Plant structures and their functions
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
... organisms are the main .... of food and therefore ....
1. photosynthetic organisms
2. producers
3. biomass
What type of reaction is photosynthesis?
endothermic
What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water ---> glucose + oxygen
what energy does photosynthesis use to convert CO2 and H2O into C6H12O6 and O2?
light energy
Explain the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
As temperature increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis because the enzymes gain more kinetic energy so more collisions take place.
Until past the optimum temperature when the enzymes denature
Explain the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis
as co2 concentration increases, so does the rate of PS because more raw material is available to convert into glucose
explain the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
as light intensity increases, the rate of PS increases because there is more light energy to convert into chemical energy
What are the 3 components of photosynthesis that can limit the rate
If light intensity, temperature or CO2 concentration is in short supply, the rate of photosynthesis is limited
why does the graph plateau
a further increase in light intensity makes no difference because another factor is in short supply, limiting the rate
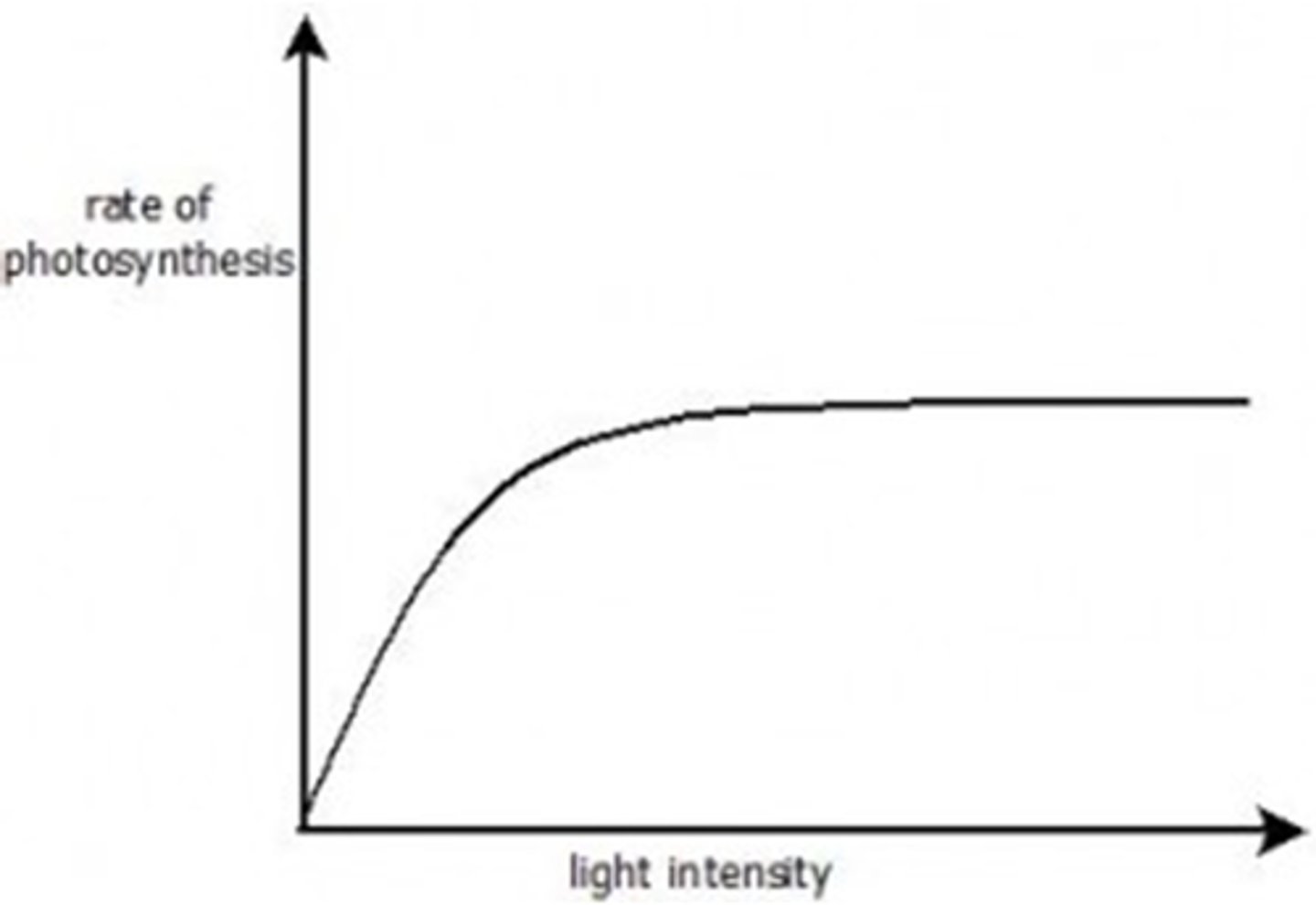
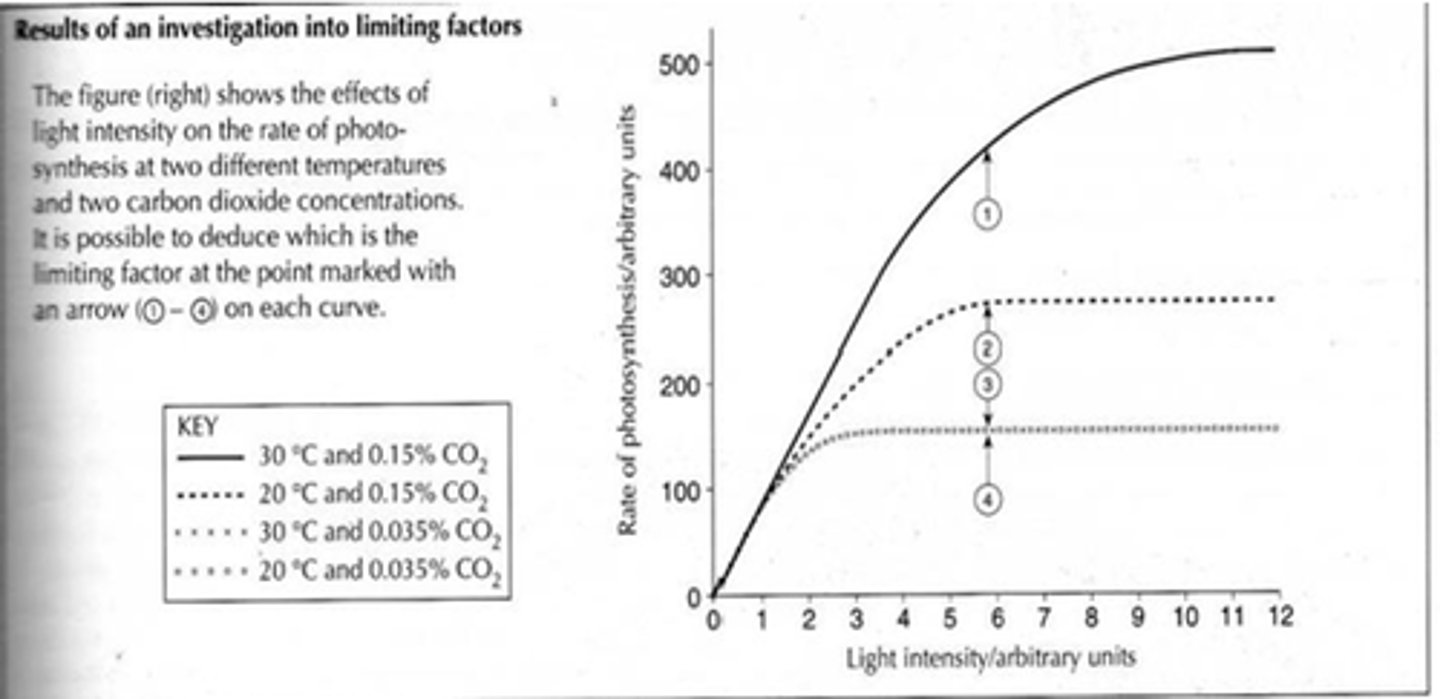
deduce from the graph the limiting factor in this experiment
temperature
Describe the CP used to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
1. In a test tube place pondweed in water
2. top with a bung and gas syringe
