Energy Stores & Transfers
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What is a system?
An object or group of objects. e.g. an apple sitting on a table is system
What happens when there is a change in a system?
Energy is transferred into or away from the system, between objects in the system or between different energy stores.
What are the three thermodynamic systems?
Open system
Closed system
Isolated system
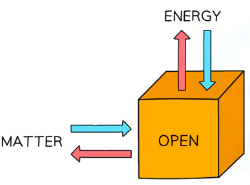
What is an open system?
A system that allows the exchange of energy and matter to or from its surroundings.
What is a closed system?
A closed system is a system where energy can be transferred within the system, but no matter can be exchanged with the surroundings. The total energy remains constant, but matter does not enter or leave the system.
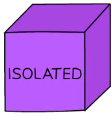
What is an isolated system?
A system that does not allow the transfer of matter or energy to or from its surroundings.
What does the principle of conservation of energy state?
That energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transferred from one object or energy store to another.
What is the total amount of energy in a closed system?
Constant.
Name all the energy stores:
Kinetic, Gravitational, Elastic, Magnetic, Electrostatic, Chemical, Nuclear, Thermal
When do objects have energy in their kinetic energy store?
Moving objects have energy in their kinetic store
When do objects have energy in their gravitational potential energy store?
Objects gain energy in their gravitational potential store when it is above the ground or another reference point and has the potential to fall due to gravity.
When do objects have energy in their Elastic energy store?
Objects have energy in their elastic potential store if they are stretched, squashed or bent.
When do objects have energy in their magnetic energy store?
Magnetic materials interacting with each other have energy in their magnetic store.
When do objects have energy in their electrostatic energy store?
Objects with charge (e.g. protons & electrons) interacting with each other have energy in their electrostatic store.
When do objects have energy in their chemical energy store?
Chemical reactions transfer energy into or away from a substance’s chemical store.
When do objects have energy in their nuclear energy store?
Atomic nuclei release energy from their nuclear store during nuclear reactions.
When do objects have energy in their thermal energy store?
All objects have energy in their thermal energy store, the hotter the object, the more energy it has in this store.
What are the different ways energy can be transferred?
Mechanically
Electrically
By heating
By radiation
How is energy transferred mechanically?
When a force acts on an object - pulling, pushing, stretching, squashing
How is energy transferred electrically?
By a charge moving through a potential difference - e.g. current
What is energy transfer by heating? (from where and where is energy transferred)
When energy is transferred from a hotter object to a colder one - e.g. conduction.
How is energy transferred by radiation?
When energy is transferred by electromagnetic waves - e.g. visible light
Describe how energy is transferred by heating in boiling water in a kettle:
You could think of the water as the system. Energy is transferred to the water from the kettle’s heating element, by heating, into the water’s thermal energy store - causing the temperature of the water to rise.
Or you could think of the kettle’s heating element and the water together as a two-object system. Energy is transferred electrically to the thermal energy store of the kettle’s heating element, which transfers energy by heating to the water’s thermal energy store.
What is work done?
It is another way of saying energy transferred.
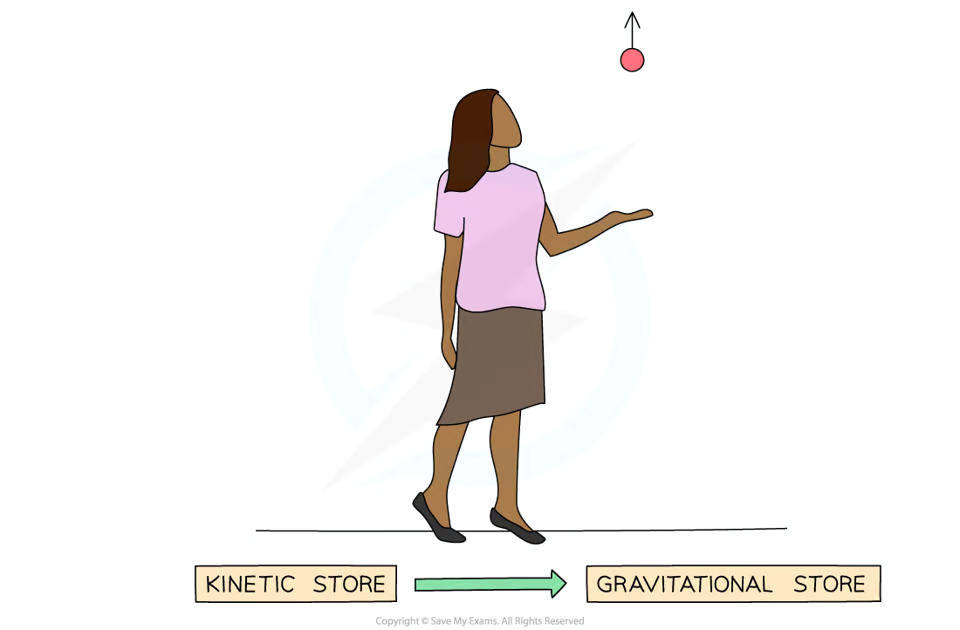
Describe how energy is transferred when a ball is thrown upwards:
The initial force exerted by a person to throw a ball upwards does work (tranfers energy). It causes an energy transfer from the chemical store in the person’s arm to the kinetic store of the ball as it begins to move. As the height of the ball increases, energy from the kinetic store of the ball is transferred to its gravitational potential store.
