Anatomy Lecture Exam 2 (1/3) - Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Components of skeletal system
Four components: Bone, Cartilage, Tendons, Ligaments
Functions of the skeletal system
Support, protection, movement, storage (calcium), blood cell production
Classification of bones
Long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
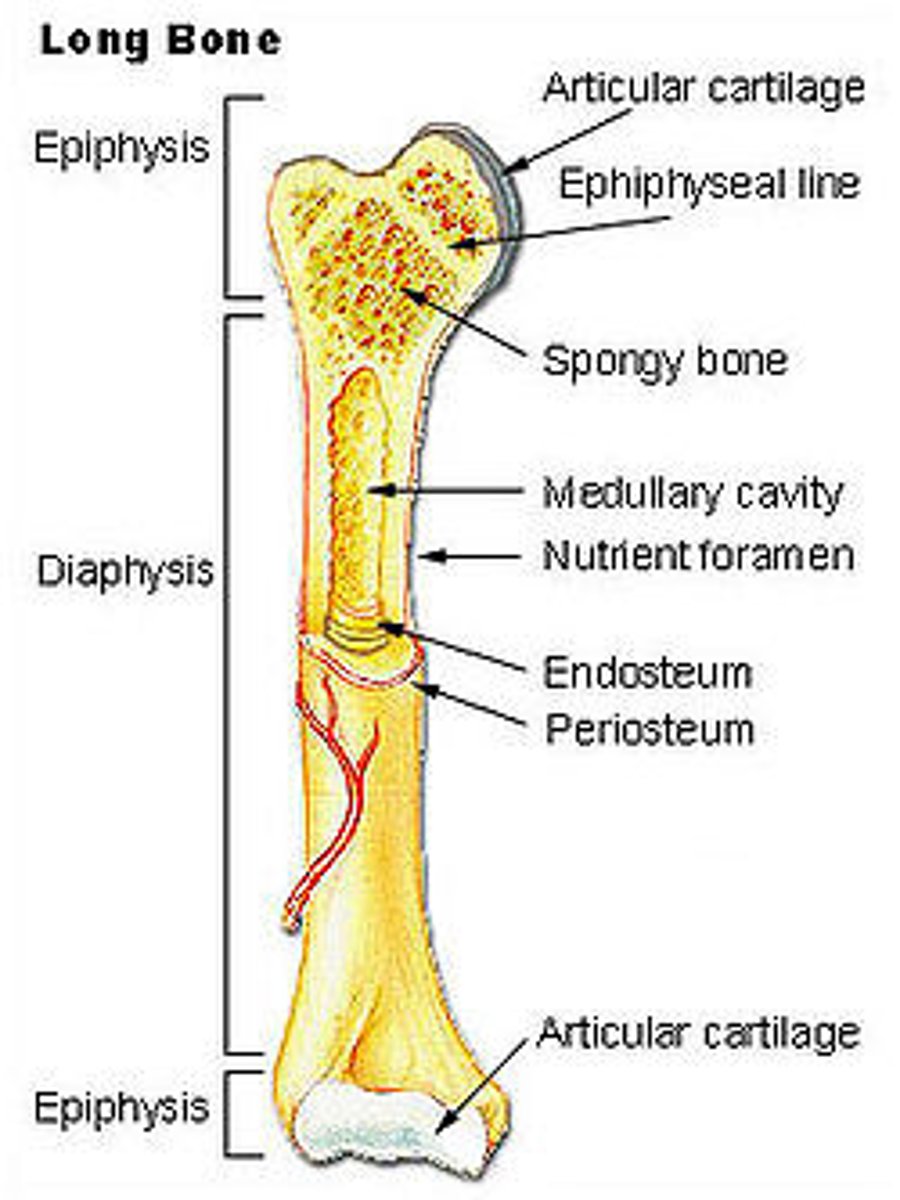
Long Bone
Features: Cylinder like shape, longer than it is wide
Functions: Leverage
Examples: Femur (thigh bone) & Phalanges (finger and toe bones)
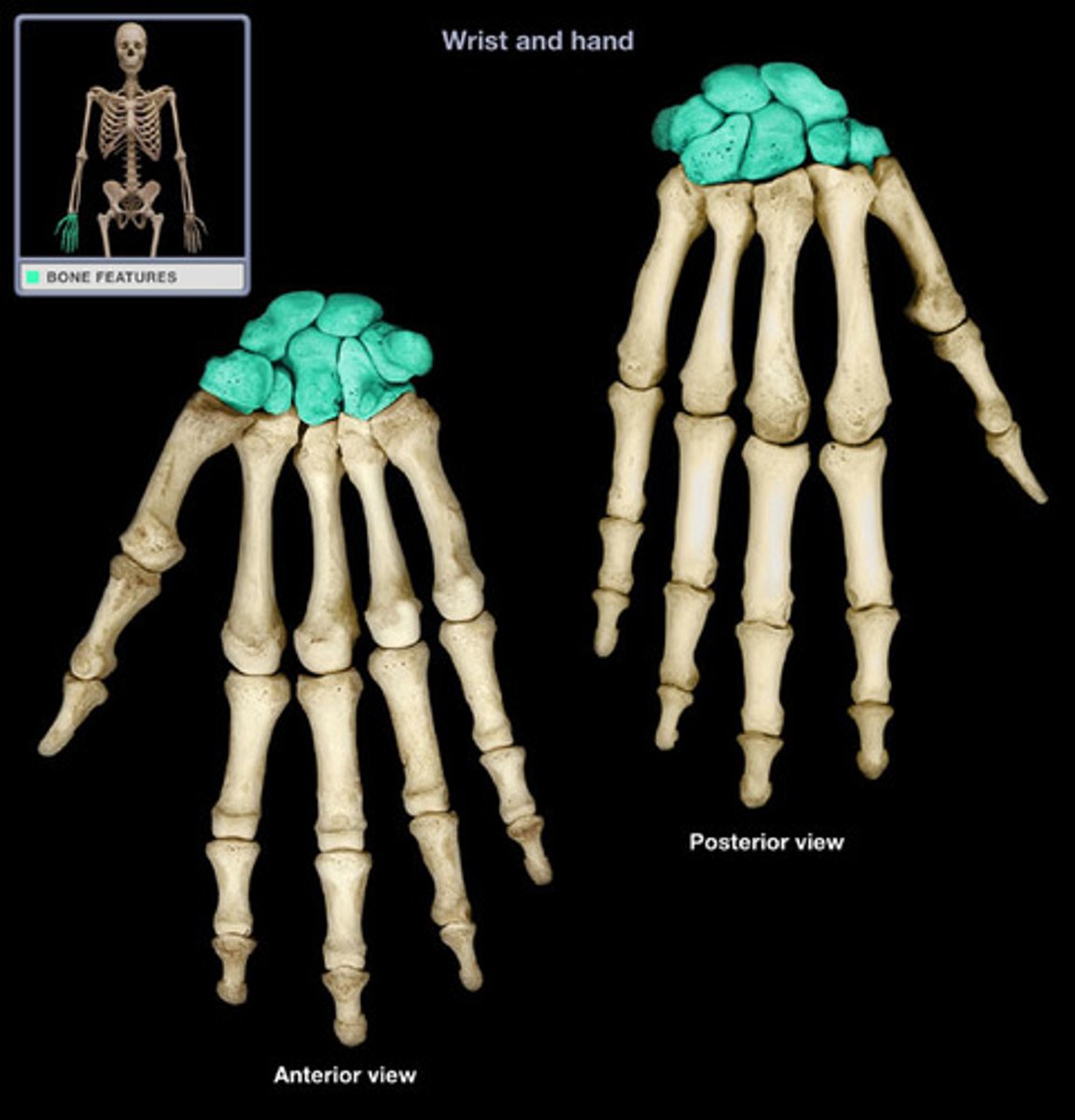
Short Bone
Features: Cube-like shape, about equal in length, width, and thickness
Functions: Stability, support, while allowing for some motion
