APES Unit 6: Energy Resources and Consumption
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Surface mining
if a resource is less than 200 feet from the surface, the topsoil and rock is removed. explosives used to break up rock. reclamation follows
overburden or spoils?
overburden: topsoil and rock above the thing that is being mined in surface mining
Spoils: the overburden when it is removed
benefits and drawbacks surface mining
+: cheap, easy, efficient
-: tears up land (temporarily) byproducts produce an acid that accumulates in waterways
Strip Mining
earthmover strips away overburden and a power shovel removes the mineral deposit. trench is filled with overburden. Leaves spoil banks
spoil banks
caused by strip mining. hills of mining waste susceptible to erosion, slow regrowth, no topsoil
contour strip mining
surface mining in a hilly area. shovel cuts terraces into hill, remove overburden and dump it into terrace below. wall of dirt is left in front of a highly erodible bank called a highwall
Mountain top removal
explosives remove the top of a mountain and expose seams. of coal. waste is dumped into valleys below, often blocking rivers and streams. “biggest of all the bummers”
Surface mining control and reclamation act of 1977
requires mining companies to resotre most surface mined land by grading and replanting it. Only partially successful bc it takes decades and arid land often ends up as a desert
underground/subsurface mining
digging a shaft down to the resource, using machinery and ppl to tear off and remove the resource
benefits and drawbacks to underground/subsurface mining
+: can get resources far underground, does not scar land
-: more expensive, more time, more dangerous
3 major impacts of mining
scarring and disruption of land surface, subsidence (cave ins), toxin laced mining waste/acid mine drainage
removing metal from ore
ore mineral is what you want, gangue is the waste material. removing ganue produces large piles of waste called tailings.
Smelting: roasts ores to release metals
cyanide heap extraction: separate gold from gold ore
which countries have the most coal?
US (22%), Russia (15%), australia (14), china (13%)
Peat
not considered coal yet, lots of moisture, not efficient
Lignite
Low heat and sulfur, Lame
Bituminous
Bad, high heat and sulfur
Anthoricte
A+, high heat, low sulfur
steps to light!
plant
compress
coal
mined
transported
power plant
crushed
set on fire
steam
wind turbine
generator
electricity
powerline
outlet/lights
gasification
turns coal into syngas
fluidized bed combustion
mixes crushed coal with limestone and sets them on fire. sulfur reacts with limestone to sulfur is removed so scrubbers are not needed. produced more heat but is costly
coal burning impacts
release CO2 into atmosphere (global warming), increases air pollution, contains mercury (harms humans and wildlife), releases nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides (acid deposition)
wet scrubbers
desulfurization and clean power plant exhaust
coal washing
crushes coal with liquid and allows impurities to settle out
flue-gas seperation
removes CO2 and makes into usable co2 (dry ice, soda)
OPEC
organization of petroleum exporting countries. saudi arabia and venezuela have 70% of oil
other names for oil
crude oil, petroleum, liquid containing hydrocarbons
Alaska Arctic National Wildlife refuge (AANWR)
Taiga and tundra biomes, 3 types of north american bears, porcupine and caribou. 4.3-11 billion barrels there=1 year of energy in US. big oil wants money, oil prices decrease, provide jobs, but native ppl on the land
Refining crude oil
heat and boil oil: gasoline boils out first, then diesel, then asphalt is last among other things
petrochemicals
any product that has a petroleum ingredient. medicine, plastics, petroleum jelly, synthetic fibers, etc
oil sands/tar sands
mix of clay,sand,water and bitumen. has to be processed before refined (costly) mostly found in Canada
oil shales
combustible mix of hydrocarbons that live in rock (kerogen). it is crushed, heated to release shale oil then heated to remove sulfur and nitrogen, then it is refined. found it wyoming, colorado, utah, can last 110 years
oil spills
Exon Valdez sea otters loose insulation ability, birds lose water repellency oil intake, fin erosion
Natural gas
russia and iran have abut half of it. versatile, clean burning. releases co2 and methane leaks
conventional natural gas
mostly methane, found above reservoirs of crude oil, can liquify and turn into lpg
unconventional natural gas
methane hydrate: coal + methane trapped under ice from anaerobic creatures
marcellus shale
pennsylvania, NY, Ohio. LOTS of natural gas
hydraulic fracturing/fracking
dig a hole, push lots of water into it, pressure breaks the rock and brings that natural gass up
benefits and drawbacks of fracking
+: less dependency on foreign oil, jobs, can make lots of money for companies
-: not regulated by clean air or water act, MASSIVE quantaites of fresh water, fracking fluid gets into water supply, kills wildlife.
solutions to fracking
increase regulation, increase monitoring, disclose chemicals in fracking fluid
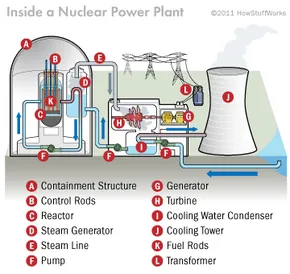
nuclear
biomass: ethanol
fermenting plants, distils sugarcane, corn. found in brazil mostly,
benefits and drawbacks of biomass: ethanol
+: biodegradable, low co2, you can drive a car with it, no sulfur
-: deforestation, increased use of fertilizers and pesticides, crops for fuel and not food
biomass: electricity
burn biomass to heat h2o and turn a turbine. charcoal
benefits and drawbacks of biomass: electricity
+: carbon neutral
-: deforestation
photovoltaic cells/solar panels
sun hits silicon and electrons move one way producing electricity. found it germany, china, southwest
benefits and drawbakcs of solar panels
+: no co2 or sulfur while producing electricity, subsidies in germany, tax breaks in US, getting cheaper over time
-: costly to manufacture, toxic chemicals from mining silicon and manufacturing, useless at nightime
active solar
mirrors direct sunlight to central collector with salt and it can use or store the energy. found it california, arizona, desert places
benefits and drawbacks of active solar
+: no pollution, energy 24/7
-: costly, need a lot of water, space and mirrors, delicate habiate with no one near to use the energy
hyrdoelectic dams
water falls through a penstock and spins a turbine. found everywhere with rivers. creates reservoirs
benefits and drawbacks to hydroelectic dams
+: flood control, cheap to maintain, increase in tourism and recreation, irrigation, run of the river
-: release methane from plants under water, fish cant move (fish ladder), high initial costs
tidal
giant dams in the ocean that spin turbines as the tides go in and out. found in coastal areas
benefits and drawbacks to tidal
+: tide is predictable, no fuel, not greenhouse gasses
-: costly to build, displaces animals, ugly, damages habitat
geothermal
underground water heated by magma, steam turns a turbine. can also do under your house with air for heating and cooling. found at hotspots with thin crust
benefits and drawbacks to geothermal
+: cheap at a reservoir, no co2
-: scarce reservoirs, not good outside of them, specific locations
wind
pressures move air to make wind and turn a turbine. found in texas, kansas, costal areas
benefits and drawbacks to wind
+: cheap to maintain, no pollution or greenhouse gasses, jobs, can grow crops or graze cattle under them
-: noise pollution, costly to build, flying animals hit them, ugly
hydrogen fuel cells
at the anode, hydrogen is oxidized and elections flow to to the cathode. at the cathode, o2 reacts with hydrogen to make water. water and heat are byproducts. found in california
benefits and drawbacks to hydrogen fuel cells
+: no co2, decrease climate change and ocean acidification,
-: costly, h2 storage, distribution system