UWORLD Pulmonary & Critical Care Step 2 CK
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
____ is characterized by an acute worsening of symptoms in a pt with chronic lung dz. Triggered by URI. Exam shows wheezes, prolonged expiration, crackles at lung base, and use of accessory muscles. ABG shows respiratory acidosis and hypoxemia.
COPD exacerbation
Anaphylactic shock what are the symptoms?
Sudden onset of symptoms in more than 1 organ system:
- Cutaneous (hives, flushing, pruritus)
- GI (lip/tongue swelling, vomiting)
- Respiratory (dyspnea, wheezing, stridor, hypoxia)
- CV (hypotension)
tx: IM EPI into the thigh
___ is common in pt with Hodgkin lymphoma tx with chemo and radiation.
Secondary malignancy
- most commonly lung (especially smokers), breast, thyroid, bone, GI (colorectal, esophageal, gastric tumors)
In low risk (< 40 years and nonsmoker) a solitary pulmonary nodule is not a sign of immediate alarm. The best approach is?
Ask for an old X-ray
- no change in the past 12 mo. it is considered benign
- CXR every 3 mo. for the next 12 mo. no growth or no symptoms it is left as such
Symptoms of theophylline toxicity?
CNS stimulation (HA, insomnia, seizures)
GI (N/V)
Cardiac toxicity (arrhythmia)
* Ciprofloxacin, cimetidine, erythromycin, clarithromycin, verapamil) can INC theophylline -> toxicity
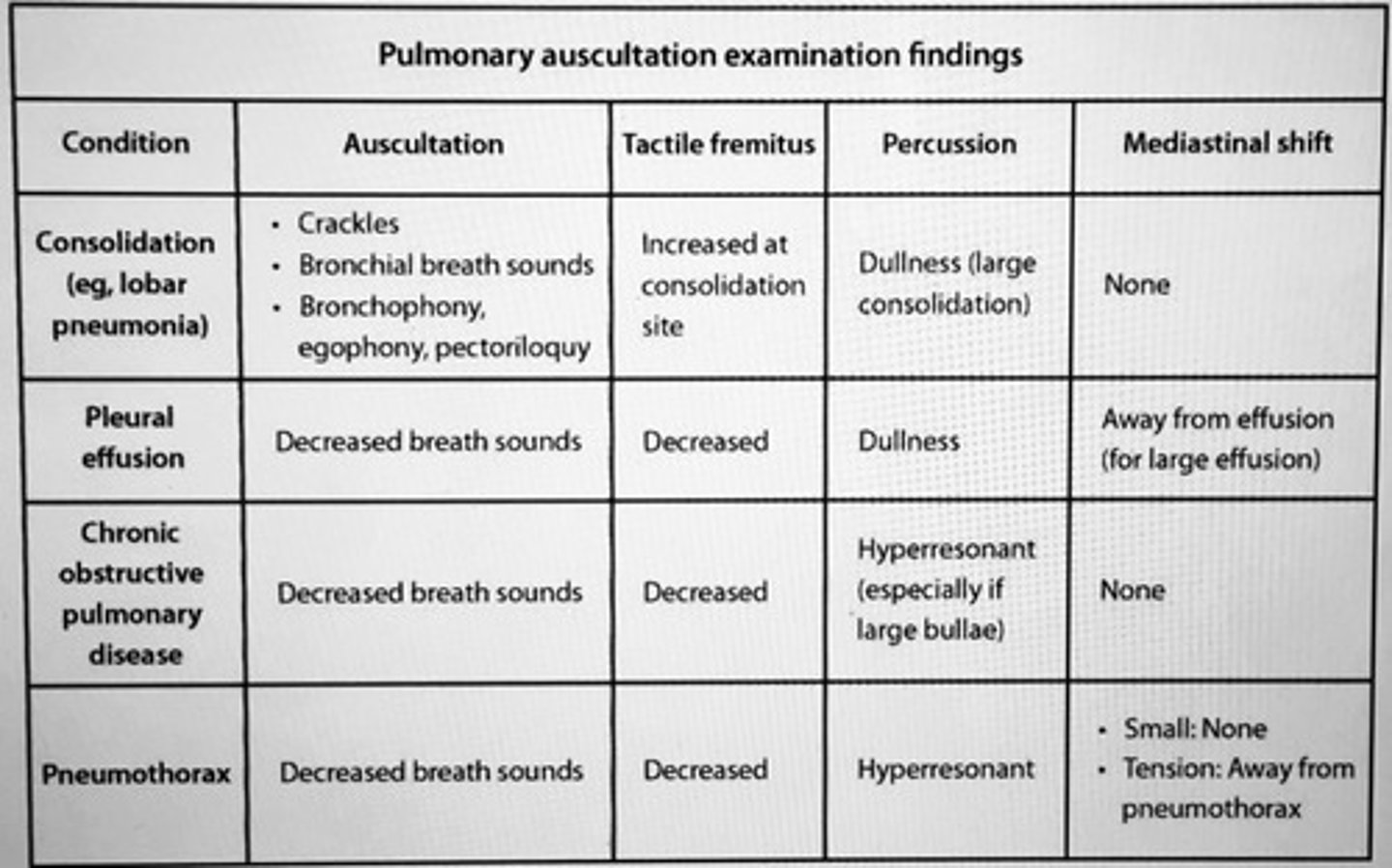
Pulmonary auscultation examination findings.