Examples: Carpals (wrist bones) & Tarsals (ankle bones)
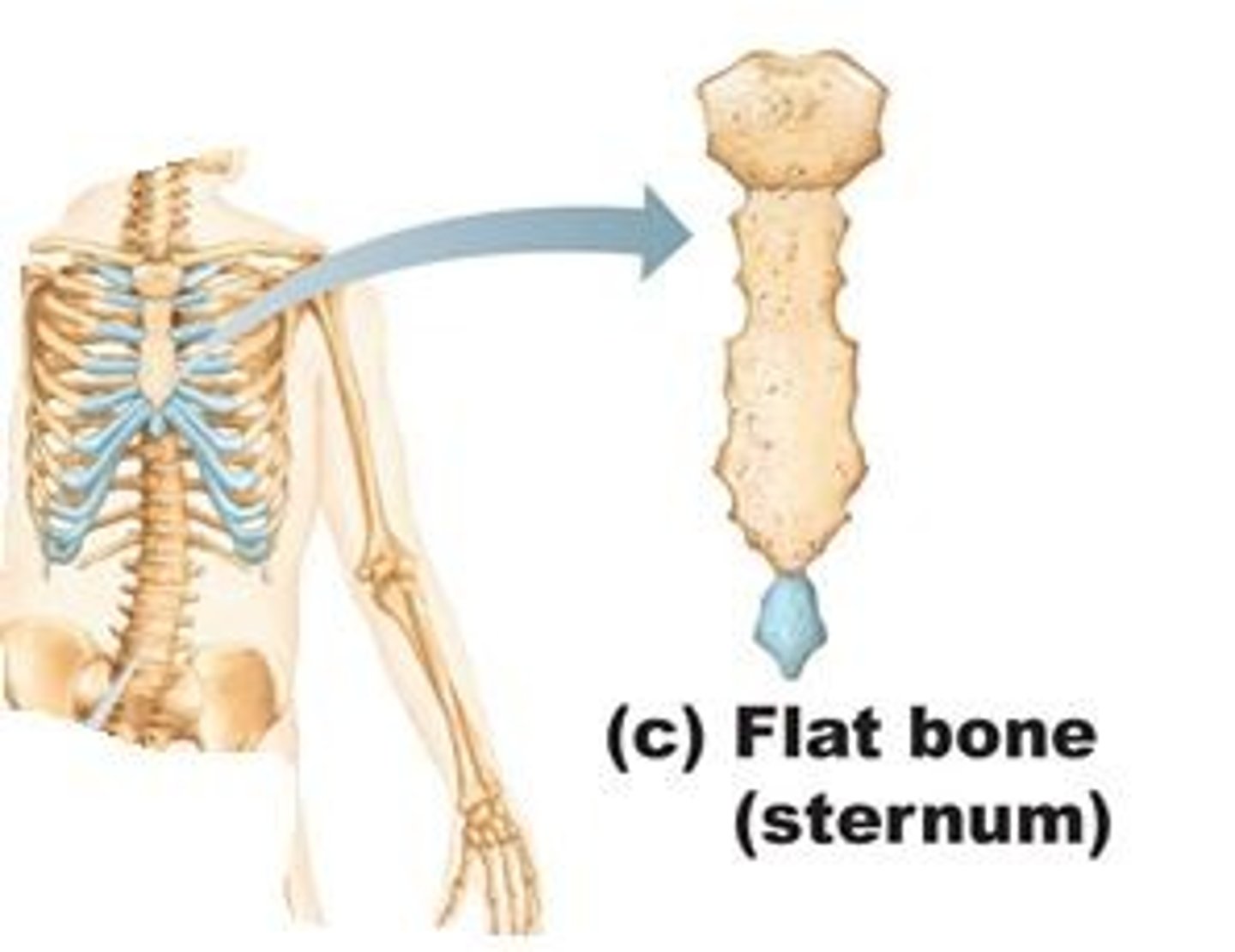
Flat Bone
Features: Thin and curved
Functions: Points of attachments for muscles; protects internal organs
Examples: Sternum & Ribs
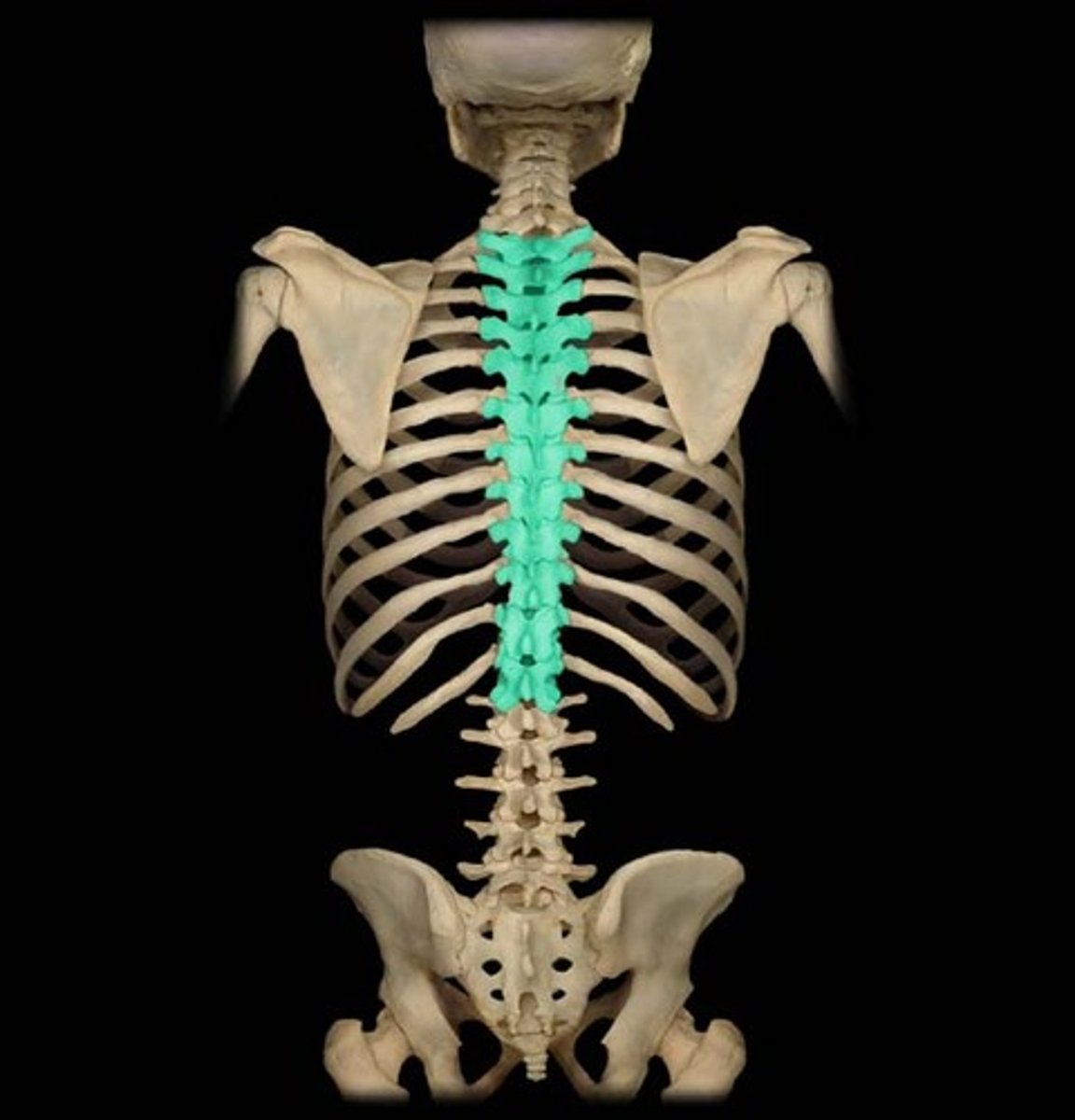
Irregular Bone
Features: Complex shape
Functions: Protect internal organs
Examples: Vertebrae & Facial bones
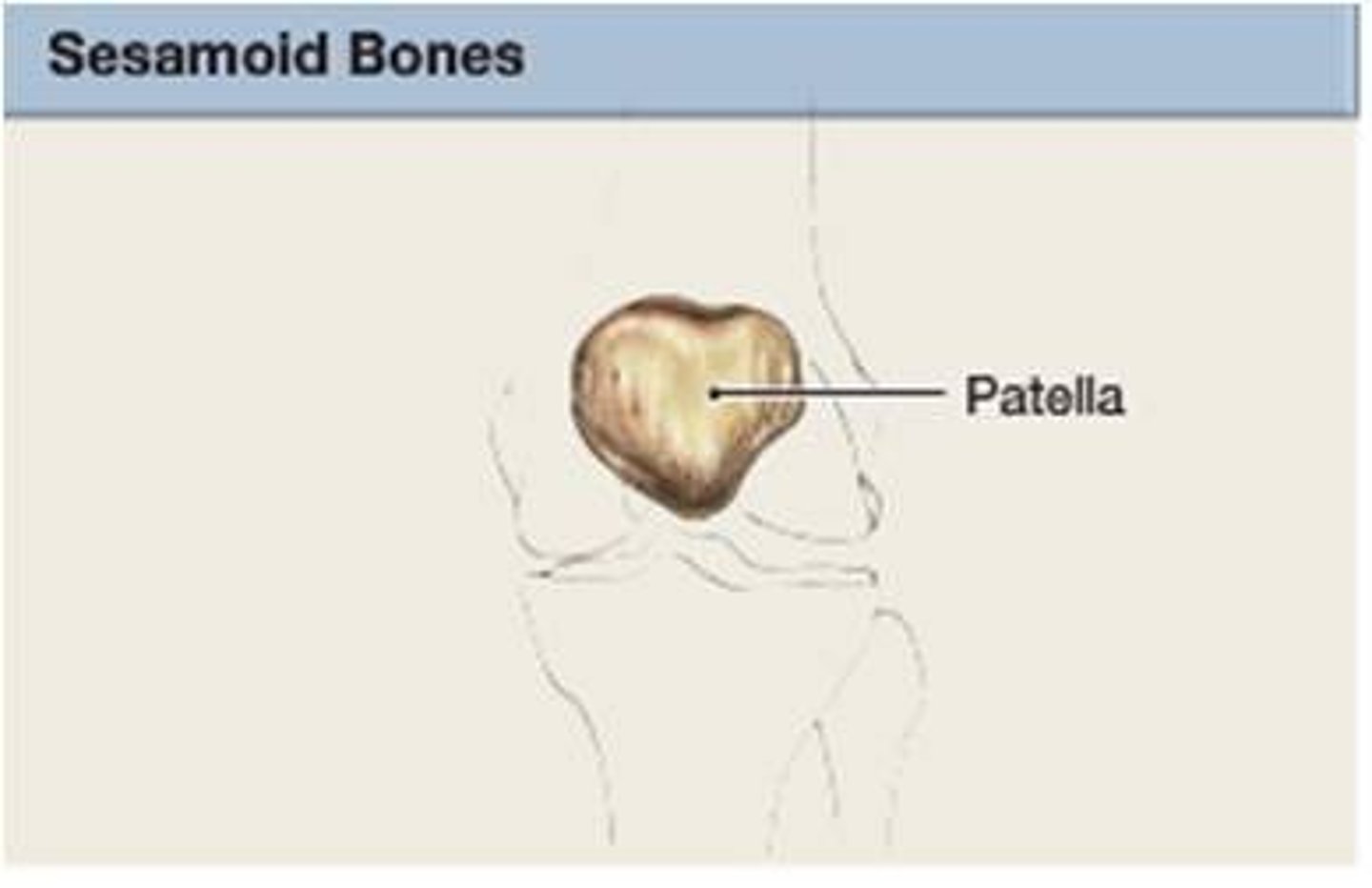
Sesamoid Bone
Features: Small and round; embedded in tendons
Functions: Protect tendons from compressive force
Examples Patellae (kneecap)
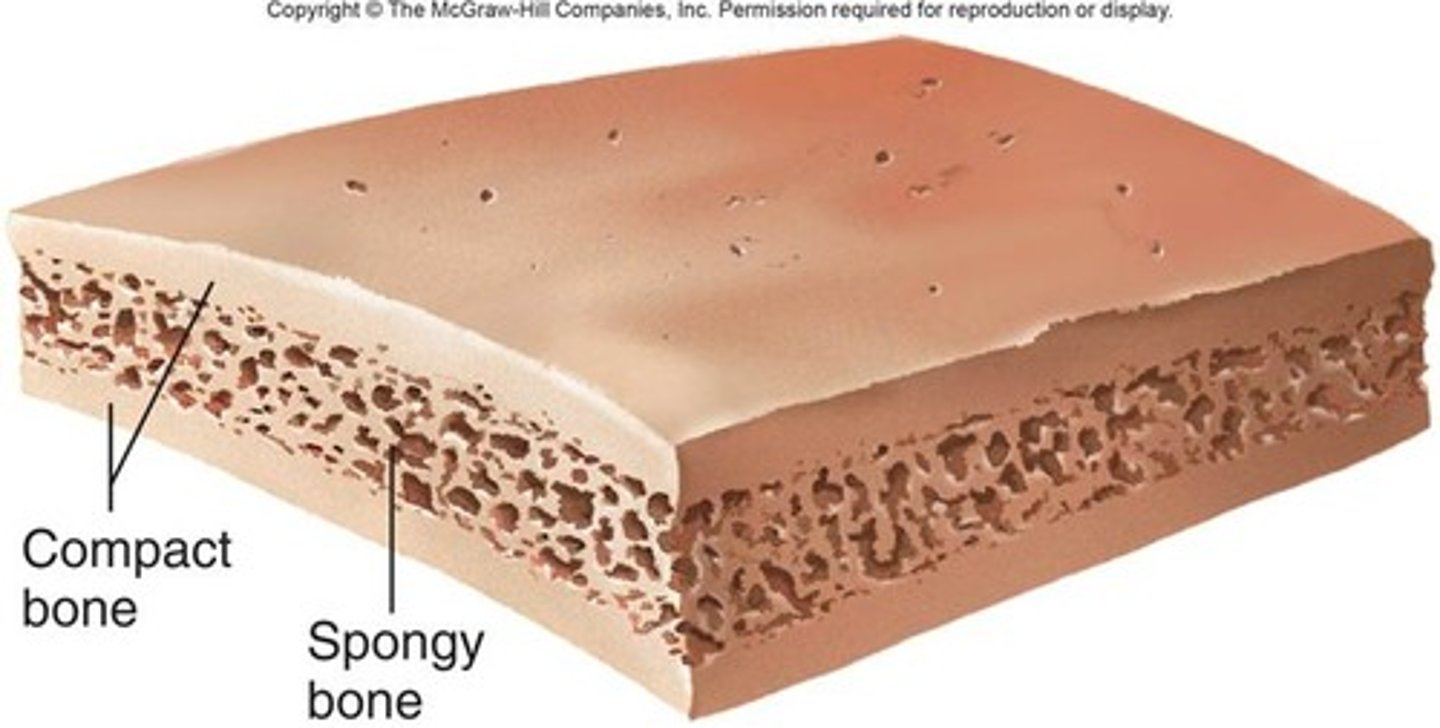
Spongy bone
Made up of trabeculae (interconnecting rods or plates of bone looks like scaffolding)
Additional Features: Spaces filled with marrow, Covered with endosteum (thin membrane of connective tissue), Orientated along stress lines
