EOT World History Review 2025
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms

Nomadic
moving from place to place without a permanent home in search of resources like food, water, and shelter
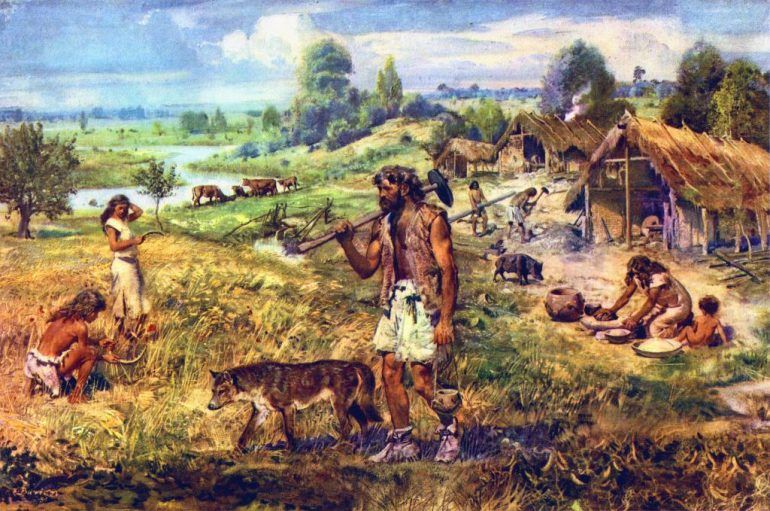

Domestication
the process of taming wild plants and animals for human use

Primary Source
a firsthand account or evidence from the time being studied, such as a diary, artifact, or document.
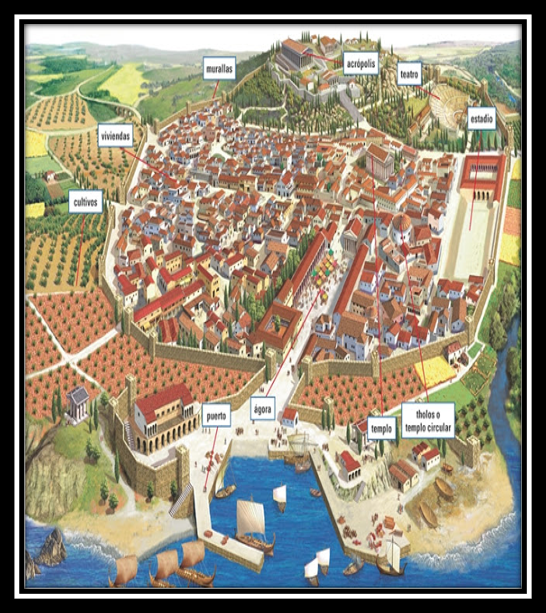
City-State
a political unit that consists of a city and surrounding farmland with its own government and laws. Found in ancient Greece, Mesopotamia, and the Maya civilization.
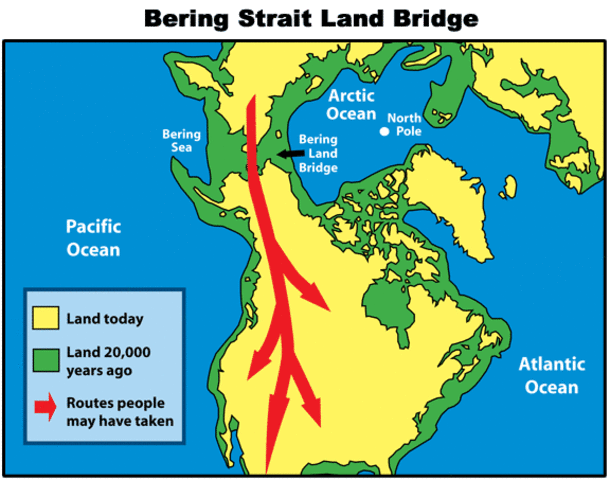
Bering Strait Land Bridge
A land bridge used during the last Ice Age so early humans could migrate from Asia to the Americas.

