Pre Assessment: Data Management Foundations
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Raw facts that are captured on printed or digital media
What is a broad definition of data?
Numbers that are captured on digital media
Raw facts that are captured on printed or digital media
Alphanumeric combinations that can be captured on media that a computer can read
Any information that can be transferred from print to digital
Facts that are collected and stored in a database system
What are data?
Facts that have been organized in a meaningful way
Facts that are the result of a query of a database system
Facts that are collected and stored in a database system
Facts that have been processed and used for decision making
It does not follow a data model.
What is a determining characteristic of unstructured data?
It does not allow copying and pasting.
It is easy to query and retrieve by business applications.
It does not follow a data model.
It is stored in rows and columns.
A
Which item represents unstructured data?
A
B
C
D
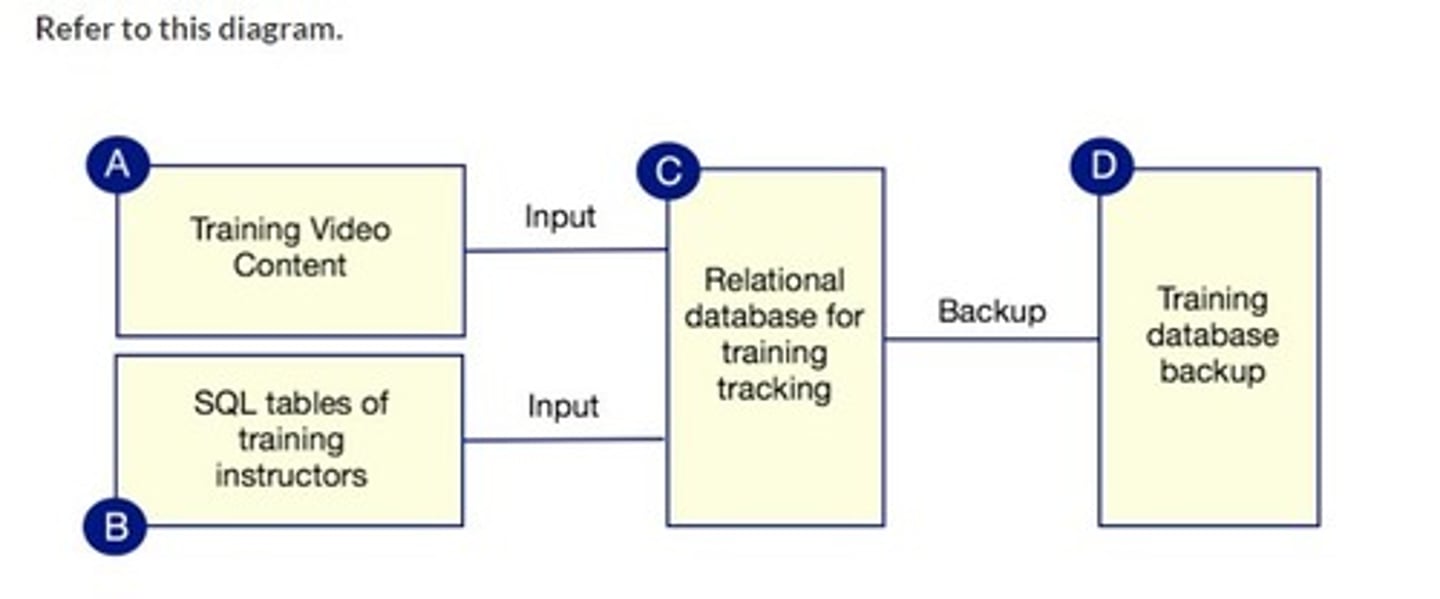