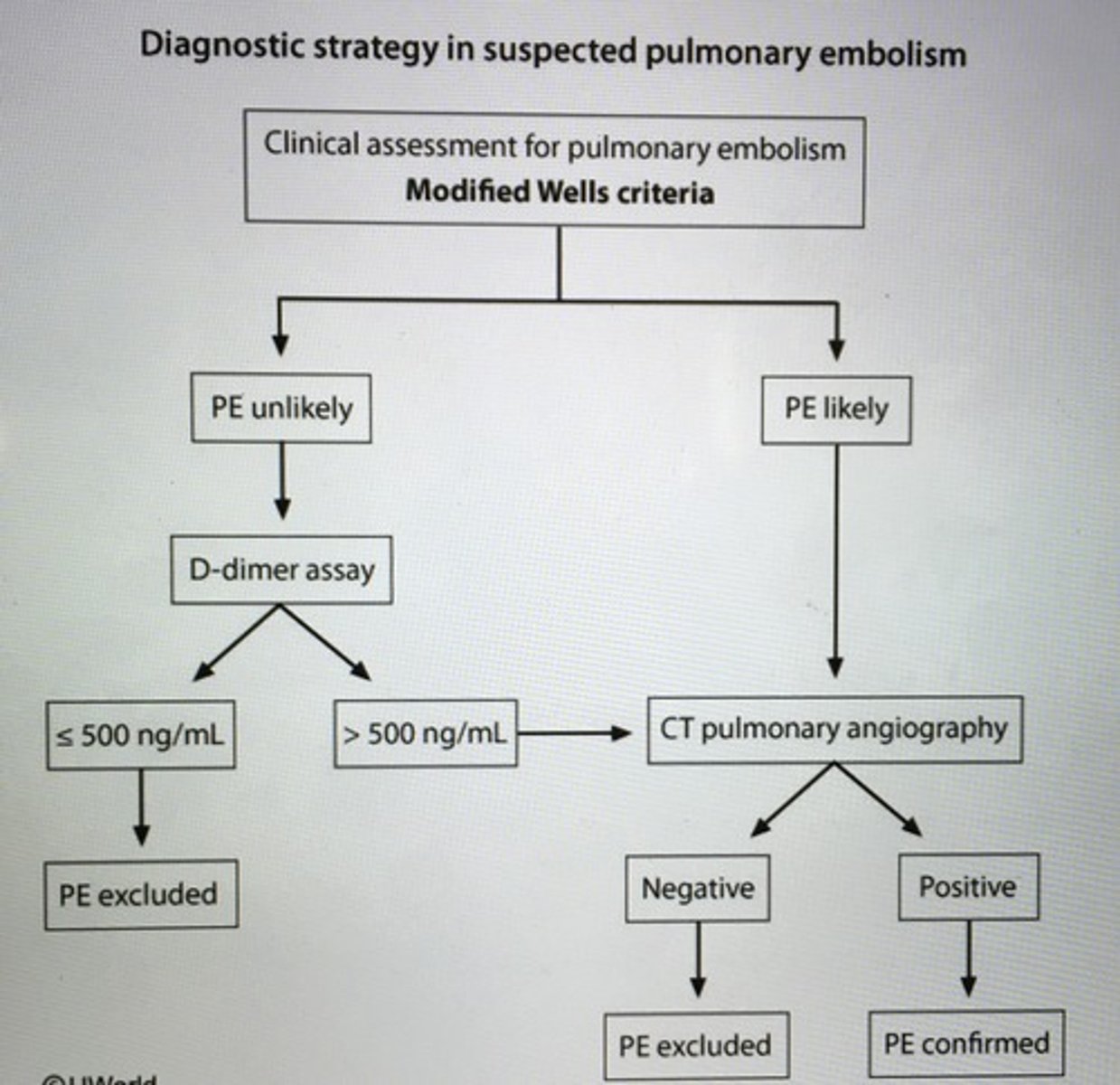
Diagnostic strategy in suspected PE
Pt with ___ usually present with signs of low arterial perfusion (hypotension, syncope) and acute dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and tachy).
