2.2 aggregate demand
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
aggregate demand
total planned expenditure at a given price level
what is AD made up of
consumption + investments + government expenditure + net trade(exports - imports)
consumption
spending by households on consumer goods and services
why are consumer goods bought
for the utility they provide
what happens to consumption as disposable income increases
increase consumption
each £1 earned
is either consumed or saved
C + S = 1
marginal propensity
average proportion of the pound
why is AD downwards sloping
as price level increases - decreas real Y(income) - less money - decrease soending - decrease consumption - decrease AD

why is the link between dispos Y and C unclear
households can also finance C through borrowing or use of savings
main determinants of C
disposable income
interest rates
consumer confidence
wealth effect
interest rates
the added price of money borrowed or saved
increase IR - increase saving - decrease C
increase IR - increase cost of borrowing- decrease C
increase IR - increase mortgage payment - decrease C
and vive versa
consumer confidense
increase confidence - i.e future job security - increase confidence to spend - increase C
increase confidence - increase borrowing - increase C
wealth effect
increase price of assets e.g house,shares,bonds - feel wealthier - increase C
use assets as collateral for borrowing
investment
total spending on capital goods in order to produce other goods and services - increasing productive capacity
i.e additions to capital stock
net investment
expands the economy by increasing capital stock it is additions not replacements.
gross investments
includes both net(new/additional) investment + replacement investment
factors influencing investment
rate of econ growth
business confidence
keynes and animal spirits
demand for exports
access to credit
influence of govt regulation
rate of econ growth
increase econ growth - encourage business to I - increase sales - increase GDP/econ growth - Increase I
this is the accelerator process
business confidence
increase business confidence - increase I
confidence is affected by businesses views on future profit + sales
Keynes and animal spirits
keynes beleived investments were partly determined by “animal spirits” i.e beleifs/instincts/hunches
decisions based on managers feeling about future economy
often “animal spirits” move collectively - herd mentality
this often result in I rising or falling significantly
demand for exports
if increase in d for uk x’s - may require increase in capacity - increase in I
interest rates
higher IR - higher cost of borrowing - investments would require higher profitabilty - decrease I
access to credit
if decrease in access to credit - decrease in I
influence of govt regulation
govt can influence business I
e.g fiscal policy - decrease corporation tax - increase I - however business may just increase dividends and not invest money which means loss for govt
govt offer incentives for businness to invest in certain areas
consequences of low rate of a capital investment
slows econ growth
weaker productivity growth - capital stock not improved - decreass in quality or quantity
impact on exports + net trade - need capacity to keep up with demand
capital stock
machinery/equipment already in place used to make other goods and services
3 types of government expenditure
current expenditure
capital expenditure
transfer payments
current expenditure
“day to day”, education health service etc
capital expenditure
investing in ifrastructure e.g new hospitals
transfer payments
transfer payments from taxpayer to specified group e.g. pensions,benefits,grants etc
the trade cycle
a repeated cycle/pattern of variations in economic growth
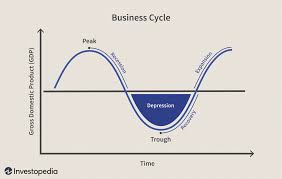
what happens to G when economy is in a slump
Increase unemployment - increase benefits - increase G
what happens when economy is growing
Decrease unemployment - decrease benefits - decrease G
fiscal policy
when gov.t deliberatley change levels of G and taxation
net trade
refers to our trade balance(exports(x)-imports(m))
trade deficit
x<m net leakage from uk
trade surplus
x>m net injection into UK
main influences on the trade balance
real income
exchange rates
state of the worlds economy
degree and global protection
non-price factors
real income
real income increase - increase spending by households - increase spending on imports
exchange rates
SPICED:
Strong Pound Imports Cheaper Exports Dearer
generally if pounds appreciates(gets stronger) this will increase M’s and decrease X’s
vice versa if pound depreciates
state of the worlds economy
if world economy grows stronger(boom)- increase real income overseas- increase D for UK X’s
likewise if global recession - decrease D for UK X’s
degree and global protection
if UK’s main export markets e.g EU,USA imposed tariffs on imports then this will decrease uk X’s
brexit has increased barries for uk X’s
non-price factors
demand for X’s will be affected by:
quality
reliability
transport costs