They contain no internal hierarchical organization.
Which is true about flat files?
They contain no internal hierarchical organization.
They have a limit of 256 records.
They can only contain two-dimensional data.
They are always encrypted.
Flat files
Which technology has no internal hierarchy?
Flat files
Heap files
Hashed tables
Relational databases
Sequentially from simple files
How were data retrieved before database management systems?
Randomly from linked files
Sequentially from simple files
Using set operations on complex files
Using relationships between logical entities
Entity types
What is the uniquely identifiable element about which data can be categorized in an entity-relationship diagram?
Entity types
Primary keys
Unary relationships
Intersection data points
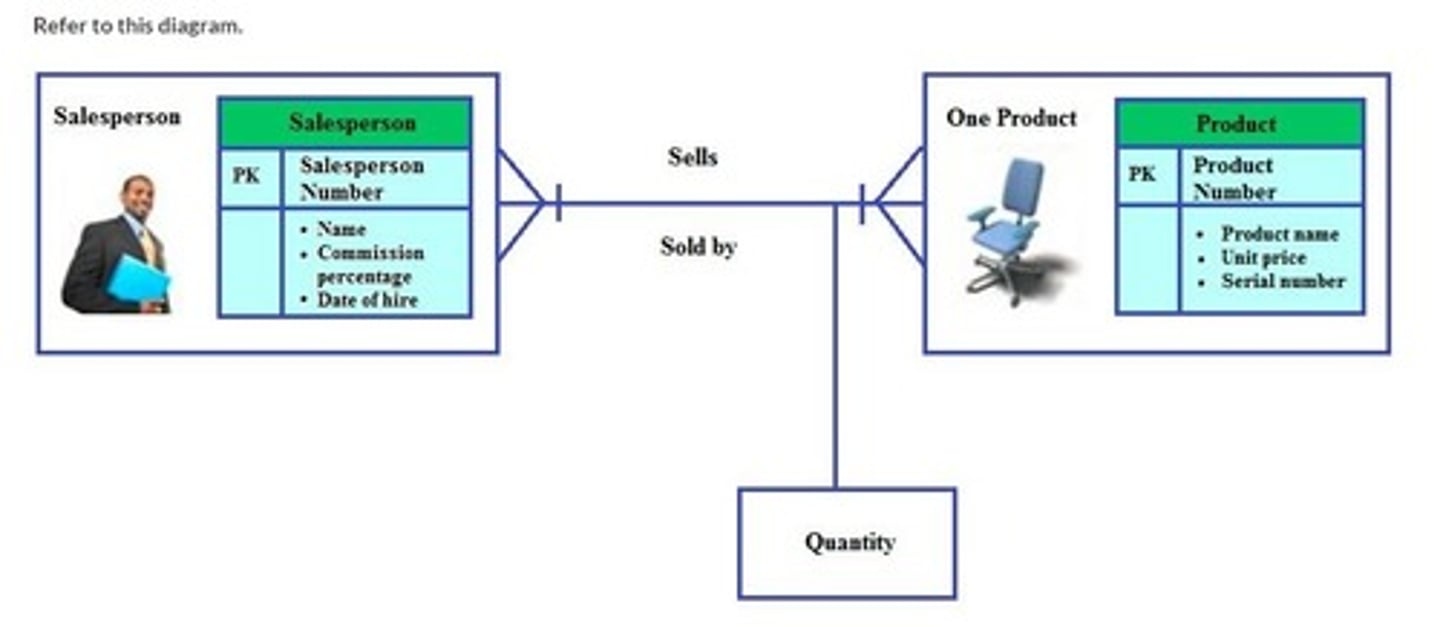
Intersection data
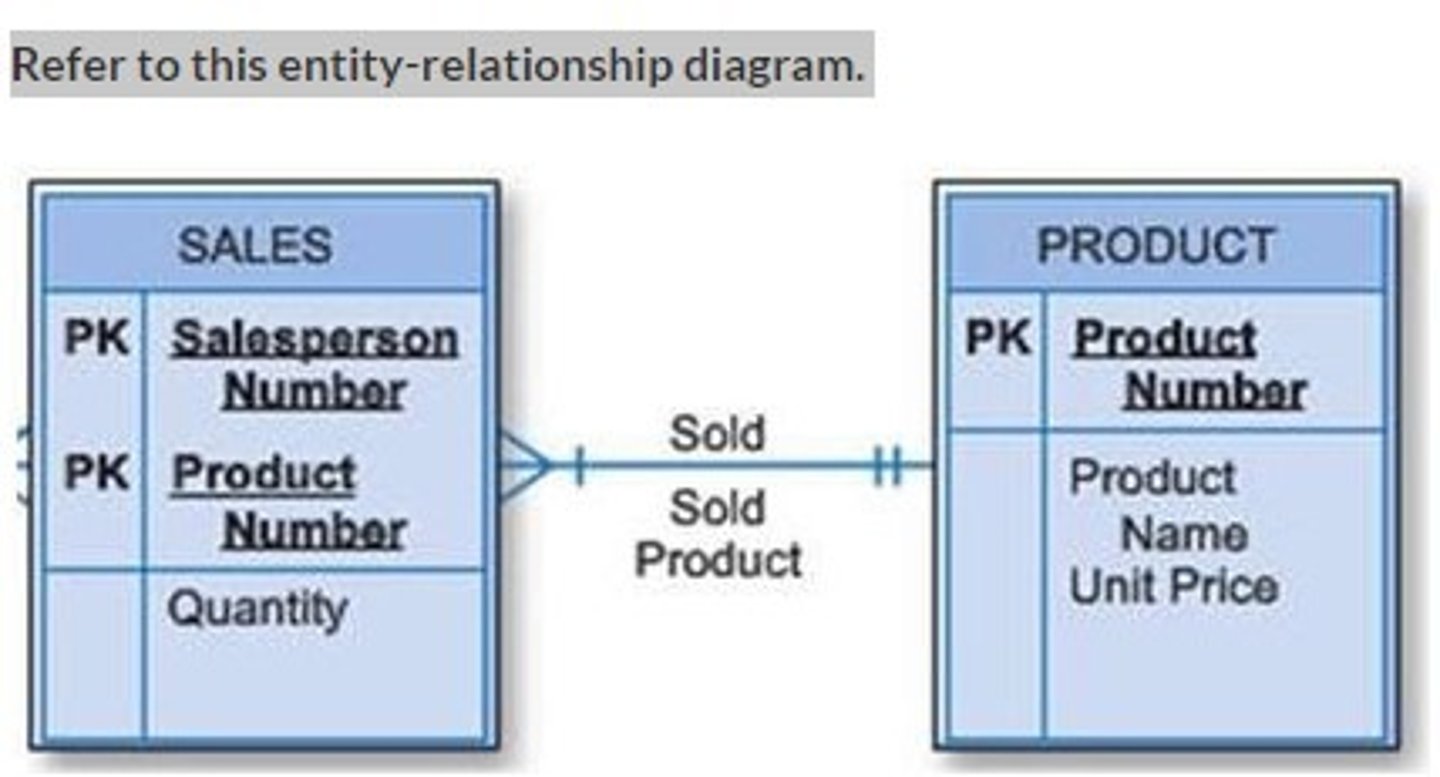
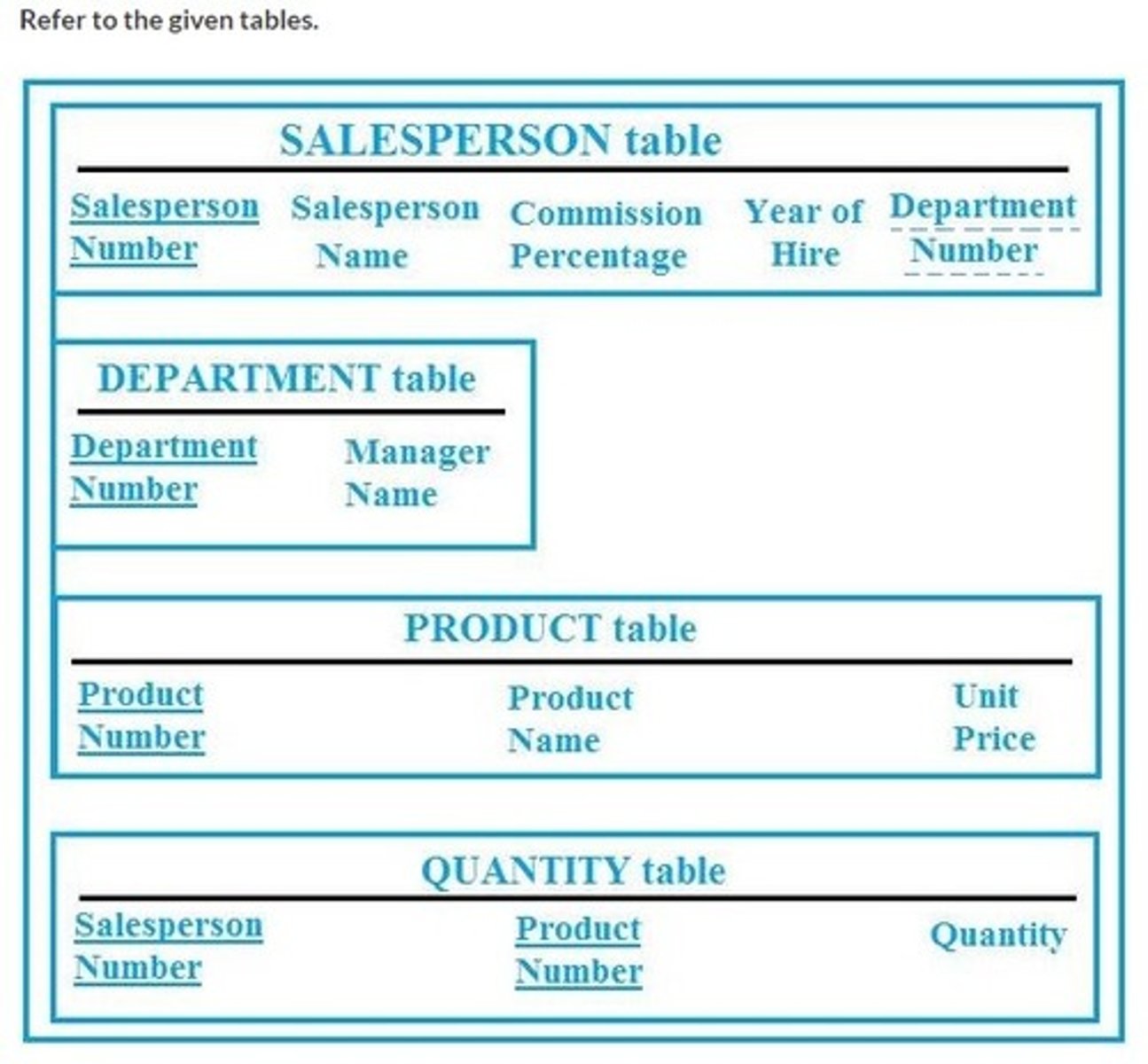
Refer to this diagram. Which classification is correct for the box marked "Quantity" in the given entity-relationship diagram?