Massive PE
- thrombus INC pulmonary vascular resistance and RV pressure, cause RV hypokinesis and dilation, DEC preload, and hypotension
- underlying malignancy (prothrombic state)
____ fungal infection endemic to Great Lakes, Mississippi, and Ohio River basins. Systemic ___ may cause skin and bone lesions in addition to pulmonary manifestations.
Blastomycosis
- Broad-based budding from sputum confirm dx
- Itraconazole or amphotericin B
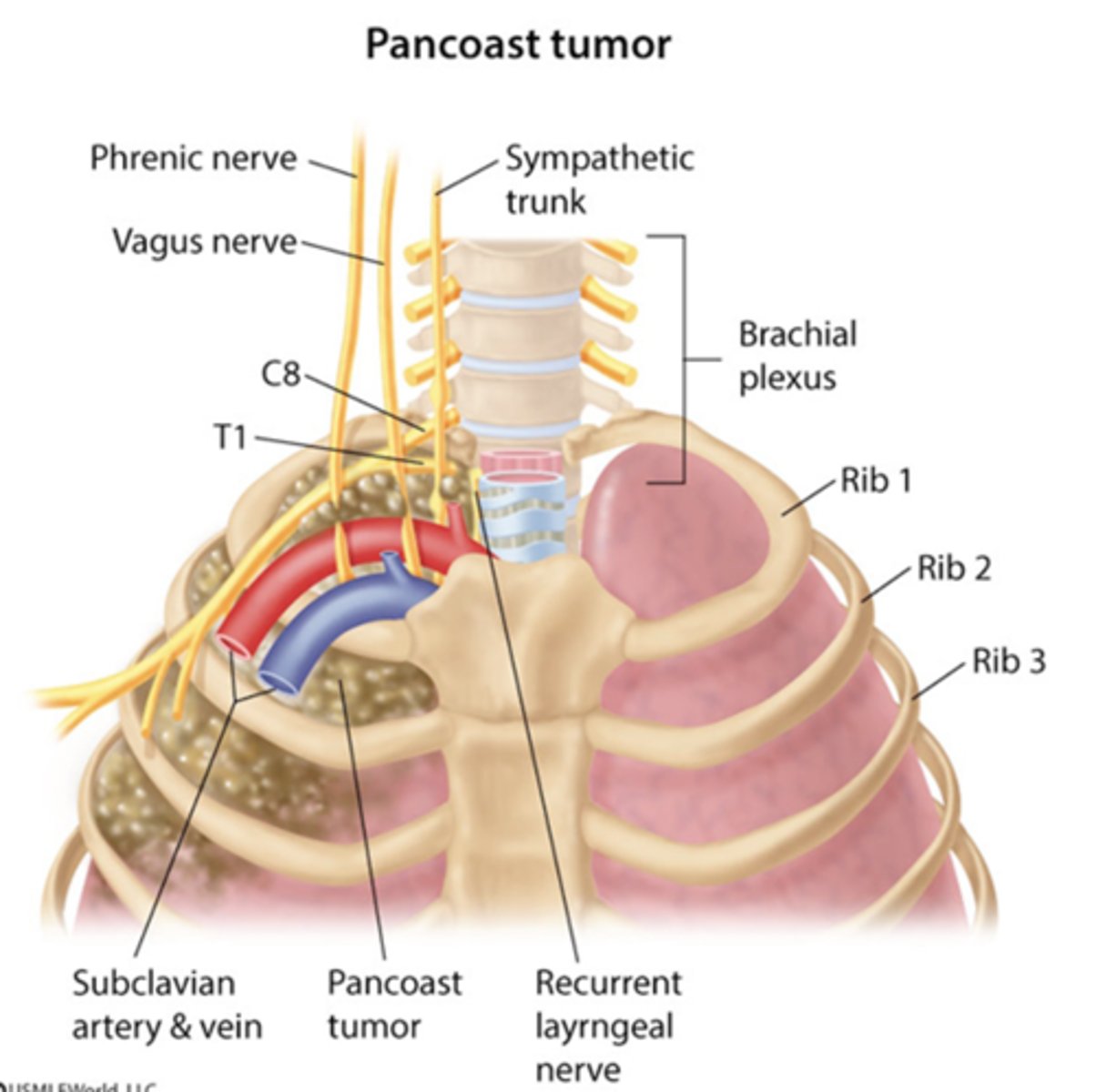
___ most commonly present with shoulder pain. Horner's syndrome, weakness atrophy hand muscles, pain and/or paresthesias in arm or forearm, enlarged supraclavicular lymph nodes.
