World History- Unit 8 (New Imperialism)
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Which was the largest empire in all of history?
Great Britain

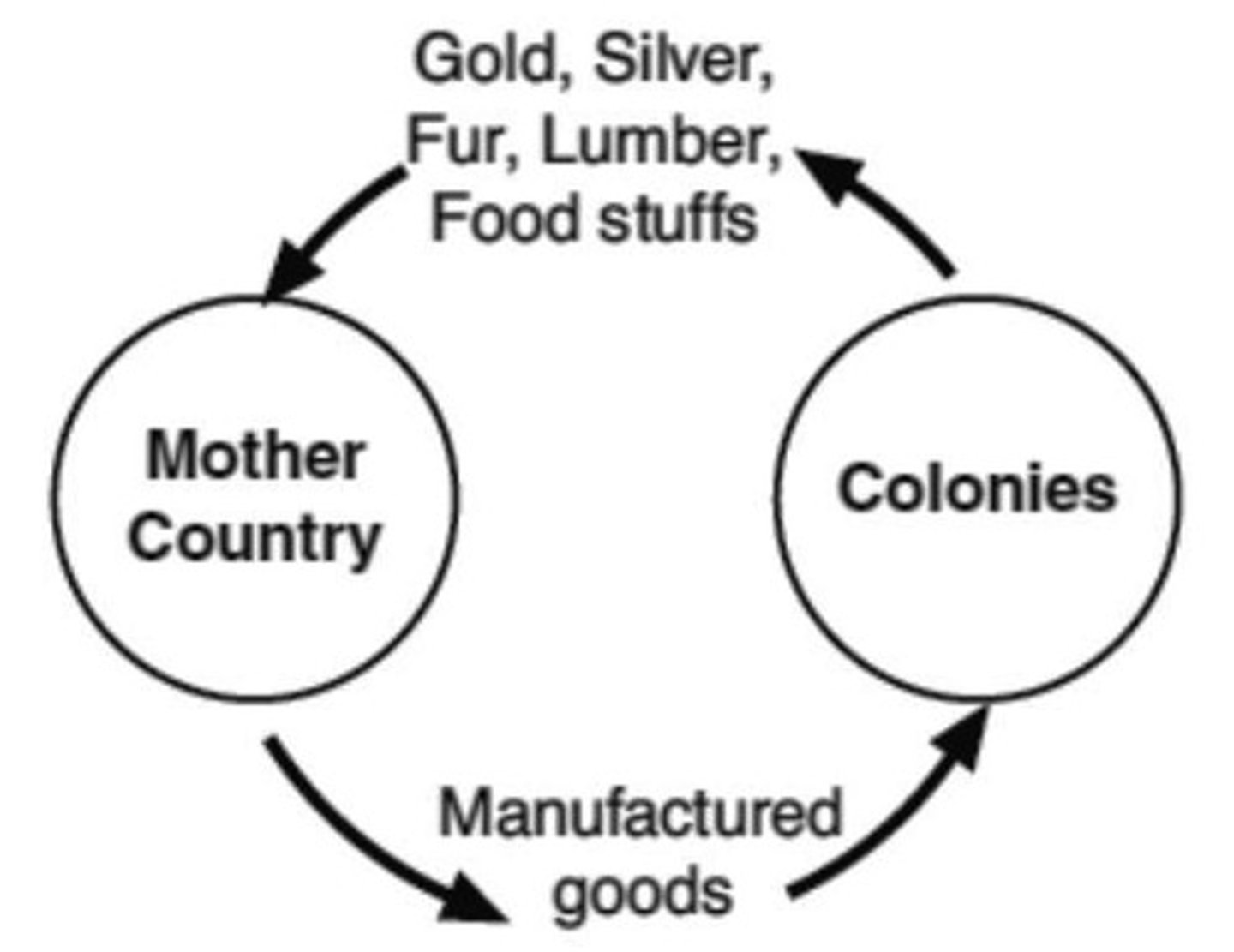
What was the main driving factor for big empires (Britain) using colonies?
Economic Motivations

Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, military force, or other means.

Economic Motivations
Reasons related to financial gain that drive a country to seek colonies.
The importance telegraphs in imperialism
Inventions that enable communication over long distances, enhancing control.

The importance of transportation in Imperialism
Technological advancements such as trains and steamboats that facilitate movement and logistics.

Steel
A strong material used for building stronger boats and weapons.

Which two continents were getting colonized the most?
Africa and Asia
Who was doing the most colonizing?
Europeans
Why was colonizing cheaper than trading with other countries?
Other countries put tariffs on products

What did ironclad warships, gunboats, and naval blockades do to help the Europeans get colonies?
Allowed control of sea routes and coastal cities, as well as intimidating

Europeans have _________ power compared to the countries they were colonizing
unmatched

How did railroads and steamships help Europeans during their conquest?
Provided faster travel

How were European soldiers better than Native soldiers?
Europeans were highly trained, had industrialized weapons, and were more organized than Natives
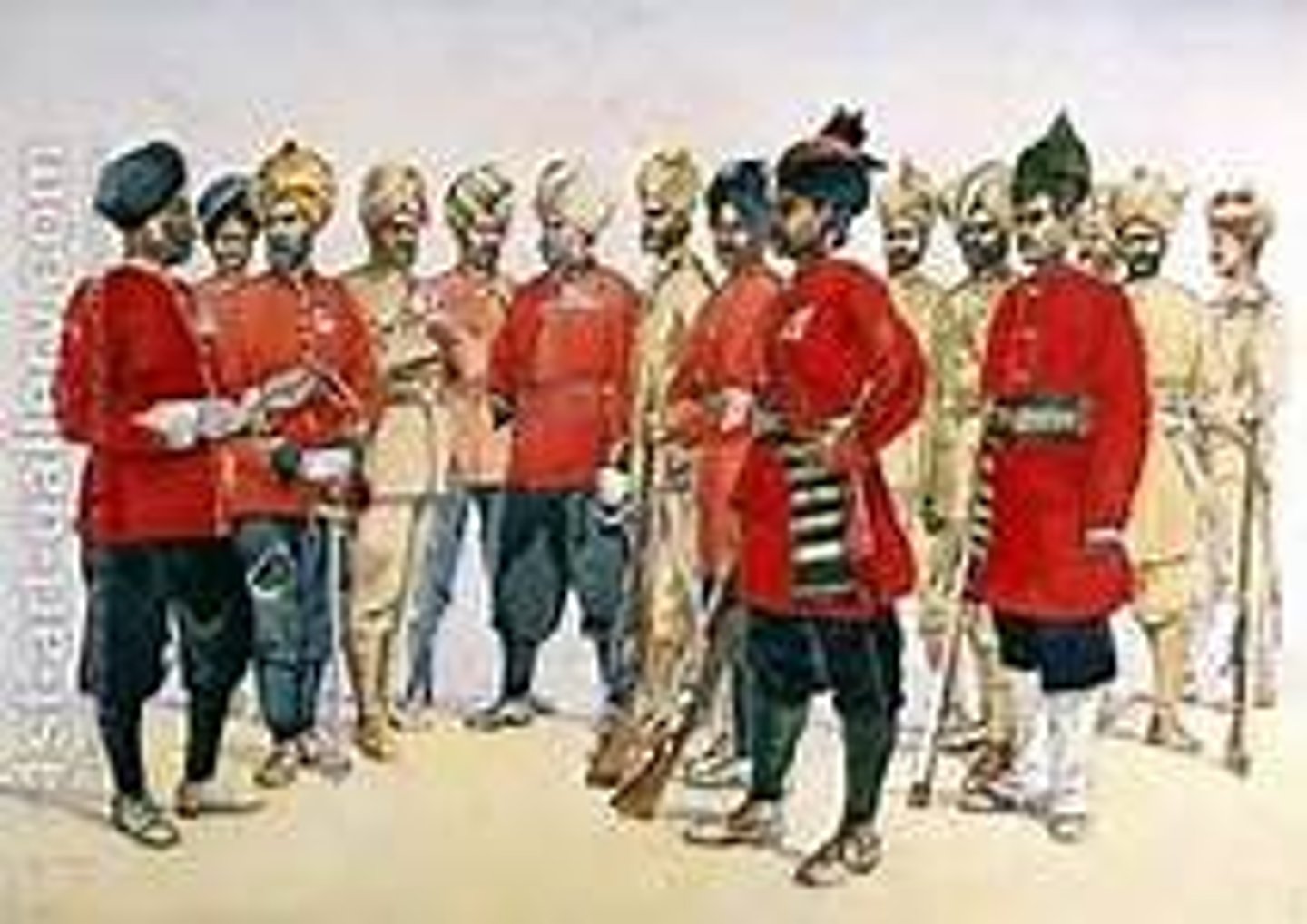