Fertile
Soil or land that is rich in nutrients that is good for growing crops (agriculture)
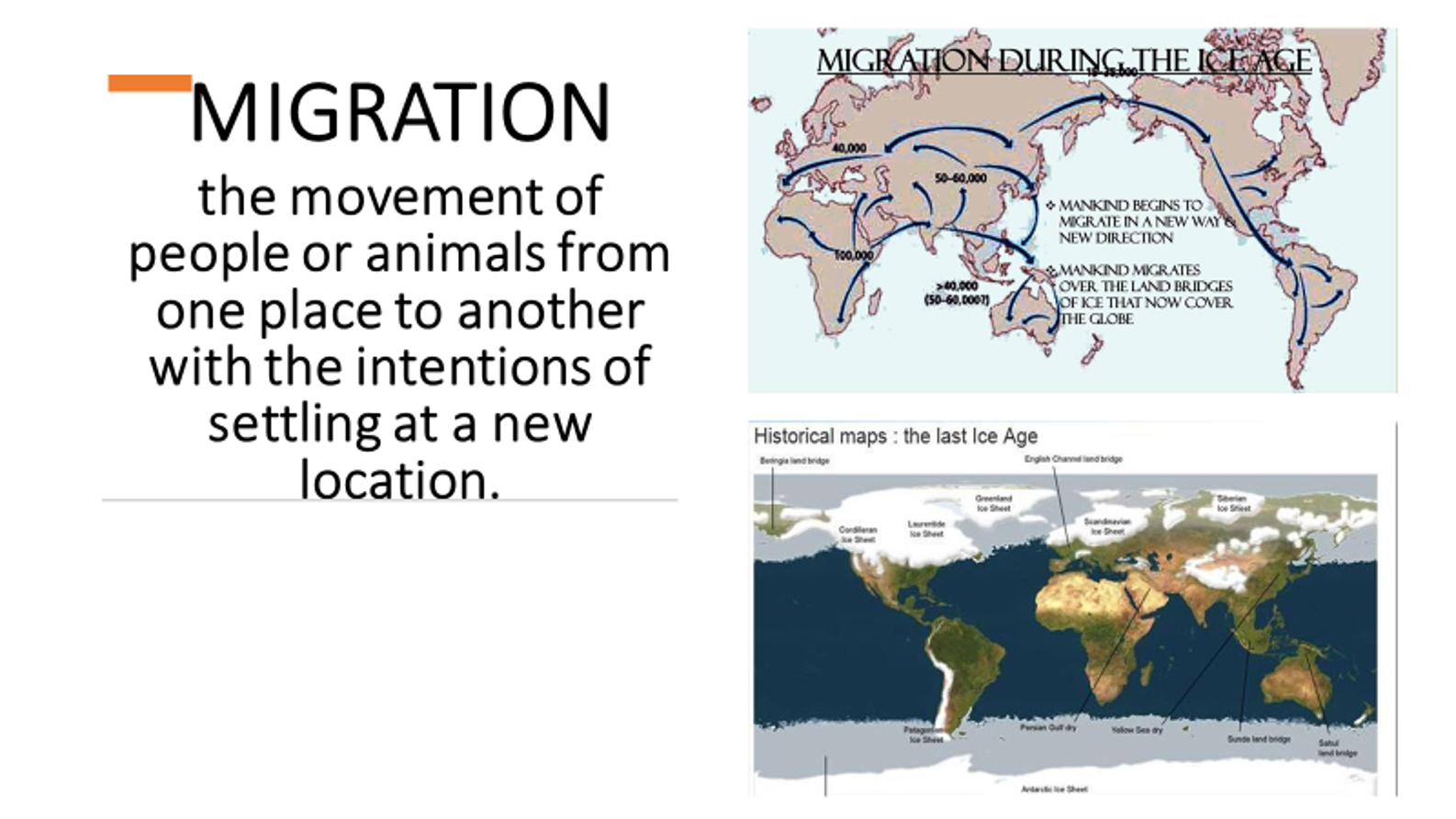
Migration
The movement of people from one place to another, often for the purpose of settling in a new location.
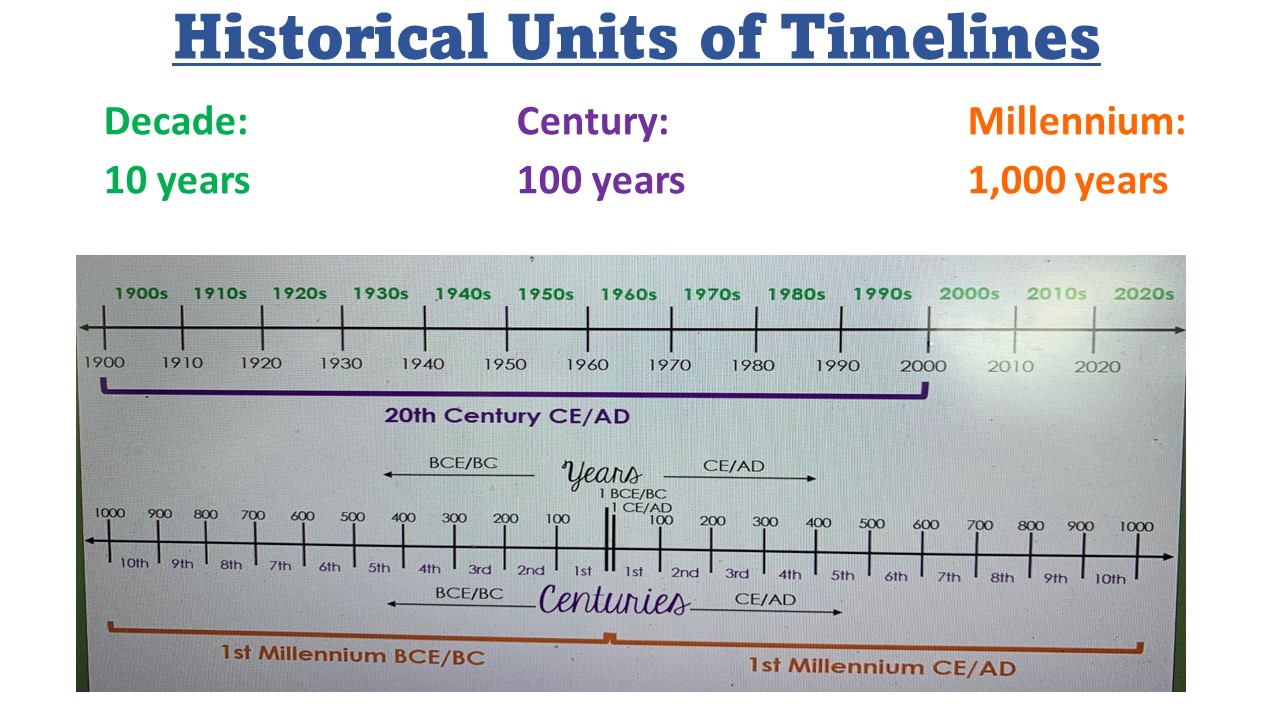
Century
A period of one hundred years.