Pancoast tumors (superior pulmonary sulcus tumors)
- CXR in pts with suspected lung cancer
___ is the most common cause of malignancy associated SIADH.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
- also associated with ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (Cushing syndrome) and Lambert-Eton syndrome.
Squamous cell carcinoma in the lung is generally associated with?
Cavitary lung lesions and hypercalcemia
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (clubbing) is usually associated with lung ___.
Adenocarcinoma
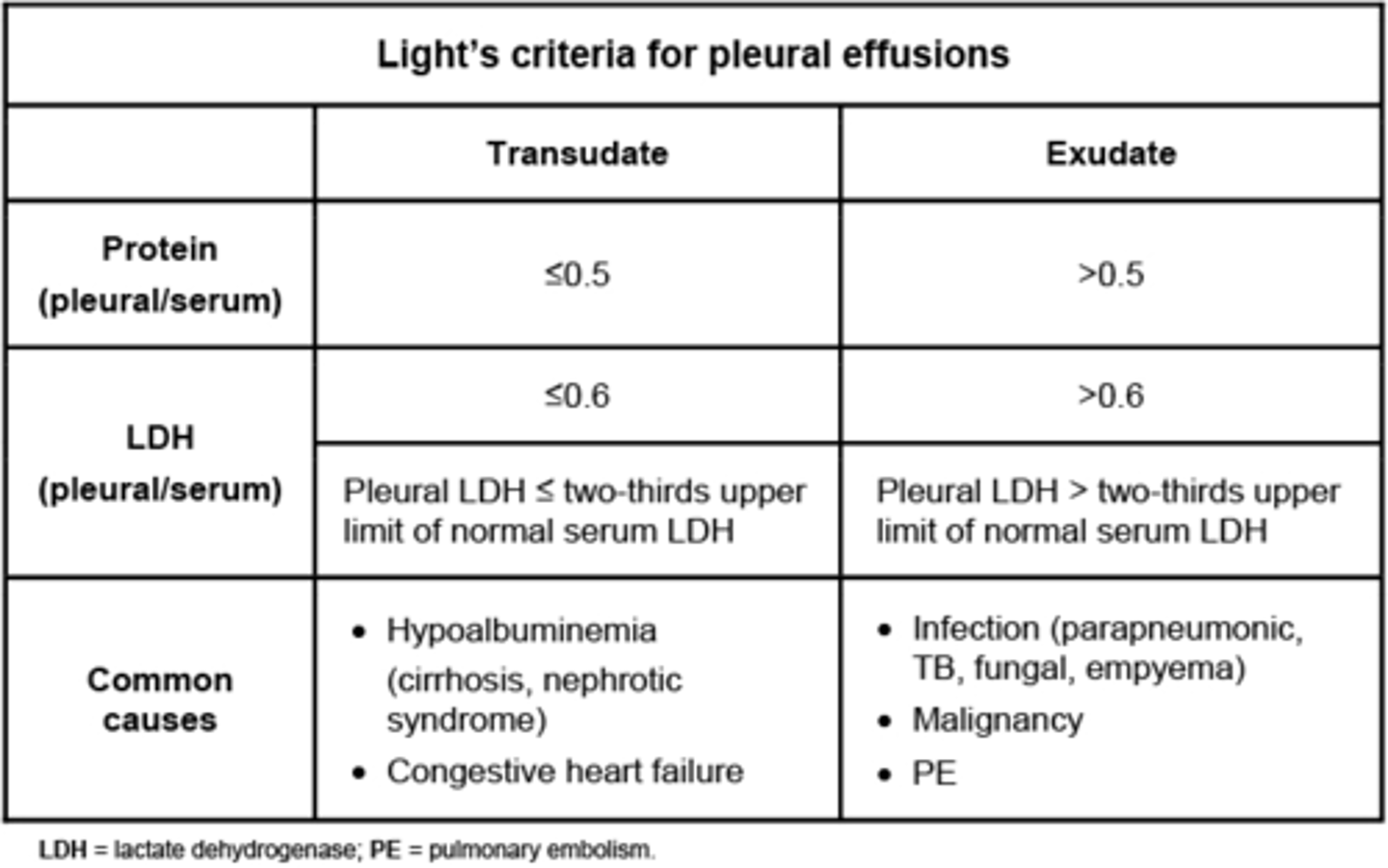
Light's criteria classify an exudate as having at least one of the following?