What did Europeans do to "pacify" natives who resisted?
Extreme acts of violence, such as in the Indian Rebellion of 1857

Who is Cecil Rhodes?
European merchant/leader who got rich from diamonds and gold from Africa.
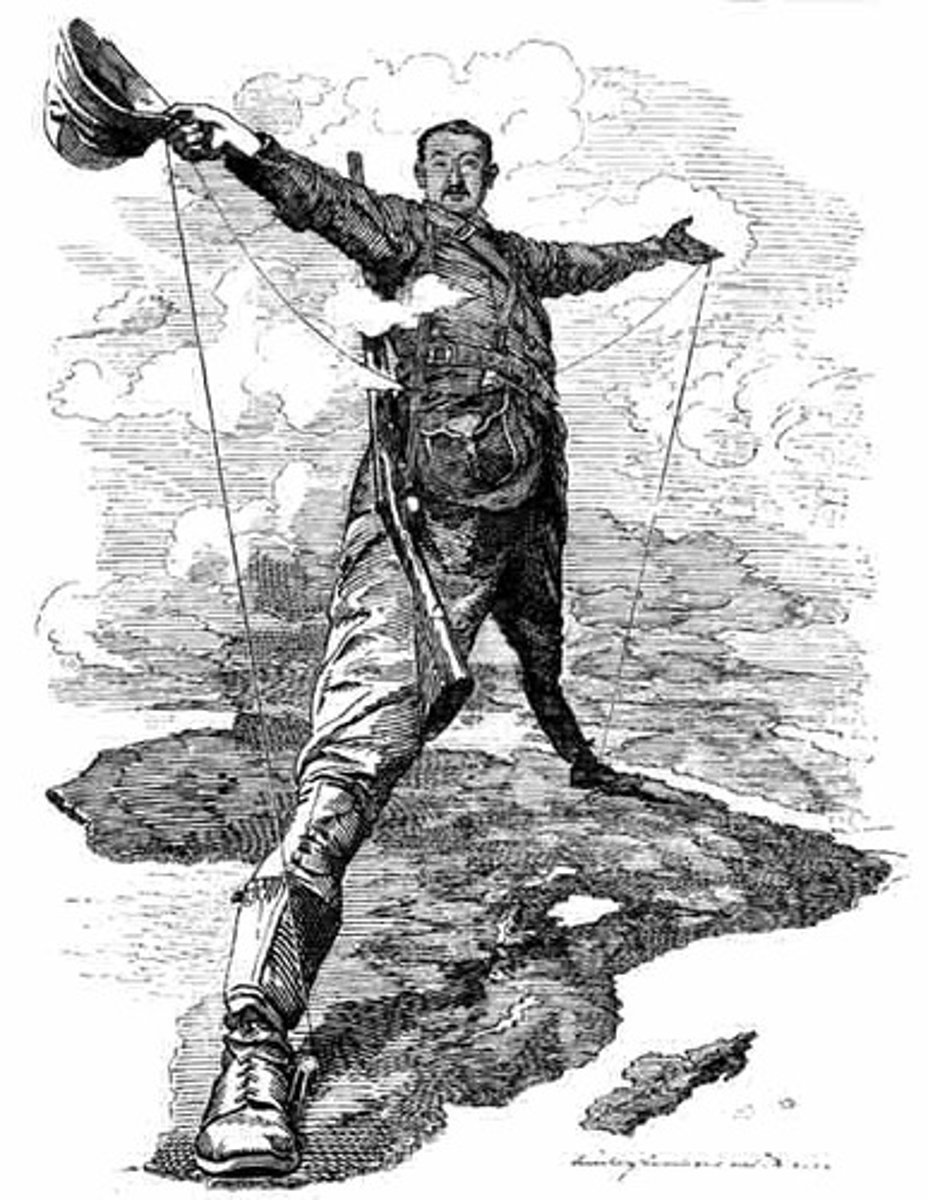

What did Cecil Rhodes rely on to keep a grip on his colonies?
Military power
Cecil Rhodes ____ _________ of colonies for economic gain
took advantage

What were many leaders of colonies' excuses for violence against natives?
It was for "order, progress and harmony"- the good of the colony to become "civilized"

What kind of policy did people like Cecil Rhodes have?
Expansionist policies

Why were Indigenous people excluded from leadership positions in European Imperialism?
Europeans were strong believers in white supremacy.
European education, architecture, culture and government in colonies- what is this called?
Assimilation

direct rule vs. indirect rule
dr: local elites are removed from power and replaced by officials from a mother country
ir: a colonial power that cooperates with local rulers to achieve goals

How did Imperialist governments make rebels against them look?
Evil savages

What were the economic motivations for New Imperialism?
Needing raw materials and markets to sell their stuff on
What is economic imperialism?
An independent but less developed country controlled by private business interests rather than other governments

What is Social Darwinism?
The belief that those who are successful got their because they were the "fittest," and that those in poverty were there based on their own failings. A justification for wealth inequality.
In Social Darwinism, it says that "the strong should _______ over the weak"
triumph/dominate

Social Darwinism was used to _______ imperialism/colonialism.
justify

What is the White Man's Burden?
The European belief that they were superior to other people (racist), they felt it was their "burden" or responsibility to "civilize" the people (places) they conquered.

