ORAL MODIFIED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
formulations are prepared using substances or procedures, which, separately or together, are designed to control the rate or place at which active ingredients are released in the GI tract
How does the pharmocopeia define modified release systems?
formulations prepared using substances or procedures, which, separately or together, are designed to control the rate or place at which active ingredients are released in the GI tract
delayed release or extended release
What is delayed release?
gastro-resistant or enteric systems
application of a thin layer of material (coating) to the surface of a tablet, capsule, mini-tablet or pellet to delay release of drug to the small or large intestine
What classes of medicines should be enterically coated?
Medicines that:
by prolonged contact cause irritation to the stomach
are rendered inactive or decomposed by the gastric juice
arrive in the intestine as concentrated as possible
Enteric coatings dissolve upon reaching a certain threshold __.
Enteric coatings dissolve upon reaching a certain threshold pH.
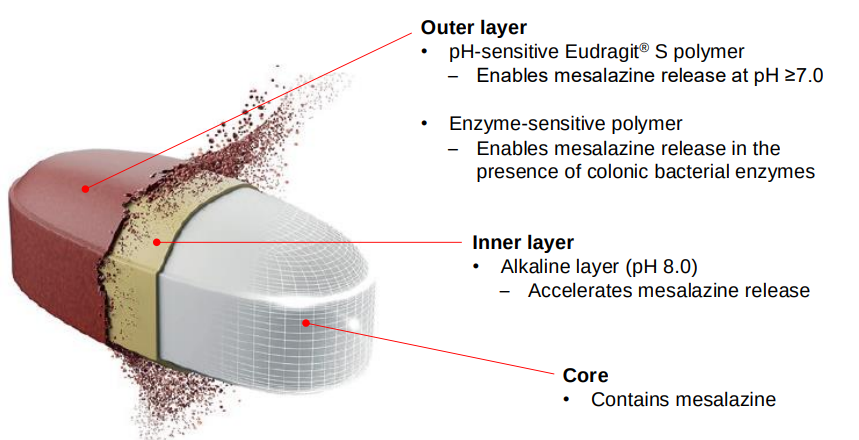
Outline the diff pH sensitive polymers for delayed release film coating.

Outline the structure of the New Mesalazine drug product.
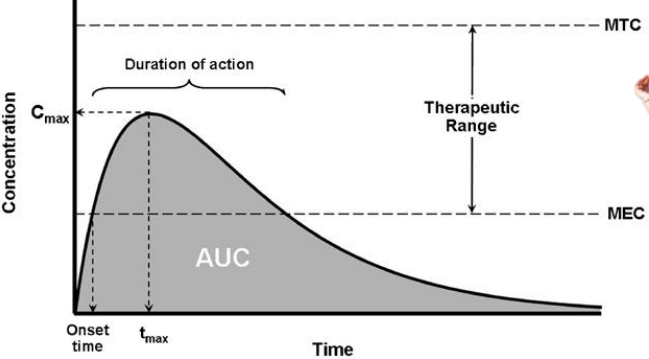
What is an extended release system?
dosage form used to release medication in a controlled manner during an extended period of time & reduces the frequency of dosing.
What else is extended release drug systems known as?
Controlled release
Sustained Release
Prolonged Release
Gradual Release
Slow Release
Long Acting
How do we find biological half life?
less than 2hrs or more than 8hrs is not ideal to formulate into MR systems, 4hrs would be a good half life to formulate into a MR system

What are the limitations
Drugs with ‘absorption windows’
Drugs with very short half lives
Variable conditions/transit throughout the GI tract
Size of formulation
Dose-dumping
Economy
Outline the diff between Single unit & multi-unit systems.
Single-unit: Tablets and capsules
Dose of drug within a single unit
Multi-unit: Pellets, mini-tablets and granules
Dose of drug distributed among several units
How do extend drug release?
Incorporating some form of physical or chemical barrier into the dosage form to slow drug release
Dissolution controlled release
Diffusion controlled release
Osmosis
Explain Dissolution-controlled release.
Dissolution-controlled release: The drug is released as the barrier dissolves in the body. As the barrier dissolves, it lets the drug go.