1. Pleural fluid protein/serum protein ration > 0.5
2. Pleural fluid LDH/serum LDH>0.6
3. Pleural fluid LDH>2/3 of the upper limit of normal LDH
- pleural fluid acidosis (pH< 7.20)
- low pleural fluid glucose < 60 (due to complicated parapneumonic effusion, rheumatoid pleurisy, drug induced lupus, TB, malignancy)
* if these negative then fluid is transudative
___ found in middle mediastinum.
Bronchogenic cysts -> middle
Thymoma -> anterior mediastinum
Neurogenic tumors -> posterior mediastinum
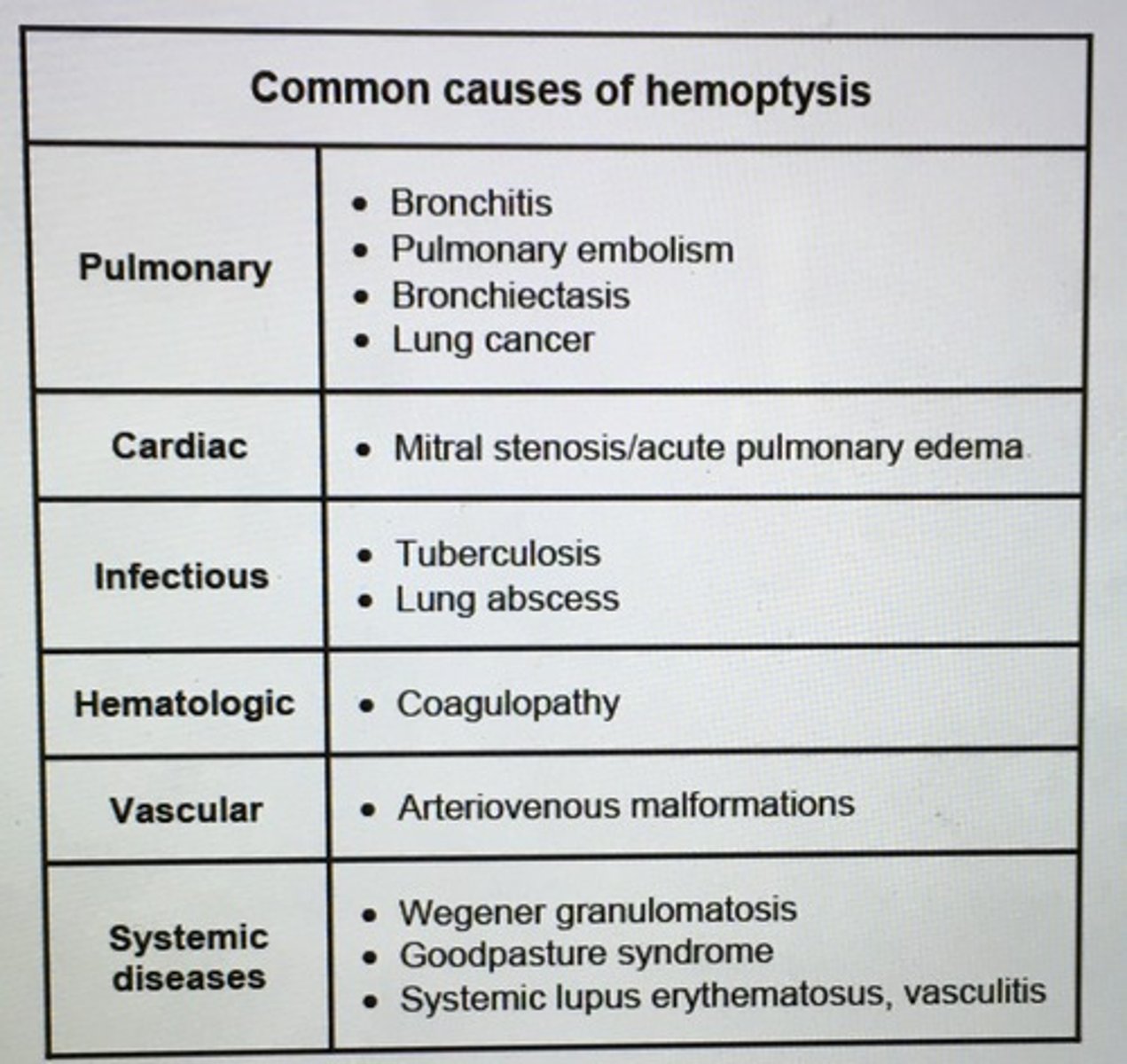
Causes of hemoptysis
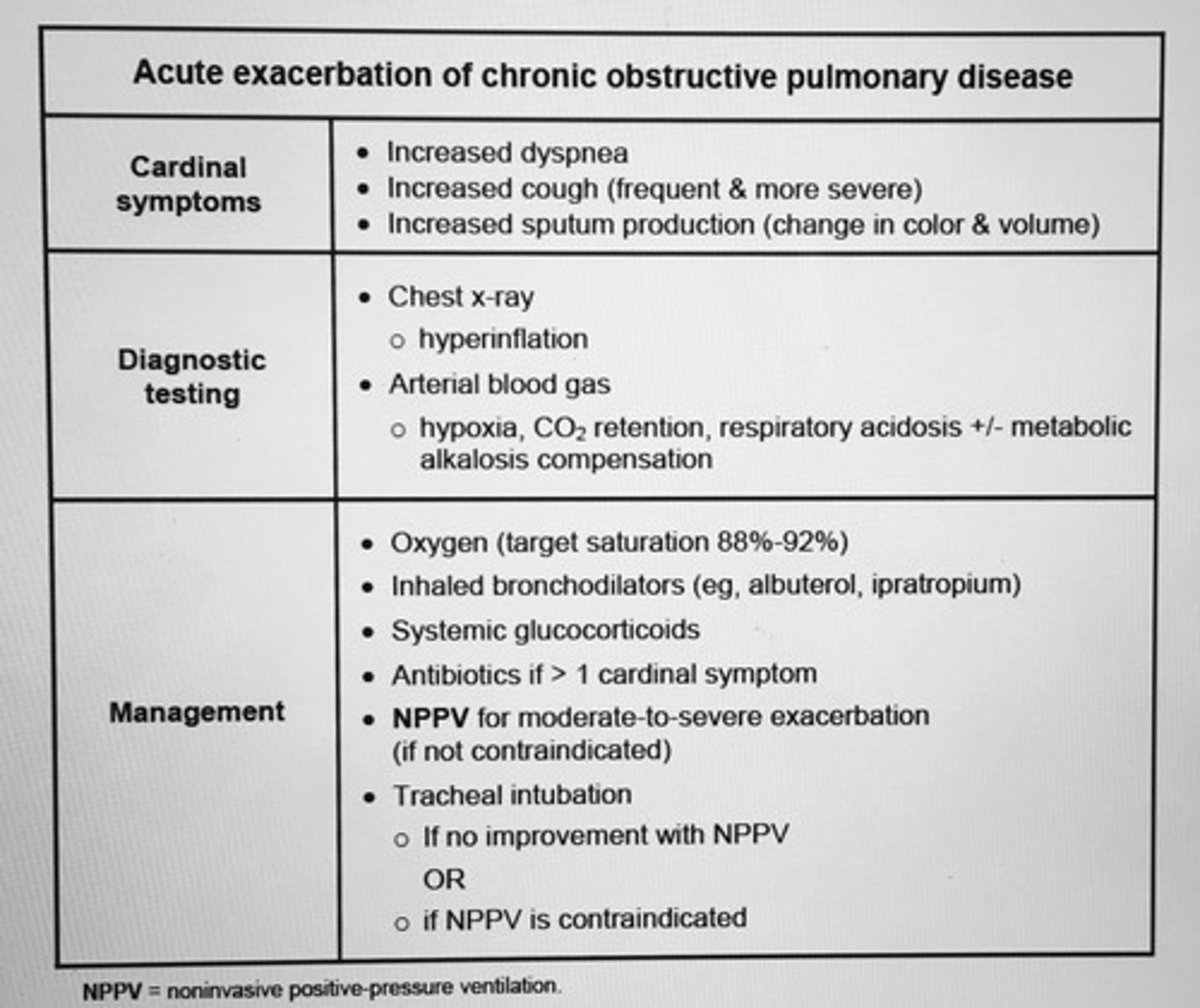
Acute exacerbation of COPD
Cardinal symptoms (INC dyspnea, cough, sputum production
- moderate to severe exacerbation
- needing mechanical ventilation
The goal INR for an idiopathic VTE tx with warfarin or atrial fibrillation.
2.5 acceptable range 2.0-3.0
- adequate anticoagulation w/o an excessive risk of bleeding
Criteria for initiating long-term O2 therapy in COPD?