What is scientific racism?
The use of scientific theories to support or validate racist attitudes or worldviews.
What does scientific racism support regarding human beings?
The classification of human beings into distinct biological races.
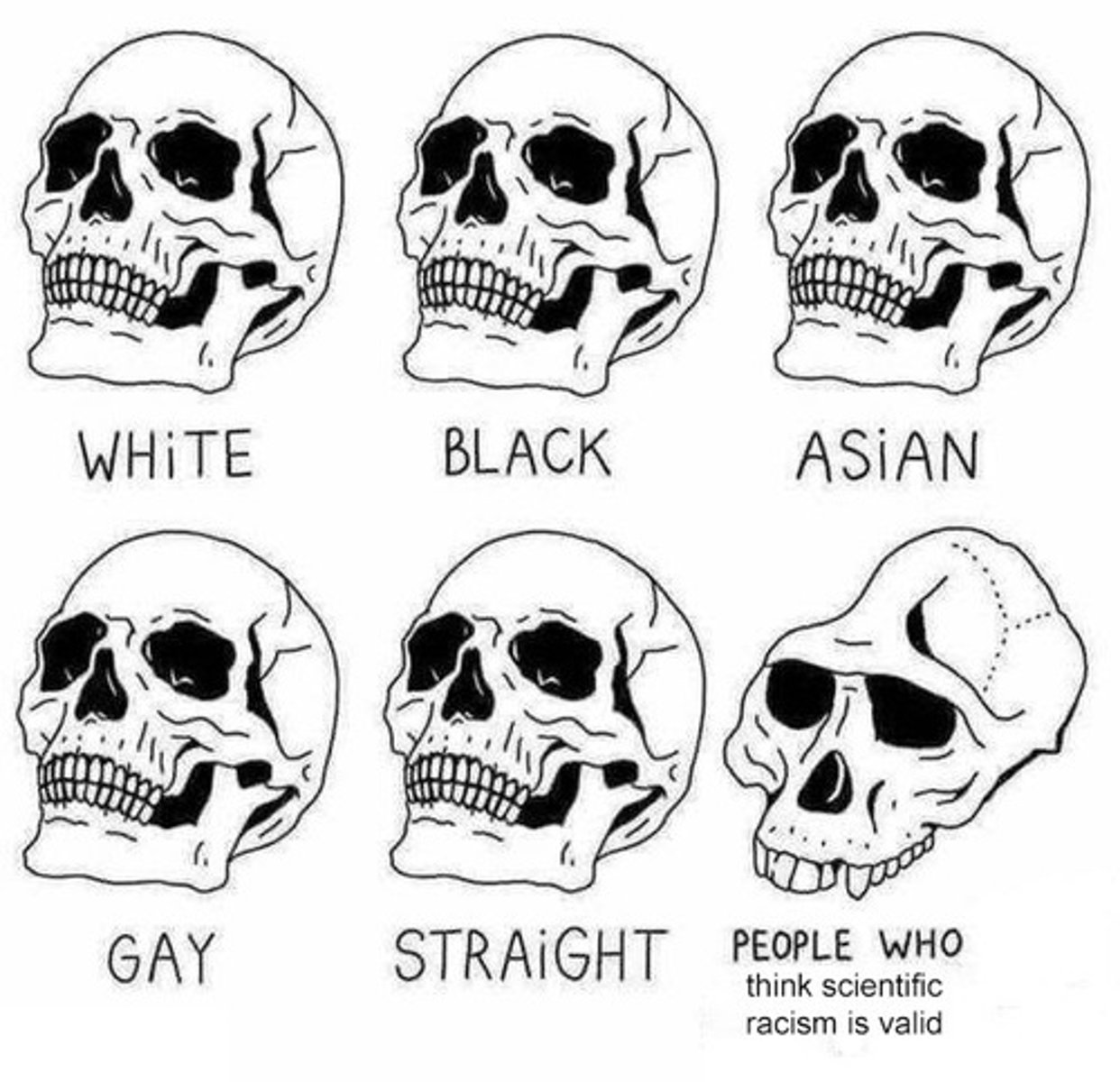
How were non-white cultures seen by white people?
They were seen as "primitive" and "less evolved"

What were seen as "blessings of civilization" by Europeans?
-Christianity
-New tech
-New medicine
-European infrastructure
-European education
-European customs

Thomas Malthus
He said human population can outgrow food supply; result will be war, famine, disease.
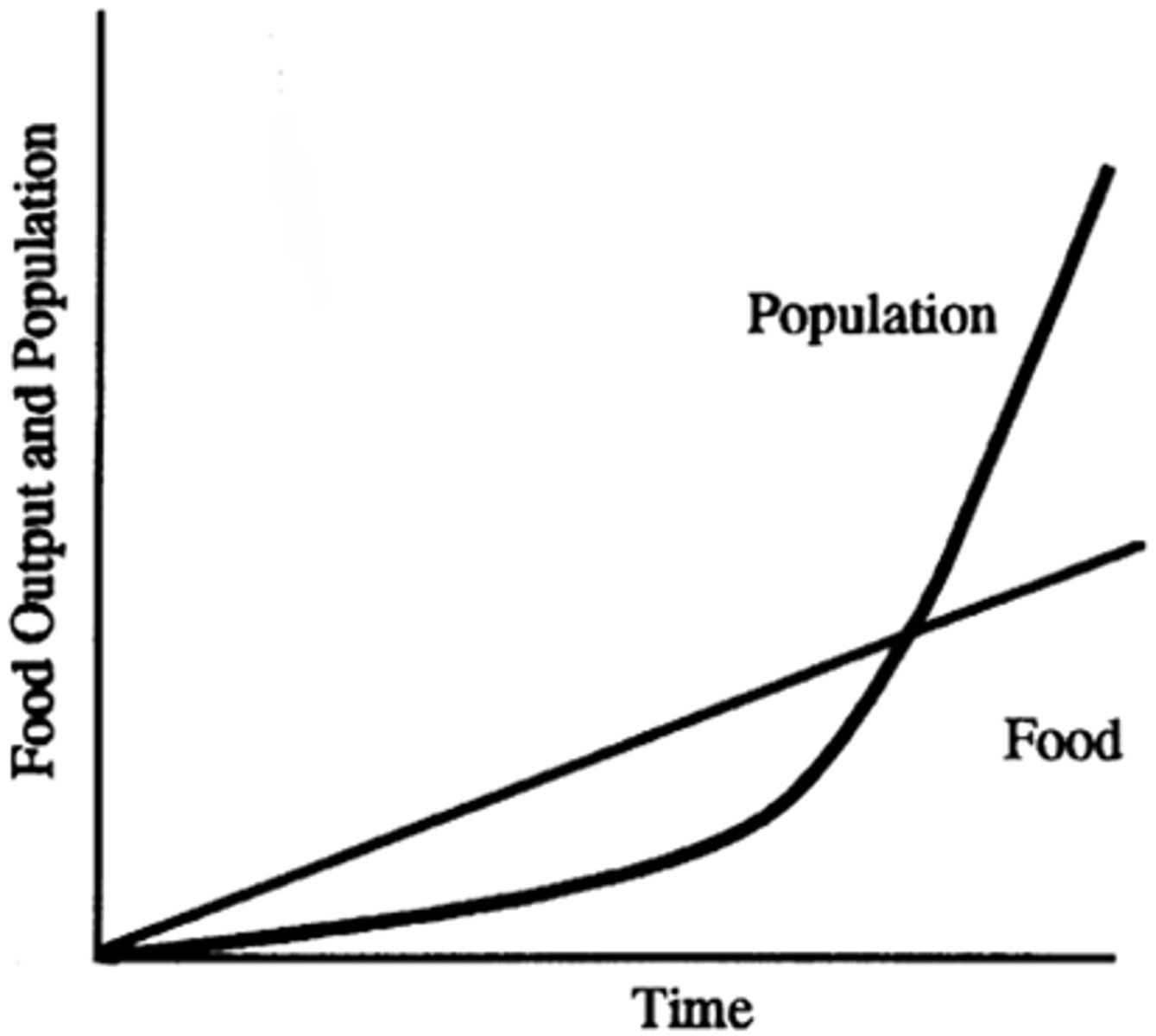
How did Thomas Malthus' ideas influence imperialists?
The imperialists said that they need to make sure that the white race survives and used this to justify genocide against races other than white. Europeans also fought for the right for colonies because the world was now seen as a "struggle for existence"
What did the spreading of the "blessings of civilization" cause for the people who were being colonized?
Loss of culture
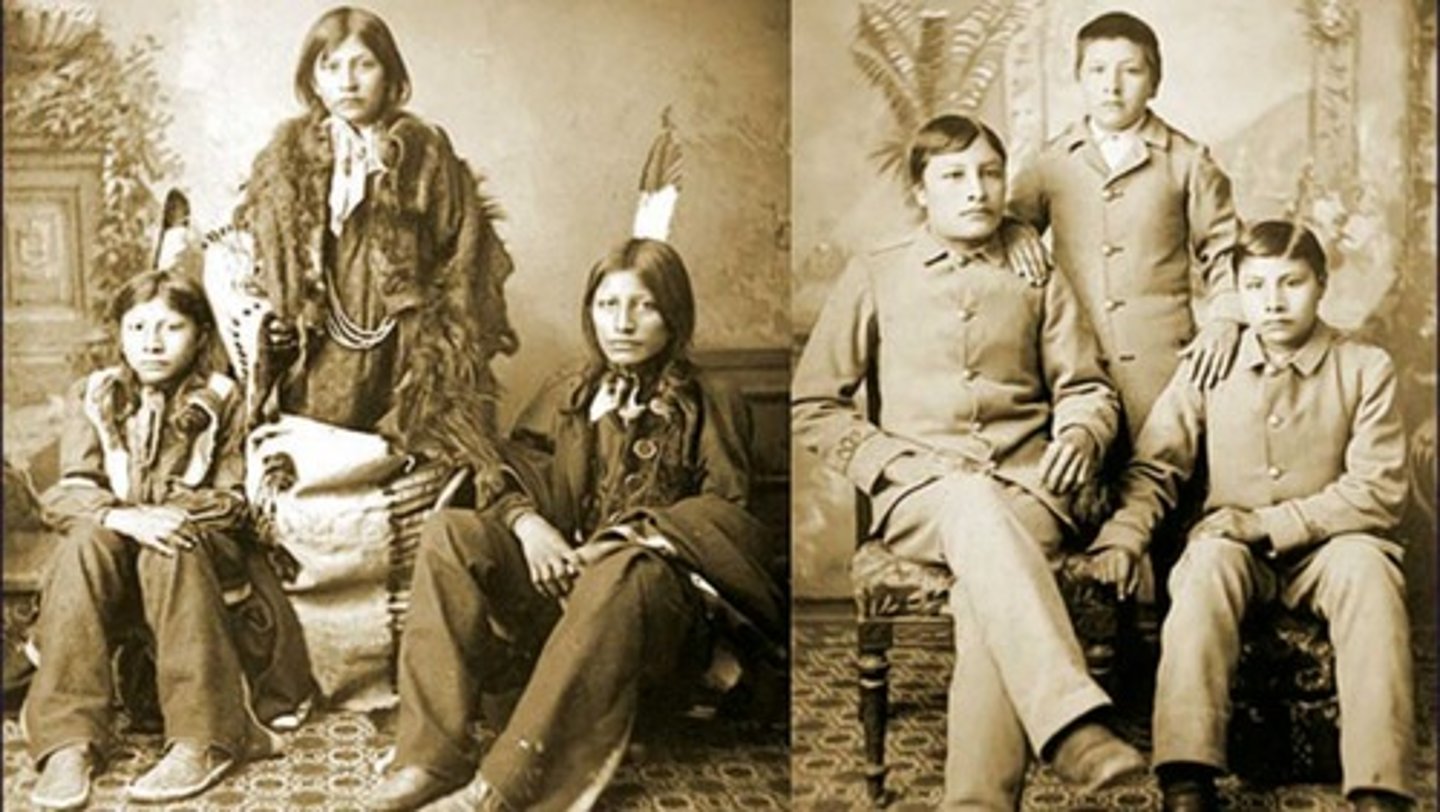

