Medicinal Chemistry of Antidepressants
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the MOA of MOST antidepressants
Inhibit reuptake of NE and/or 5-HT from synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic terminal
What is the MOA of SOME antidepressants
Have antagonist activity at neurotransmitter receptors (NMDA. 5-HT. H1, alpha2)
Inhibits the degradation of monoamine neurotransmitters (NE, 5-HT)
Blocks reuptake of dopamine
Fluoxetine has greater SERT selectivity compared to NET selectivity because…
Fluoxetine is marked as a racemic mixture of R- and S- enantiomers
The S- enantiomer is highly selective for SERT (100:1)
R- is only 8;1 for SERT
Averages about 30:1, so not as potent as other SSRIs/SNRIs/TCAs
What are TCA’s?
6-7-6 tricyclic structure that has great lipophilicity/CNS activity
Have a similar pharmacologic profile for reuptake inhibition and adverse effects arising from blocking receptors (H1, M1, a1)
T/F: The improved side effect profiles of SSRIs and SNRIs have decreased the use of TCAs
True, TCAs are dirty drugs (aka hit other receptors)
Histamine H1 receptors (causing sedation/weight gain)
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (causing dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention)
Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors (causing orthostatic hypotension)
Tertiary vs secondary amine side chain chemistry in TCAs are important for…
Binding selectivity to SERT vs NET
Adverse effects
Tertiary TCA’s are selective for _____ while secondary amine TCA's are selective for ____
Options:
SERT
NET
Tertiary —> SERT
Secondary —> NET
How do TCAs block SERT and NET?
When TCAs bind to SERT or NET, it causes a conformation change that decreases the binding affinity of 5-HT to SERT or NE to NET
What type of TCA’s have greater adverse effects?
Tertiary amines
Sedation (H1)
Orthostatic hypotension (a1)
Dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation (M1)
What are tertiary amines still used if they have more side effects?
Sedation —> desirable for insomnia pts
Better response as it has SERT>NET affinity
How is overdose possible with TCAs, but not SSRI/SNRIs?
Both TCAs and SSRIs/SNRIs increase serotonin and norepinephrine
But TCAs also block many other critical receptors (like muscarinic, histamine, and alpha-1) and affect cardiac ion channels, especially fast sodium channels in the heart.
Difference between citalopram vs escitalopram
Citalopram —> racemic mixture of R- and S- enantiomers
R- enantiomer binds with less affinity and selectivity to SERT
Has no 5-HT reuptake inhibition activity
Likely impedes the activity of the S-enantiomer by occupying SERT binding sites
Escitalopram —> S- enantiomer of citalopram and has high affinity for binding to SERT/is potent for SERT
What drug is sometimes abbreviated as ODV in practice?
Stands for O-desmethyl venlafaxine
Trazadone is a
_____ SERT inhibitor
_____ at 5-HT1a receptors
Weak
Antagonist
Vilazodone…
_____ SERT
_____ _____ at 5-HT1a receptors
Inhibits
Partial agonist
Vortioxetine…
_____ SERT (lower activity at NET)
_____ at multiple 5-HT receptors
Inhibits
Antagonist
T/F: antidepressants are not extensively metabolized
False
T/F: many antidepressants have active metabolites that extend their duration of activity
True
T/F: CYP3A4 is the primary isoform metabolizing TCAs and plays a major role in metabolism of other antidepressants
False,
CYP2D6
T/F: The metabolism of bupropion and desvenlafaxine is the same relative to most antidepressants
False,
Different relative to most antidepressants
T/F: CYP inhibition is common in antidepressants
True
Why do citalopram and escitalopram have different CYP isoforms as their major metabolizing isoform?
P450’s also have steroisomer activity
S- enantiomers → 2D6
R- enantiomers → 2C19
Why is the major metabolizing enzyme for desvenlafaxine different from other antidepressants?
It’s already demethylated
Why do you need to watch out when switching a patient from fluoxetine to another antidepressant?
Dosing as fluoxetine and its common metabolite, Norfluoxetine, has really long half lives
Fluoxetine → ~50 hrs
Norfluoxetine → ~200 hrs (even longer than parent drug)
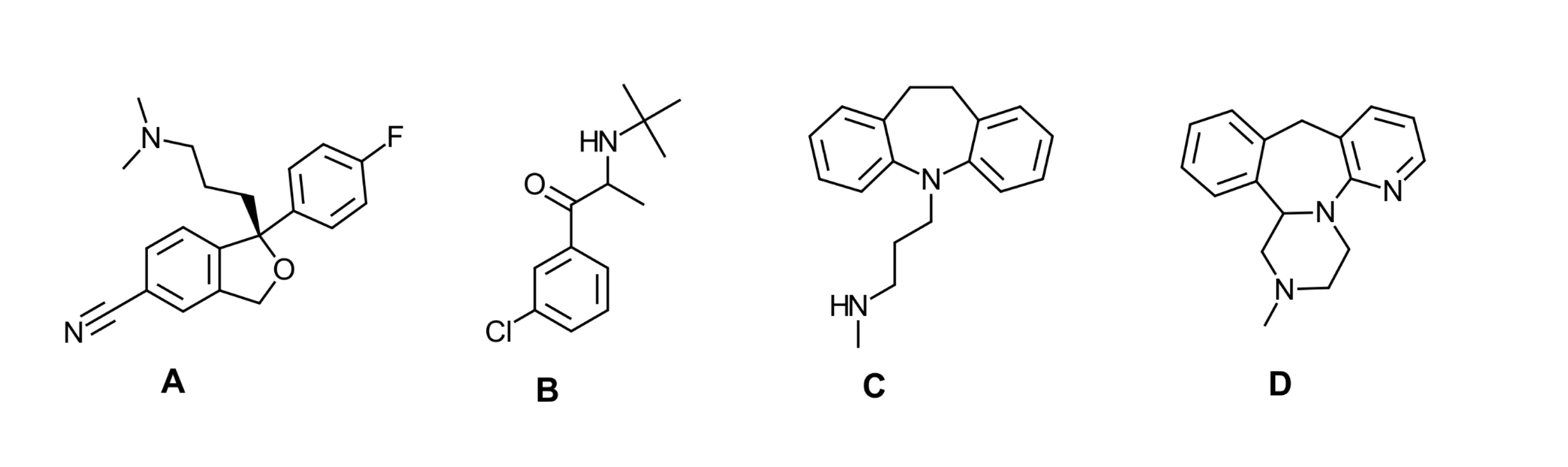
Which of the following depicts and enantiopure drug product?
A
A patient is taking an antidepressant mentions to you that they feel “dizzy and wobbly” when they stand up. Of the following, which is the most likely explaination for their symptoms?
a. Blockade of a1 receptors
b. Blockade of M1 receptors
c. Inhibition of NET
d. Induction of CYP metabolism
a. Blockade of a1 receptors
Which chemical feature of TCAs contributes to most adverse effects arising from receptor blockade (as compared with non-TCA antidepressants)
a. Amphoteric acid/base properties
b. Covalent binding with target site
c. Lipophilicity of TCAs
d. Shape of TCA structure
d. Shape of TCA structure
Fluoxetine SERT/NET selectivity looks like that of an SNRI. However, fluoxetine is classified as an SSRI due to its overall serotonergic activity. Which of the following is NOT part of the explaination for this apparent discrepancy?
a. Fluoxetine is a prodrug
b. Fluoxetine is metabolized to an actvive metabolite
c. S-norfluoxetine is more selective for SERT than R-norfluoxetine
d. S-norfluoxetine is more potent than R-norfluoxetine for inhibiting SERT
a. Fluoxetine is a prodrug