chemistry semester 2 final
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
The volume, shape, compression, flow, and diffusion of an object is best said to be influenced by its ___________.
intermolecular forces
Always/Sometimes/Never: Liquids assume the shape of their container.
always
Are liquids compressible?
No, not significantly
Which state has the highest levels of interparticle attraction?
Solids
The state of a substance depends largely on the __________ of the particles and the ________ attractions.
average kinetic energies, interparticle
What is the definition of intermolecular forces?
attractive or repulsive electrostatic forces between molecules
True/False: Covalent bonds are a type of intermolecular forces.
False, they are a type of intramolecular forces.
What are the four intermolecular forces (relevant to this class)?
Dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, ion-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
Which are stronger, intermolecular or intramolecular forces?
intramolecular forces
What is the difference between intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces?
intermolecular forces are between particles in a substance, and intramolecular forces are in a bond. in water, the intermolecular forces are in between the H2O molecules, while the intramolecular forces are in between the hydrogen and oxygen.
Metals have high electrical conductivities because ______.
the electrons in the metal are delocalized.
Which intermolecular force is considered the strongest?
Hydrogen-bonding
Which intermolecular force is considered the weakest?
Dispersion forces
Intermolecular forces determine ___________behavior, while intramolecular forces determine________ behavior.
physical, chemical
True/False: All substances have dispersion forces.
True
What causes dispersion forces?
the constant movement of electrons creates temporary dipole moments, because electrons are not always evenly spaced. the temporary dipole moment in one molecule attracts/effects another
In what type of molecules are dispersion forces the only force present?
nonpolar molecules
True/False: Dipole-Dipole forces are only present in certain types of polar molecules.
false— all polar molecules have dipole dipole forces
Increasing polarity of a substance means __________ dipole dipole interaction.
increasing
Why are hydrogen bonds an especially strong intermolecular force?
Hydrogen’s one electron means the atomic radius is incredibly small, and a shorter ‘bond’ is a stronger one.
Hydrogen bonds always include:
a hydrogen bonded to something electronegative, almost always O F or N
Ion-Dipole forces exist between _____.
an ion and a polar molecule
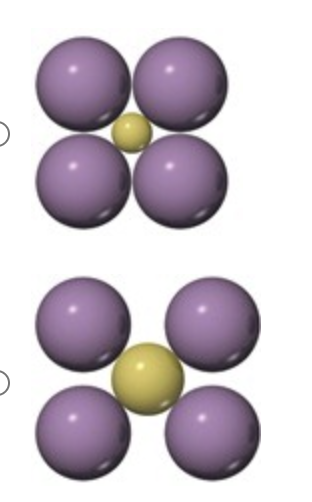
Which arrangement of cations (yellow) and anions (blue) in a lattice is the more stable and why?
the bottom arrangement because in the other structure very close contacts among like-charged particles produce strong electrostatic repulsions.
In molecular solids, the melting point ________ the increasing strength of covalent bonds.
is unrelated to
For molecular solids, the melting point generally_________ increasing strength of the intermolecular forces.
increases with
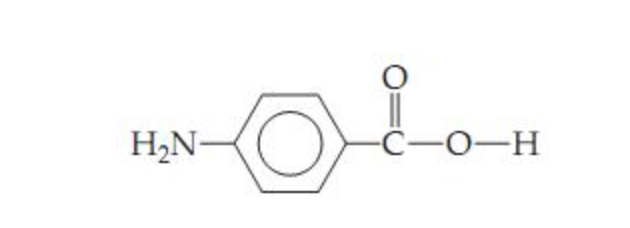
Is this molecule a better starting material for an addition polymer or a condensation polymer? why?
condensation polymer, because The amine group of one molecule can react with the carboxylic acid group of an adjacent molecule to form an amide linkage, and eliminate a water molecule.
Vulcanization is described as____?
The process of making rubber stiffer by forming bonds between the chains.
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of _______ attraction.
dipole-dipole
Viscosity ________ as intermolecular forces increases.
increases
Melting point ________ as intermolecular forces increases.
increases
If a fluid is more viscous, then the fluid moves _________ (faster/slower).
slower
Polarizability is higher in molecules with ______ electrons.
more
Boiling point _______ as intermolecular forces increase.
increases
Surface tension _______ as intermolecular forces increases.
increases
Vapor pressure _________ as intermolecular forces increases.
decreases
Vapor pressure measures _________.
a substance’s tendency to vaporize
Ionic solids dissolved in polar solids have _______ forces and ______ forces.
dispersion, ion-dipole
London forces increase when ____________ or _______________.
the number of e- in a species increases, or molecules without branches have stronger dispersion forces.