What did advanced weapons, railroads and radios do for imperial powers?
Helped them control large territories
What is gunboat diplomacy?
Using military force to force a country to negotiate, speak softly and carry a big stick
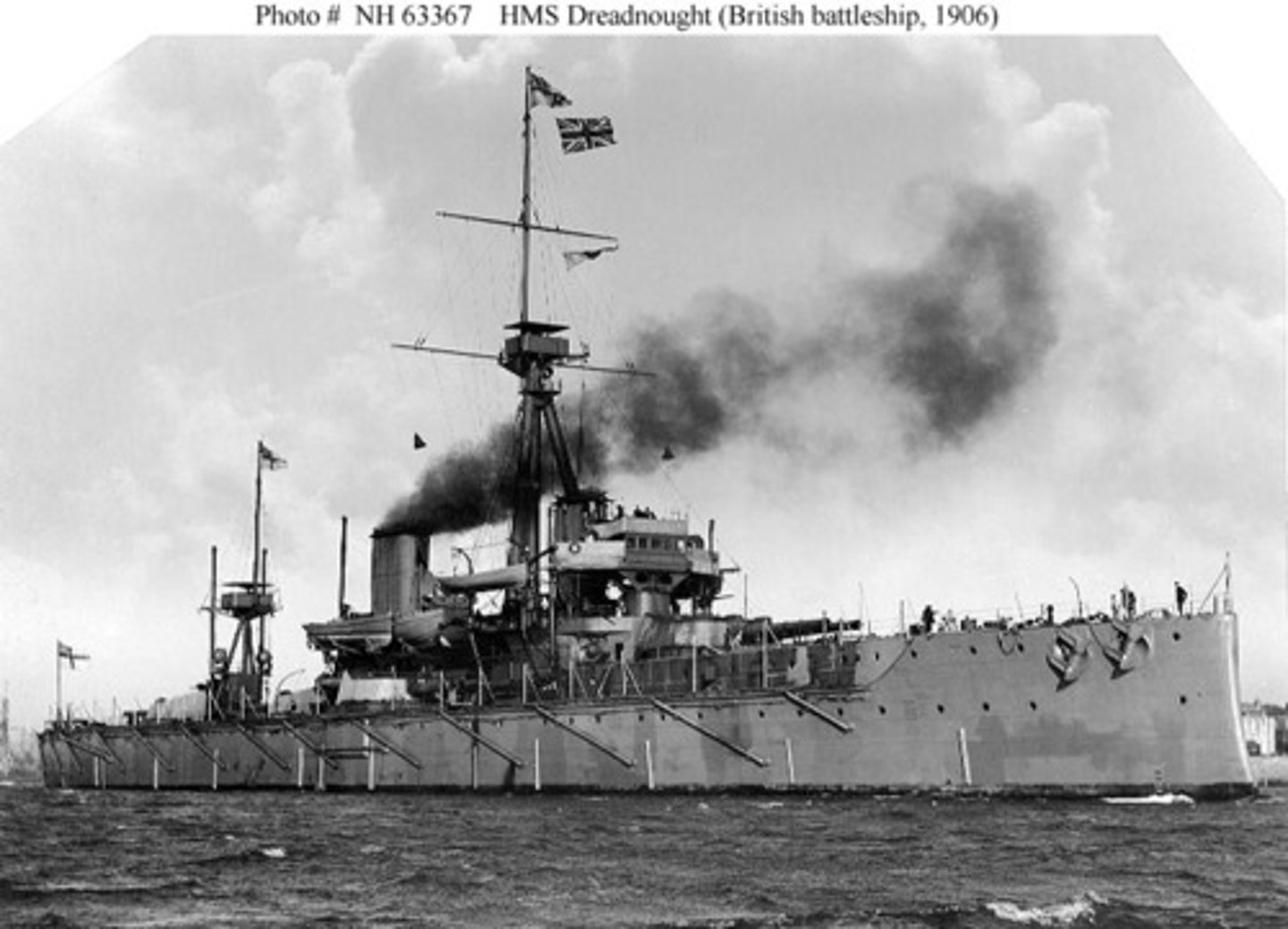

What is colonialism?
Colonialism is where one nation assumes control over another.