1. All COPD pts with PaO2 < 55 or SaO2 < 88% on room air
2. Pt with for pulmonate, evidence of pulmonary HTN or hematocrit > 55 should be started on home O2 when PaO2 56-59 with SaO2 > 89%
3. Home O2 also be used pt who have a resting awake PaO2 > 60 mm with SaO2 > 90 if they become hypoxic during exercise or sleep (nocturnal hypoxia)
* Dose O2 titrated such as SaO2 maintained > 90% during sleep, normal waking and at rest (survival benefit when O2 used minimum 15 hours/day)
Right heart catherization in pts with massive PE show?
Elevated RA and pulmonary artery pressure -> normal PCWP
syncope and shock
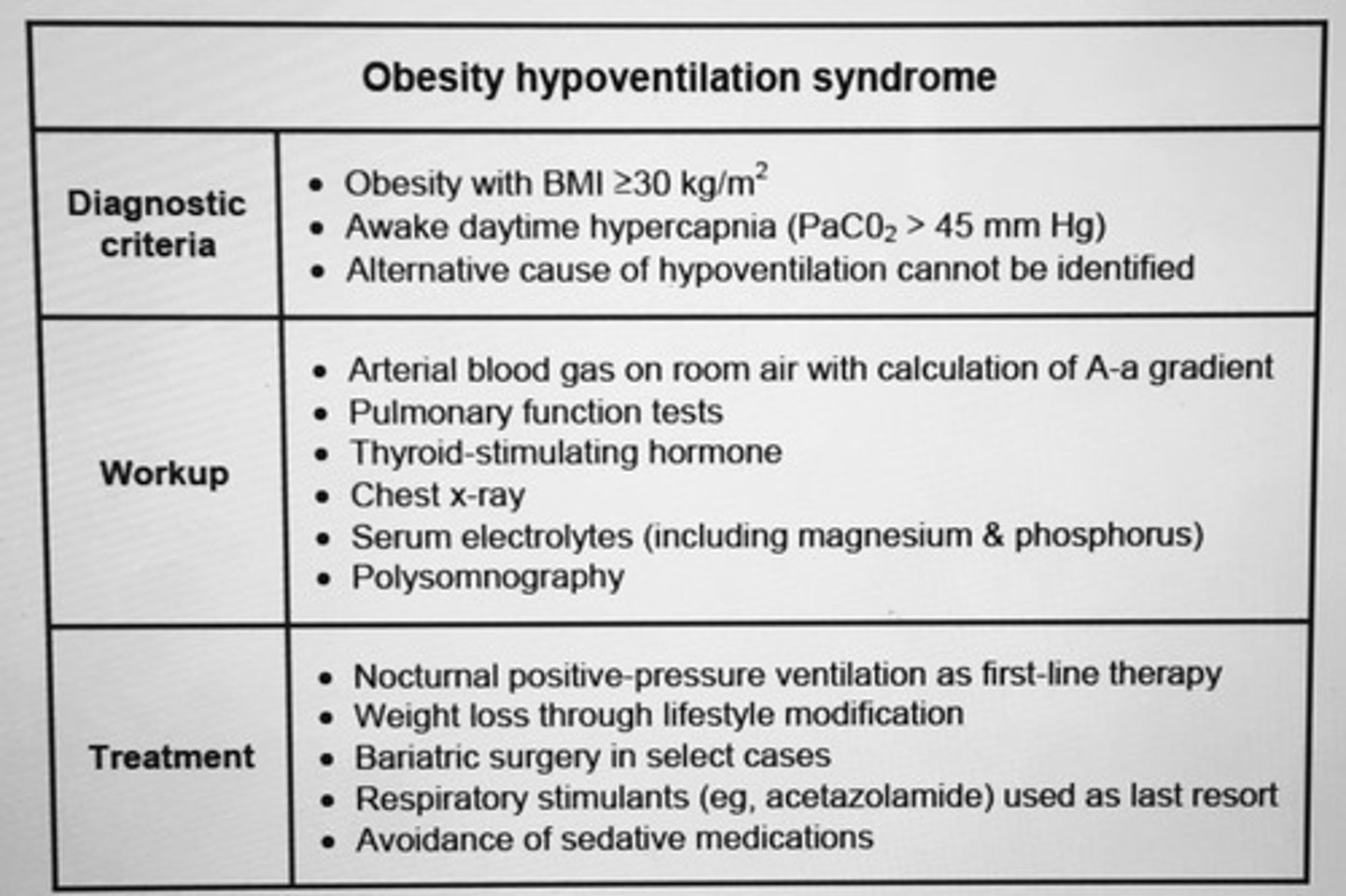
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
___ productive cough, hemoptysis, and recurrent fever. Wt loss may be present. Imaging shows upper lobe cavitary lesions. Pt recent travel to Mexico.
