It applications
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Which of the following is not a valid edition of Windows?
Corporate
True or False. Operating system power management features may sometimes disable USB devices.
True
The Start menu is activated by selecting the ____ or by pressing the ____ or Windows logo key on the keyboard.
Start button or Start
Instant Search
Windows feature allowing rapid search of apps, data folders, messages, and the web.
Windows 11 taskbar is located where?
on the center
Windows 10 taskbar is located where?
on the left
What are the two main interfaces for administering windows
The Windows Settings app and Control Panel
Windows settings
Touch-enabled interface for managing user and system settings in Windows.
This version of settings app has no “home” page
Windows 11
Control Panel
Legacy management interface for configuring user and system settings in Windows.
user account
controls access to the computer
Account settings
Windows Settings pages relating to user account creation and maintenance.
User Accounts applet
Control Panel app relating to user account creation and maintenance.
User Account Control (UAC)
a system to prevent unauthorized use of administrator privileges.
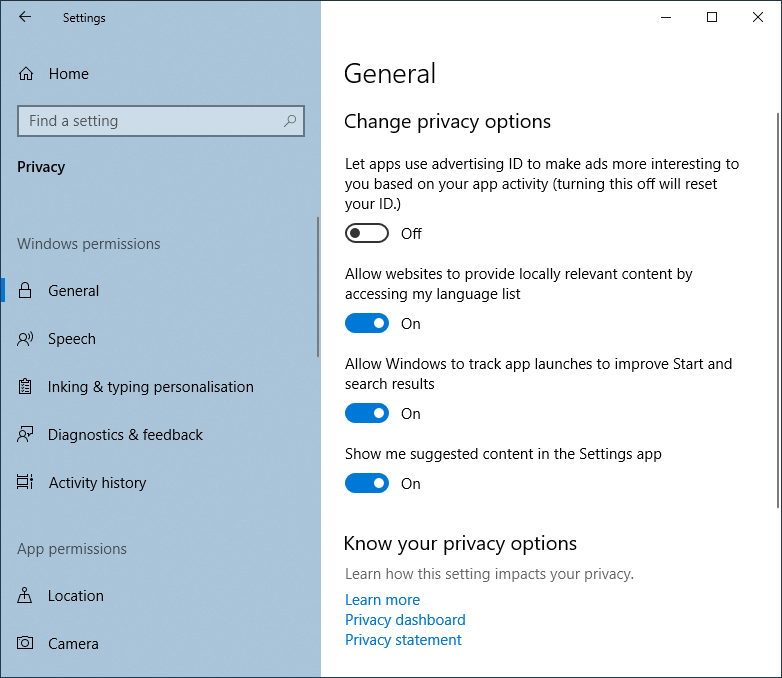
Privacy settings
govern what usage data Windows is permitted to collect and what device functions are enabled and for which apps
Time & Language Settings
Windows Settings pages allow changes to default data formats (date, currency, and so on), location information, and keyboard input locale.
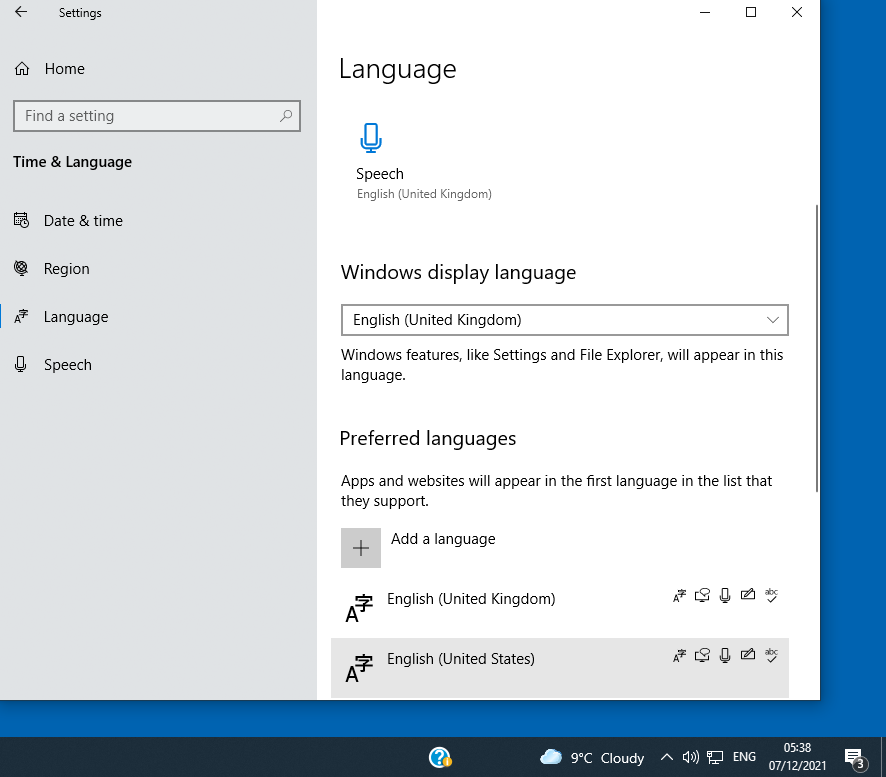
Personalization Settings
allow you to select and customize themes, which set the appearance of the desktop environment.