What is imperialism?
Imperialism refers to political or economic control, either formally or informally.

How can colonialism and imperialism be differentiated in simple terms?
Colonialism can be thought of as a practice, while imperialism is the idea driving that practice.
what
what

What is indirect rule?
Colonial government in which local rulers are allowed to maintain their positions of authority and status

Who was in charge of the British South Africa Company?
Cecil Rhodes

Trains allowed the British to control a whole lot of people with...
less people in their army
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: End of the trade of enslaved people
Britain halted coastal trade, but inland continued.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Exploration
19th-century expeditions aimed to map Africa's resources.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Henry Morton Stanley
Explorer linked to King Leopold II's Congo ambitions.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Capitalism
Shift from slavery to legitimate trade in Africa.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Steam engines
Enabled navigation of Africa's rivers for exploration.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Iron-hulled boats
Revolutionized maritime access to inland Africa.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Quinine
Extracted from cinchona tree; treated malaria effectively.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Medical advances
Improved European survival rates in Africa's diseases.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Politics
European nations sought empires post-unification of Germany.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Military innovation
New weaponry gave Europeans significant combat advantages.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Percussion caps
Improved ammunition design enhanced weapon efficiency.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Breech-loading rifle
Faster loading and firing compared to muskets.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: African Association
Founded in 1788 to promote African exploration.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Timbuktu
Fabled city sought by early European explorers.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Congo River
Key area for European colonial ambitions.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Plantations
Established for cash crops like rubber and sugar.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Cash crops
Agricultural products grown for profit in Europe.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Suez Canal
Strategic waterway sought by Britain for control.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Carl Peters
German journalist who followed Stanley's exploration model.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Yellow fever
Disease that remained a challenge for European explorers.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Royal African Company
Sent Europeans to Africa, many perished from diseases.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Livingstone
Explorer known for his travels and humanitarian efforts.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: European dominance
Political maneuvering aimed at maintaining power through colonies.
Causes of the Scramble for Africa: Explorers' motivations
Shifted from curiosity to economic exploitation.
What makes a "developed" country?
Modern tech, modern infrastructure, increased GDP per capita, more education
What makes a less "developed" country?
Poor infrastructure, small military, unemployment, decreased GDP per capita,
cottage industry, less resources

What is the Great Divergence?
The increase in dispersion of incomes throughout the world.

What is associated with the Great Divergence?
Modern economic growth has taken hold in some countries but not in others.
Sepoy
Indian soldiers

Forms of Imperial Rule
Direct rule, indirect rule, protectorate, sphere of influence

What are spheres of influence?
Areas in which countries have some political and economic control but do not govern directly.
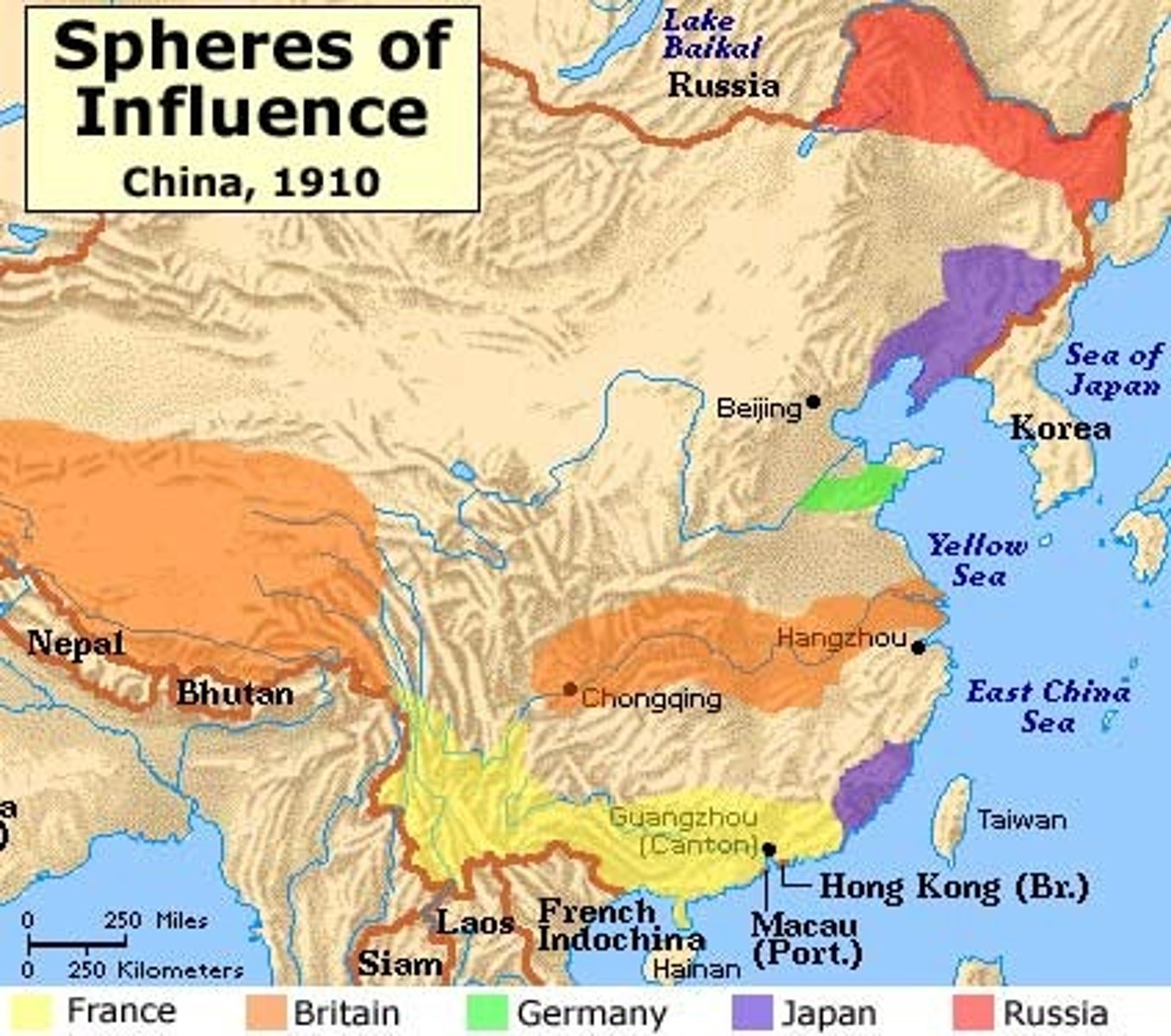
Protectorate
Country with its own government but under the control of an outside power

What is the Suez Canal?
A ship canal in northeastern Egypt linking the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
What does the Suez Canal facilitate?
Shorter trade routes.
What's the goal of an extractive colony?
Profit

