Unit 1: DNA
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, molecule that encodes inherited genetic information
nucleotide
building block; each comprised on a sugar-phosphate backbone (of pentose and sugar) and one of 4 bases
what is DNA’s overall charge?
the phosphate group having a negative charge gives the overall DNA a negative charge as well
why do bases have their complimentary pair?
because that pairing (A+T or G+C) is the most energetically favorable
what carbon are the base pairs attached to?
carbon 1
adenine and thymine H bonds
forf 2 H bonds
cytosine and guanine H Bonds
form 3 H bonds
antiparallel strands
because of the way the H bonds form, it forces the sugar-phosphate backbone to go in opposite directions: 5’ to 3’ and 3’ to 5’
functional consequence of this base pairing
each strand of DNA contains a sequence of nucleotides exactly complimentary to the opposite strand. this allows one strand to act as a template to make a copy of the other strand during DNA replication
semi-conservative replication
each daughter DNA molecular contains one strand from the parent DNA molecular and one newly synthesized strand
chromosomes
separated into manageable units that are organized spatially
organized subunits of the genome
each 23 occupies its own space in the nucleus
(think organized and rolled spools of yarn)
nucleosomes and chromatin
wound tightly to maximize space, leaving specific parts available for use
genome
the complete sequence of DNA (genetic information) present in a cell or organism
gene
unit of genetic information
what does each chromosome equal?
1 molecule of DNA
diploid
2 copies of every chromosome: 1 from biological mother and 1 from biological father
chromatin
fibers made up of packed nucleosomes
half protein + half DNA
nucleosome
DNA wound tightly around proteins called histones
histones
proteins
breakdown/steps of condensed DNA
DNA wounds around proteins called histones become a nucleosome (beads on a string)
then, other proteins are added to each wound that allow for nucleosomes to be tightly packed
then, packed even more tightly into a fiber called chromatin (30-nm fiber)
lastly there is chromatin folding with loops of 30-nm fibers
chromatin can exist in two structural/function states
heterochromatin and euchromatin
heterochromatin
highly condensed, gene-poor, and transcriptionally silent (genes not accessible)
euchromatin
less condensed, gene-rich, and more easily transcribed (the genes are accessible)
how does the structural state of chromatin impact DNA’s function?
decondensed: for access
condensed: for storage
not just for storage: the cell decides which genes need to be accessed to do the specific work at a particular time
controls access to regions of DNA for: replication, expression, and repair