Ease of access
settings configure input and output options to best suit each user, such as vision hearing and interaction
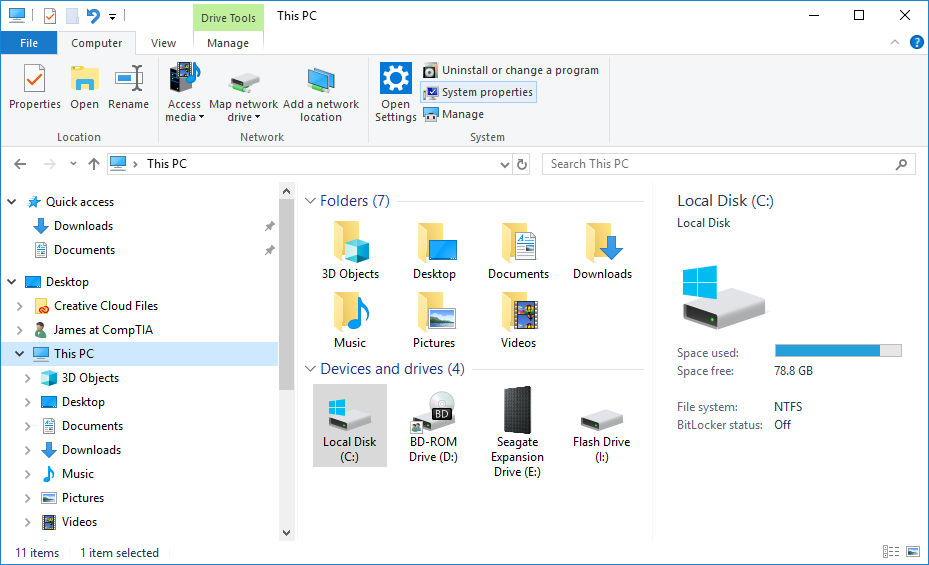
File Explorer
enables you to open, copy, move, rename, view, and delete files and folders.
User account (file explorer)
Contains personal data folders belonging to the signed-in account profile.
Onedrive (file explorer)
If you sign into the computer with a Microsoft account, this shows the files and folders saved to your cloud storage service on the Internet.
This PC (file explorer)
Also contains the personal folders from the profile but also the fixed disks and removable storage drives attached to the PC.