What was the Boer War?
A conflict in which the Boers and the British fought for control of territory in South Africa.
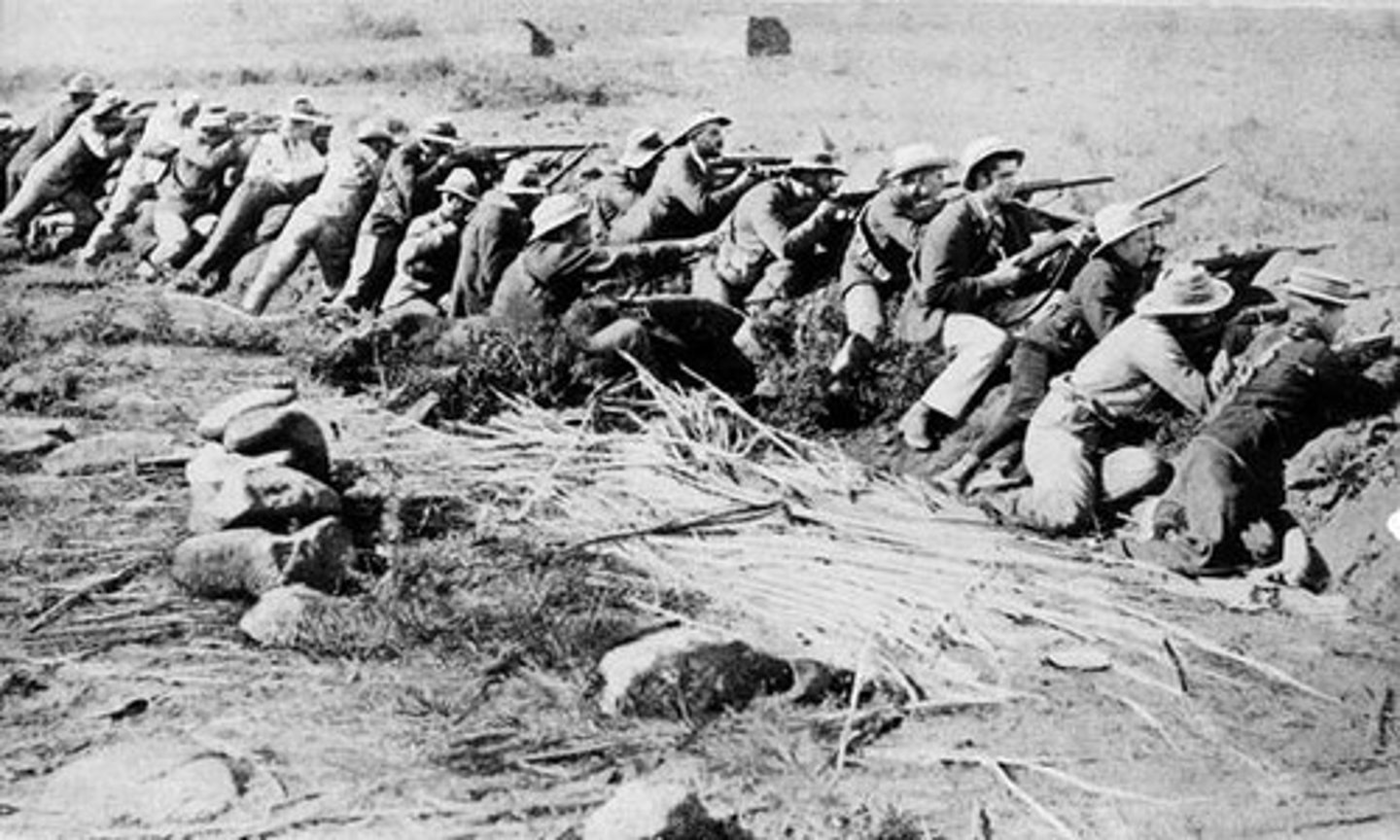

Who were the main parties involved in the Boer War?
The Boers and the British.
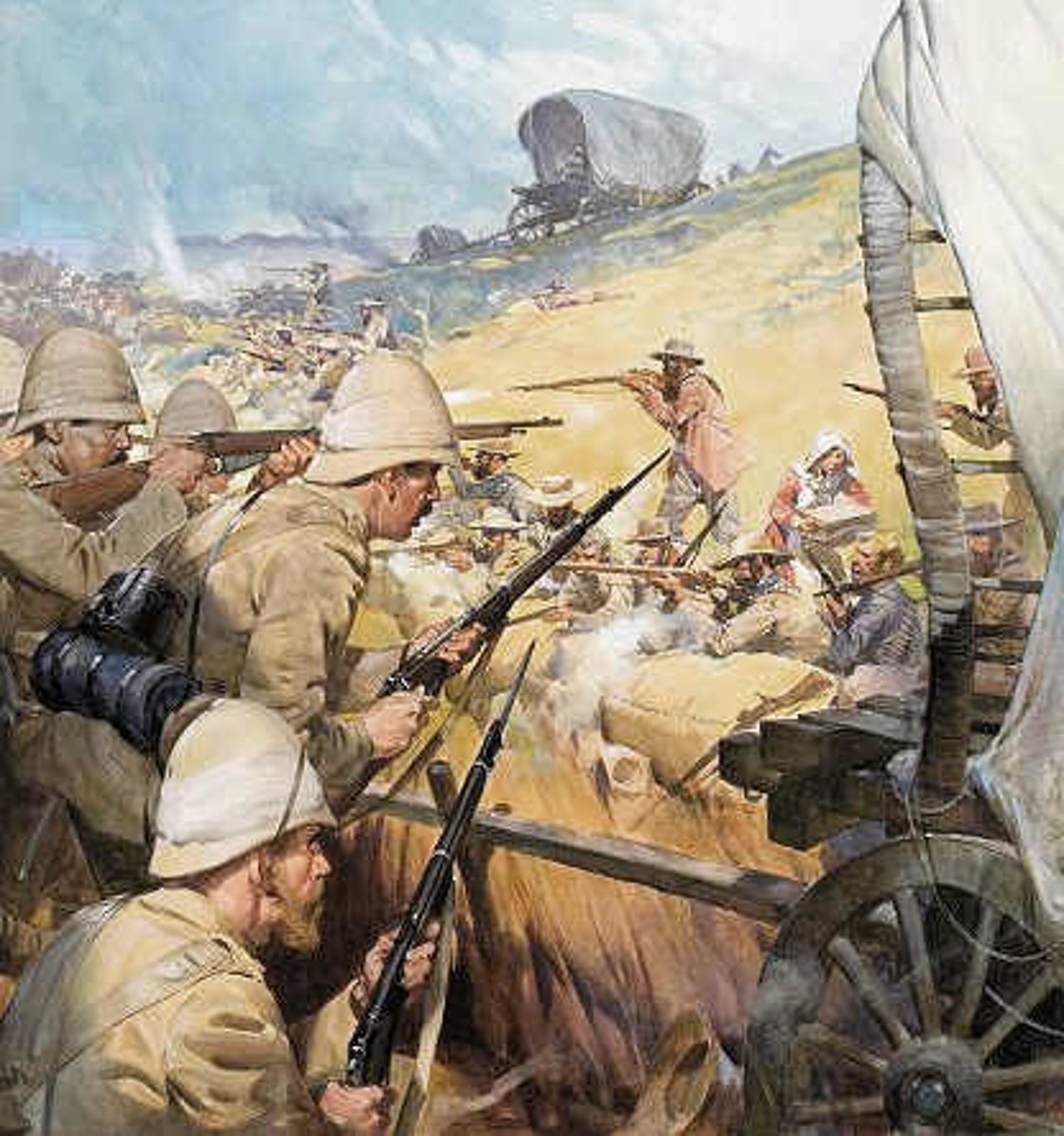

Where did the Boer War take place?
South Africa.
Why did Britain want to destroy the Indian textile industry?
So that the british could get more profit

