WATER AND LIFE
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the water cycle and what are its key stages?
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface, involving processes like evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
What does a phase diagram show regarding water, and what are the phase transitions of water?
A phase diagram shows how water changes between solid, liquid, and gas states depending on temperature and pressure. The main phase transitions are freezing, melting, condensation, and vaporization.
What is sublimation, and how does it differ from other phase transitions?
Sublimation is the process where a solid directly turns into a gas, skipping the liquid phase, such as dry ice turning into carbon dioxide gas.
Why is water essential for life, and what are its key biological functions?
Water is essential for life because it facilitates biochemical reactions, helps transport nutrients, and regulates temperature. It also plays a vital role in digestion and excretion.
How does water's polar molecular structure affect its biological role?
Water's polarity allows it to form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules, contributing to its cohesion and adhesion properties, which are essential in biological processes like nutrient transport.
What are cohesion and adhesion in water, and how do these properties function in nature?
Cohesion refers to water molecules sticking to each other, while adhesion refers to water molecules sticking to other materials. These properties help water move through plants and in biological systems.
What is photosynthesis, and what is the chemical equation for it?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight. The equation is:
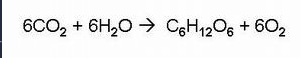
What is cellular respiration, and what is the chemical equation for it?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The equation is:
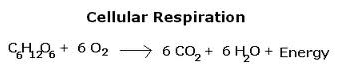
How does water's solvent property benefit living organisms?
Water's ability to dissolve many substances, such as salts and sugars, makes it an excellent medium for chemical reactions in living organisms, facilitating nutrient transport and waste removal.
Why is water's high heat capacity important for regulating the environment?
Water's high heat capacity means it can absorb or release large amounts of heat without significant temperature changes, helping to stabilize temperatures in both organisms and ecosystems.
What is the significance of water's high evaporation heat?
Water's high heat of evaporation allows it to cool the environment and living organisms through processes like sweating, helping to maintain body temperature.
Why does ice float on water, and how is its density different from liquid water?
Ice floats on water because it is less dense than liquid water. This happens because the molecules in ice are arranged in a structure that is more spread out than in liquid water.
How does the water cycle impact climate regulation?
The water cycle helps regulate climate by distributing heat through ocean currents, reflecting sunlight through ice, and contributing to the greenhouse effect via water vapor in the atmosphere.
How do ocean currents influence the climate, and what role does water play in this?
Ocean currents transport heat across the globe, which helps moderate temperatures. Water's high heat capacity allows it to store and transport large amounts of thermal energy, influencing local and global climates.
What is hard water, and why can it be problematic?
Hard water contains high levels of calcium and magnesium ions, which can cause scale buildup in pipes and reduce the effectiveness of soaps and detergents.
What methods are used to soften hard water, and how do they work?
Hard water can be softened using ion exchange resins, which replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions, reducing hardness and preventing scale buildup.
What is condensation, and how does it differ from vaporization?
Condensation is the process by which gas turns into liquid when it cools down. Vaporization, on the other hand, is the process by which a liquid turns into a gas when it gains heat.
What is the difference between fog, dew, and frost in terms of condensation?
Fog forms when water vapor condenses into small droplets suspended in the air. Dew occurs when water vapor condenses on cool surfaces at night, and frost forms when water vapor directly turns into ice on cold surfaces.
How does rain form, and what is the process of precipitation?
Rain forms when water vapor in clouds condenses into droplets that become heavy enough to fall to the ground due to gravity. Precipitation refers to any form of water that falls from the atmosphere, including rain, snow, and hail.
What is acid rain, and how does it form?
Acid rain is formed when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, emitted by industrial processes, react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form sulfuric and nitric acids, which fall as acidic precipitation.