3. record how far away the test tube is from the lamp and measure the volume of gas produced by the pondweed
4. repeat experiment at different distances from lamp
rate of photosynthesis is ..... proportional to light intensity
directly
rate of photosynthesis is ..... proportional to the distance from light source
inversely
Why is rate of PS directly proportional to light intensity
Becuase the greater intensity of light, the more photons (light energy) hit the chloroplasts in the leaf, and the more PS can occur at once
Why is the rate of PS inversely proportional to the distance from light source
Becuase as distance from light source increases, rate of PS decreases
Inverse square law
light intensity = 1/distance²
function of a root hair cell
To absorb water and mineral ions for the plant (via osmosis and active transport)
Explain root hair cell adaptations
1. large surface area to volume ratio so more water can move in by osmosis
2. large permanent vacuole keeps a steep concentration gradient so water can enter root hair cell quicker
3. lots of mitochondria to provide energy for active transport to take up mineral ions
function of xylem cells
To transport water and mineral ions from the roots to the leaves
Adaptation of xylem cells
lignified dead cells are hollow and are joined end-to-end to form a continuous tube so water and mineral ions can move through
Function of phloem cells
to carry the products of photosynthesis (sucrose) to all parts of the plant
Adaptation of phloem cells
cells are alive with lots of mitochondria in the companion cells to release energy to transport sucrose around the plant
Define transpiration
the evaporation of water vapour from the leaves and stems of plants due to the water potential gradient between the leaves and roots
Where does transpiration occur?