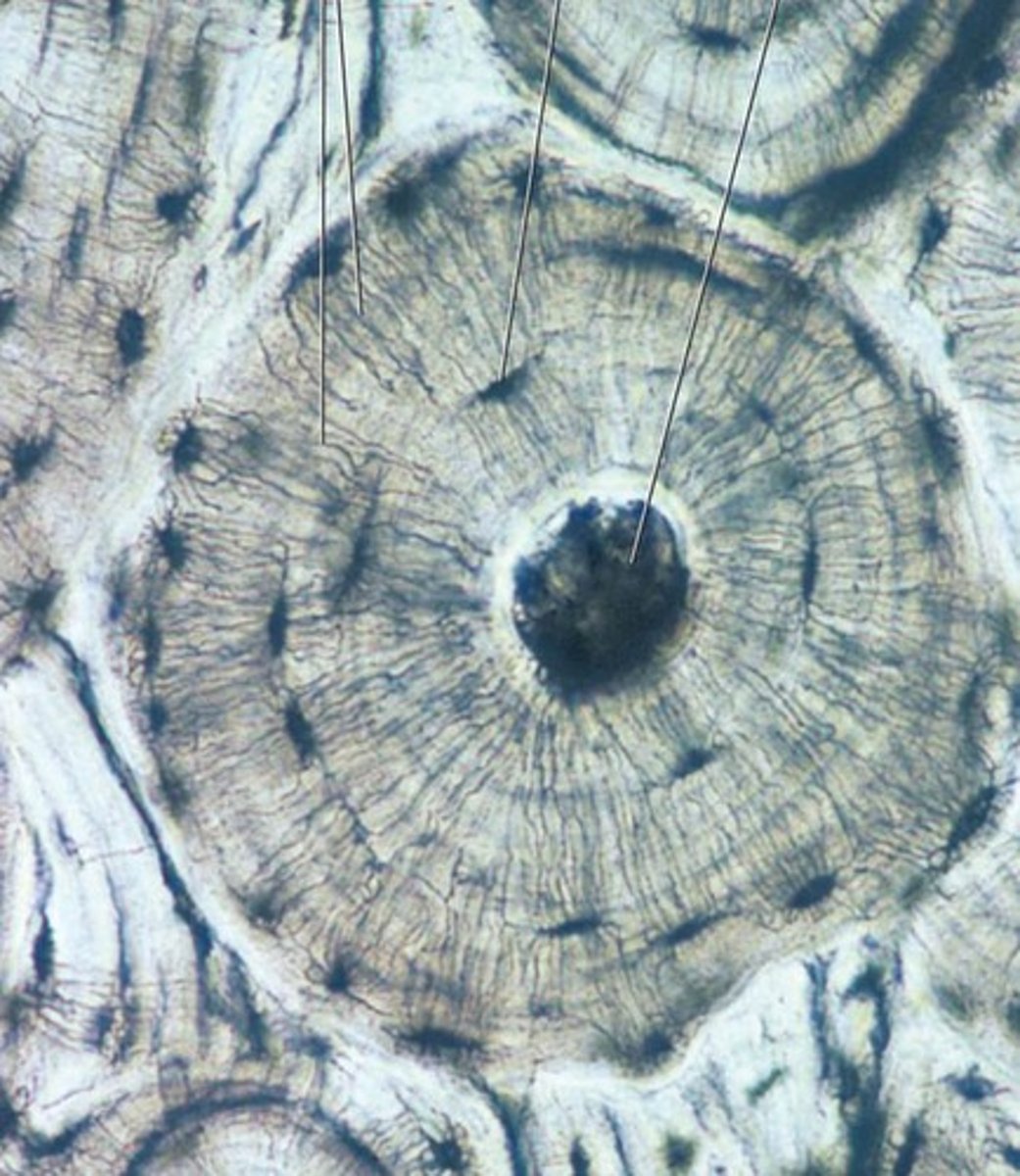
Compact bone
Made up of osteons (cylindrical units of bone)
Additional Features: Blood vessel-filled central canal
Diaphysis
The shaft or central part of the long bone; made up of compact bone
Epiphysis
The end of a long bone; made up of spongy bone
Proximal and distal epiphysis ends
Epiphyseal plate
A layer of cartilage in long bones that is responsible for bone growth and length.
Becomes the epiphyseal line when the bone stops growing
Medullary Cavity
The hollow space in the center of a long bone that contains bone marrow
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
Long Bone: Periosteum
Dense, white fibrous membrane that covers bone
