Chapter 23: Structure of The Flowering Plant
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Functions of Root System
anchor plant into ground, absorb water and minerals, transport absorbed minerals to shoot, storage of food
Types of Root
tap root, fibrous root, adventitious root
Radicle
young root
Tap Root
one main long root that comes from the radicle, present in dicots
Plants with Tap Roots
dandelion, carrot
Fibrous Root
formed when radicle dies and leaves equal sized roots coming out of the stem, present in monocots
Plants with Fibrous Roots
daffodil, grass
Adventitious Root
these do not grow from the radicle, and are found in odd places
Examples of Adventitious Roots
ivy, strawberry plant
Root Zones
zone of protection, meristematic zone, zone of elongation, zone of differentiation
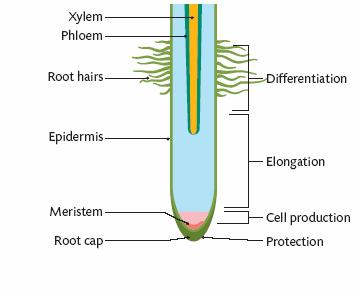
Zone of Protection
root cap protects the meristem as it pushes through soil
Meristematic Zone
region of active cell production where mitosis occurs
Apical Meristems
found at root and shoot tips, responsible for lengething roots and shoots
Lateral Meristems
found at side of plants, responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots
Zone of Elongation
region of the root or shoot where cells elongate due to newly formed cells absorbing water and plant regulators, contributing to the growth of the plant's length
Zone of Differentiation
the region of the root or shoot where cells undergo specialization into various cell types, contributing to the formation of different tissues in the plant
The Shoot System
the part of the flowering plant that includes stems, leaves, and flowers, responsible for photosynthesis, support, reproduction, and transport of nutrients.
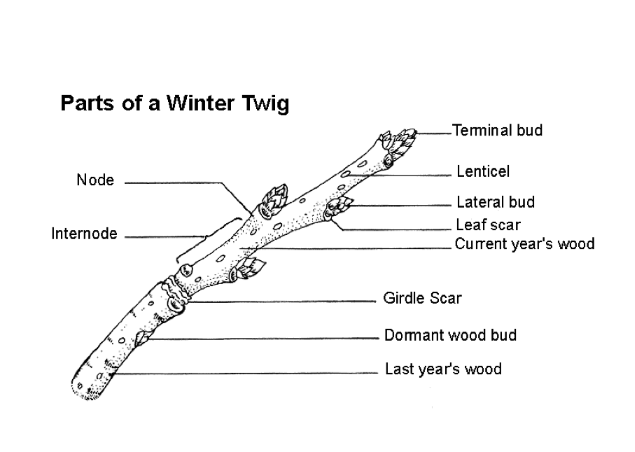
Twig Diagram
terminal bud, lenticel, lateral bud, leaf scar, current years wood, girdle scar, dormant wood bud, last years wood, node, internode
Leaves
the main sites of photosynthesis and transpiration, also known as lamina
Petiole
the stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem, supporting the leaf and facilitating transport of nutrients and water
Sessile
a type of leaf that is directly attached to the stem allowing for a more compact structure
Parallel Venetion
veins parallel to eachother, found in monocots
Net Vention
veins are branched, found in dicots
Plant Tissue
meristematic, dermal, ground, vascular
Meristematic Tissue
simple cells with no vacuoles, responsible for mitosis
Dermal Tissue
protective cover on stem, leaves and root, stops entry of pathogenic organisms, designed to absorb water and minerals at root tips
Adaptation of Dermal Cells
waxy layer to prevent water loss
Ground Tissue
fills interior of the plant body, stores food and provides strength to the plant
Vascular Tissue
transport substances within the plant, two types are xylem and phloem
Xylem
transports water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves, provide mechanical support, said to be dead
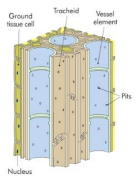
Xylem and Phloem Location
located in roots, stem, leaves and flowers
Xylem Types
xylem tracheids, xylem vessels
Xylem Tracheids
long cells tapered at both ends, contains pits, only found in conifers, contains lignin
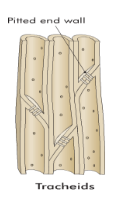
Xylem Vessels
form when numerous cells join end to end, wider than tracheids and are stacked together, forms a continuous conducting tube, contains pits, contains lignin
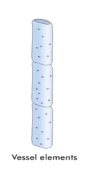
Use of Pits in Xylem
allows water and minerals to move sideways from cell to cell
Use of Lignin in Xylem
structural polysaccharide used to strengthen walls
Phloem
transports food made in the leaves, companion cells within controls sieve tube element, are elongated cylindrical cells stacked end to end.