Quantity data
Modality data
Intersection data
Product sales data
Event
Which data classification is an entity?
Event
Duration
Directions
Attendance
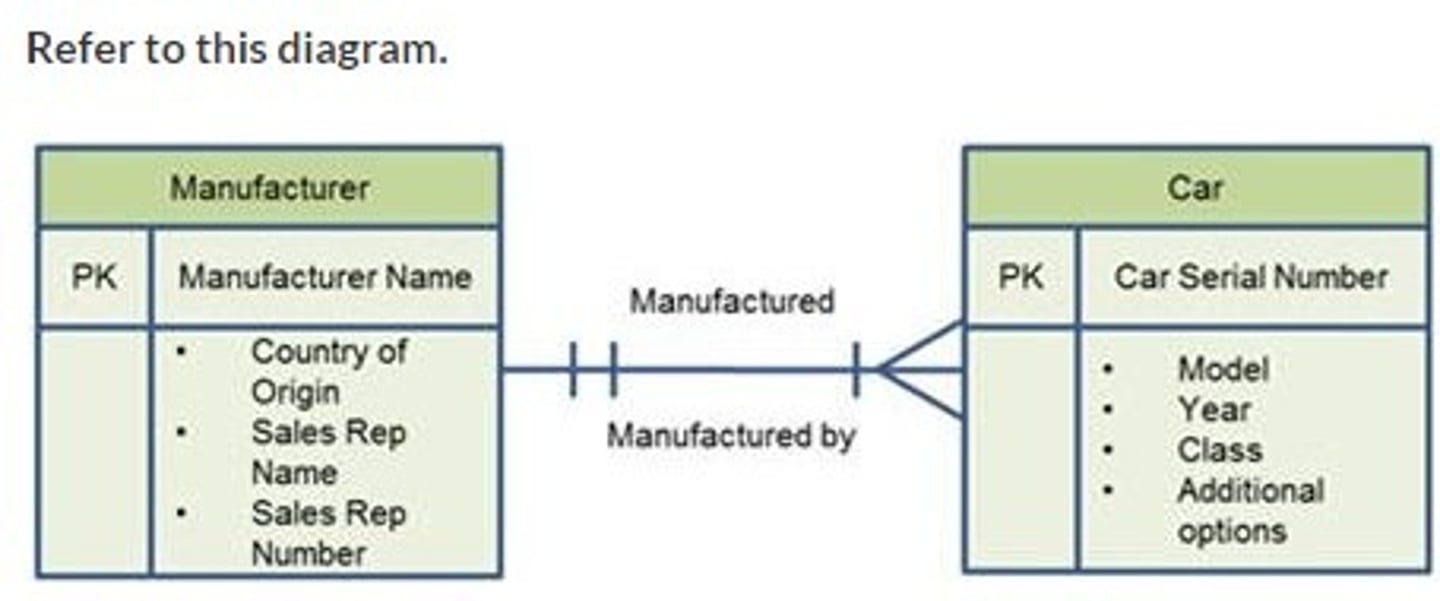
One manufacturer created at least one of the agency's cars.
Refer to this diagram. What is the entity-relationship diagram about a car rental agency showing?
An agency's cars were provided by multiple manufacturers.
One manufacturer created at least one of the agency's cars.
The model, year, and class of the car are part of the primary key.
The manufacturer maintains database records for its sales representatives.
Many-to-many
A salesperson is authorized to sell 12 products; a product can be sold by 10 salespersons. Which kind of binary relationship is described in this example?
One-to-one
One-to-many
Many-to-many
Associative
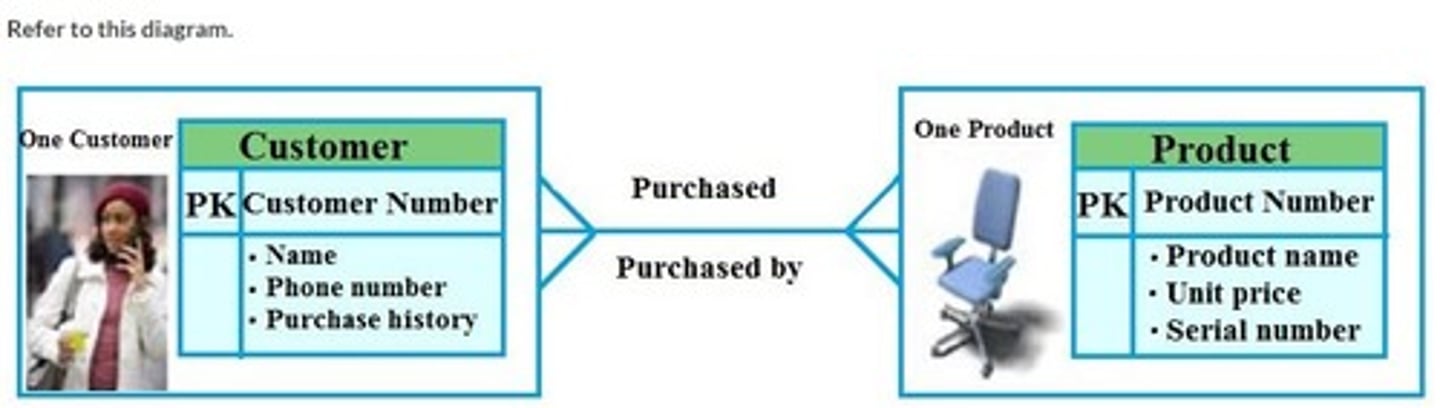
Many customers to many products
Refer to this diagram. Which relationship does the cardinality in the diagram represent?