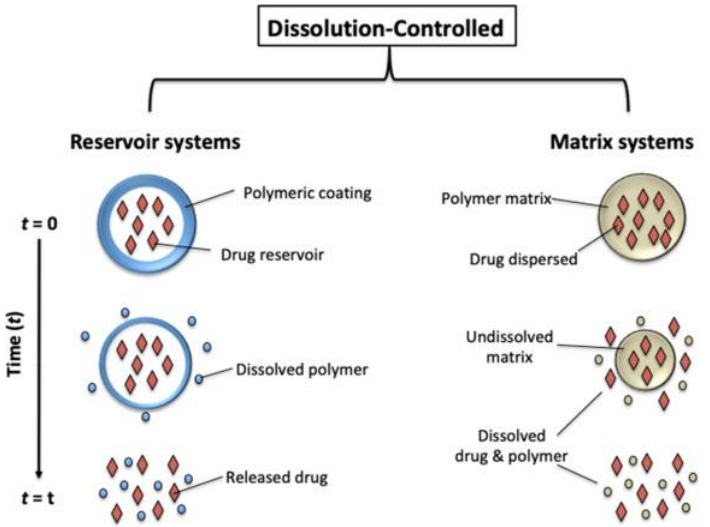
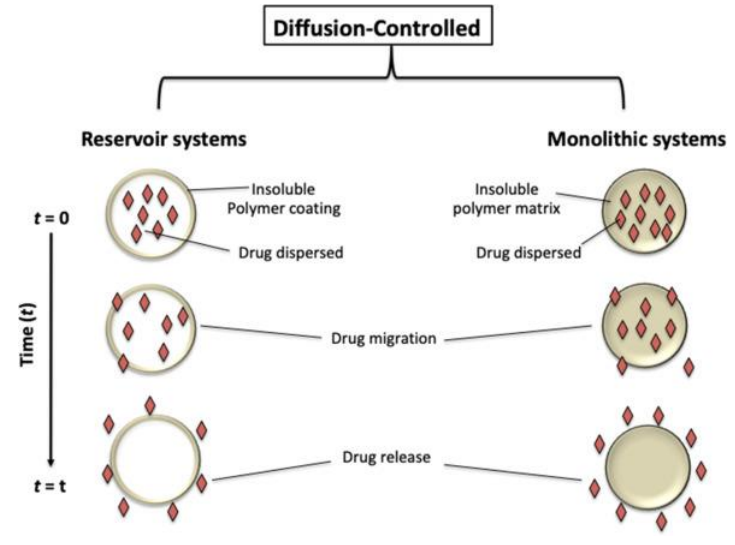
Explain Diffusion-controlled release.
Diffusion-controlled release: The drug is released by slowly moving through a non-dissolving barrier. The barrier doesn’t dissolve, it just lets the drug pass through slowly.
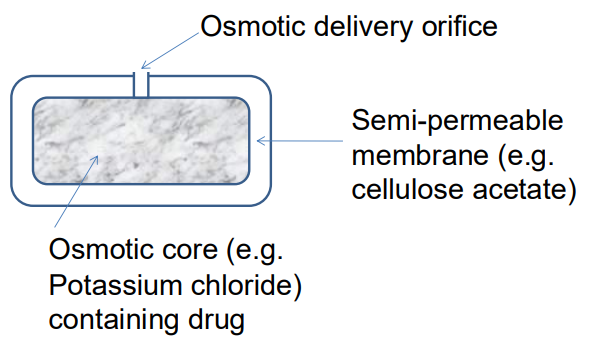
Explain osmosis-controlled release
Osmosis-controlled release: The drug is released by water entering the dosage form, creating pressure that pushes the drug out through a semi-permeable membrane.
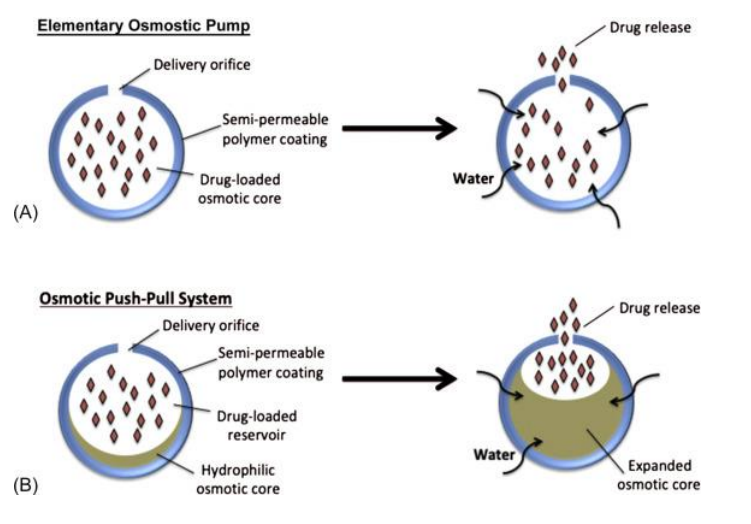
Outline the structure of an osmotic system.