Scribes
people who were trained to write and keep records in ancient civilizations
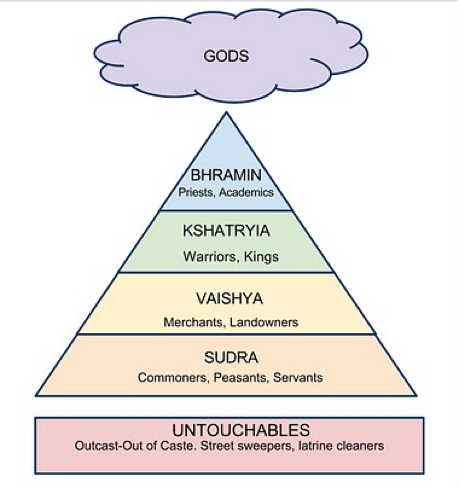
Caste System
A hierarchical social structure found in India, dividing society into rigid groups based on birth, occupation, and social status.

Direct Democracy
A system of government in which citizens directly participate in decision-making and creating laws like found in ancient Athens. In a representative democracy, citizens elect representatives to govern instead.

Republic
A form of government in which citizens elect representatives to govern on their behalf.
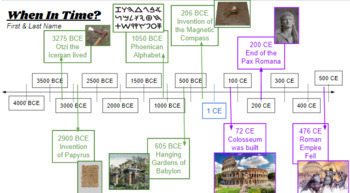
Common Era
written as CE, it is the non-religious or secular way to define time periods after the traditional date of the birth of Jesus Christ beginning at 1 CE.
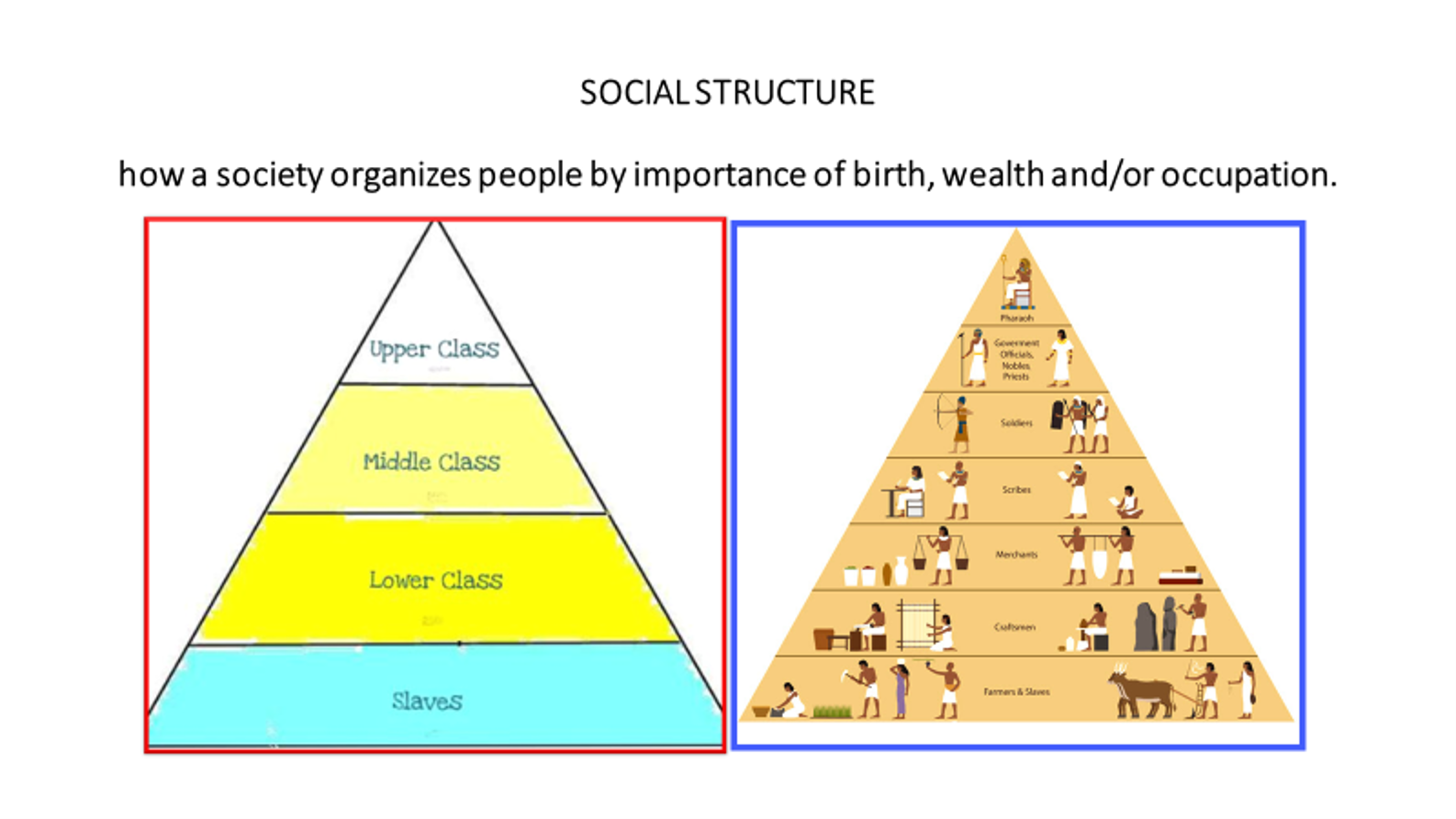
Social Structure
The hierarchical organization of society, dividing individuals into different levels based on factors such as wealth, occupation, and social status.