Many customers to many products
One customer to many products
One customer to many product numbers
One customer to one product number
Many customers to one product
There are many customers, but the cardinality indicates one customer.
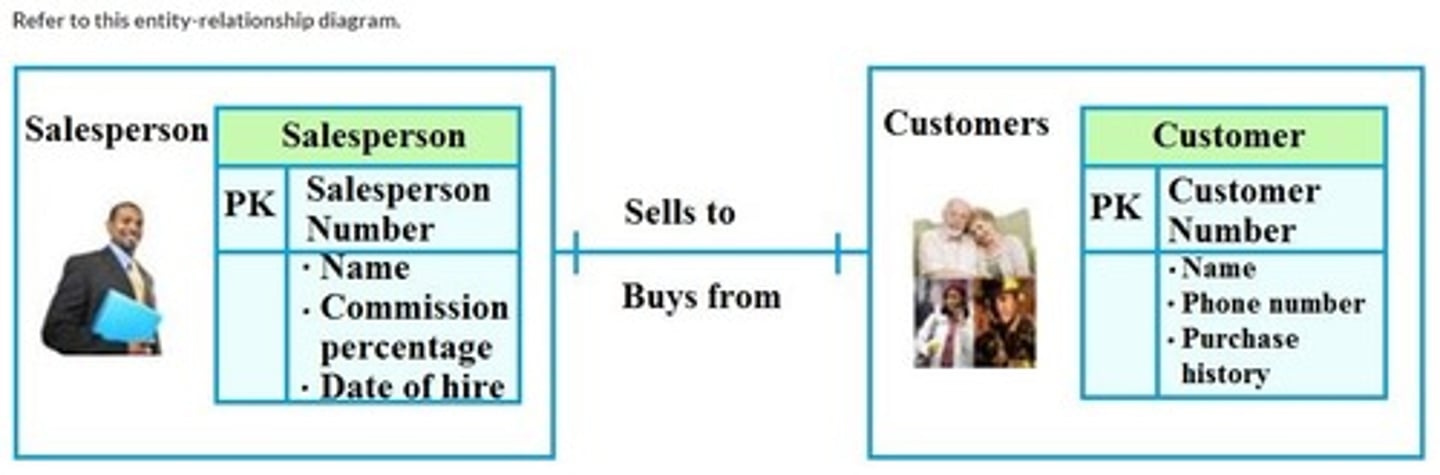
Refer to this entity-relationship diagram. How is the cardinality of the customers misrepresented?
There is one customer number, but the cardinality indicates many customers.
There are many customers, but the cardinality indicates one customer.
There is more than one salesperson, but the cardinality indicates multiple salespersons.
The cardinality of the salesperson number and the customer number do not match.
A minimum of zero customers
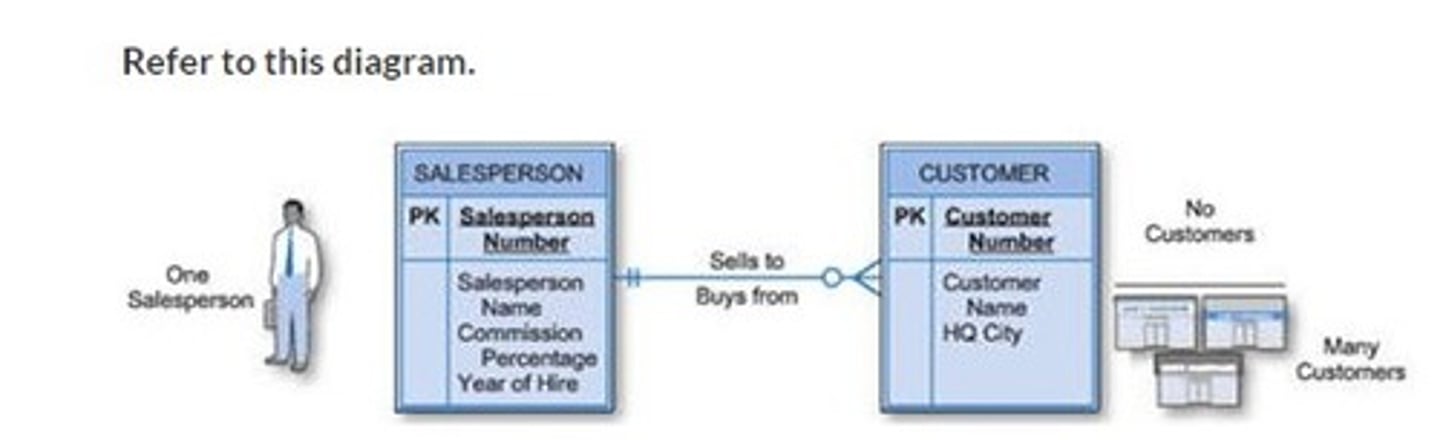
Refer to this diagram. What is the correct way to read the modality on the right side of the association?
A maximum of one customer
A maximum of many customers
A minimum of zero customers
A maximum of zero customers
At least one
Refer to this entity-relationship diagram. What is the modality of the product?