Describe how energy is transferred when a moving object (car) hits an obstacle:
When a car is moving, energy in the chemical store of the fuel is transferred to the kinetic store of the car. When a car hits an obstacle, speed of the car decreases very quickly causing energy to be transferred from the car’s kinetic store to other stores - e.g. the elastic potential & thermal energy stores of the object & the car body, some energy may be transferred away by sound waves.

Describe how energy is transferred when a car slow down:
When a car is moving, there is energy in its kinetic store. As it slows the friction between the car’s brakes and its wheels does work and causes an energy transfer, by heating, to the thermal store of the surroundings.

What happens when a ball is dropped from a height?
The ball is accelerated by gravity & the gravitational force does work. As it falls, energy is transferred from the balls gravitational potential store (g.p.e) to its kinetic store.
What can be said about a falling object when there is no air resistance?
Energy lost from the g.p.e store = Energy gained in the kinetic energy store

What is energy in the kinetic energy store defined as?
The amount of energy an object has as a result of its mass & speed.
When an object speeds up…
Energy is transferred to its kinetic energy store
When an object slows down…
Energy is transferred away from its kinetic store.
What does the energy in the kinetic energy store depend on?
The mass & speed of the object.
When is there more energy in an objects kinetic energy store?
When the object has a greater mass OR is going at a faster speed.
What is the equation used to calculate Kinetic energy?
Ek = ½ × m × v2
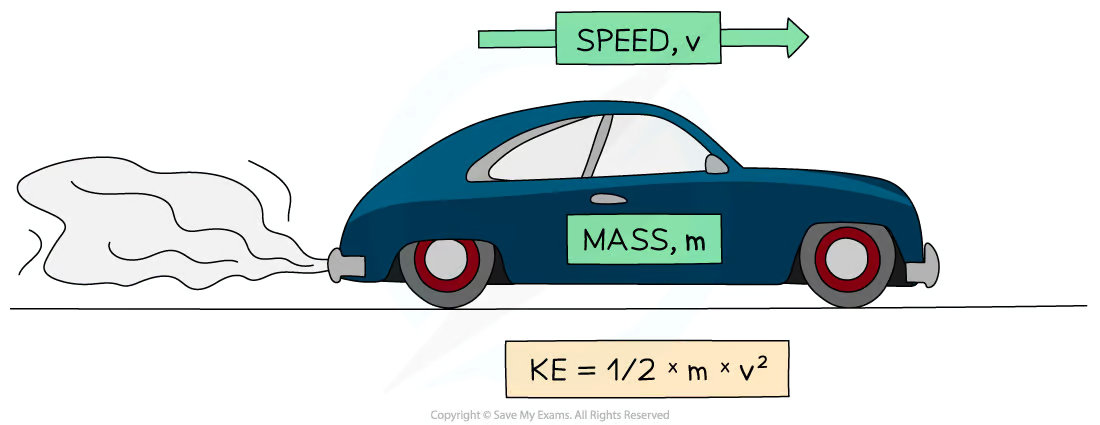
What is Kinetic energy (Ek) measured in?
Joules (J)
What is the mass (m) of the object measured in?
Kilograms (kg)
What is the speed (v) of the object measured in?
Metres per second (m/s)
Calculate the kinetic energy store in a vehicle of mass 1200kg moving at a speed of 27m/s.
mass = 1200g, speed = 27m/s
E = ½ mv²
E = ½ × 1200 × 27²
E = 437,400J, round to 2s.f. = 440,000J
What is gravitational potential energy?
The energy an object has due to its height in a gravitational field.
If an object is lifted up…
Energy is transferred to its gravitational potential store.
If an object falls…
Energy is transferred away from its gravitational potential store.
The higher the object is lifted…
The more energy is transferred to the g.p.e. store.
What does the amount of energy in a gravitational potential energy store depend on?
The objects mass, its height and the strength of the gravitational field the object is in.
What is the equation used to calculate the gravitational potential energy of an object?