Through the stomata (pores) on primarily on the lower epidermis
What is the role of the stomata?
Stomata are tiny pores on the underside of the leaf, these control the gas exchange in the leaf. Each stoma can be opened or closed, depending on how turgid the guard cells are
How do the stomata operate?
Guard cells control the opening and closing of the stomata. The more water in the cell, the more turgid the guard cells become, opening the stomata more
How does light impact the opening and closing of the stomata?
The guard cells open the stomata in the light, because that's when photosynthesis occurs when water is needed, and close in the dark to save water
Why are most of the stomata on the underside of the leaf?
To retain more water because they are not directly in the sun so less evaporates from heat
How does the transpiration stream work?
1. water is lost at the leaves by transpiration
2. To replace the lost water, water is drawn out of the xylem into the leaves
3. Root hair cells draw in water from the soil by osmosis to replace water in xylem, resulting in a continuous transpiration stream
Define translocation
the movement of sucrose made in the leaves up or down the phloem, for use immediately or for storage
Where does translocation occur?
Phloem
Give 4 adaptations of the leaf for photosynthesis and gas exchange
Stomata: allow gas exchange and transpiration for photosynthesis
Chlorophyll: green- most efficient colour for absorbing light so as much light as possible is absorbed for photosynthesis
Thin leaves: means that oxygen and co2 only have a short diffusion pathway
Large surface area: leaf can absorb more light at once, maximising rate of photosynthesis
How does temperature affect the rate of transpiration?
Increase of temp=increased rate of transpiration
Because water is gaining kinetic energy from heat and evaporating faster
How does light intensity affect the rate of transpiration?
Increase of light intensity= increased rate of transpiration
Because the more intense the light, the wider the stomata so more water can diffuse outwards
How does wind speed affect the rate of transpiration?
Increased wind velocity= increased rate of transpiration
Because high wind speed moves saturated air away from the leaves, maintaining a high concentration gradient
How to calculate the rate of transpiration?
distance moved by bubble/time taken
Explain 3 adaptations of plants adapted to extreme conditions
No/small leaves: reduces amount of water lost as a result of transpiration
Waxy cuticle: prevents the evaporation of water in environments where water is scarce
Stomata: can adjust to conditions to prevent water loss
What is phototropism?
Response to light
What is gravitropism?
response to gravity
What does it mean if the tropism is positive?
Grows towards the stimulus
What does it mean if the tropism is negative?
Grows against the stimulus
What does it mean if plant shoots are positively phototrophic?
Means they grow towards the light- important for maximum light capture for photosynthesis
What is an auxin?
Growth hormone
How do auxins work in shoots?
When a plant is in the light, the shades side accumulates more auxin
The cells on the shaded side elongate so the shoot bends towards the light to maximise light capture for photosynthesis
This makes shoots positively phototropic
How do auxins work in roots?
Root growing sideways has more auxin on the lower side
In a root auxin inhibits growth so the top cells elongate, the root bends downwards
This makes roots positively gravitropic
Commercial uses of auxins
Weedkillers
Rooting powders
Commercial uses of gibberellins
Germination
Fruit and flower formation
Production of seedless fruit
Commercial uses of ethene
Fruit ripening