Endosteum
A thin membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of a bone
Long Bone: Endosteum
lines the medullary cavity
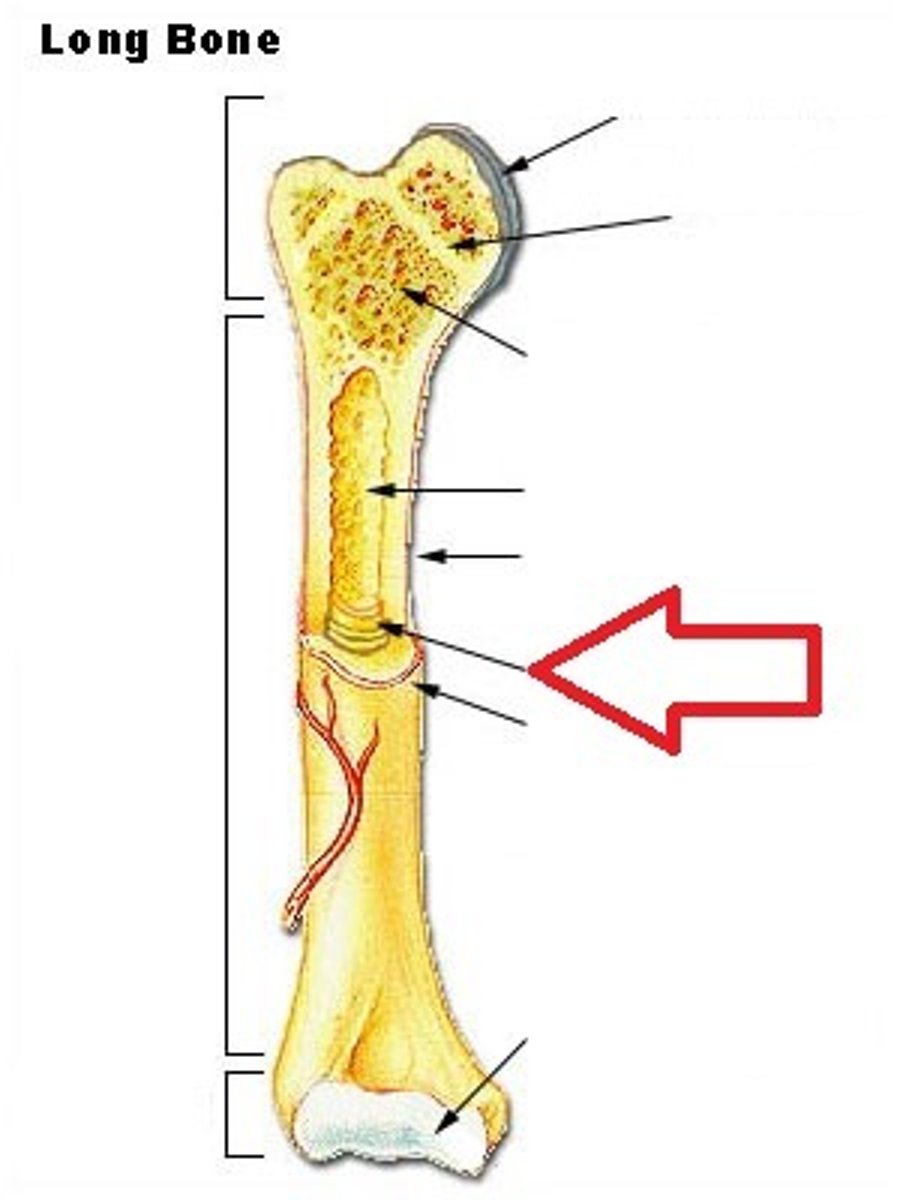
Proximal epiphysis
The end of bone closest to the trunk of the body
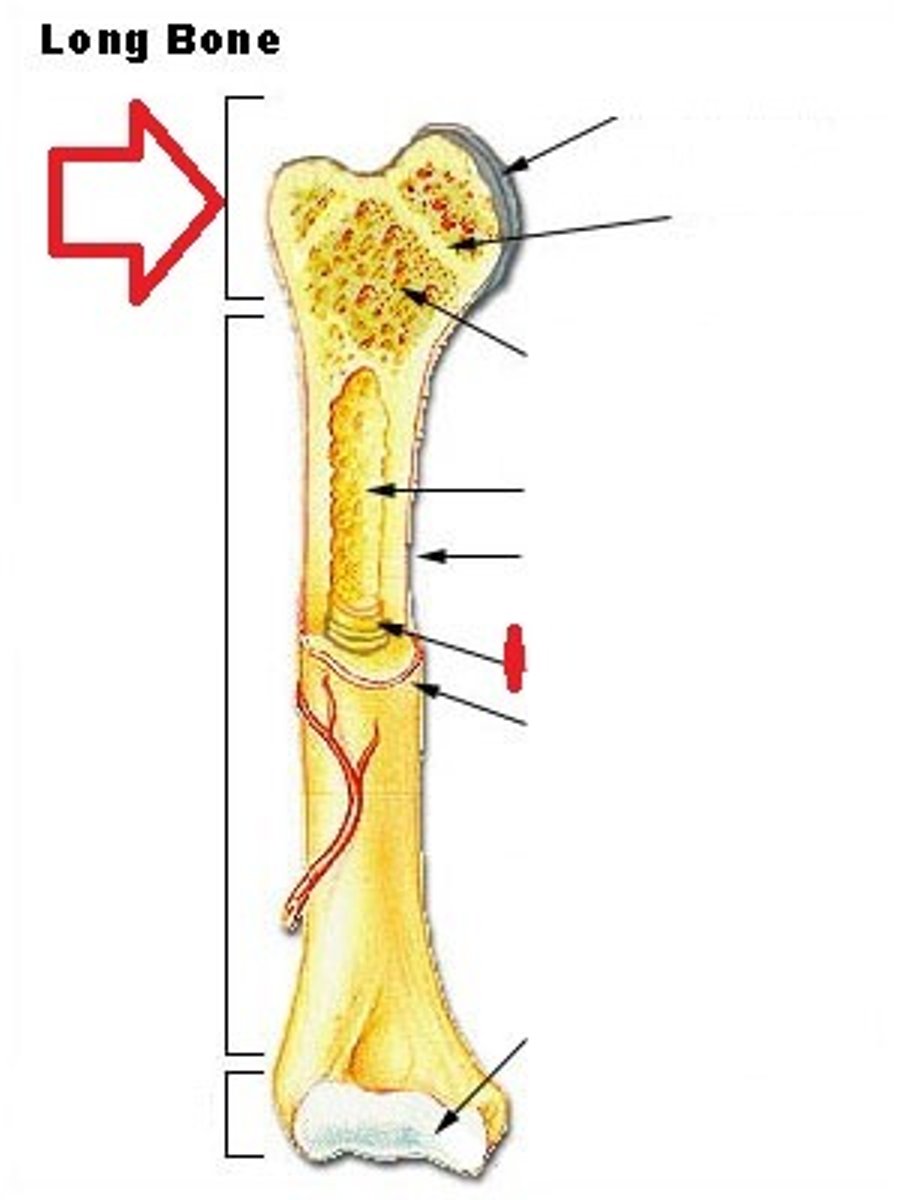
Distal epiphysis
The end of bone furthest to the trunk of the body
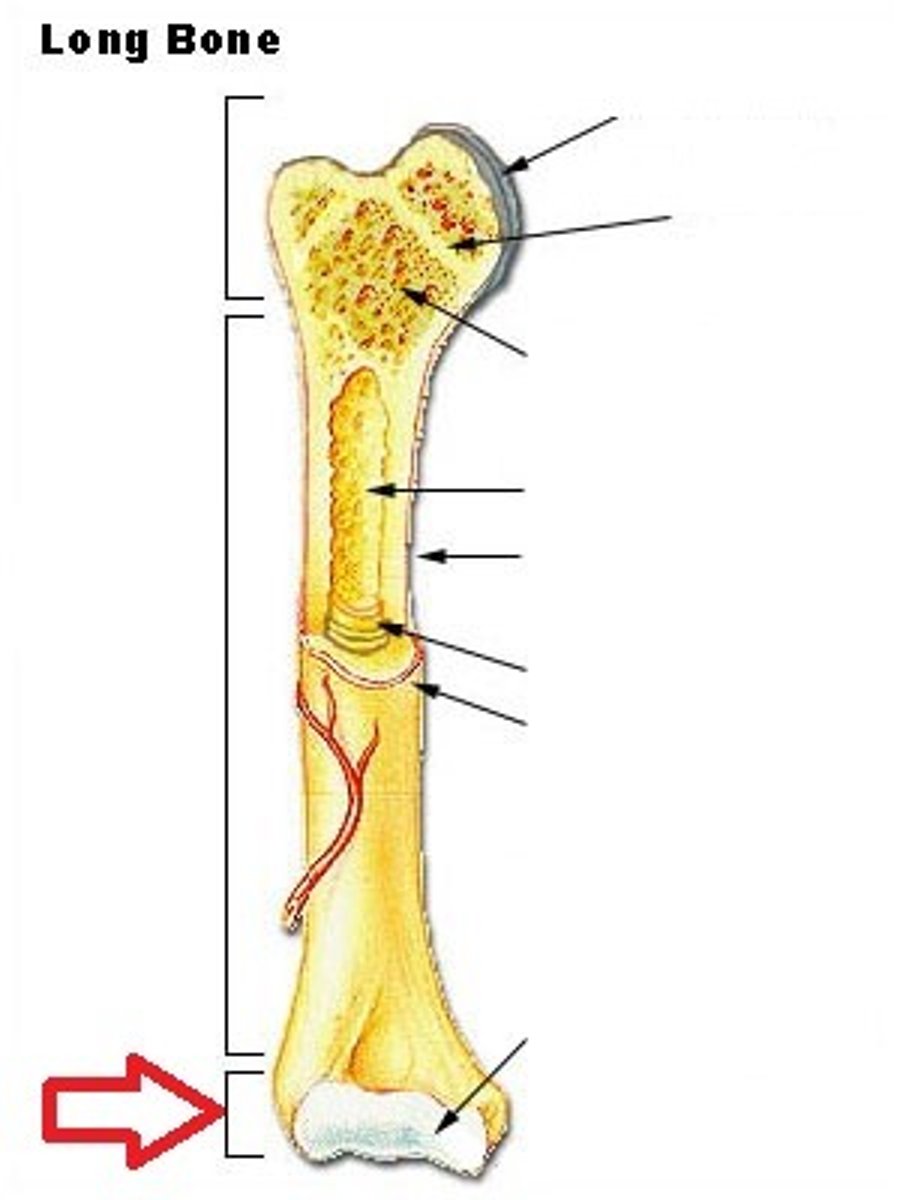
Epiphysis is covered with...
articular cartilage, this acts a shock absorber
Flat Bone Structure
No diaphyses or epiphyses. Sandwich of spongy bone between compact bone.
Irregular bone Structure
Spongy bone that is covered with a thin layer of compact bone
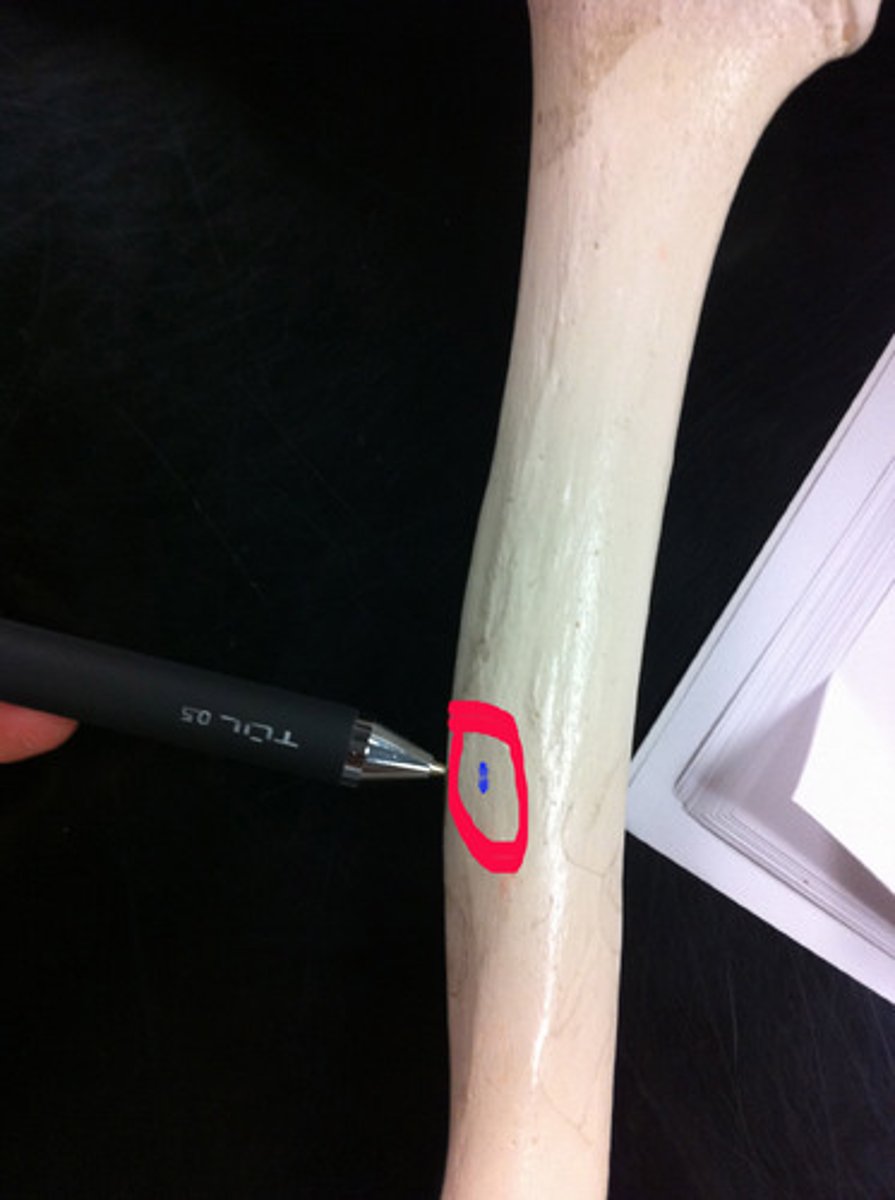
Spongy bone and medullary cavity receive nourishment from...