What was the Herero and Nama Genocide?
A campaign of racial extermination and collective punishment against the Herero people.
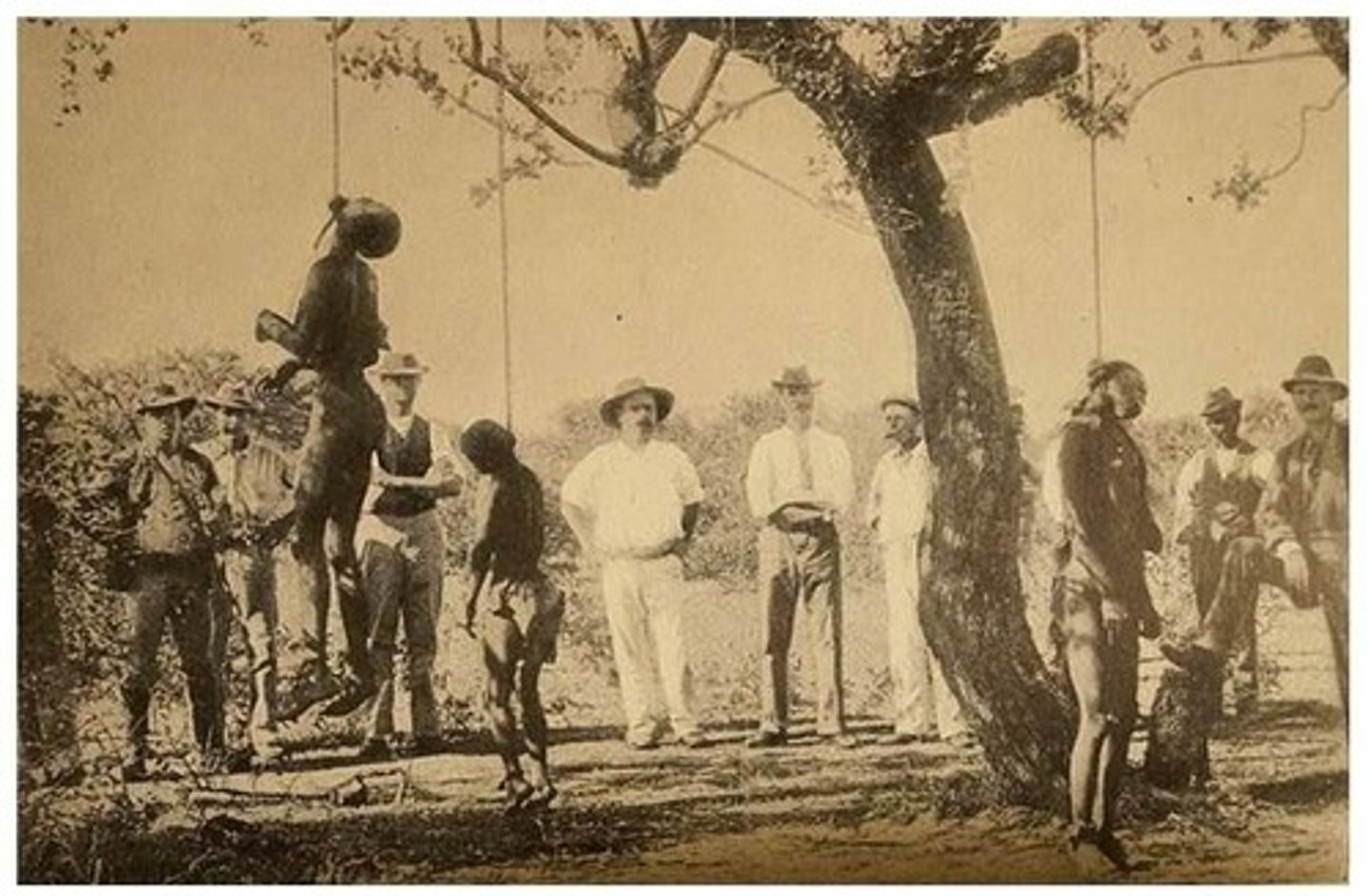

Where did the Herero and Nama Genocide take place?
In German South West Africa, now known as Namibia.
What is the significance of the Herero and Nama Genocide in history?
It is considered the first genocide of the 20th century.
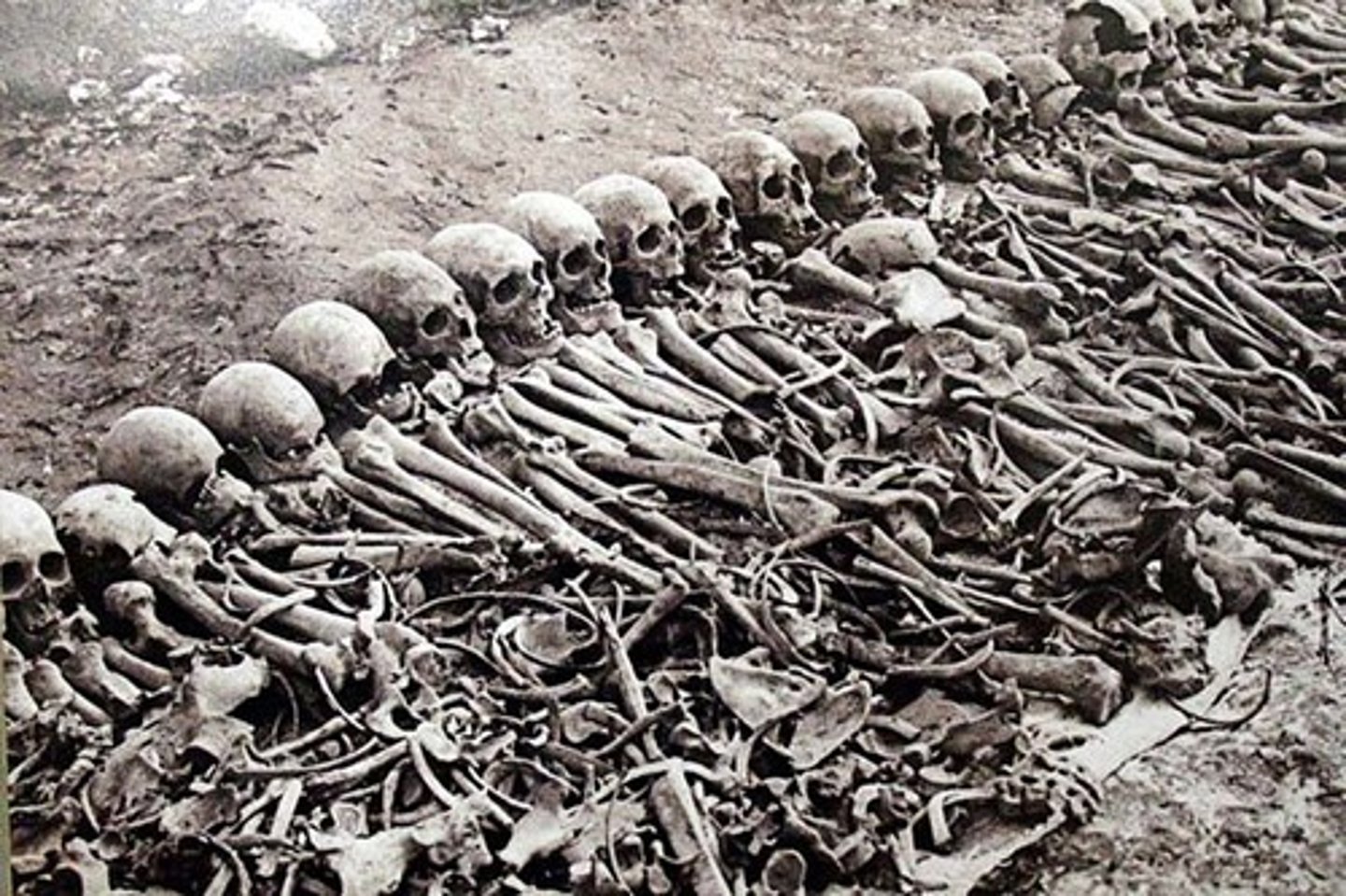