Hunter-Gatherer
A member of a nomadic group whose food supply depends on hunting animals and collecting plant resources; this is the lifestyle of humans before the invention of agriculture.

Roman Republic
The period of ancient Roman civilization in which people elected representative to rule Rome. It lasted from 509 BC- 27 BC when the Roman Empire began.
Anno Domini
A Latin term meaning "in the year of our Lord," written as AD, it is the Christian way to define time periods after the traditional date of the birth of Jesus Christ beginning in 1 AD.

Food Surplus
extra food

Polytheism
belief in many gods

Monotheism
belief in one god

Aqueduct
a bridge-like structure that carries water to cities used by the ancient Romans and the Aztecs

philosophy
the pursuit of knowledge about the nature of the world and society.

Pharaoh
the title of ancient Egyptian rulers, considered as both gods and kings in ancient Egypt.
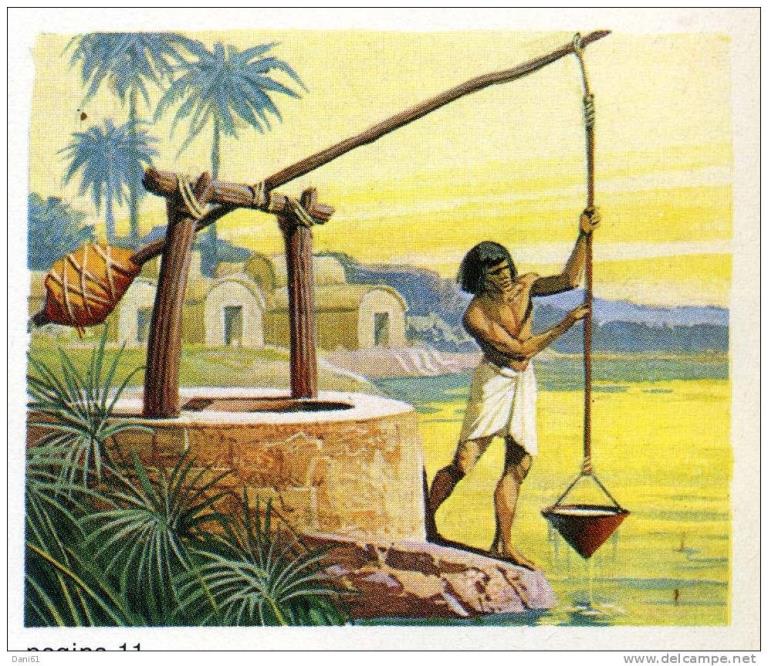

Shadoof
an ancient irrigation tool used in Egypt to lift water from the Nile for agricultural purposes.

currency
money

Pax Romana
Roman Peace; a period of relative peace and stability across the Roman Empire lasting approximately 200 years.