Ep = mgh
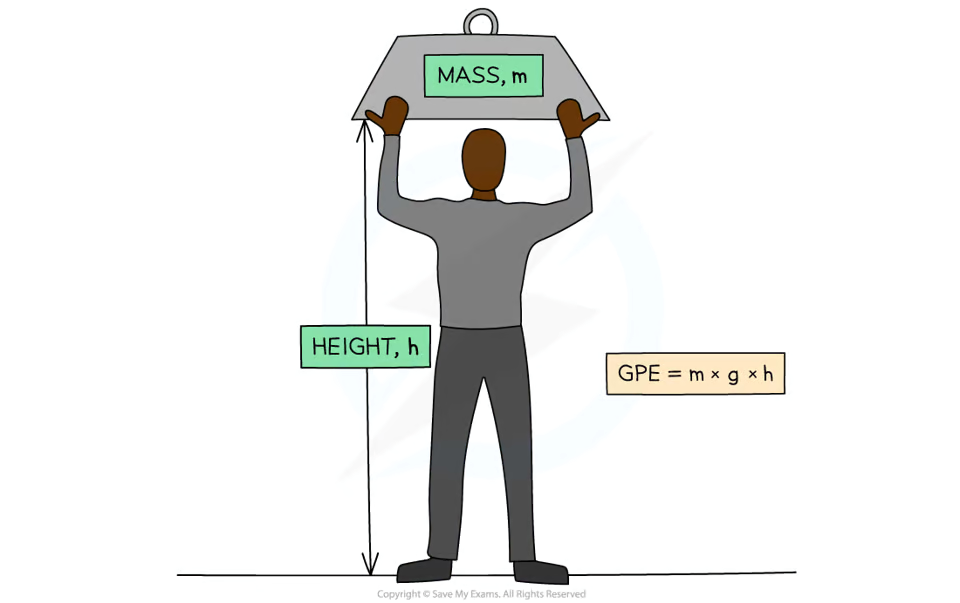
What is the gravitational potential energy (Ep) of the object measured in?
Joules (J)
What is the mass (m) of the object measured in?
Kilograms (kg)
What is the gravitational field strength (g) measured in?
Newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
What is height measured in?
Metres (m)
What is the gravitational field strength on Earth?
Approximately 9.8N/kg.
A man of mass 70kg climbs a flight of stairs that is 3m higher than the floor. Gravitational field strength is approximately 9.8N/kg. Calculate the energy transferred to the man’s gravitational potential energy store.
E = mgh
E = 70 × 9.8 × 3 = 2058J
What is elastic potential energy?
The energy stored in an elastic object when it is stretched, compressed, or deformed.
What happens when a spring is stretched or compressed?
Work is done on the spring which results in energy being transferred to the elastic potential energy store of the spring.
What happens when a spring is released from being stretched or compressed? (related to transfer of energy)
Energy is transferred away from its elastic potential store.
What equation is used to calculate the amount of energy in the elastic potential energy store of a stretched spring?
Ee = ½ × k × e2
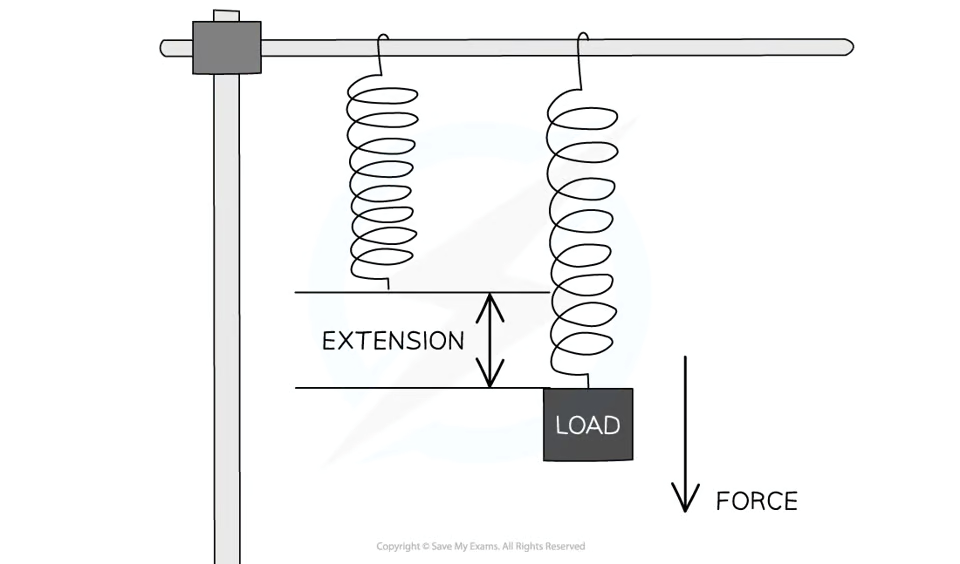
What is elastic potential energy (Ee) measured in?
Joules (J)
What is spring constant (k) measured in?
Newtons per metre (N/m)
What is extension (e) measured in?
metres (m)
Up to what point can the elastic potential energy equation be used?
So long as the limit of proportionality has not been exceeded then the equation can be used.
A mass is attached to the bottom of a hanging spring with a spring constant of 250N/m. It stretches from 10.0cm to 11.4cm. Calculate the elastic potential energy stored by the stretched spring.
extension = 11.4 - 10 = 1.4cm = 0.014m
E = ½ke²
E = ½ x 250 × 0.014² = 0.0245, 2s.f. = 0.025J