arteries that pass through the compact bone
Nutrient foramen
A small opening in the shaft of a long bone that allows a nutrient artery to pass through and supply the bone with nutrition

Bone matrix
The tissue that surrounds bone cells, and is made up of minerals and collagen fibers that give bones their strength and stiffness
If mineral is removed bone becomes too bendable
If collagen is removed bone becomes too brittle
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
Lacuna
A small cavity or space in bone or cartilage that contains an osteocyte, which is a bone cell
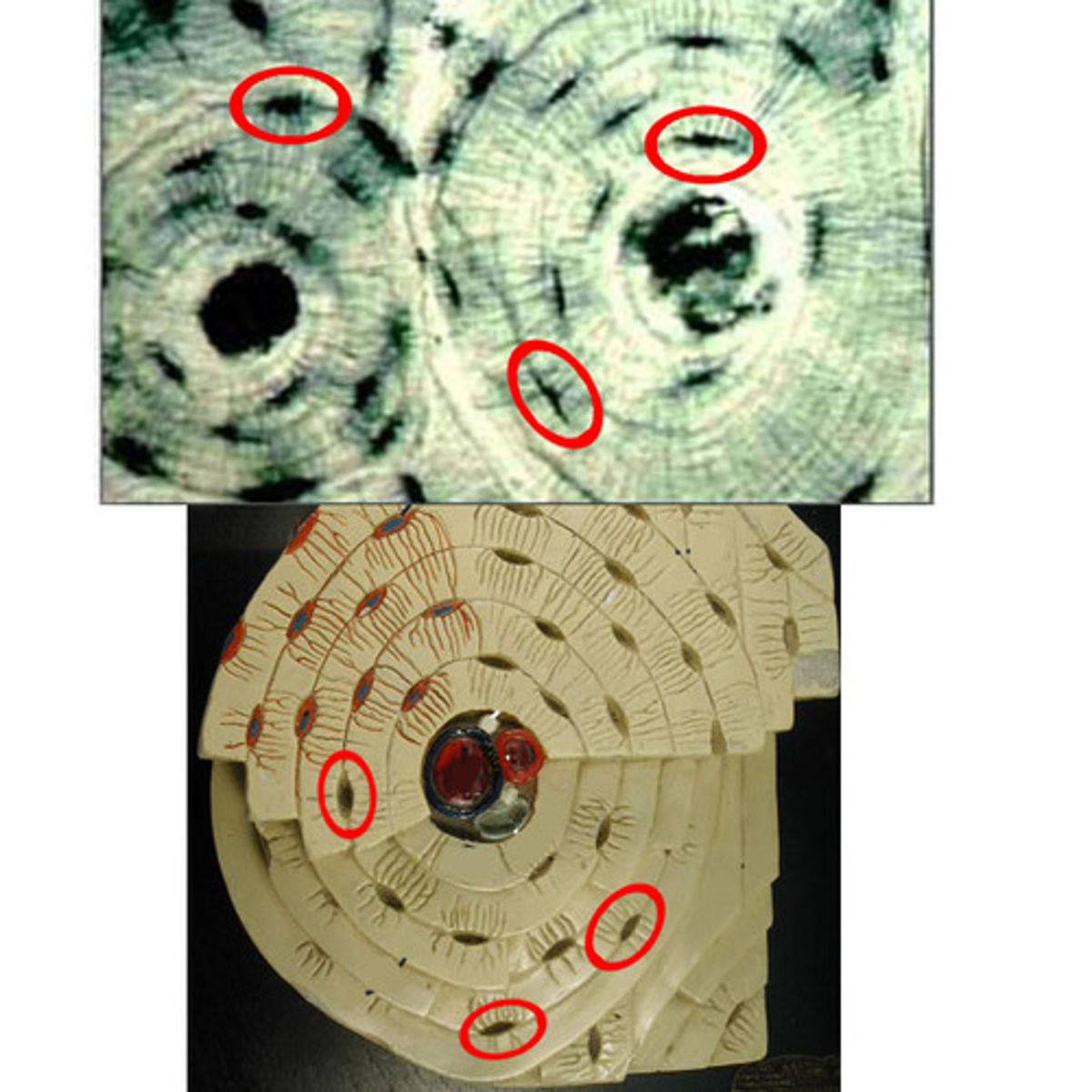
Osteocytes are located in...
lacunae
Canaliculi
Hair like canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal, used for communication and nutrition distribution
Osteoblasts
Cells that form and grow bone tissue
Ossification
Process of bone formation by osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Cells that break down bone tissue to help maintain a healthy skeleton
Osteogenic cells
Stem cells that differentiate (become) into osteoblasts and osteocytes
Osteoblasts and osteocytes are incapable of...