Network (file explorer)
Contains computers, shared folders, and shared printers available over the network.
Recycle bin (file explorer)
Provides an option for recovering files and folders that have been marked for deletion.
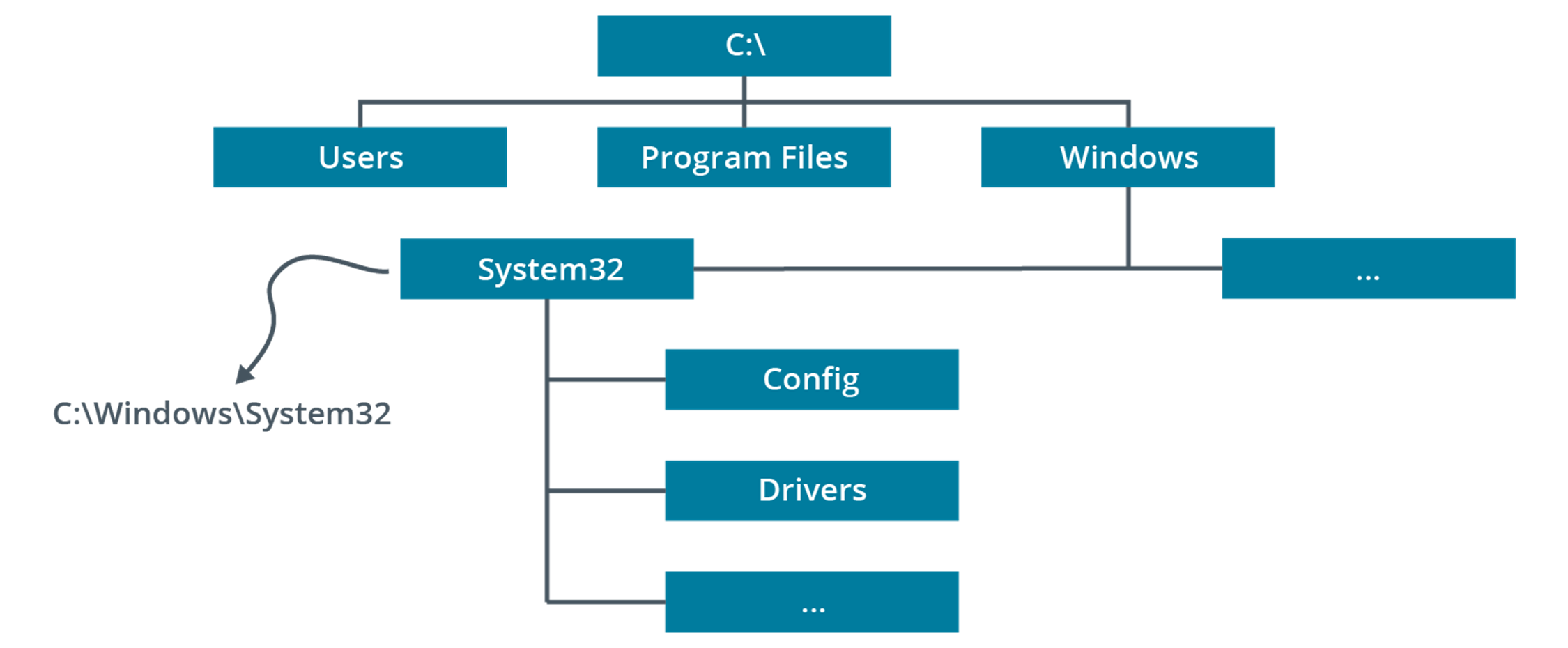
System files
are the files that are required for the operating system to function
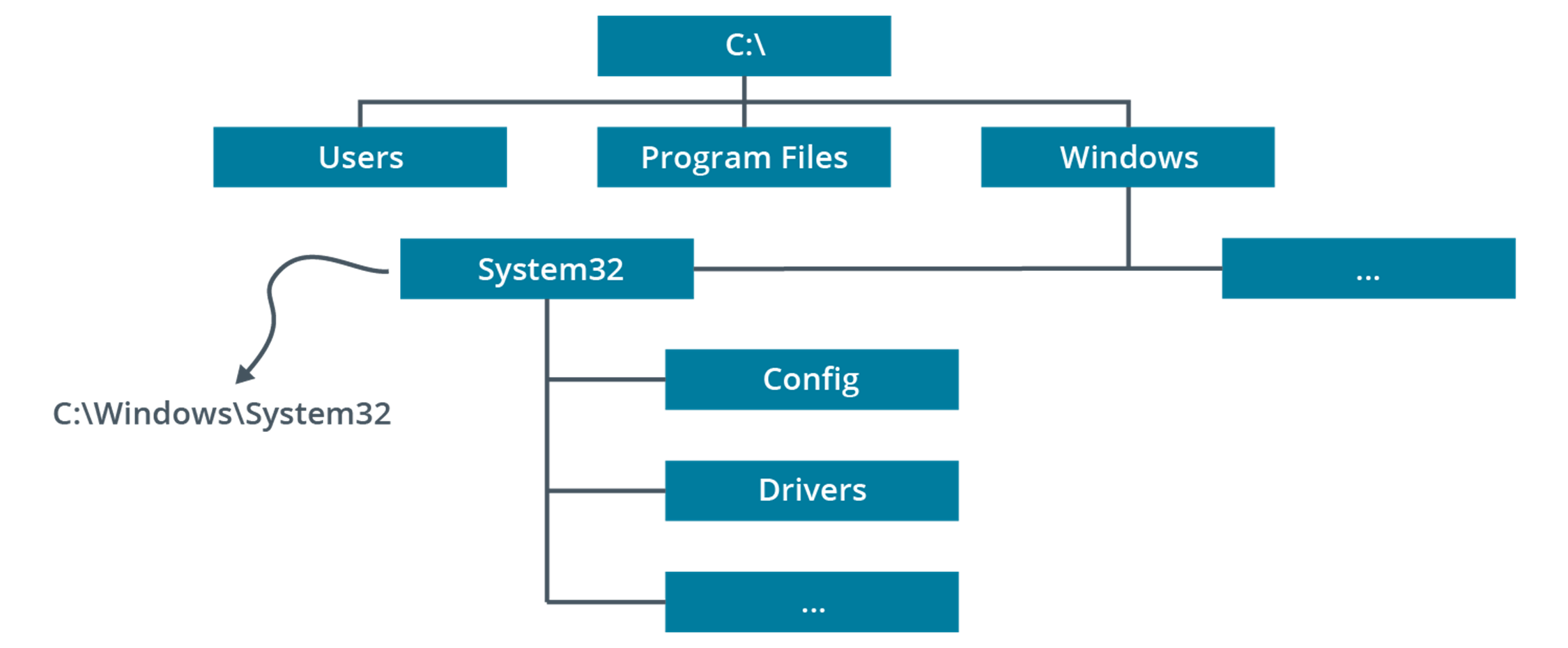
Windows (system files)
The system root, containing drivers, logs, add-in applications, system and configuration files (notably the System32 subdirectory), fonts, and so on.