Traits of Civilization
The characteristics that define a civilization, including cities, religion, technology, social structure, writing, culture, and organized government.
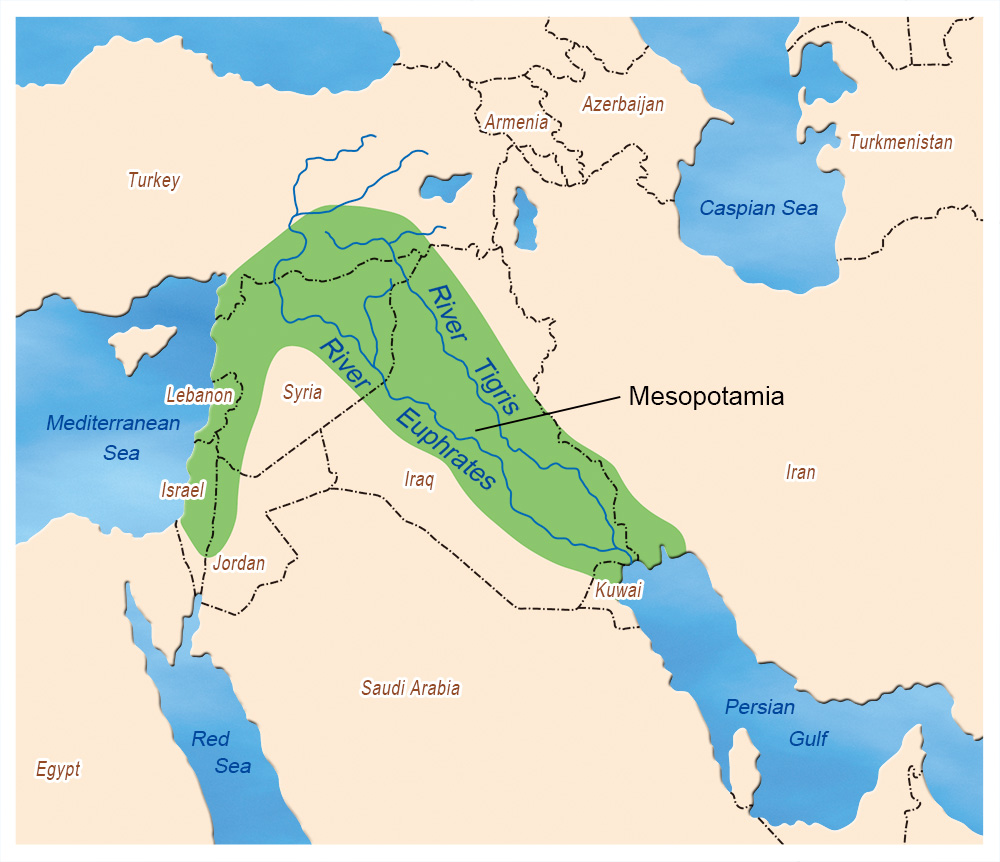
Fertile Crescent
a historical region in the Middle East known for its rich soils and early agricultural development, including the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.

Great Wall of China
A series of fortifications built along the northern borders of China to protect against invasions and raids.

Cuneiform
An ancient writing system used in Mesopotamia, characterized by wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets.