Two
At least one
Two or more
Dependent on the quantity
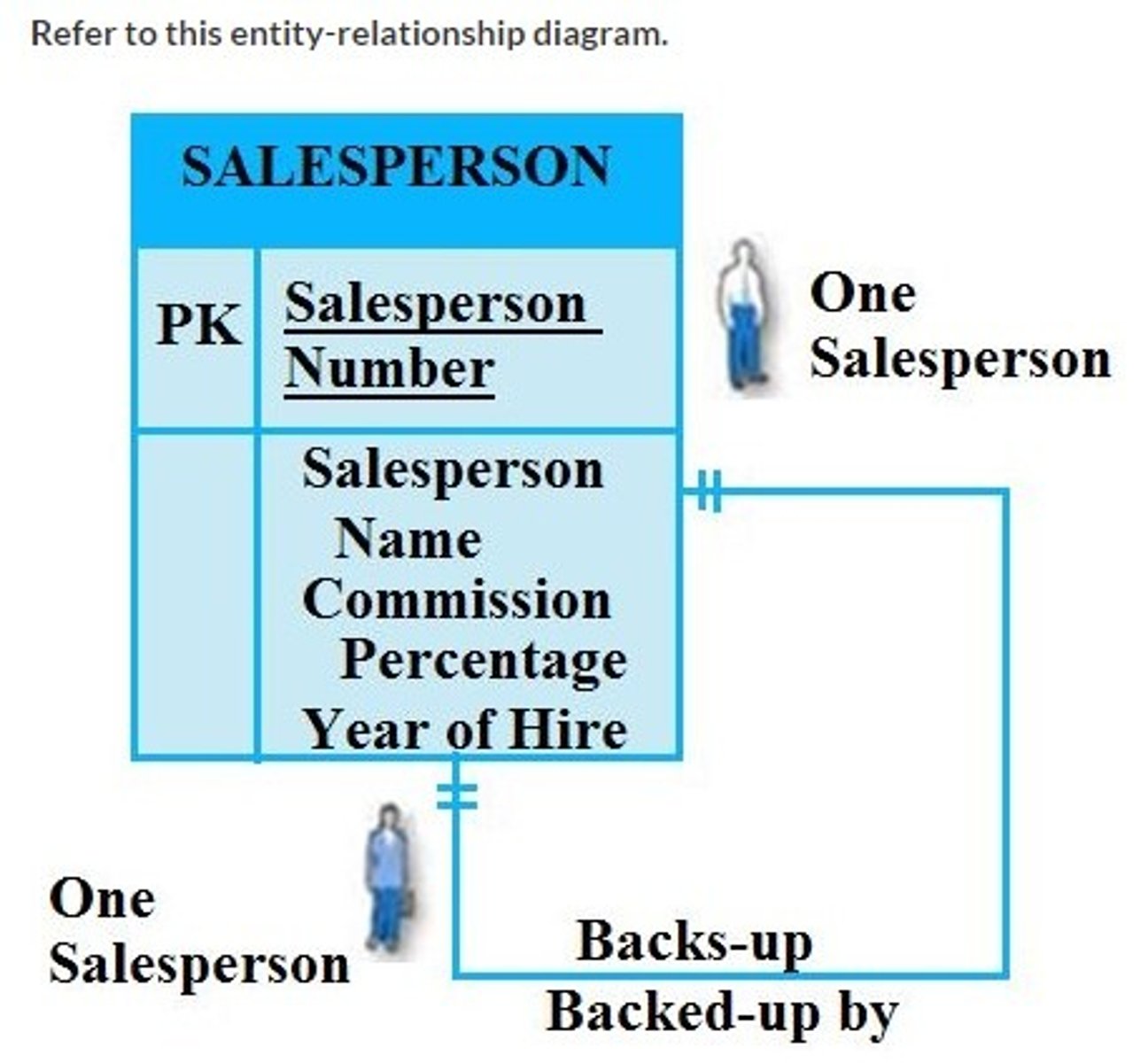
Unary one-to-one
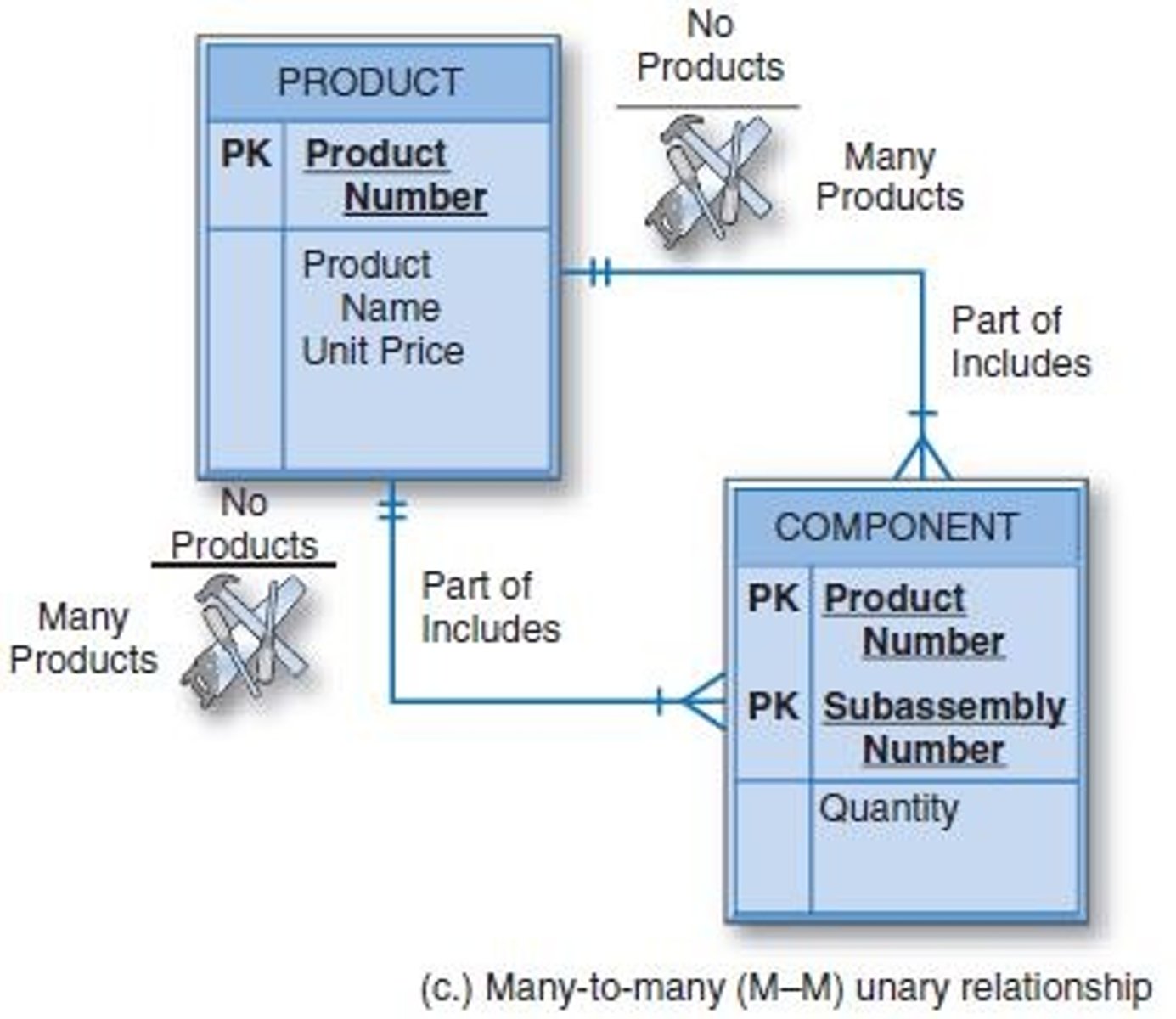
Refer to this entity-relationship diagram. Which kind of relationship does this diagram depict?
Unary one-to-one
Binary one-to-one
Unary one-to-many
Binary one-to-many
Unary many-to-many
Refer to this entity-relationship diagram. Which kind of relationship does this diagram depict?
Unary one-to-many
Binary one-to-many
Unary many-to-many
Binary many-to-many
Insert, Delete, Update
Which three kinds of rules for referential integrity are provided by modern relational database management systems? Choose 3 answers
Sort, insert, Retrieve
Insert, Delete, Update
Query, Sort, Delete
Delete, Insert, Sort
Insert, Update, Sort
Delete, Query, Insert
Reference to data in one relation is based on values in another relation.