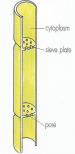
Sieve Plates
allow cytoplasm to pass from cell to cell, each one has a companion cell connected by cytoplasmic connections
Monocotyledon
one cotyledon, vascular bundles are scattered, parallel veins, flowers have petals in multiple of 3
Dicotyledon
two cotyledons, vascular bundles in ring shape, dendritic veins, flowers hace petals in multiples of 4/5
Tropism
growth response of a plant to a stimulus
Phototropism
growth of a plant in response to light
Function of Phototropism
allows plant to recieve maximum amount of light for photosynthesis
Geotropism
growth in response to gravity
Function of Geotropism
allows root to get the water and nutrients it needs from the soil, and raises the leaves into light for photosynthesis
Thigmotropism
growth of a plant in response to contact
Function of Thigmotropism
gives support to the plant
Hydrotropism
growth of a plant in response to water
Function of Hydrotropism
allows plant to get maximum water it can get
Chemotropism
growth of a plant in response to chemicals
Function of Chemotropism
allows plants to move towards useful minerals, and away from harmful chemicals
Plant Growth Regulators
chemicals that interact with one another to control a particular development or response
Location of Plant Growth Regulators
produced in meristems and transported through vascular systems
Examples of Plant Growth Regulators
auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, ethene
Auxin
promote cell enlargement and growth, involved in phototropism and apical dominance, can be used to kill weeds
Gibberellin
causes stem lengthening, mobilise the stored food in germinating seeds, break dormancy in buds and seeds in spring
Cytokinins
stimulate cell division and trigger leaf growth in spring
Abscisic Acid
triggers bud and seed dormancy in autumn and inhibits cell growth
Ethene
promotes ripening of fruit and the fall of leaves, flowers and fruits
Structure of the Flower
sepal, ovule, ovary, petal, style, filament, stigma, anther
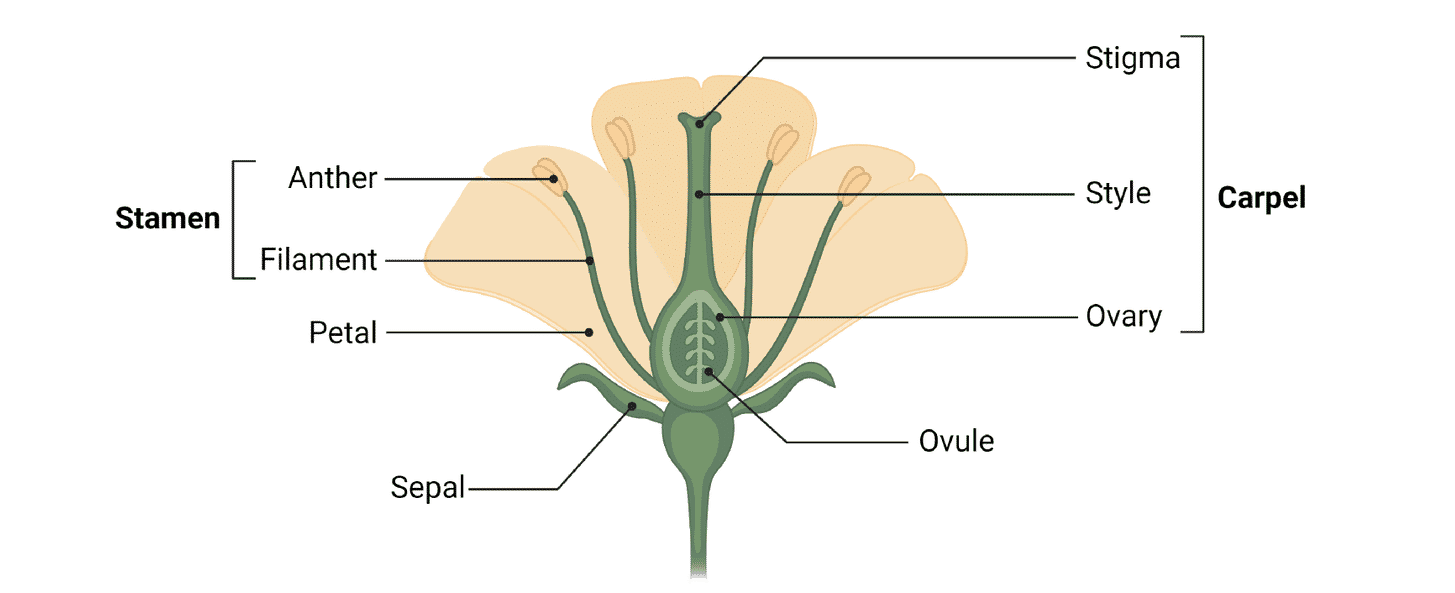
Stamen
male part of plant, filament, anther
Carpel
female part of plant, stigma, style, ovary