Hammurabi’s Code
a set of written laws established by Hammurabi, king of Babylon, the earliest written legal codes in history, detailing laws and punishments.
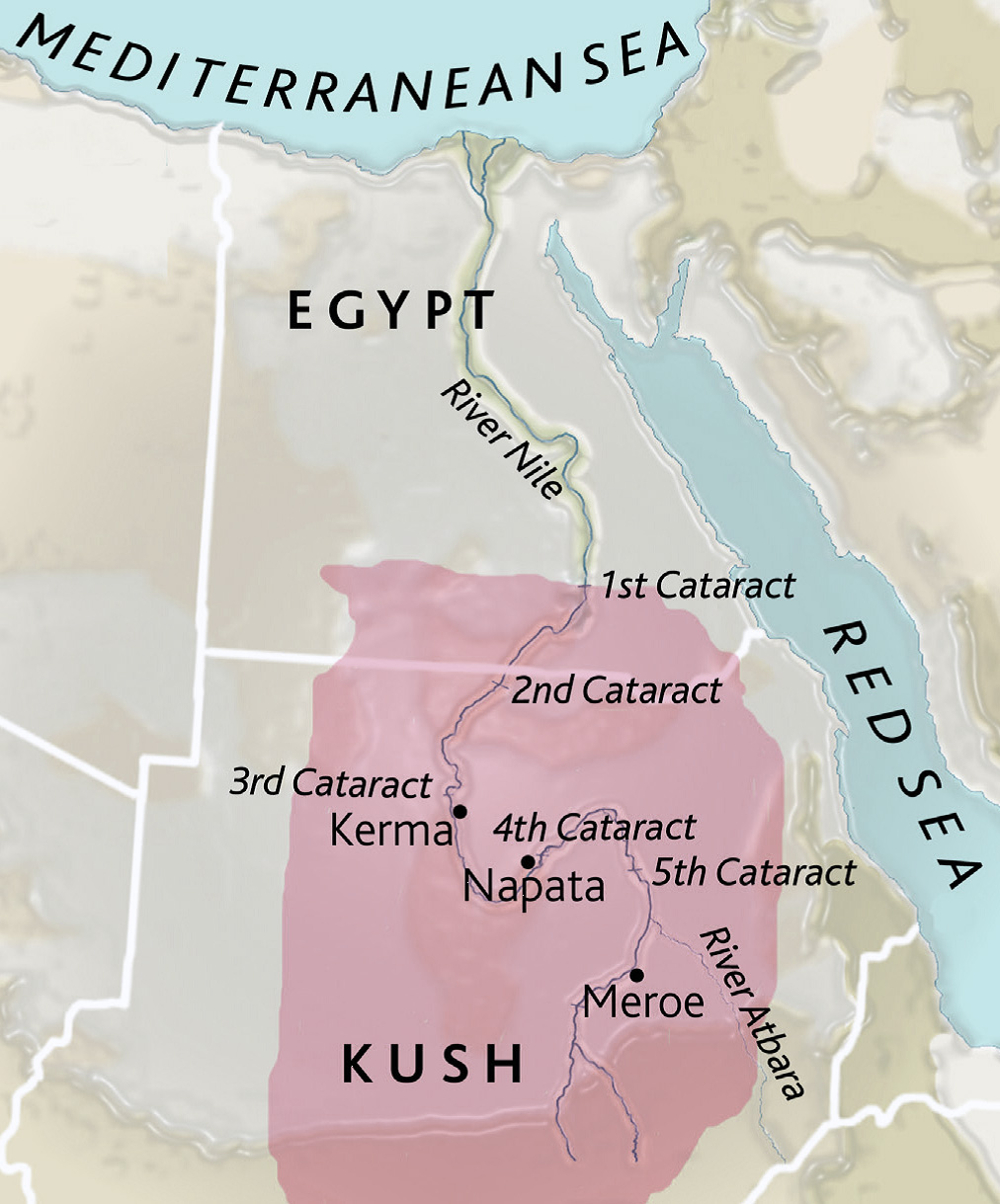
Kush Kingdom
An ancient kingdom located in what is now Sudan, known for contributions to culture and trade in Africa.
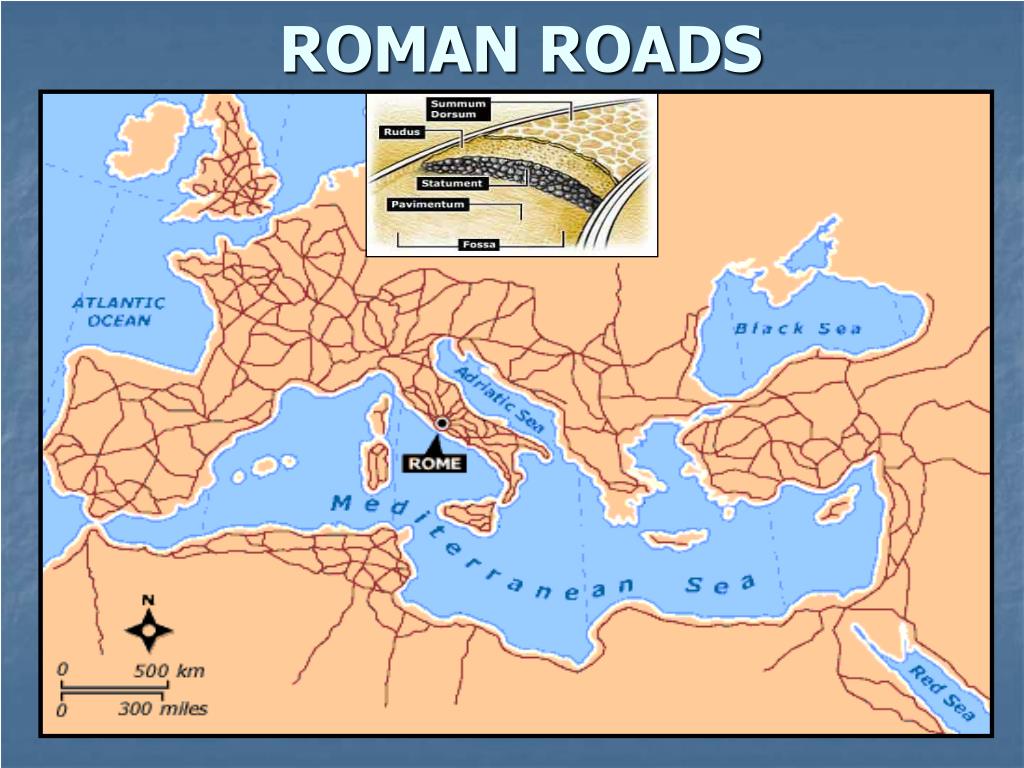
Roman Roads
a network of highways built by the Roman Empire that made trade and military operations easier across its vast territories.