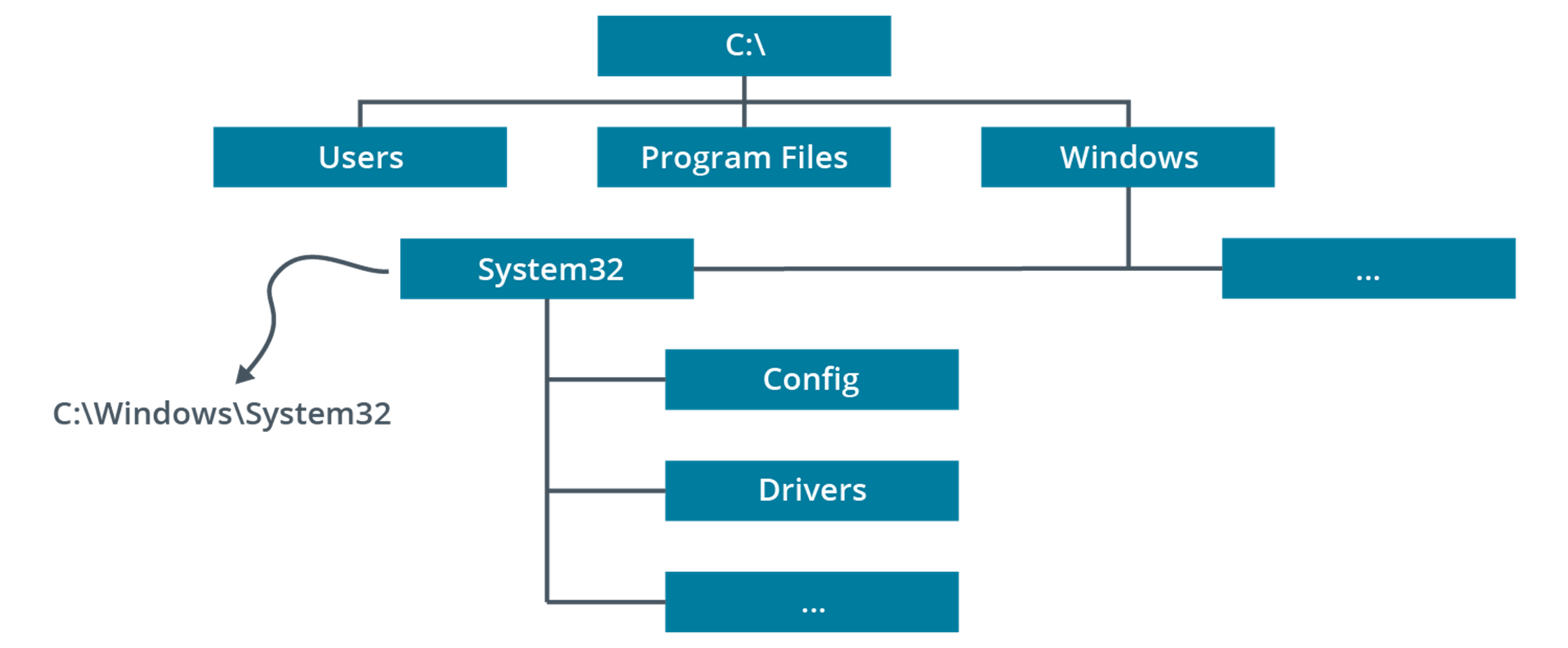
Program Files\Program Files (x86) (system files)
Subdirectories for installed applications software. In 64-bit versions of Windows, a Program Files (x86) folder is created to store 32-bit applications.