structure of nucleosomes
DNA: about 147 base pairs are wrapped around around the protein core (1 and 2/3rds of the way); negative charge
protein core: octomer of histone proteins; positive charge
histones play an important role in condensing chromatin
opposites attract —> tight interaction
chromatin remodeling enzymes
modify histone tails to impact chromatin packing
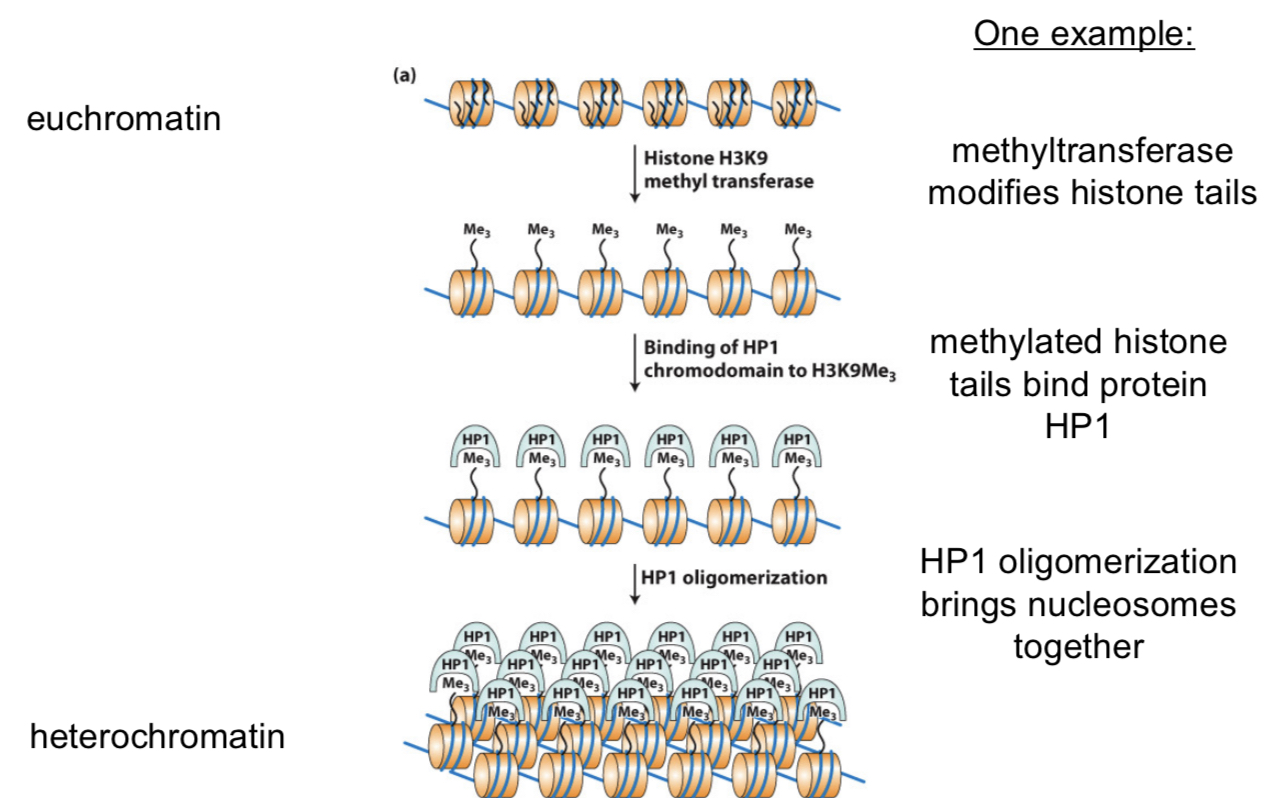
histone H3
methyltransferase modifies histone tails by transferring methyl groups onto histone tails (histone H3 for this example). this makes the tails for accessible since they become popped up.
the methylated histone tails bind to protein HP1. The tails are now available for something to attach to them after being methylated
HP1 oligomerization (many units come together) brings nucleosomes together. HP1 binds to itself which pulls all nucleosomes to on another and condenses
methyltransferase
transfers enzyme methyl groups
does methylation of histone tails increase or decrease gene expression
increase in condensation —> decrease in gene expression (less accessible)
You are studying HP1, a protein involved in condensing chromatin, by making mutations in HP1 and studying their effect on the formation of heterochromatin in a eukaryotic cell. Predict what effect each mutation would have on the condensing of chromatin.
Compared to normal (“wildtype”) HP1, a mutant version of HP1 that oligomerizes more strongly would":
A. enhance heterochromatin formation
B. inhibit heterochromatin formation
C. have no effect on heterochromatin format
A
You are studying HP1, a protein involved in condensing chromatin, by making mutations in HP1 and studying their effect on the formation of heterochromatin in a eukaryotic cell. Predict what effect each mutation would have on the condensing of chromatin.
Compared to normal (“wildtype”) HP1, mutant version of HP1 that cannot bind H3L9Me3 would:
A. enhance heterochromatin formation
B. inhibit heterochromatin formation
C. have no effect on heterochromatin format
B
Modifications
there are three types of modifications cells use on their histone tails to regulate chromatin packing: methylation, phosphorylation, acetylation
modifications are site-specific, not random
phosphorylation
addition of phosphate group, -PO4
acetylation
addition of acetyl group, -COCH3, catalyzed by histone acetyltransferases. “opens” the chromatin and increases gene expression (DNA is more accessible)
methylation
addition of methyl group, -CH3
deacetylation
removal of acetyl group, catalyzed by histone deacetylases
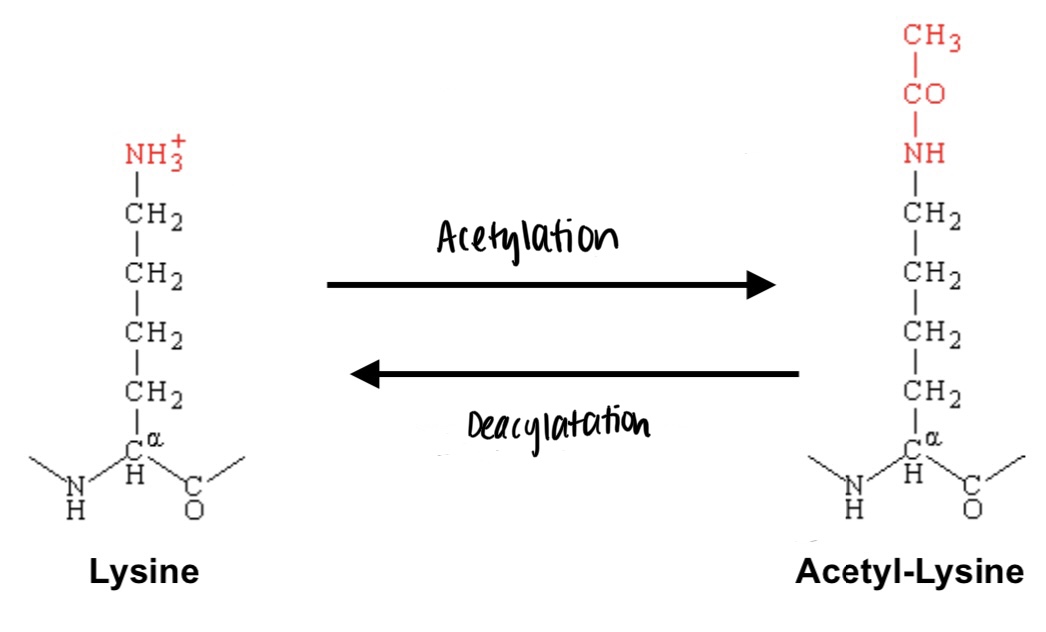
Based on the chemistry of the acetylation of lysine, would you expect this histone tail acetylation to tighten or loosen the interaction between the histone and the DNA wrapped around it?
