3.1 market structures
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Assumptions of a monopoly
One firm in the industry
Controls price or output
Profit maximisation
Barriers to entry
Unique good or service sold
Barriers to entering a monopoly market
Legal
Ownership of a patent
Capital investment/startup costs
Brand proliferation
Advantages of a monopoly
Economies of scale
Guaranteed supply of product
Stable employment
Innovation
What does SPECS stand for
Super Normal Profits
Price
Equilibrium
Cost
Scarcity
Disadvantages of a monopoly
Higher prices
Inefficient
Lack of innovation
Loss making state monopolies

SPECS for a monopoly
Super normal profits are earned as average revenue exceeds average cost, this is because barriers to entry exist
Price is at P1 and Produces at Q1
Equilibrium is at E where marginal cost equals marginal revenue and marginal cost is rising
Cost is shown at C1
Scarcity the firm is not making efficent use of scarce resources as it is not producing at the lowest point in the AC curve
Conditions needed for price discrimination
Some monopoly power
Separation of markets
Consumer price elasticity
Conditions needed in a consumer for price discrimination
Indifference
Ignorance
Attitude to the gods (e.g. snob goods)
First degree of price discrimination
Monopolists identify groups who are willing to pay more (e.g. doctors, lawyers) and charge higher prices. This is to eliminate consumer surplus
Second degree of price discrimination
Giving discounts to bulk buying
Third degree of price discriminatin
When monopolists identify groups with different PEDs and charge them accordingly (e.g. cinema tickets for students)
Regulation
Controlling of an activity by means of rules and legislation
Positives of regulation
Protects public welfare (e.g. safe working conditions)
Companies which break laws can be closed
Corrects market failures
Negatives of regulations
Impedes profitability (e.g. excess paperwork)
Net cost on society (adds to the cost of doing business)
Inefficient (takes time to implement)`
Deregulation
Removing barriers to entry for an industry
Positive effects for consumers of deregulation
Lower prices
Increased availability of service
Negative effects for consumers of deregulation
Decline in standards
Disruption to service (e.g. new industrial action)
Positive effects for employees of deregulation
New job opportunities with new suppliers
Negative effects for employees of deregulation
Reduced job security (may loose their jobs due to rationalisation)
Positive effects for firms of deregulation
Increased profits (if they expand their business to meet the new competition)
Negative effects for firms of deregulation
Decreased profitability (if they loose their market share and experience a loss of business)
Features of an oligopoly
Few sellers in the industry
Interdependence of firms (they do not act independently)
Product differentiation occurs
Barriers to entry exist
Aims of an oligopoly
Prevent government intervention in the market (they don’t want them earning SNPs)
maintain adequate profit levels