What is an important aspect of "referential integrity"?
Primary keys refer to data in particular relation.
Reference points are placed by the database in each record during backups.
The relationships between entities and attributes are called referrals.
Reference to data in one relation is based on values in another relation.
WHERE COMMPERCT=15;
Refer to the given SQL statement. SELECT SPNUM, SPNAME FROM SALESPERSON. What is the correct line to add to the end of this statement to find salespersons with a commission percentage of 15?
* COMMPERCT=15;
IF COMMPERCT=15;
AND COMMPERCT=15;
WHERE COMMPERCT=15;
Replace COMMPERCT, YEARHIRE with an asterisk
Refer to the given SQL statement. SELECT COMMPERCT, YEARHIRE FROM SALESPERSON WHERE SPNUM=22; How should this statement be altered to retrieve the entire record instead of the commission percentage and year of hire?
Replace WHERE SPNUM=22; with WHERE SPNUM=*
Replace COMMPERCT, YEARHIRE with an asterisk
Replace COMMPERCT, YEARHIRE with ALL
Replace SALESPERSON with ALL
AND CUSTNUM>1000;
A manager asks an employee to list attributes of the customers that are headquartered in Los Angeles and that have a customer number higher than 1000. Refer to the given SQL statement prepared by this employee. SELECT CUSTNUM, CUSTNAME, HQCITY FROM CUSTOMER WHERE HQCITY=‘Los Angeles’ Which line should go at the end of this statement?
AND CUSTNUM>1000;
AND CUSTNUM>=1000;
WHERE CUSTNUM<1000
WHERE CUSTNUM>=1000;
ORDER BY modifies the presentation of data results and DISTINCT filters data results.
What is a key difference between the DISTINCT and ORDER BY statements, in SQL SELECT commands?
ORDER BY does not alter the presentation of data results and DISTINCT modifies data results.
ORDER BY modifies the presentation of data results and DISTINCT filters data results.
ORDER BY changes the order of results in the database and DISTINCT changes the order of results in the view only.
ORDER BY changes the order of results in the view only and DISTINCT changes the order of results in the database.
ORDER BY SATCITY, CUSTNAME;
Which SQL statement alphabetizes customer names within the same satellite-office city?
ORDER BY CUSTNAME, SATCITY;
ALPHA BY CUSTNAME, SATCITY;
ORDER BY SATCITY, CUSTNAME;
ALPHA BY SATCITY, CUSTNAME;
WHERE SALESPERSON.SPNUM=SALES.SPNUM AND SALES.PRODNUM=PRODUCT.PRODNUM
The given SQL statement is intended to list the names of the products of which salesperson Fox has sold more than 500 units. SELECT PRODNAME FROM SALESPERSON, SALES, PRODUCT ? ? AND SPNAME=‘Fox’ AND QUANTITY>500; Which set of lines should replace the question marks to make this statement work?
WHERE SALESPERSON.SPNUM=PRODUCT.PRODNUM AND SALES.PRODNUM=PRODUCT.PRODNUM
WHERE SALESPERSON.SPNUM=SALES.SPNUM AND SALES.PRODNUM=PRODUCT.PRODNUM
WHERE SALESPERSON.SPNUM>SALES.SPNUM AND SALES.PRODNUM=PRODUCT.PRODNUM
WHERE SALESPERSON.SPNUM=SALES.SPNUM AND SALES.PRODNUM=SALES.SPNUM
FROM PUBLISHER, BOOK
The given SQL statement is intended to query how many books there are with at least 800 pages from publishers in Los Angeles, United States. SELECT COUNT(*) ? WHERE PUBLISHER.PUBNAME=BOOK.PUBNAME AND CITY=‘Los Angeles’ AND COUNTRY=‘United States’ AND PAGES>=800; With which line should the question mark in this statement be replaced?
FROM PUBNAME.BOOK
FROM PUBLISHER, BOOK
WHERE PUBNAME = BOOK
WHERE PUBLISHER = BOOK
SELECT StoreID, City FROM SuppliersWHERE City IN ('Atlanta', 'Los Angeles', 'New York');
Which SQL statement will retrieve rows for all stores in Atlanta or Los Angeles or New York?
SELECT StoreID, City FROM SuppliersWHERE City IN ('Atlanta', 'Los Angeles', 'New York');
SELECT StoreID, City FROM SuppliersWHERE City BETWEEN 'Atlanta' AND 'Los Angeles' AND 'New York';
SELECT StoreID, City FROM SuppliersWHERE City BETWEEN 'Atlanta' OR 'Los Angeles' OR 'New York';
SELECT StoreID, City FROM SuppliersWHERE (City='Atlanta' AND City='Los Angeles' AND City='New York');
List all entries in the PRODUCT table.
Refer to the given SQL statement to answer the following question: SELECT * FROM PRODUCT; What would this SQL statement accomplish?
List all PRODUCT from the * table.
Delete all products from the PRODUCT table view.
Delete all entries in the PRODUCT table.
List all entries in the PRODUCT table.
Improved query response times
A product-marketing company publishes an Internet-based newsletter about their new products to increase their customer base. What is an advantage that this company will gain from investing in a relational database management system that will store customer information?
Increased sales
Lower advertising costs
Improved query response times
Decreased skill acquisition times
It enables data sharing. It permits storage of vast volumes of data.
In which two ways does a database management system environment increase effectiveness in working with data? Choose 2 answers
It enables data sharing. It duplicates redundant data for security.
It permits storage of vast volumes of data. It increases the complexity rules by which data is organized.
It enables data sharing. It permits storage of vast volumes of data.
Customer names
Sales data, detailing the customer names, products sold, and salespersons, is kept in a database. Which kind of data in this database would qualify as intersection data related to both the product and salesperson entities?
Quantity
Products
Salespersons
Customer names
Primary key
What is an attribute or group of attributes that uniquely identify a tuple in a relation?
Index key
Foreign key
Primary key
Physical key
A domain of values
What is necessary for a primary key in one relation of a database to match with its corresponding foreign key in another relation of the same database?
A domain of values
Intersection data
An attribute name
A quantity
The alternate key
What uniquely identifies each entity in a collection of entities but is not the primary key?
The foreign key
The secondary key
The alternate key
The master key
Candidate key
What is a term for a set of columns in a table that can uniquely identify any record in that table without referring to other data?
Foreign key
Primary key
Alternate key
Candidate key
It is copied to the index.
What happens to the original data in database indexing?
It is moved to the index.
It is copied to the index.
It is compiled by the DBMS.
It is translated into hexadecimals.
To retrieve data directly using a pointer
Why are indexes created in a physical database design?
