part 2: GASES
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Weak intermolecular forces of attraction
They have kinetic energy that produces rapid motion
Fill all available spaces
Are mostly invisible
Compressible
Properties of Gas
A gas consists of small particles that are in constant and random motion
Gas particles are very small compared with the average distance that separates them
Gas particles are constantly colliding with each other and the walls of their container
No forces of attraction or repulsion exist between any two gas molecules
Average kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gas
Robert Boyle
Proponent of Boyle’s Law
Mariotte’s Law
Boyle’s Law is also known as?
Boyle’s Law
Pressure is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to Volume
Constant T and n (amount of Gas)
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2
Related to 3rd postulate
P1V1 = P2V2
Formula of Boyle’s Law
Jacque Charles
Proponent of Charles’ Law
Charles’ Law
Volume is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to Temperature
Constant P and n (amount of Gas)
Formula: V1T2 = V2T1
V1T2 = V2T1
Formula of Charles’ Law
Amonton’s Law
Gay Lussac’s Law is also known as?
Joseph Louis Gay Lussac
Proponent of Gay Lussac’s Law
Gay Lussac’s Law
Pressure is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to Temperature
Constant V and n (amount of Gas)
Formula: P1T2 = P2T1
Related to 5th postulate
P1T2 = P2T1
Formula of Gay Lussac’s Law
Combined Gas Law
Volume is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to Temperature, and INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to Pressure
Constant n (amount of Gas)
Formula: P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
Formula of Combined Gas Law
Amedeo Avogadro
Proponent of Avogadro’s Law
Avogadro’s Law
Volume is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to Amount of Gas
Constant T and P
Formula: N1V2 = N2V1
N1V2 = N2V1
Formula of Avogadro’s Law
Ideal Gas Law
Formula: PV = nRT
Application of Ideal Gas Law Equation
Pressure
Volume
Temperature
Amount of gas
Weight of gas
Molecular weight
Density
PV = nRT
Formula of Ideal Gas Law
STP = Temp = 0°C / 273K
Pressure = 1atm
1 mole of Gas = 22.4L
Molar Gas Volume
0.082057 L.atm/K.mol
1.987 cal/mol.K
8.3k joules/mol.k
Molar Gas Constant
Real Gas Law
Van der Waals Equation for Real Gases is also known as?
Van der Waals Equation for Real Gases
Modification of Ideal Gas Law
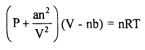
Formula of Van der Waals Equation for Real Gases
John Dalton
Proponent of Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure
The total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the individual component gases
Formula: PTOTAL= P1 + P2 + P3 ……
PTOTAL= P1 + P2 + P3 ……
Formula of Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure
Thomas Graham
Proponent of Graham’s Law of Effusion
Graham’s Law of Effusion
The rate of Effusion of Gas is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to the square root of mass of its particles
William Henry
Proponent of Henry’s Law of Gas Solubility
Henry’s Law of Gas Solubility
At constant Temperature, the amount of dissolved gas is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid
58.33 psi
Sample problem: BOYLE’S LAW
A tire with a volume of 12.41 L reads 47 psi on the tire gauge. What is the new tire pressure if you compress the tire and its new volume is 10 L.
a. 22.32 psi
b. 12.21 psi
c. 32.12 psi
d. 58.33 psi
13.33 mL
Sample problem: BOYLE’S LAW
A syringe has a volume of 20mL. The pressure is 3.0 atm. What must be the final volume to change the pressure to 4.5 atm?
a. 21mL
b. 35.2 mL
c. 22.4 mL
d. 13.33 mL
24.17 L
Sample problem: CHARLES’ LAW
A hot air balloon is under a constant internal pressure. If its volume is 25 liters at a temperature of 30°C, what will be its volume at a temperature at 20°C
a. 24.17 L
b. 16.12 L
c. 35.62 L
d. 42.19 L
12.89 L
Sample problem: COMBINED GAS LAW
A 10 L air sample has a pressure of 800 torr at -50°C. What will be the volume of air be at STP?
2.17 mol
Sample problem: AVOGADRO’S LAW
4L of container is known to contain 0.965 mol of gas. More gas is then added to the container until it reaches a final volume of 9.00 L. Assuming the pressure and temperature of the gas remain constant. Calculate the number of moles of gas added to the container.
12.34 atm
Sample problem: DALTON’S LAW
What is the total pressure of a 10 L gas tank containing 4 moles of Helium and 1.1 mole of Oxygen gas @ 295K?
32g
Sample problem:
Determine the weight of the unknown gas at STP and its molecular weight is 32 g/mole
50.27g/mol
Sample problem:
Find the molecular weight of the unknown gas if its density is 5.71g/L having a pressure of 2.88 atm in 309 K
Anesthetic Gases
Compressed and Liquefied Gases
Gas Sterilant
Pharmaceutical Gases
Nitrous oxide
Halothane
Isoflurane
Anesthetic Gases
Nitrous oxide
Most widely used anesthetic gas
Halothane
Anesthetic of choice for children and asthmatic patients
Isoflurane
Anesthetic of choice for neurosurgery
Nitrogen
Carbon dioxide
Compressed Gas
Butane
Isobutane
Propane
Liquefied Gas
Gas sterilant
Used for sterilization of heat-labile substances
Ethylene oxide
Formaldehyde gas
Gas sterilant