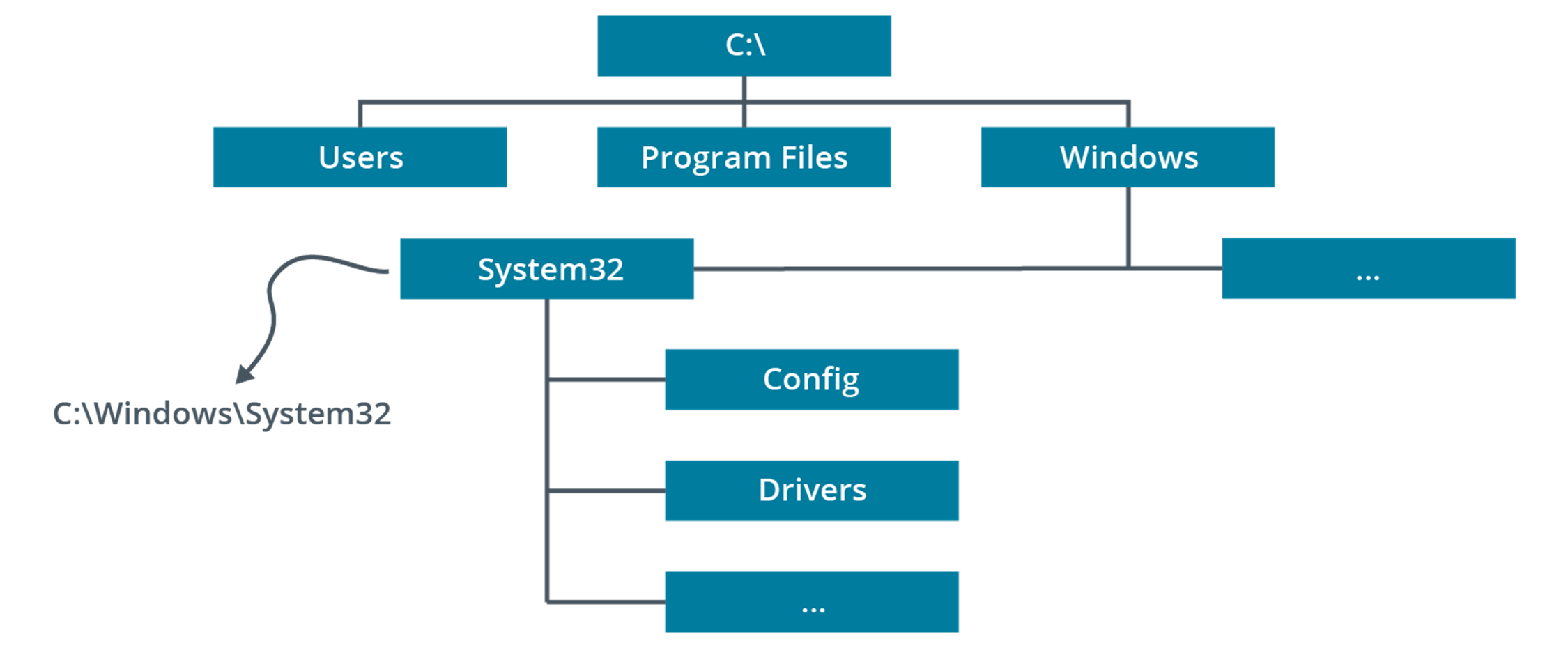
Users (system files)
Storage for users' profile settings and data. Each user has a folder named after their user account. This subfolder contains NTUSER.DAT (registry data) plus subfolders for personal data files. The profile folder also contains hidden subfolders used to store application settings and customizations, favorite links, shortcuts, and temporary files.
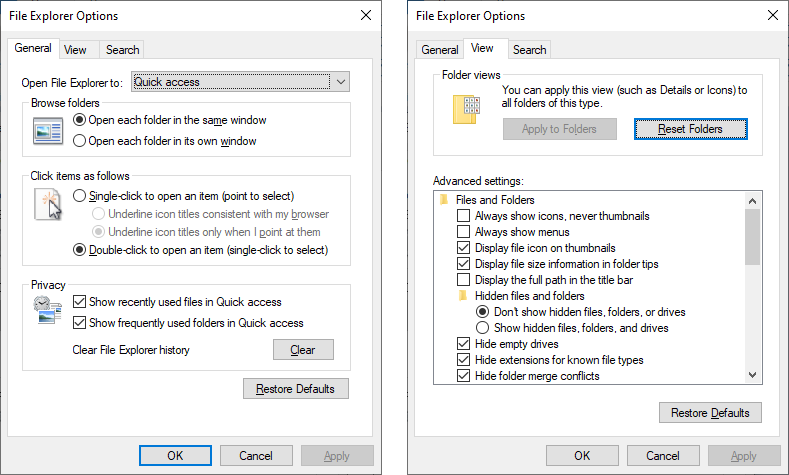
File Explorer Options
applet in Control Panel governs how Explorer shows folders and files
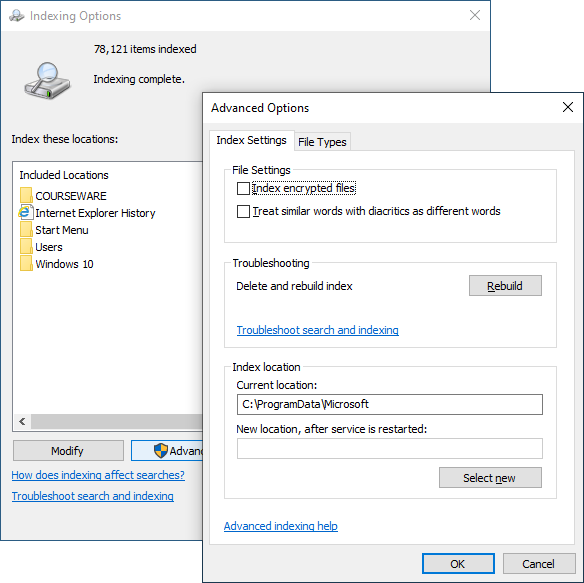
Indexing Options
Control Panel app related to search database maintenance.