mitosis, osteogenic cells are used to replace them
Bone Markings
Surface features on a bone
Bone Marking Classes
Three: Articulations, Projections, Holes
Articulation
A joint, or the place where two or more bones meet
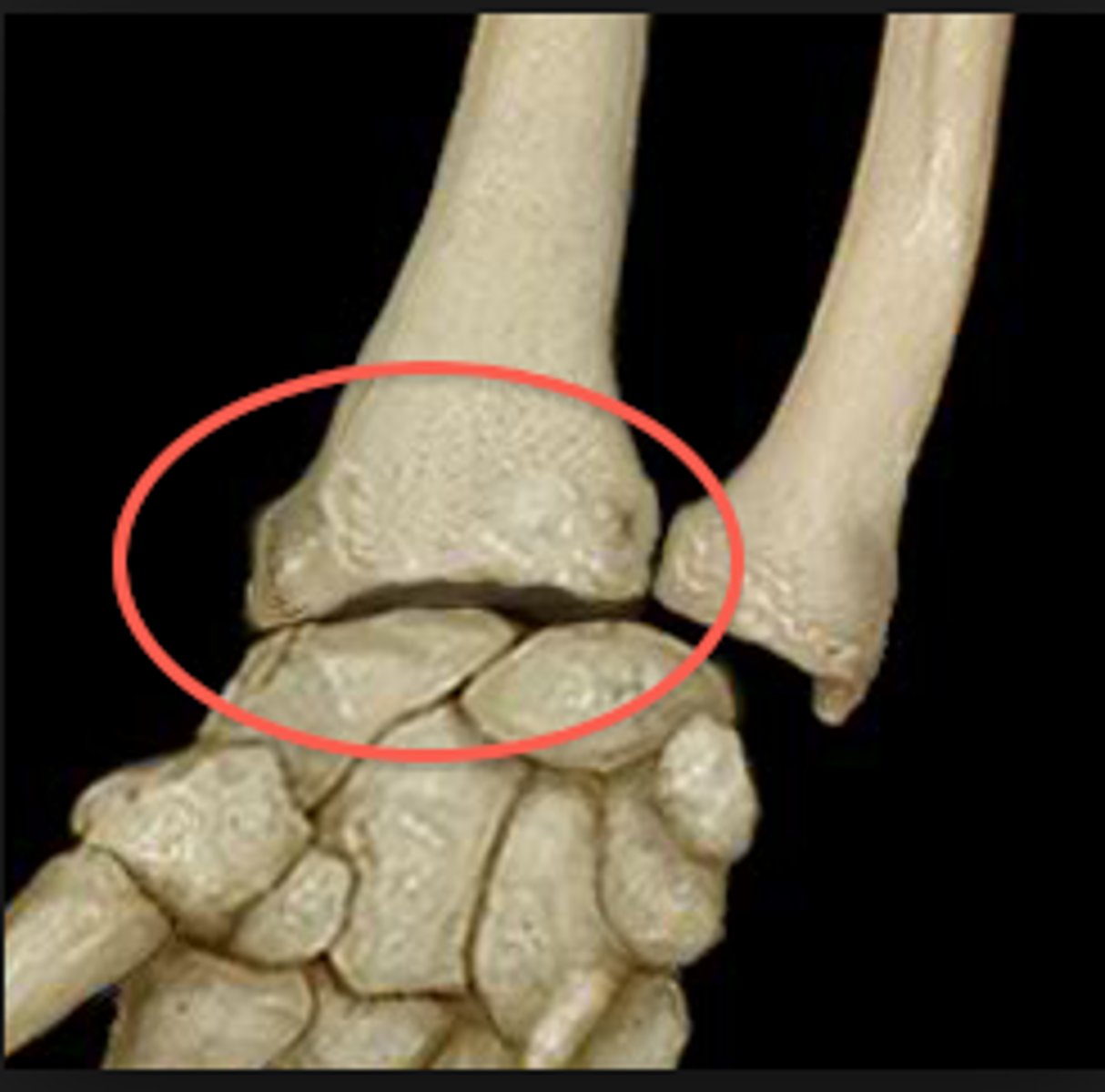
Projections
A part of a bone that sticks out from the bone's surface
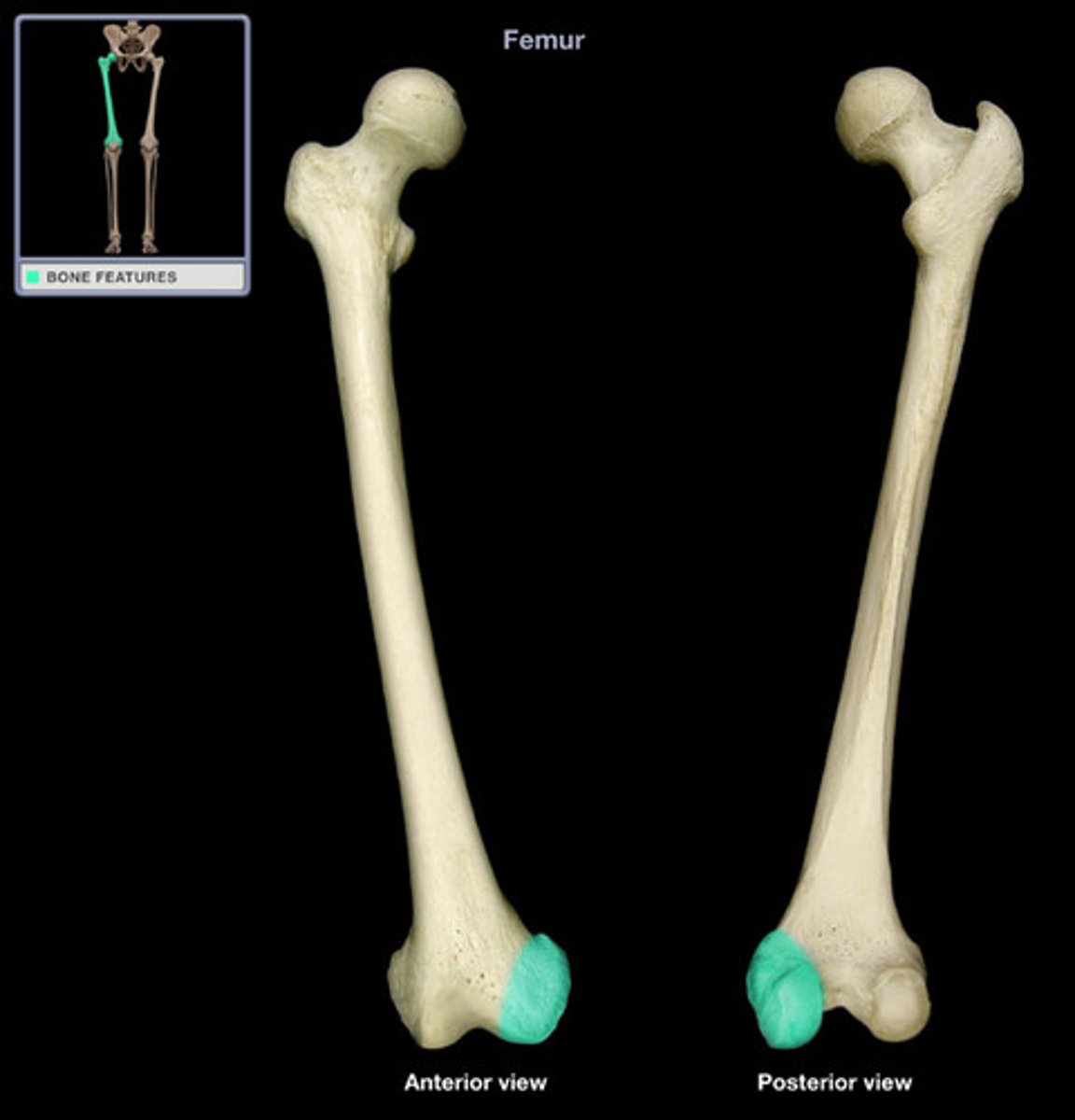
Holes
Refers to foramens (literal holes or gaps)
Foramen
A hole through which nerves and blood vessels pass
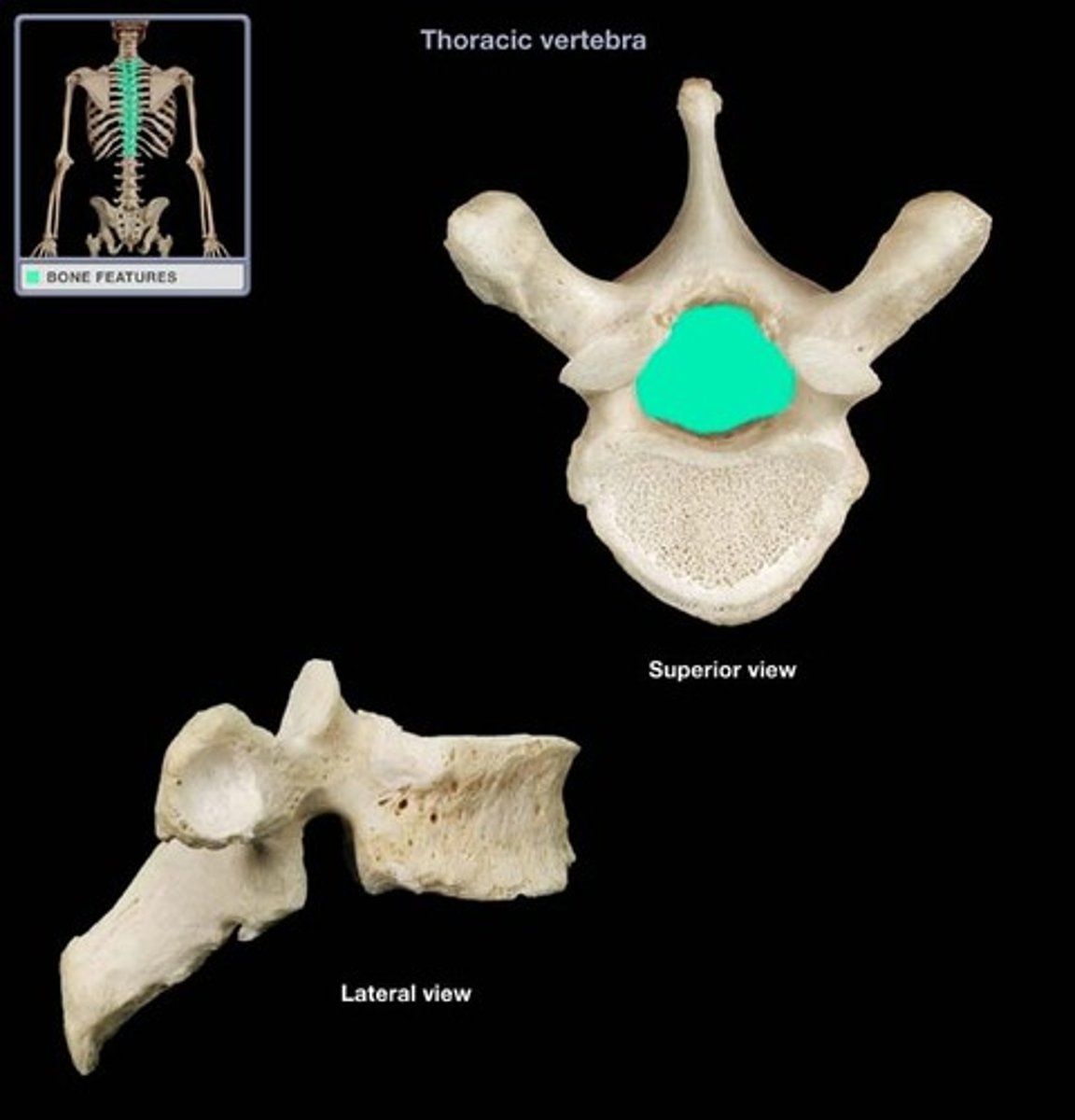
Intramembranous ossification
A process that forms bones directly from mesenchymal tissue (embryonic tissue)
Takes place in connective tissue membrane
Produces flat bones of skull and clavicle (collarbone)
Intramembranous ossification forms...
Forms many skull bones, part of mandible, diaphysis of clavicles (collarbone)
Intramembranous ossification takes place in...
Takes place in connective tissue membrane
Endochondral ossification
The process of replacing hyaline cartilage with bone
Takes place in cartilage
Endochondral ossification takes place in...
cartilage, specifically hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces
Ossification (osteogenesis)