Barriers to entering an oligopoly market
High start up cost
Limit pricing (existing firms may have agreed to a low price)
Economies of scale in the market
Brand proliferation
Why consumers might prefer price competition
Lower prices
Higher disposable income
More choice
Why consumers might prefer non price competition
Stability in prices
Better quality commodities
Loyalty programs
Oligopoly demand curve
Kinked demand curve
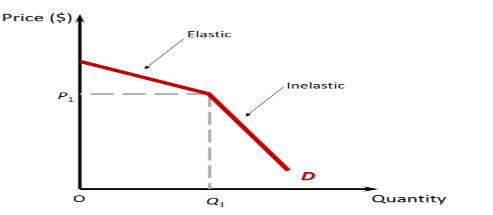
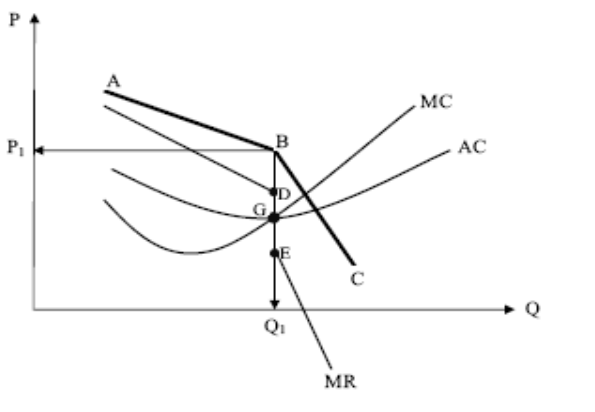
SPECS of an oligopoly
Supernomal profits are earned as average revenue is greater than average cost, barriers to entry exist
Price is shown at P1 and it produces at Q1
Equilibrium occurs at G where marginal cost equal marginal revenue and marginal cost is rising
Cost is shown at point G
Price is sticky, if costs rise between points D&E then the market price will remain at P1
Rigidity in price
Oligopolistic markets tend not to change their price as it would lead to a huge fall in revenue
Collusion
Rival sellers in the industry come together for mutual benefit
Explicit collusion
Separate companies jointly decide a specific course of action and form a cartel
Implicit collusion
No formal agreement exists between firms but they each recognise that joint profits would be higher if firms acted as a monopoly
Types of collusion
Reducing policies to stop new entrants joining the market
Sales territories
Implicit collusion
Advantages of an oligopoly for consumers
Price stability (non price competition)
Quality of product improves
Advantage of an oligopoly for firms
High profit levels
Changes in a market which allows a monopoly to become an oligopoly
Increased number of firms in the market
Removal of barriers to entry
Assumptions underlying imperfect competition
Many sellers in the industry
Differentiation occurs
Freedom of entry and exit
Firms attempt to maximise profits
Advantages of imperfect competition
Greater choice
Lower prices
Innovation
Disadvantage of imperfect competition
Inefficient (does not produce at lowest point on AC curve)
Excess capacity (less is produced as money is spent on ads)
Monopoly power (price exceeds marginal cost meaning it has monopoly power)
Ways product differentiation can be achieved
Branding
Product innovation
Competitive advertising
Why imperfect competition is wasteful
Inefficient use of resources (dont produce at lowest point on AC curve)
Competitive advertising (all firms take part in it, increases prices and pushes up costs)
Disadvantages of advertising for the consumer
Increased prices
Misleading information
Unnecessary pollution (e.g. leaflets)
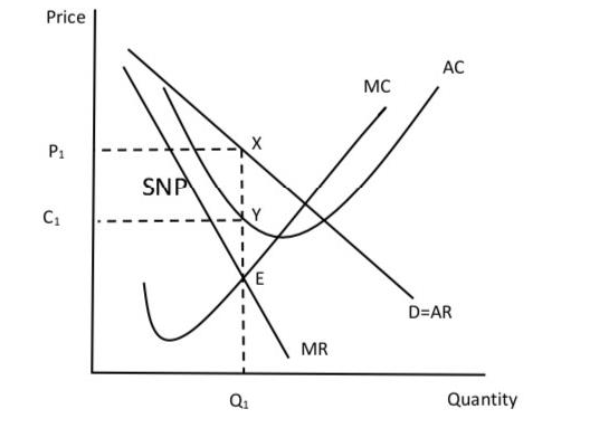
SPECS of imperfect competition in the short run
Supernormal profits are earned as average revenue exceeds average cost
Price is shown at P1 and the firm produces at Q1
Equilibrium is shown At E where the marginal cost equals marginal revenue and marginal cost is rising
Cost is shown at C1
Scarcity, the firm is not making efficient use of scarce resources as they do not produce at the lowest point on the AC curve