Standby /Suspend to RAM
Cuts power to most devices (for example, the CPU, monitor, disk drives, and peripherals) but maintains power to the memory. This is also referred to as ACPI modes S1–S3.
Hibernate /Suspend to Disk
Saves any open but unsaved file data in memory to disk (as hiberfil.sys in the root of the boot volume) and then turns the computer off. This is also referred to as ACPI mode S4.
Windows Defender Firewall
determines which processes, protocols, and hosts are allowed to communicate with the local computer over the network.
Advanced sharing settings
is a Control Panel applet that shows status information.is a Control Panel applet that configures network discovery (allows detection of other hosts on the network) and enables or disables file and printer sharing.
Network Connections (ncpa.cpl)
is a Control Panel applet for managing adapter devices, including IP address information.
Network & Internet
is the modern settings app used to view network status, change the IP address properties of each adapter, and access other tools.
Network and Sharing Center
is a Control Panel applet that shows status information.
The Internet Options Control Panel
applet exposes the configuration settings for Microsoft’s Internet Explorer (IE) browser.
Administrative Tools
Folder in Control Panel containing default Microsoft management consoles used to configure the local system.
Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
contains one or more snap-ins that are used to modify advanced settings for a subsystem, such as disks or users.
Computer Management (compmgmt.msc)
The default management console with multiple snap-ins to schedule tasks and configure local users and groups, disks, services, devices, and so on.
Defragment and Optimize Drives (dfrgui.exe)
Maintain disk performance by optimizing file storage patterns.
Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe)
Regain disk capacity by deleting unwanted files.
Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc)
Review system, security, and application logs.
Local Security Policy (secpol.msc)
View and edit the security settings.
Resource Monitor (resmon.exe) and Performance Monitoring (perfmon.msc)
View and log performance statistics.
Registry Editor (regedit.exe)
Make manual edits to the database of Windows configuration settings.
Services console (services.msc)
Start, stop, and pause processes running in the background.
Task Scheduler (taskschd.msc)
Run software and scripts according to calendar or event triggers.
WINDOWS + X or right-clicking the Windows button
shortcut menu with links to the main management utilities
( WINDOWS + R) Run dialog
can be used to execute a program with switches that modify the operation of the software.
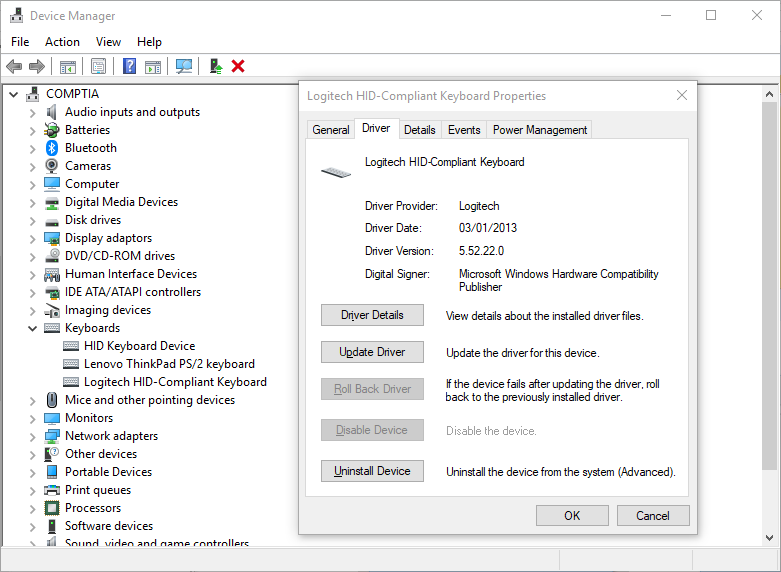
Device Manager (devmgmt.msc)
allows you to view and edit the properties of installed hardware. You can change hardware configuration settings, update drivers, or remove/disable devices.