Process of bone formation; created from cartilage or fibrous tissue
Methods of Ossification
intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification
Centers of ossification
locations in membrane where ossification begins
Fontanels
Soft spots on a baby's skull where the skull bones are not yet joined together
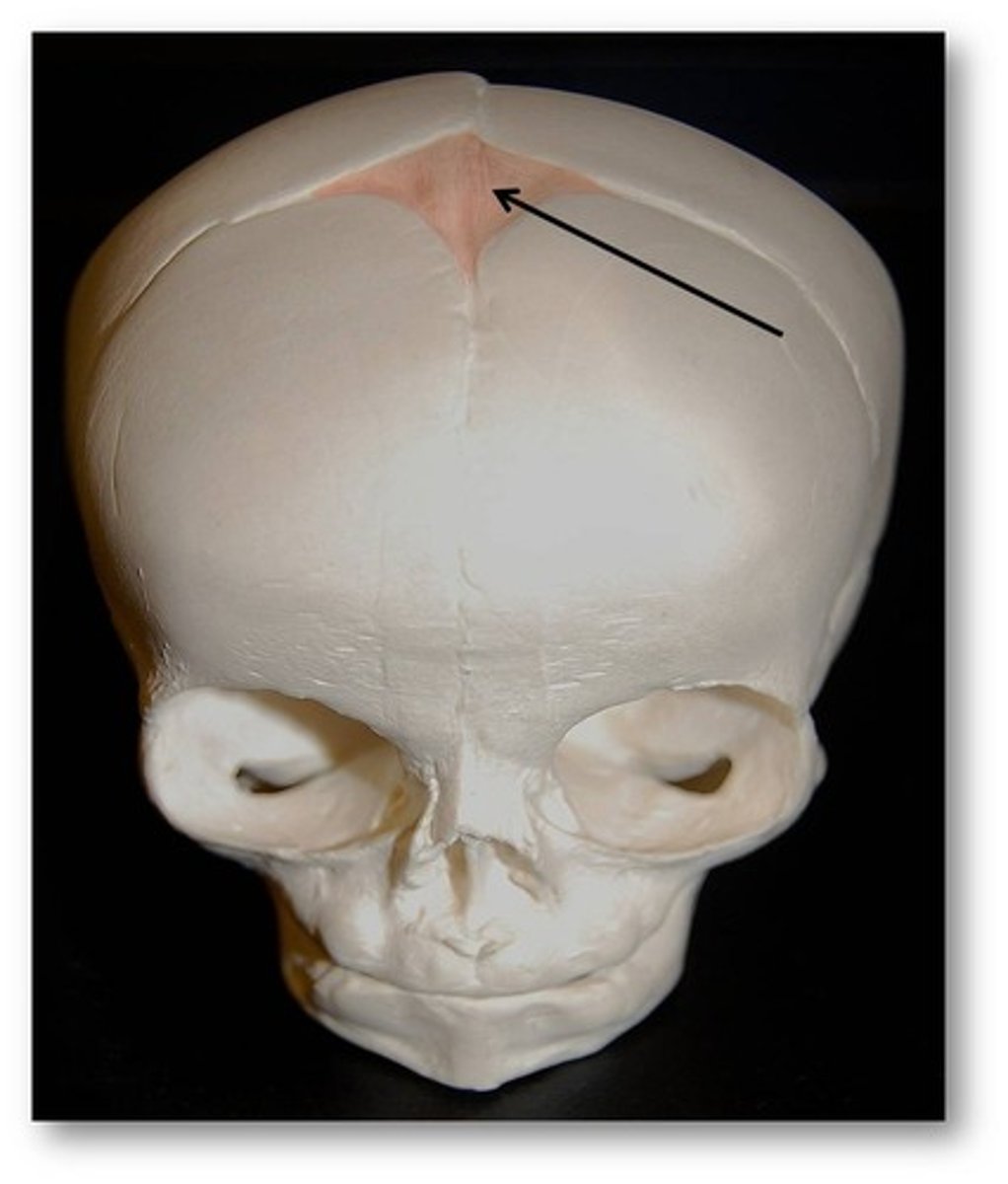
Intramembranous Ossification Steps
1. Early osteoblasts appear in the ossification center.
2. Osteoblasts secrete uncalcified matrix that hardens in a few days (calcification)
3. Once hardened, osteoblasts become osteocytes.
4. Osteogenic cells differentiate into new osteoblasts.
5. Trabecular bone forms (scaffold like bone) and compact bone develops on the surface.
Endochondral Ossification Steps
The process where a baby's bones develop from a cartilage template, essentially "replacing" the cartilage with bone as the body grows
1. Around 6-8 weeks after conception, mesenchymal cells become chondrocytes.
2. The perichondrium forms and becomes vascularized (gets blood supply).
3. Blood vessels cause mesenchymal cells to turn into osteoblasts, forming a bone collar.
4. Chondrocytes die as the matrix hardens, creating space in the center of the bone.
5. Blood vessels invade, bringing osteogenic cells with them.
6. A secondary ossification center forms at the ends of the bone (the cartilage remains until after birth).
7. The epiphyseal plate remains between the primary and secondary ossification centers for bone growth
Chondrocytes
Cells that make up cartilage
a connective tissue that provides structural support and protects bones at joints
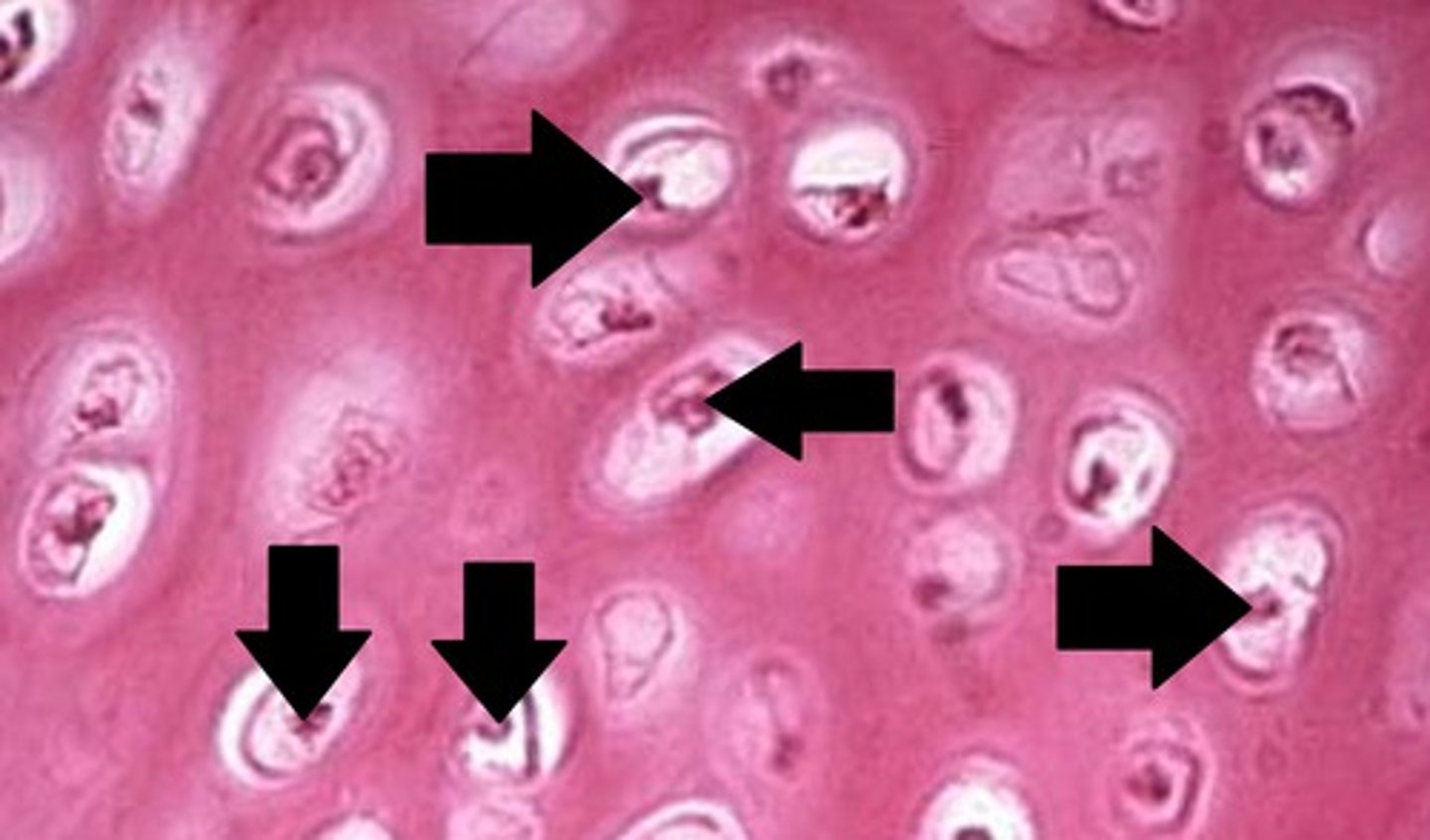
Perichondrium
A dense layer of fibrous connective tissue that covers the surface of most of the cartilage in the body
Periosteal bud
A vascular tissue that contains blood vessels, osteoprogenitor cells, and hemopoietic cells that invade the center of a developing bone
Hematopoietic cells
Blood forming cells
Osteoprogenitor cells
Bone stem cells
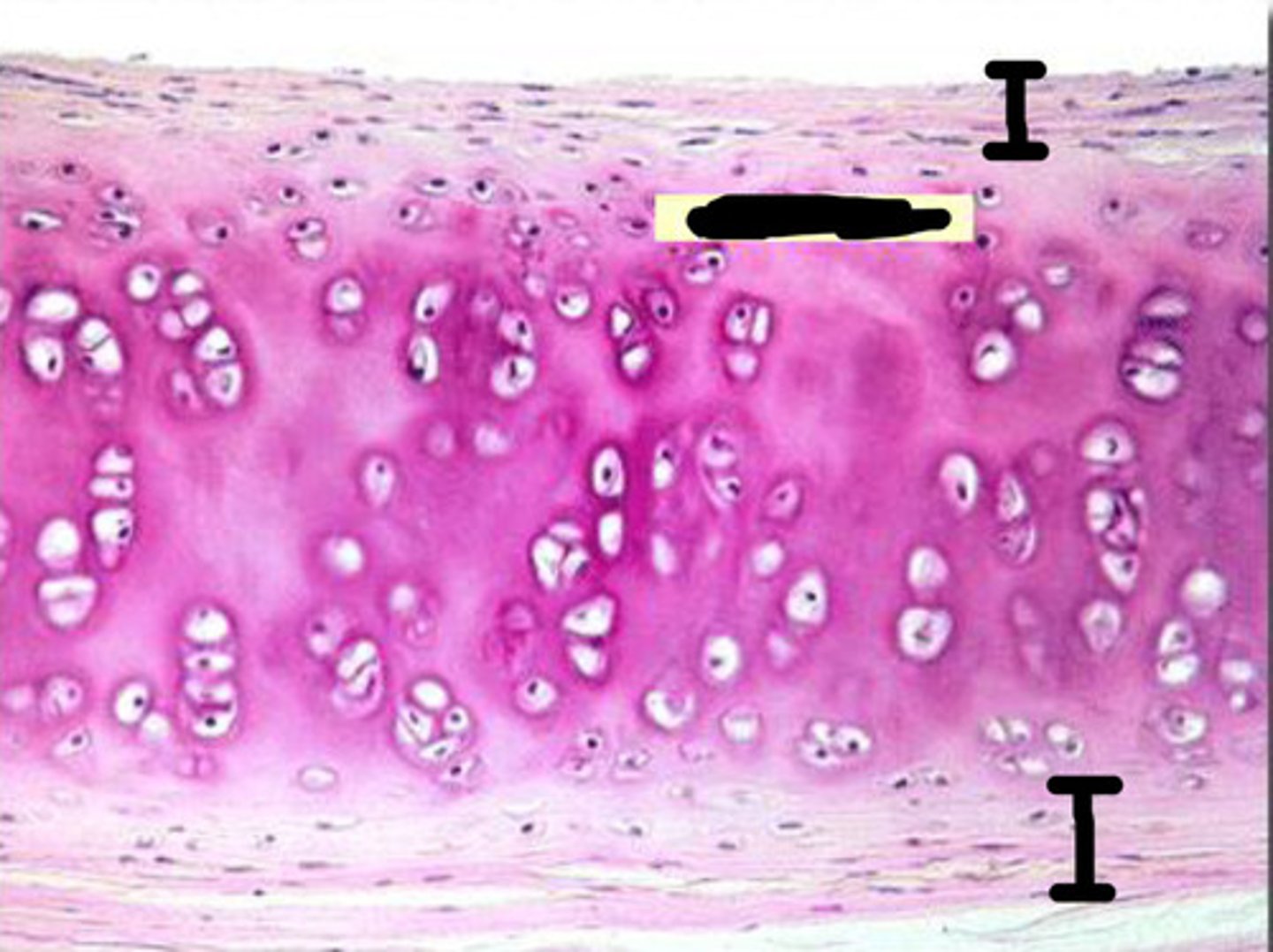
Zones of the Epiphyseal Plate
1. Zone of resting cartilage
2. Zone of proliferating cartilage
3. Zone of hypertrophic cartilage
4. Zone of calcified cartilage
5. Zone of ossification
Zone of resting cartilage
Slowly dividing chondrocytes
Zone of proliferating cartilage
New cartilage is made as chondrocytes divide and form stacks of cells
Zone of hypertrophic cartilage
Chondrocytes grow larger and mature.
Zone of calcified cartilage
The matrix hardens (calcifies), and chondrocytes die.
Zone of ossification
The cartilage is replaced by bone tissue.