To group data into aggregations
To iterate across data in a sequence
To retrieve data directly using a pointer
To summarize data into dimensions for a cube
To optimize data retrievals
Why is an index created on a database column?
To optimize data integrity
To optimize data updates
To optimize data retrievals
To optimize data insertions
Data normalization
What is a methodology for organizing attributes into tables?
Data normalization
Data redundancy
Data indexing
Data compression
Functional dependency
What is the term for the value of one particular attribute associated with a specific single value of another attribute?
Functional dependency
Transitive dependency
Decomposition
Normalization
First normal form
Refer to the given table. In which state are attributes shown?
Unnormalized
First normal form
Second normal form
Third normal form
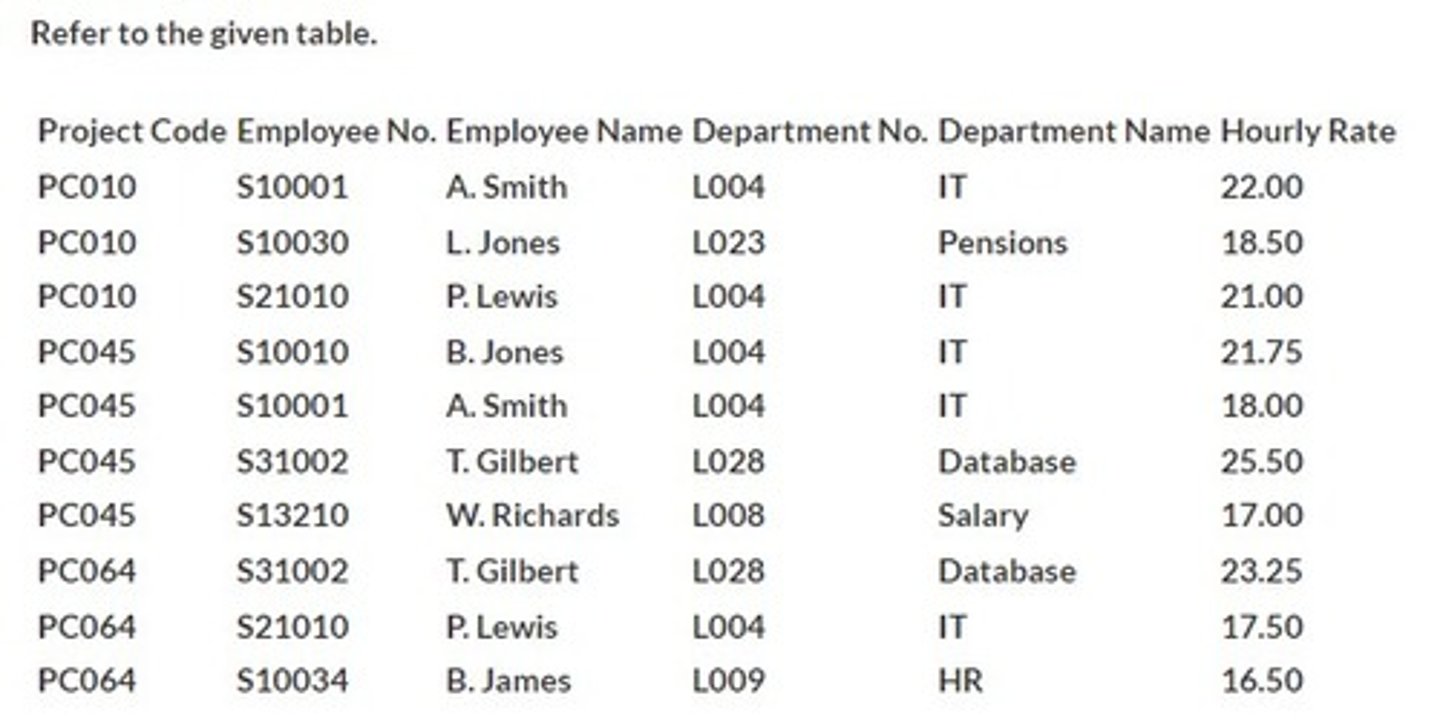
The attributes are all single valued.
Refer to the given table. Which factor determines whether the table is in first normal form?
There are no functional dependencies.
The fourth column shows the foreign keys.
The attributes are all single valued.
The first column is in numerical order.
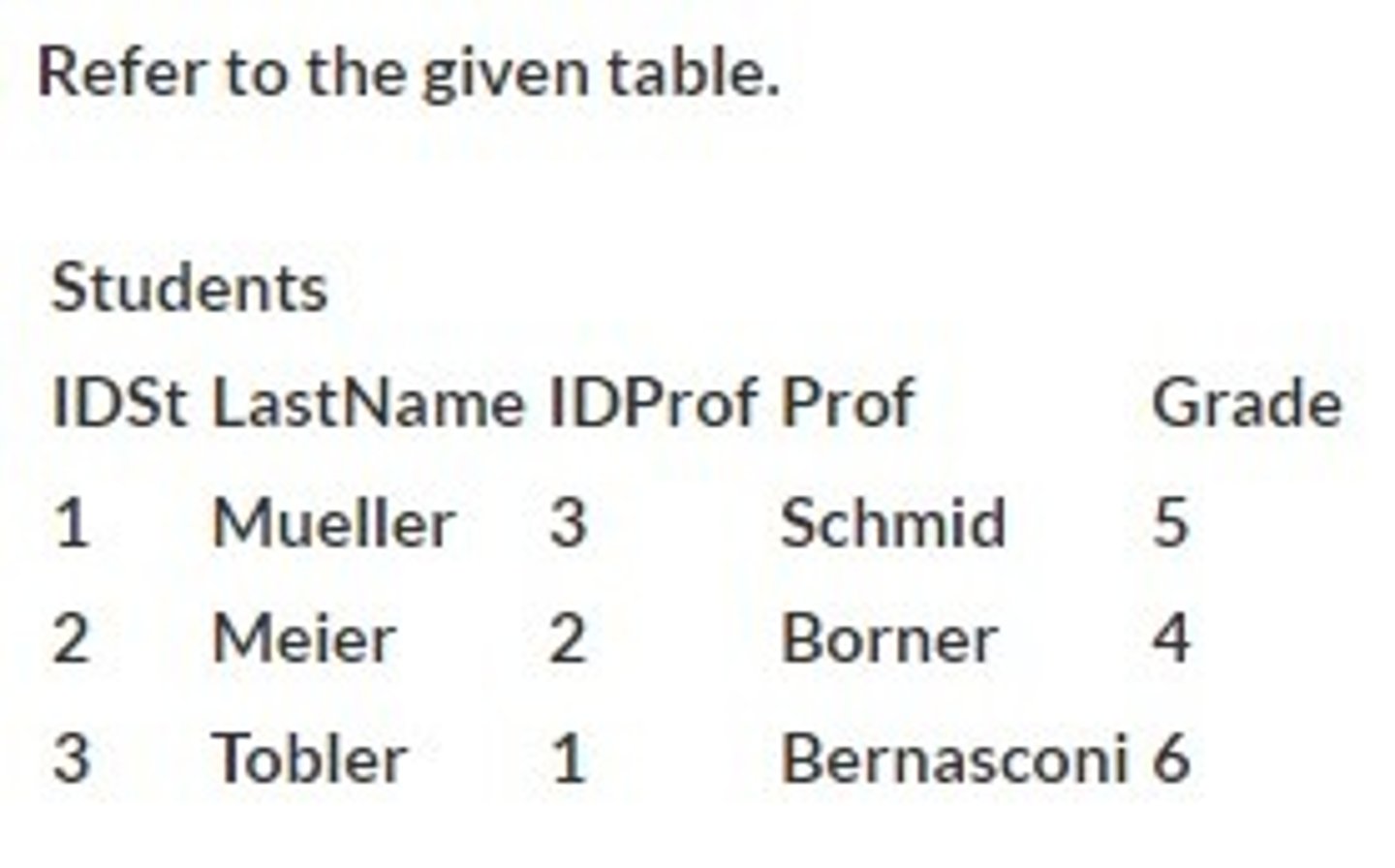
Third normal form
Refer to the given tables. The primary key in the first table is ID, and the primary key in the second is Code. How advanced are the two tables in the normalization process?