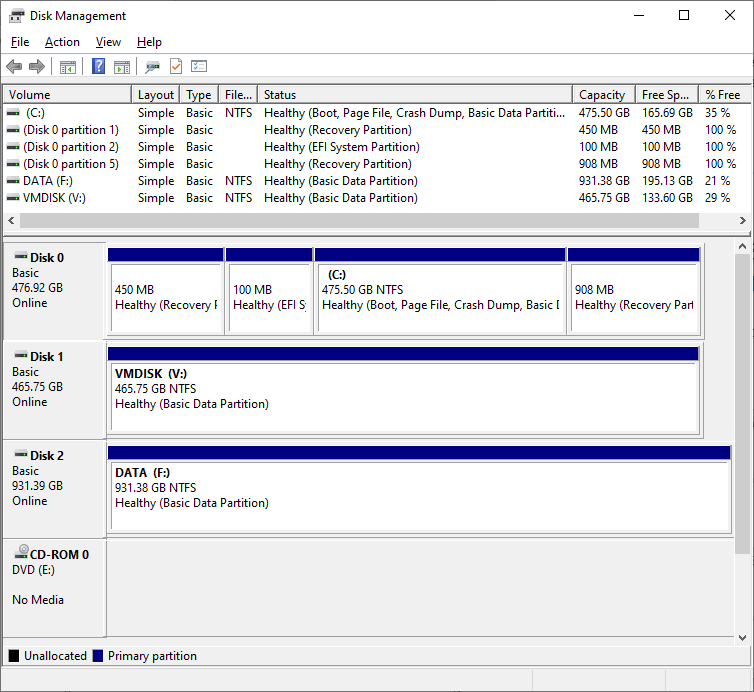
Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc)
console displays a summary of any fixed and removable disks—hard disk drives (HDDs), solid state drives (SSDs), and optical drives—attached to the system.
Initializing disks (Disk Management console)
If you add an unformatted HDD, SSD, or thumb drive, you will be prompted to initialize it. You can choose whether to use the master boot record (MBR) or Globally Unique ID (GUID) Partition Table (GPT) partition style for the new disk. MBR and GPT refer to the way the partition information is stored on the disk.
Partitioning (Disk Management console)
Each disk must be configured with at least one partition. You can create a new partition by right-clicking on an area of unpartitioned space. A wizard will prompt you to choose how much of the unallocated space to use and to select a file system.
Formatting (Disk Management console)
A new partition must be written with a file system—typically NTFS—to allow Windows to write and read files. The simpler FAT32 file system might be used for small, removable drives. You can also reformat existing partitions. This will delete all files from the volume. Along with the file system type, you can choose a volume label and allocation unit size.
Repartitioning (Disk Management console)
Existing partitions can be expanded if there is unpartitioned space. Partitions can also be removed or shrunk to make space available.
Configuring dynamic disks (Disk Management console)
If there is more than one disk available, a new dynamic volume can be configured. Dynamic volumes use multiple devices to implement some type of software RAID redundancy, such as mirroring.
(Disk Maintenance Tools) Fragmentation
(Disk Maintenance Tools) Capacity
(Disk Maintenance Tools) damage
Defragment and Optimize Drives tool (dfrgui.exe)
runs various operations to speed up the performance of HDDs and SSDs:
Disk Clean-up (cleanmgr.exe)
tracks files that can be safely erased to reclaim disk space
Task Scheduler (taskschd.msc)
runs commands and scripts automatically
Local Users and Groups (lusrmgr.msc)
console provides an advanced interface for creating, modifying, disabling, and deleting user accounts
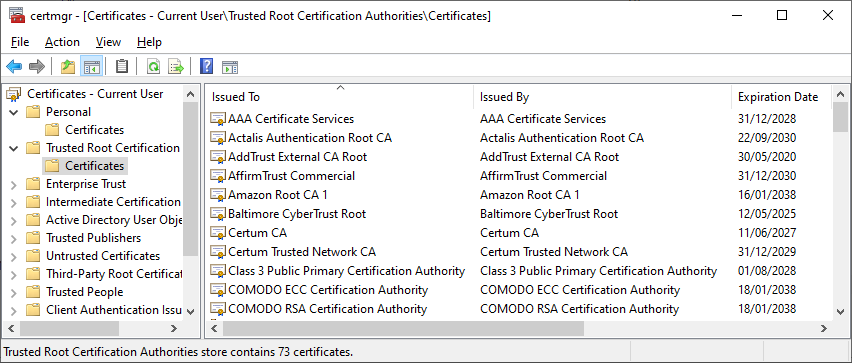
Manager console (certmgr.msc)
shows which certificates have been installed and provides a mechanism for requesting and importing new certificates.