Wolff's law
Bone is modeled and remodeled based on stresses applied to it
Paget's disease
A disease of unknown origin that is characterized by abnormal bone growth and weakening
Incomplete Fracture
Bone is not broken all the way through
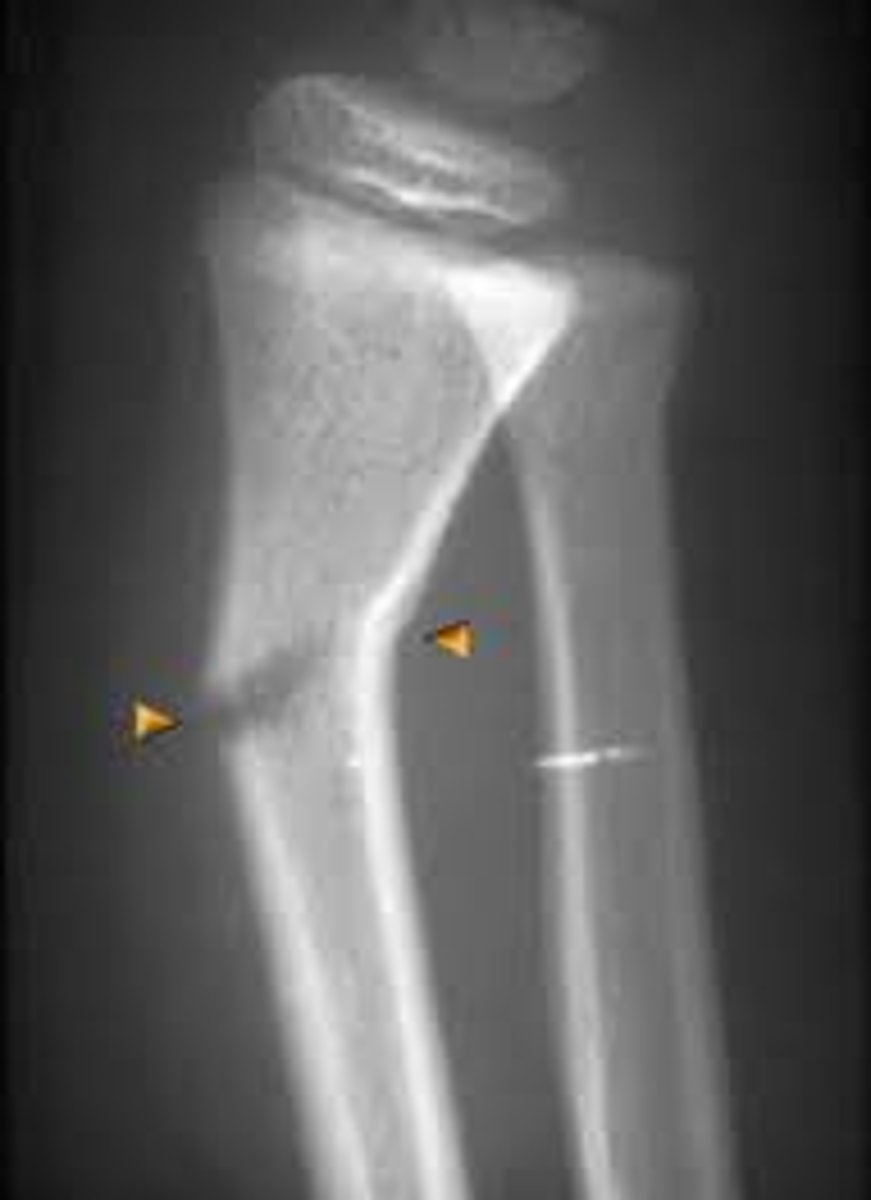
Complete Fracture
Bone is broken all the way through
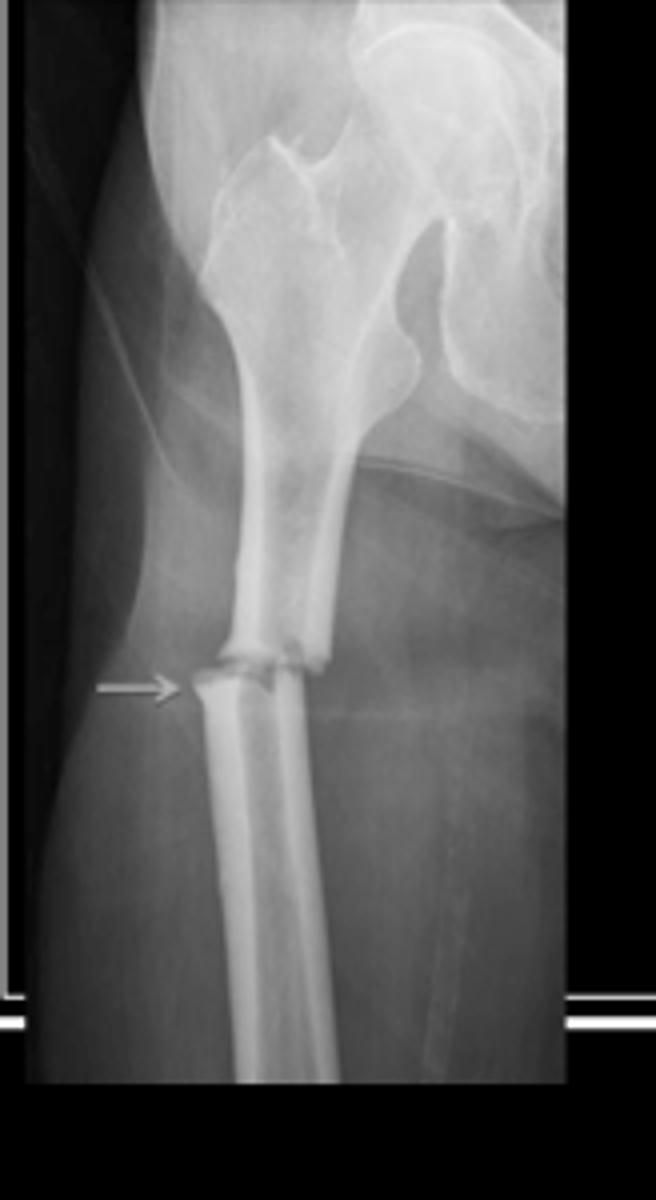
Communited fracture
Bone is splintered or crushed
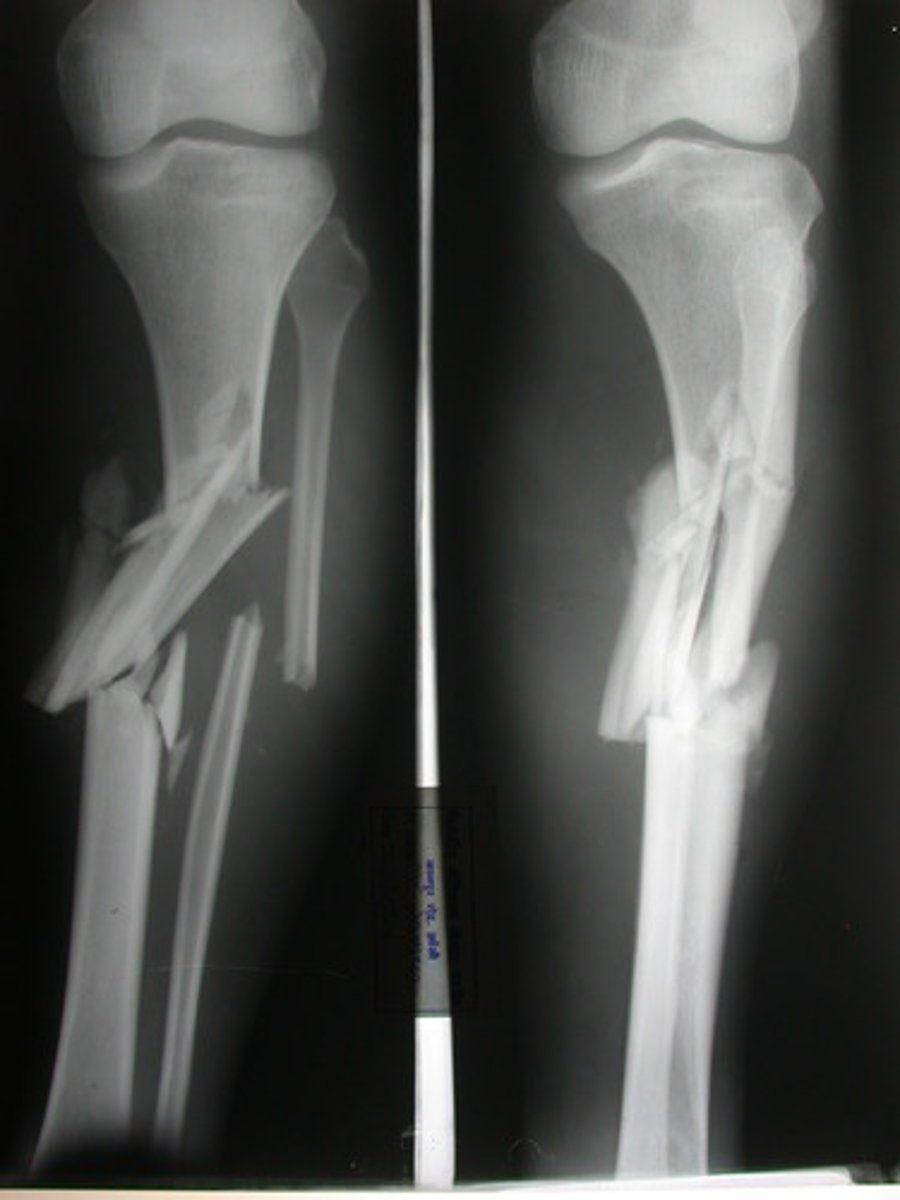
Bone Repair
1. Hematoma formation
2. callus formation
3. callus ossification (Callus replaced by spongy bone)
4. bone remodeling (Replacement of spongy bone and damaged material by compact bone & sculpting by osteoclasts)
Hematoma
A solid swelling of clotted blood within the tissues.
Factors affecting bone growth
Hormones (Estrogen and testosterone) and vitamins (Vitamin D, Vitamin C)
Three hormones that control blood calcium levels
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), Calcitriol, Calcitonin
Parathyroid Hormone
Released when blood calcium levels are too low and activates osteoclasts, causes calcitriol to be released
Hypocalcemia
Low levels of calcium
Hypercalcemia
High levels of calcium, can cause kidney stones
Calcitriol
A hormone produced from vitamin D that, increases blood calcium by stimulating intestinal absorption of calcium
(Acts in essentially the same manner as parathyroid hormone)
Calcitonin
Lowers blood calcium levels, counter acts the parathyroid hormone by inhibiting osteoclast
Effects of aging on the skeletal system...
Bone Matrix decreases
Bone Mass decreases
Increased bone fractures
Bone loss causes deformity, loss of height, pain, stiffness
Stooped posture
Loss of teeth
Homeostatic relationship between skeletal system and other organ systems...
1. Skeletal System provides support for body organs including the skin.
2. Skeletal system is dependent upon skin to provide vitamin D
3. Skeletal system works with muscles to provide movement