Waves
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What do all waves do?
Transfer energy from one place to another
How do transverse waves move?
They move up and down in movements called oscillations
The oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
Not all transfer require a medium
How do longitudinal waves move?
Moves particles side to side
Has areas of compressions (close together particles) and rarefactions (spaced out particles)
The oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Require aa medium to travel through the air e.g. air, a liquid or a solid
What are oscillates?
Move backwards and forwards
Key fact on waves
In ripples on the water or sound waves in the air, it is the wave that moves and not the water or air
What is amplitude?
The maximum displacement of a point on a wave away from its undisturbed position
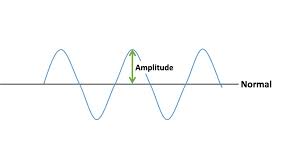
What is wavelength?
The distance from a point on one wave to the equivalent point on the adjacent wave
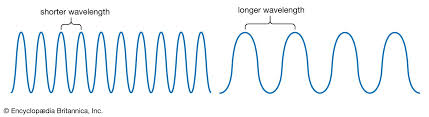
What is the symbol for wavelength?
Lambda λ
How do we measure wavelengths on longitudinal waves?
Measure from one compression to next compression
Measure from one rarefaction to next rarefaction
What is the frequency?
The number of waves passing a point each second
1Hz = 1 wave per second
What is a period?
The time (in seconds) for one wave to pass a point
Period (s) = 1 / frequency Hz
What is the equation for wave speed?
V = F x λ
Required practical 8: Ripple tank
Use a ripple tank (a shallow tray of water that has a vibrating bar that creates waves across the water surface which is connected a to a power pack) which a lamp above it and a sheet of white paper under it
Record the waves on a mobile phone
Wave length
To measure the wave length place a ruler on the paper and then freeze the image of the waves
Measure the distance between one wave and ten waves further - divide the number you get buy ten to get the average length
Frequency
Place a timer next to the paper and count the number of waves passing a point in one second
Required practical 8: Waves in a solid
A string with one end attached to a vibration generator and the other end of the string attached to a hanging mass
The vibration generator is attached to a signal generator which allows us to change the frequency of vibration of the string so when the power is turned on the string vibrates
This creates a standing wave due to an effect called resonance
To measure the wavelength of the wave we use a ruler
Measure from the wooden bridge to the vibration generator
Use the wave speed equation
You can read the frequency from the signal generator
What is a electromagnetic waves?
Transverse waves
They transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
What colour has a low/high frequency and long/short wavelength?
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet
Low frequency High frequency
Longer wavelength shorter wavelength
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
Radio, Microwaves, Infrared, Visible light, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma Rays
Low frequency High frequency
Long wavelength Short wavelength
Abbreviation for the electromagnetic spectrum
Raw - radio
Meat - microwave
Is - infrared
Very - visible light
Unsanitary - ultraviolet
eXcept - x-ray
Giraffe - gamma rays
Features of electromagnetic spectrum
Don’t need a medium to travel
All travel at the same speed at a vacuum - speed is 300,000,000m/s
Different materials absorb, transmit or reflect electromagnetic waves
What is refraction?
The change in direction of a wave (like light) as it passes from one medium to another, due to a change in speed
What are the key points of refraction?
Waves can change direction when they change speed, moving from one medium to another
What happens when wave fronts travel through glass?
When the wavefronts move into the glass, parts of the wavefronts slow down
This causes those parts of the wavefronts to get closer together and gets smaller
This causes the waves to change direction towards the normal (refracting)
When waves speed up, they change direction away from the normal
Required practical 10: Infrared
Use a Leslie’s cube (has a shiny metallic side, white side, shiny black side and matt black side)
Fill the cube with hot water and point an infrared detector at each of the four surfaces and record the amount of infrared emitted (keep the same distance between the two so the experiment is repeatable)
The matt black emits the most infrared emission and the shiny metallic emits the least infrared emission
Matt black , shiny black, white, shiny metallic
What can you use instead of infrared detector?
Paint light bulb black - less detectable
How is the absorbance of infrared emissions absorbed?
Place a infrared heater and on either side place two metal plates
One plate has been painted with shiny metallic paint and the other side painted matt black
On the other side of the plates, use Vaseline to attach a drawing pin
Switch on the heater and start timing
The temp of the metal plate increases as the infrared is absorbed
Record the time it takes for the Vaseline to melt and the drawing pins to fall off
It falls off the matt black plate first as it absorbs more infrared and infrared tends to reflect from shiny metallic
What happens when electromagnetic waves are absorbed?’
Changes take place in atoms or the nuclei of atoms
What happens when atoms are heated?
Electrons move from one energy level to a higher one
When it returns to its original energy level, it generates an electromagnetic waves
What happens when there is a change on the nucleus?
Gamma rays can be emitted by the nucleus of atoms
Once the gamma ray has been emitted, the nucleus has less energy then it had at the start
What happens when electromagnetics are absorbed?
Cause changes to atoms e.g. electrons can change energy levels
What are the hazards of electromagnetic waves?
Potentially very hazardous
Ultra violet waves can cause risks of skin cancer and cause skin to age prematurely
X-rays and gamma rays are ionising radiation - knock electrons off atoms and can cause mutation of genes
What is the dose of radiation measured in?
Sieverts or millisieverts
How are radio waves produced?
When electrons oscillate (move backwards and forwards) in electrical circuits
These radio waves can be absorbed
This causes electrons in the circuit to oscillate
This creates a alternating current with the same frequency as the radio waves
What are radio waves used for?
Radio and TV signals
What is terrestrial TV?
Received using a aerial
Why are radio waves used?
They can travel long distances before being absorbed e.g. buildings and trees
Can reflect off a layer of charged particles in the atmosphere
What are microwaves used for?
Heating food because most foods contain water molecules which absorb the energy of microwaves
What is infrared used for?
Used to cook food in ovens and in electrical heaters - infrared is easily absorbed
Infrared cameras - check for heat
What are visible light used for?
Communication using fibre optics (think strands of glass which transmit pulses of light down these fibres to carry information)
Used to carry telephone and cable TV signals
What is ultraviolet used for?
Energy efficient light bulbs
Tanning beds
What are gamma rays and x-rays used for?
Medical imaging
Gamma rays are used to detect cancers
Used in medical treatments e.g. cancer