digital certificate
is a means of proving the identity of a subject, such as a user, computer, or service. The validity of each certificate is guaranteed by the issuing certification authority (CA)
Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc)
provides a more robust means of configuring many of these Windows settings than editing the registry directly
Registry Editor (regedit.exe)
views or edit the registry
registry
structured as a set of five root keys that contain computer and user databases
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) database
governs system-wide settings
HKEY_USERS database
includes settings that apply to individual user profiles, such as desktop personalization
HKEY_CURRENT_USER
is a subset of HKEY_USERS with the settings for logged in user
Hives
The registry database is stored in binary files
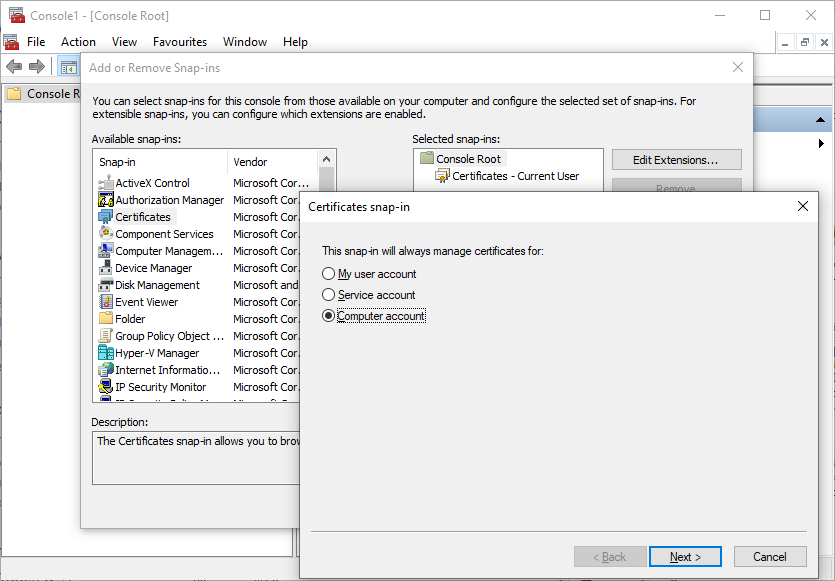
Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
is a container for one or more snap-ins
A user is curious about the low-level data the system stored concerning their profile and wants to explore the file which contains it. In Windows, where does the user look?
NTUSER.DAT (registry data)
A security-conscious user limits what usage data Windows permits to collect. They also limit what device functions it enables and for which apps. Where does the user accomplish this?
Privacy settings
A user wants to optimize their Windows 10-based computer. The user pokes around in the system settings applet on their computer. What can the user NOT configure in the system settings applet?
File Explorer
A new user requests that a few settings be configured to increase the comfortability while using a company computer. In particular, the user requests that the narration feature be enabled. Where does a support technician find this feature in the Ease of Access settings in Windows 10?
Vision
An enthusiastic computer user wants to test out the new Windows 11 desktop. Which of the following has become more easily accessible using Windows 11?
Multiple desktops
The receptionist at a record label company connects a phone to a computer so the songs already downloaded on the phone will play. Where does the receptionist set this up?
Device settings
A user wants to experiment with virtualization by enabling Microsoft's virtualization solution. Where can the user go to enable this?
Features
An administrator is configuring a user's computer and is currently utilizing the User Accounts applet in the Control Panel. What is the administrator doing?
Changing UAC settings
A technician assists a visually impaired person by making the text on their computer screen larger. Where can the technician configure this?
Ease of access
A user is experimenting with the fast startup option to see if it really makes booting faster. What should they expect?
The computer will boot faster after being shutdown.
Which of the following changes have been made to the Taskbar compared to Windows 10?
Center aligned, wider icon spacing for better touch support
Which of the following changes has been made to the Start menu from windows 10 to windows 11?
All apps accessed via button
What is the function of sticky keys?
Use key combos without having to hold two keys at once
A user upgrading to Windows 11 is not able to launch an app they previously accessed by scrolling through the Start menu. What TWO ways could the user access the app?
Click All apps to access the scrollable list of apps, Pin the app shortcut to the Start menu
What is the function of the following icon?
Switch between windows and desktops
True or false? Windows 11 has removed the ability for users to configure privacy settings.
False
What is the primary difference between a standard user account and an administrative user account?
An administrative user account can reconfigure the operating system whereas a standard one cannot
True or False. Date and Time formats are the same globally. Changes to data and time formats are purely based on preferences.
False
Which item should be selected from Settings in order to change tray icon behavior?
Personalization
What is the purpose of pinning an application to the taskbar?
It makes the application easier to locate and launch.
In which type of lab can you change your response to a scored item?
Assisted
True or false? Labs have a recommended duration but can be extended from this to any amount of time.
false
Each account can be assigned ____ or ____ to make OS configuration changes
Rights, privileges
Standard users have privileges on their _____ only, rather than the whole computer.
Profile
Windows account can either be configured as a local-only account or linked to a _______
Microsoft account