Secondary Sources
Sources written after an event, NOT A PRIMARY SOURCE. Examples include textbooks, movies, articles, documentaries.
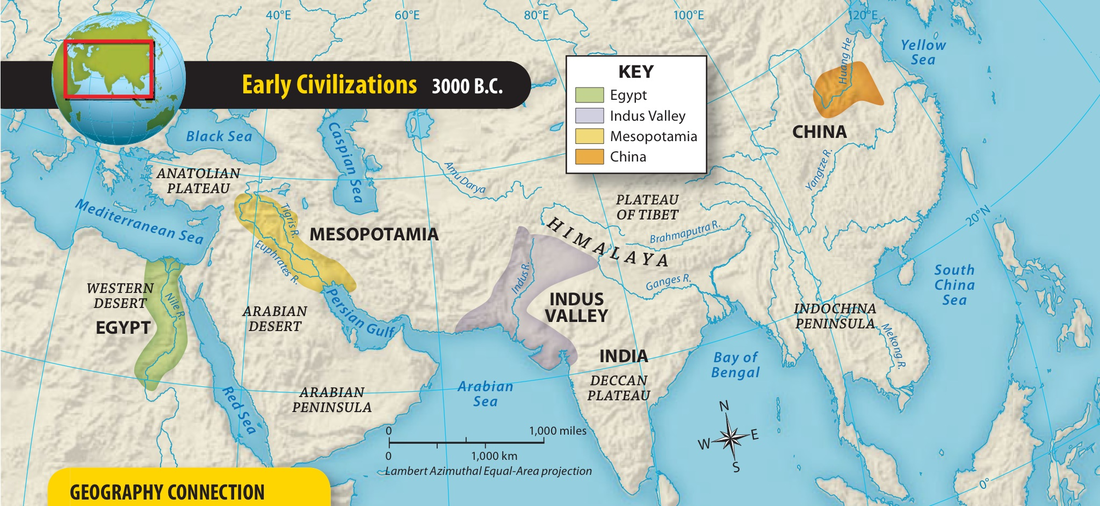
River Valley Civilizations
Early societies that developed along major rivers, including ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China

Paleolithic Era
The earliest period of human history, characterized by the development of stone tools and a hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
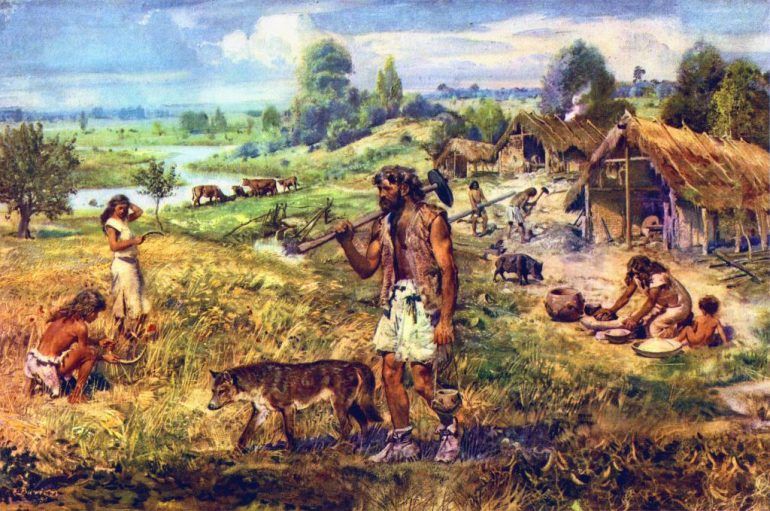

Neolithic Era
The period following the Paleolithic, marked by agriculture, permanent village settlements, and the domestication of animals.
Athens
A powerful city-state in ancient Greece known for its philosophical, political, and cultural developments, and the birthplace of democracy.

Sparta
A prominent city-state in ancient Greece known for its military discipline, rigorous training of citizens, and a social structure centered around warfare.