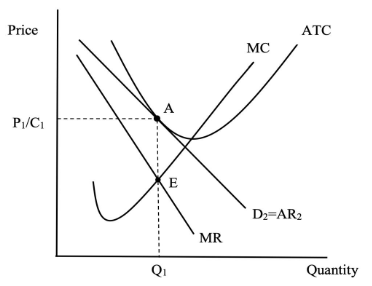
SPECS of an imperfect competition in the long run
Supernormal profits are NOT earned as the firm earns normal profits because they are producing where average revenue is equal to average cost
Price is shown at P2 and the firm produces at Q2
Equilibrium is shown at point X where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue and marginal cost is rising
Cost is shown at C1
Scarcity, The firm is not making use of efficient resources as they do not produce at the lowest point on the AC curve
Assumptions underlying perfect competition
There are many sellers in the industry
Homogenous goods are sold
Freedom of entry and exit
Each firm attempts to maxamise profits
Reasons a firm in perfect competition do not advertise
Homogenous goods sold
Little additional revenue
Benifits the entire industry
Advantages of perfect compitition
Low prices
No advertising
Disadvantages of a perfect compitition
Little choice
No R&D
Price taker
A firm which must accept the price as set by the market
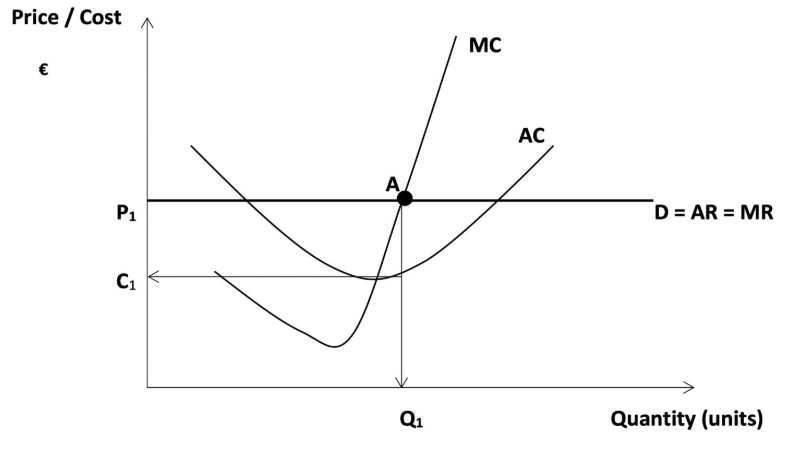
SPECS of an imperfect compitition in the short run
Supernomal profits are earned as average revenue exceeds average cost
Price is shown at P1 and quantity Demanded is shown at Q1
Equilibrium is shown at A where marginal cost equals marginal revenue and marginal cost is rising
Cost is shown at point C1
Scarcity, firms are not making efficent use of scarce resources as they do not produce at the lowest point on the AC curve
SPECS of an imperfect competition in the long run
Supernormal profits are NOT, normal profits are earned as average revenue equal average cost
Price is shown at P2 and quantity demanded at Q2
Equilibrium occurs at point A where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue and marginal cost is rising
Cost is shown at point A
Scarcity, The firm IS making use of scarce resources as it produces at the lowest point on the AC curve
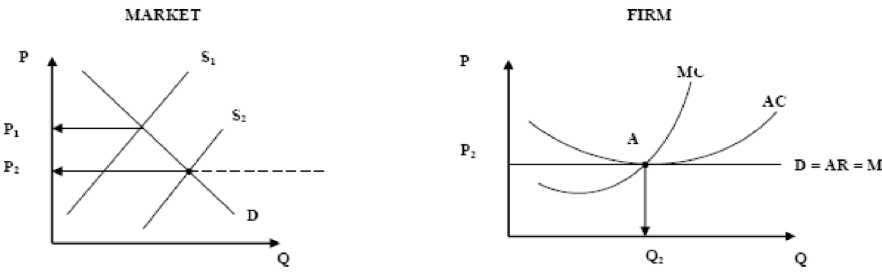
Non SPECS perfect compition in the long run
Market supply curve shifts out to the right as more firms enter the industry
This causes the market price to fall
The individual firms demand curve falls, which forces the firm to lower its price (as they are price takers)
Firm will produce a smaller quantity
Amount of SNPs earned will continue to fall until they are eliminated
Only normal profits are earned
When should you use specs form an imperfect long run?
When you have NOT just awnsered a short run question
How perfect compitition benifits the consumer
Prices are kept to a minimum as no SNPs are earned
Firms produce at the lowest point on the AC curve encouraging low prices
How perfect competition benifits the economy
Economic resources of a country are maximised as they are being used in their most efficent manner
Factors of production in the economy are being used at their most efficent level meaning consumers are not overcharged (only normal profits)
Low concentration on the HHI
<1,500
Medium concentration on the HHI
1,500-2,500
Highly concentration on the HHI
>2,500