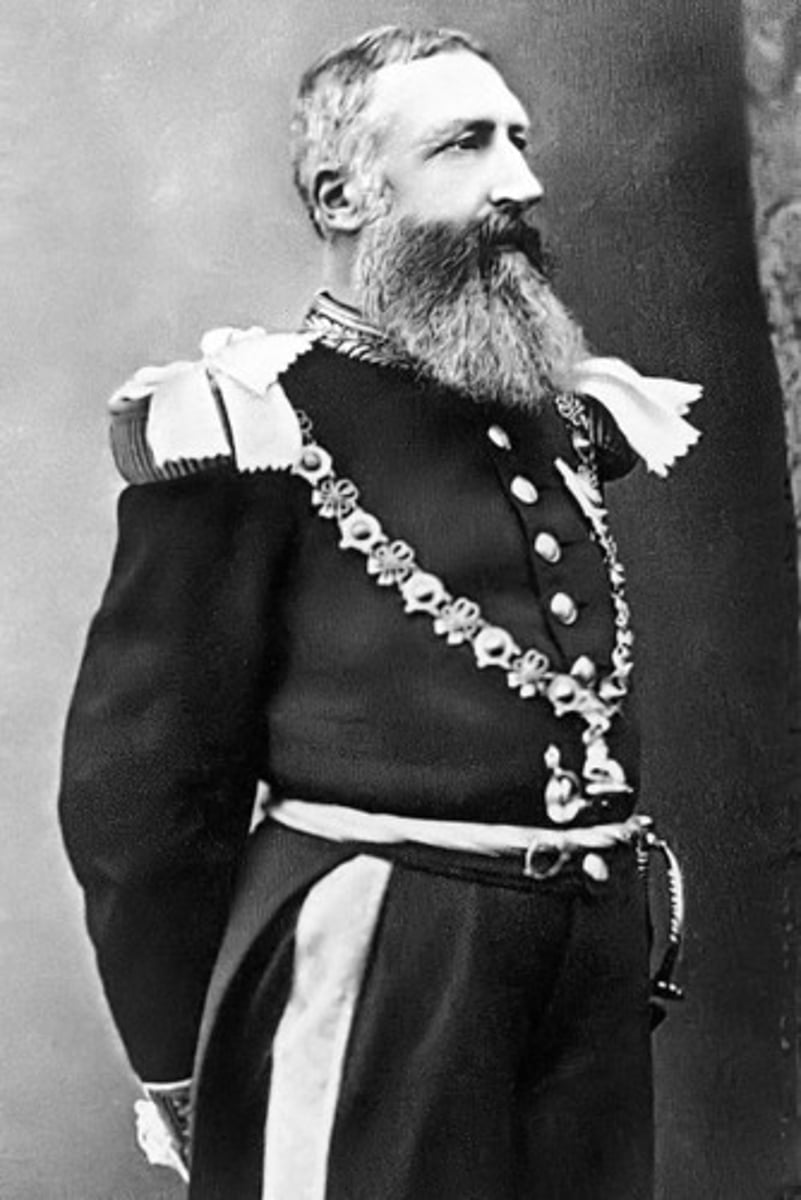
King Leopold II's reign of terror
For over twenty years, King Leopold II of Belgium enslaved the people of the Congo for the rubber trade. He killed an estimated 8-12 million people.

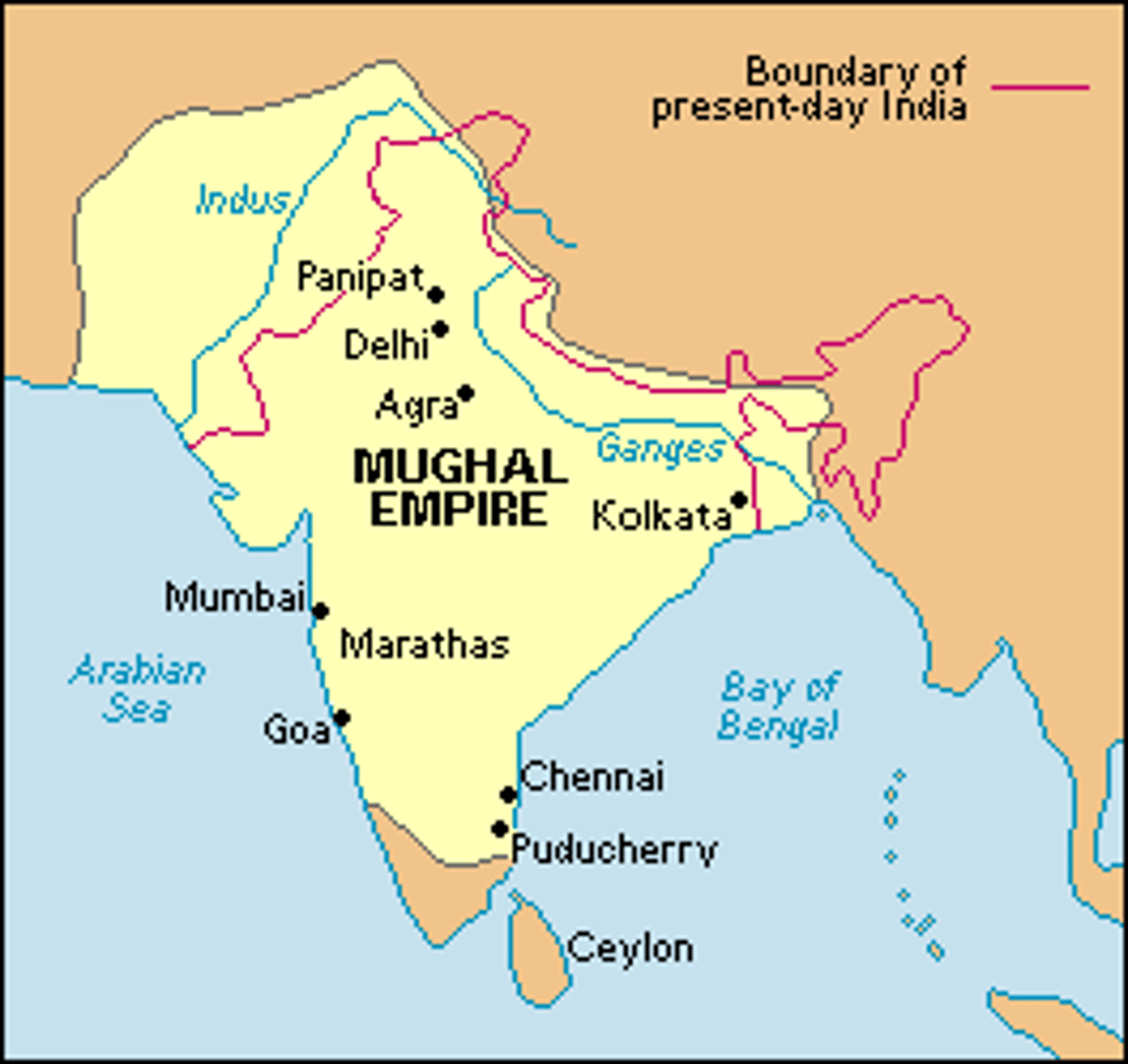
Mughal Empire Decline
there was a civil war between Muslims and Hindus