Unnormalized
First normal form
Second normal form
Third normal form
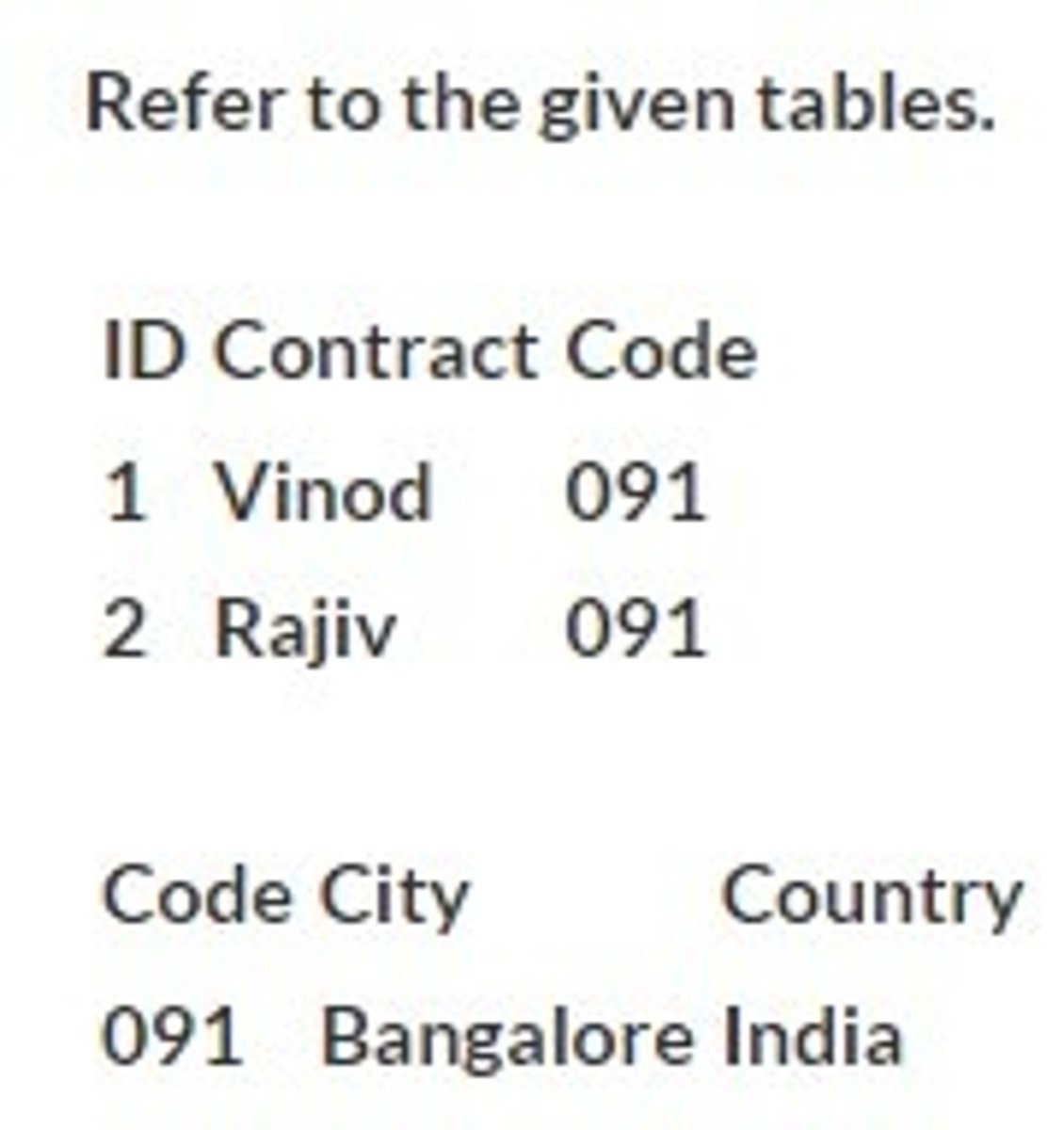
The tables are completely free of data redundancy.
Refer to the given tables. Which characteristic points to the tables being in third normal form?
Each primary key has a functional dependency on every other primary key in the table.
"Salesperson Number" appears in more than one table.
The tables are completely free of data redundancy.
The attributes are all single valued.
Increased profitability and increased throughput
Which set of results should a company expect from implementing a business intelligence system?
Increased profitability and increased throughput
Reduced hardware redundancy and decreased workloads
Increased profitability and reduced hardware redundancy
Riskier capital and asset investments and increased throughput
Monitor refreshing volume and frequency
Which issue is focused on the loading component of extract, transform, load (ETL)?
Monitor refreshing volume and frequency
Denormalizing and renormalizing the data
Mapping keys from one system to another
Determining the content of the data
Transformation
During which step in the extract, transform, load (ETL) process are raw data sets aggregated?
Loading
Extraction
Conversion
Transformation
Denormalization
Prediction classifies objects according to an expected future behavior.
How is prediction distinguished from estimation in data mining?
Prediction is used to look at historical data only.
Estimation assumptions do not need to be tested.
Prediction classifies objects according to an expected future behavior.
Estimation divides small collections of entities into smaller groups of similar entities.
Between objects
Where does affinity grouping occur in data mining?
Among entities and target applications
Between entity group names
Between objects
Among clusters