it would loosen the interaction between the histone and the DNA wrapped around it. lysine is positive, so with the addition of the acetyl group, the DNA (which is negative) and the lysine (the histone) will lose attraction between each other due to a lack of opposite attraction
cytosine methylation (CpG methylation)
modifications can also occur on the DNA molecule itself.
methylation on cytosines that are followed in the same DNA strand by a guanine in the 5’ to 3’ direction. (not to be confused with C=G base pairs across the two DNA strands.)
This can enhance chromatin condensation. methylated DNA can serve as a binding site for other proteins, including deacylation and other chromatin remodeling proteins that condense chromatin.
is cytosine methylation heritable? (think about semi-conservative replication of DNA)
since DNA is mirrored across both strands, it will be the correct bases when copied, allowing it to be methylated.
half is new and half is old, if the methyl group is on the old strand, it will be passed down.
DNA accessibility in cytosine methylation
cytosine methylation can make DNA less accessible.
methylated DNA can serve as a binding site for other proteins that condense chromatin
epigenetics
the study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence (a change in phenotype without a change in genotype)
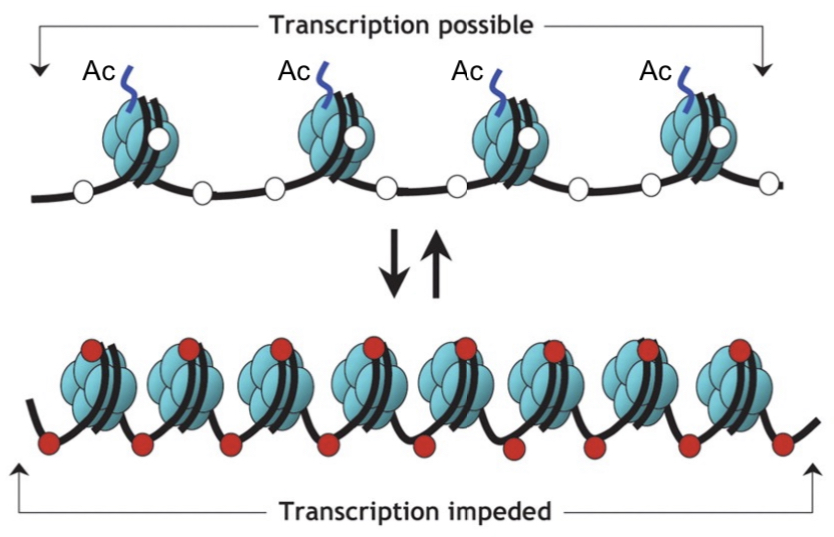
active (open) chromatin
unmethylated cytosines (white circles)
acetylated histones (Ac)
unmethylated histone tails
silent (condensed) chromatin
methylated cytosines (red circles)
decetylated histones
methylated histone tails
DNA structure
the structure of DNA provides a mechanism for its function as the molecule that encodes hereditary information
inheritance of traits
DNA is easily reproducible and stable
evolution of traits
DNA sequence is easily changeable and modular
topoisomerase
unwinds the double helix of DNA
helicase
separates double-stranded DNA into single-stranded DNA (unzips)
single stranded binding proteins
prevent complementary base-pairing at fork, keep DNA from reconnecting (keeping them separate)
primase
starts new strand by synthesizing short RNA sequence called a “primer”
DNA polymerase
starting at primer, elongates DNA polymer, catalyzing covalent bonds of sugar-phosphate backbone
adds complementary nucleotides to the free 3’ hydroxyl group of a growing DNA strand to the incoming 5’ phosphate group
uses deoxyribonucleotides to fill in the gaps left by removal of RNA primers
leading strand
continually synthesized toward replication fork
lagging strand
synthesized in sections
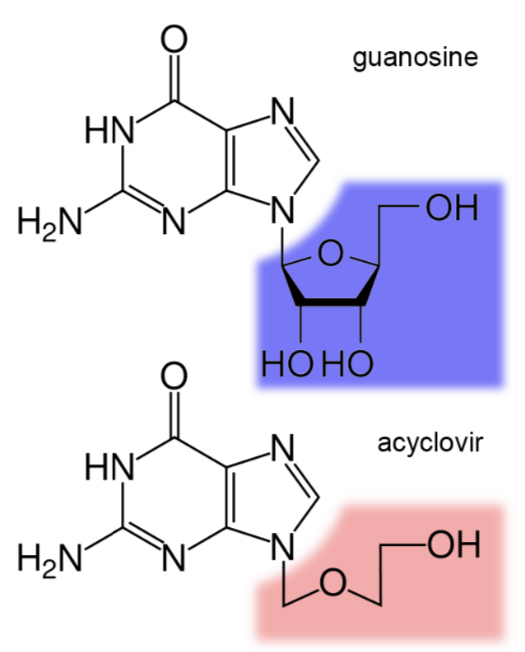
the herpes drug acyclovir works by inhibiting the synthesis of new viral DNA. acyclovir resembles the base guanine but does not contain the full 5-carbon ring of the sugar backbone.
predict how acyclovir’s structure blocks the synthesis of new viral DNA.
because DNA polymerase needs the 5-carbon sugar and phosphate group to synthesize DNA, it cannot do that because there no 5-carbon group/3’hydroxyl group, so another base cannot be added after guanine
