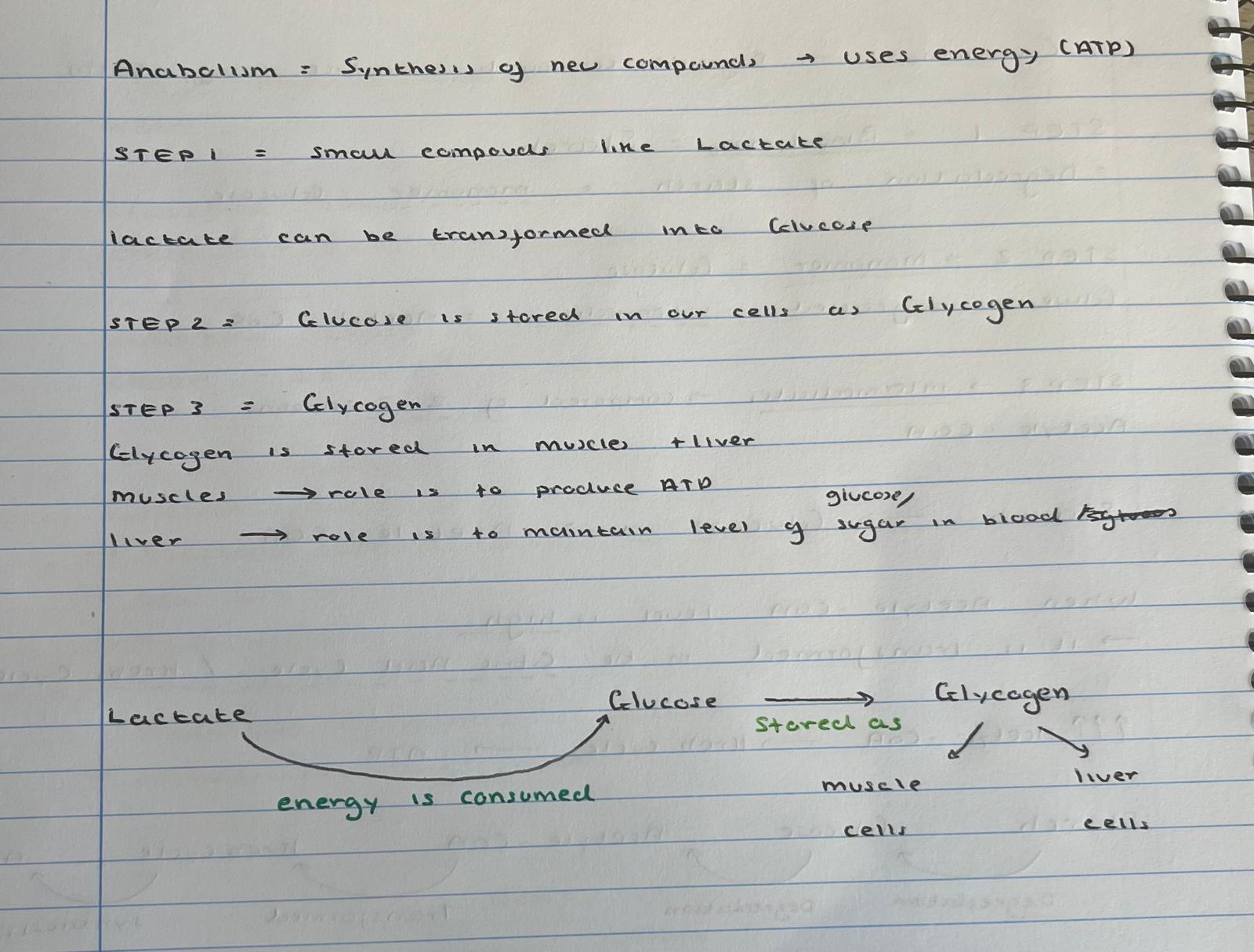
step 1 of anabolism
lactate is transformed into glucose
(energy is consumed)
step 2 of anabolism
glucose is stored as glycogen
glycogen can be stored where
muscle cells
liver cells
role of glycogen in muscle cells
produce ATP
role of glycogen in liver cells
maintain level of glucose in the blood
….1….. —energy consumed→ ….2… ——stored→…3… in …..4a+B..
lactate
glucose
glycogen
muscle cells and liver cells
anabolism - read
done