Julius Caesar
A military general in ancient Rome who played a critical role in the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. He is known for his conquests, reforms, and assassination in 44 BC.
Decade
A period of ten years
Millennium
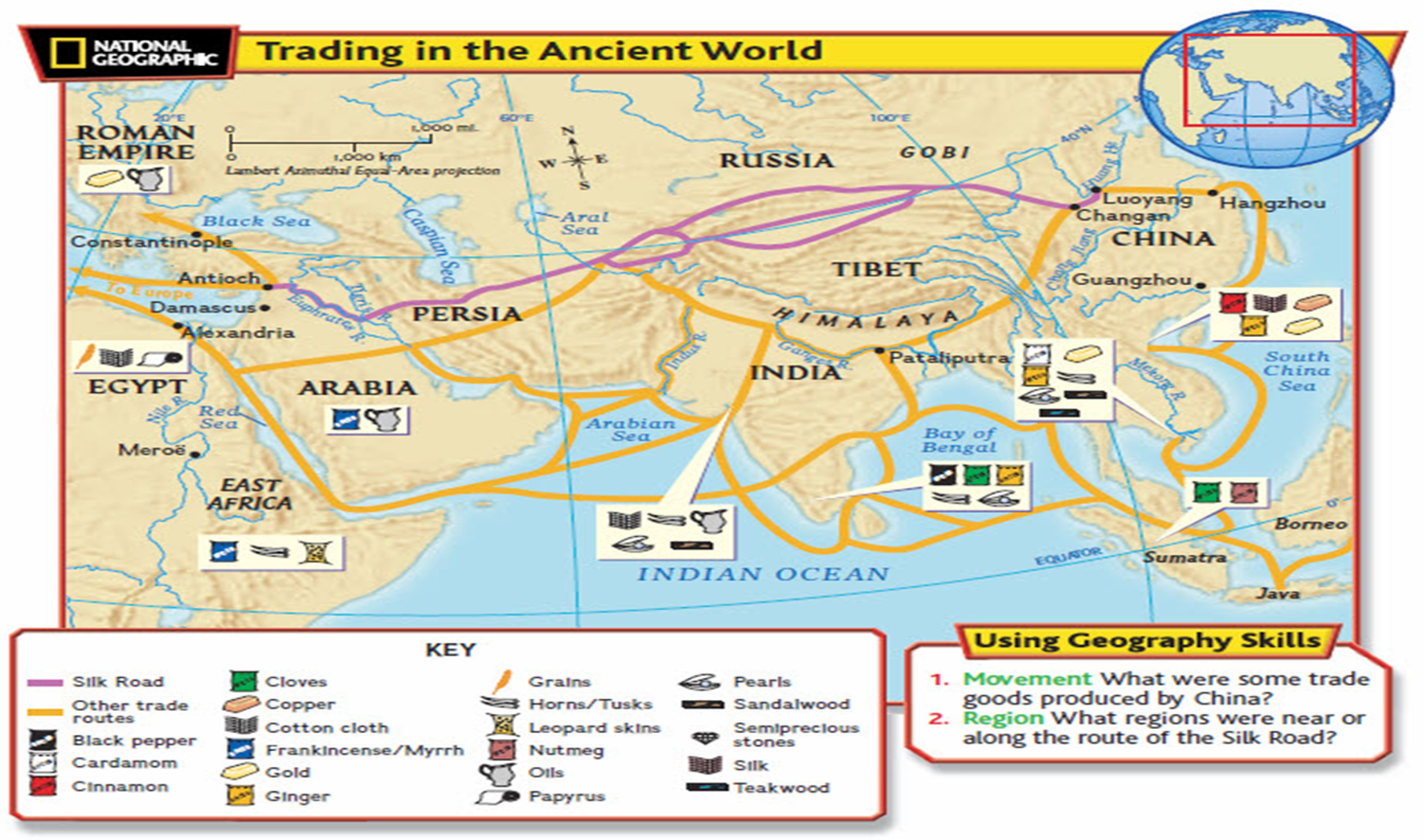
Silk Road
An ancient trade route that connected the East and West, facilitating the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas.

Neolithic Revolution
The change in human societies from hunter-gatherers to settlement in villages due to the beginning of agriculture and domestication.
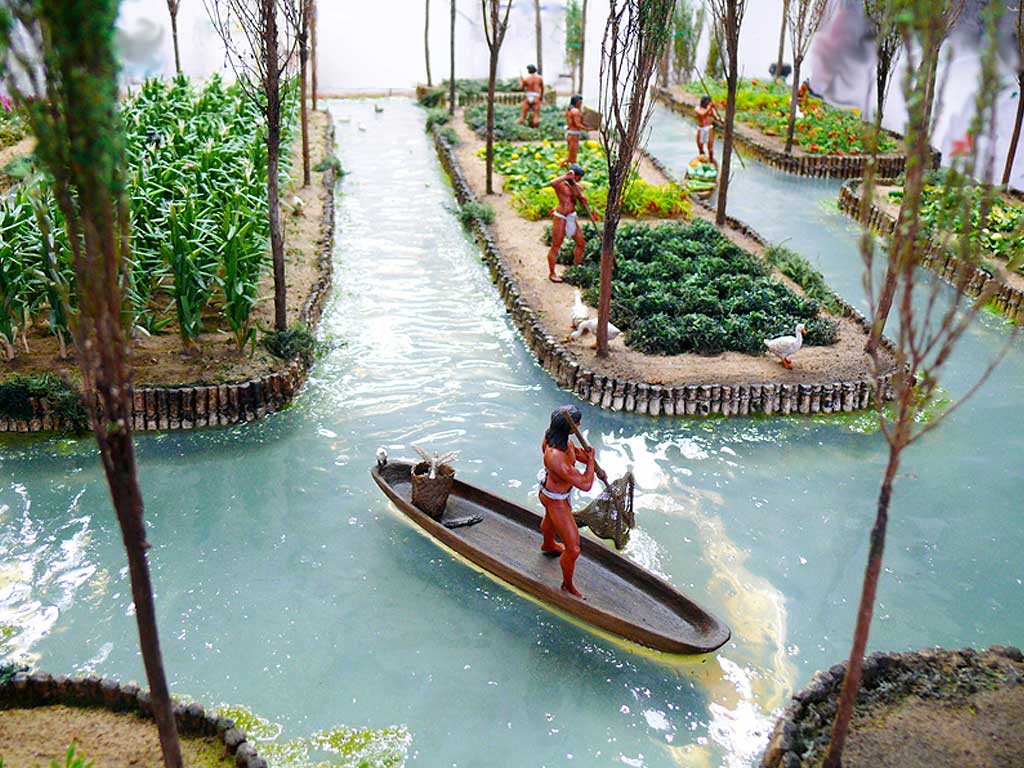

Chinampas
Floating gardens made by the Aztecs in Lake Texcoco to increase food production.
Roman Road System
A network of roads built throughout the Roman Empire to facilitate trade, military movement, and communication.