synthesis of DNA from lagging strand
primase adds RNA primers
DNA polymerase starts at the primer and elongates DNA polymer, catalyzing covalent bonds of a sugar-phosphate backbone (sections are called Okazaki fragments)
exonuclease removes RNA primer
DNA polymerase fills in the gaps
DNA ligase catalyzes the covalent bonds of the sugar-phosphate backbone, sews the two fragments together
exonuclease
removes RNA primer
DNA ligase
catalyzes covalent bonds of sugar-phosphate backbone of adjacent pieces of DNA (sews together)
where does DNA replication begin and end?
at the replication origin, end when it eventually meets another bubble or when it reaches the end of the molcule
replication forks
bubbles on either side of the origin. template DNA on the outside and newly-synthesized DNA on the inside
is there only one replication fork?
there can be multiple replication forks along the molecule of DNA
leading and lagging strands in the replication fork
the leading and lagging strands are relative to the replication fork
one strand can be both leading & lagging, depending on what side of the strand the fork its
because there can be multiple replication forks along on DNA molecule, the leading and lagging strands will eventually meet and merge (replication ends here or when replication meets the end of the DNA)
PCR
polymerase chain reaction
DNA replication happening in a test tube
making copies/amplifying genes of interest
primers: uses DNA primers instead of RNA primers
Taq polymerase: elongates new DNA
no replication fork
no lagging strand
denaturing
PCR uses heat to make DNA copies. enough heat to break apart the strands but not enough to break the backbone (unzipping w/heat)
which components of cellular replication machinery are no longer necessary in PCR because heat is used to separate the DNA strands?
helicase
annealing
temperature is lowered and DNA primers attach to DNA template strand
which components of the cellular replication machinery are no longer necessary in PCR because scientists design DNA primers to initiate replication?
primase: PCR uses DNA primers instead of RNA primers
exonuclease: gets rid of RNA primers, but we’re using DNA primers which gets incorporated with the strand since it’s already DNA
ligase: don’t need to be sewn up because DNA primers are staying
extension
synthesize new strand, Taq polymerase adds nucleotides to the annealed primer, extension/elongation of strand
PCR cycling
many cycles = even more copies
two methods of detection of PCR products (the DNA sueqences of interest)
by fluorescence and by gel electrophoresis
fluorescence
use primers specific to parts of genome of interest
use fluorescence to measure how many copies of the genomes of interest are present
sensitive enough to detect only 1 virus (in the example of detection of SARS-CoV-2 from nasal swabs)
gel electrophoresis
use primers specific to gene of interest
visualize PCR products as a band in a gel