TB
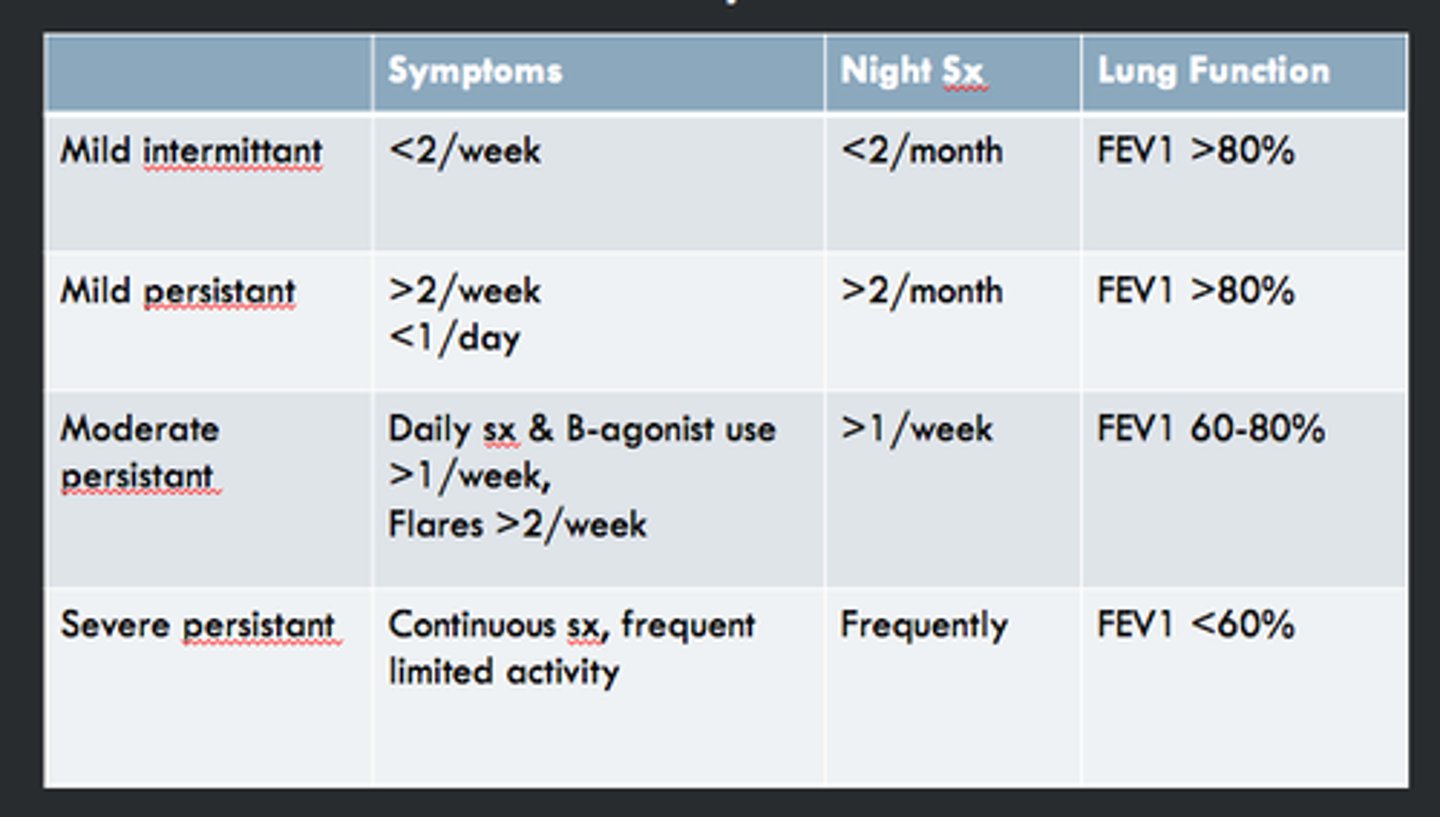
Mild intermittent asthma is?
Symptoms < 2x/week, <2 nighttime awakenings/month, normal FEV1 and no limitation on activity
- PRN albuterol inhaler
Mild persistent asthma is?
symptoms > 2 days but less than daily, nighttime awakening 3-4x/month, minor limitation in activities, normal PFTs low dose inhaled steroids should be added in addition to PRN albuterol
COPD is characterized by progressive expiratory airflow limitation which causes ___, DEC VC, and __ TLC.
Air trapping
DEC VC
INC TLC
FEV1 is disproportionately DEC compared to VC
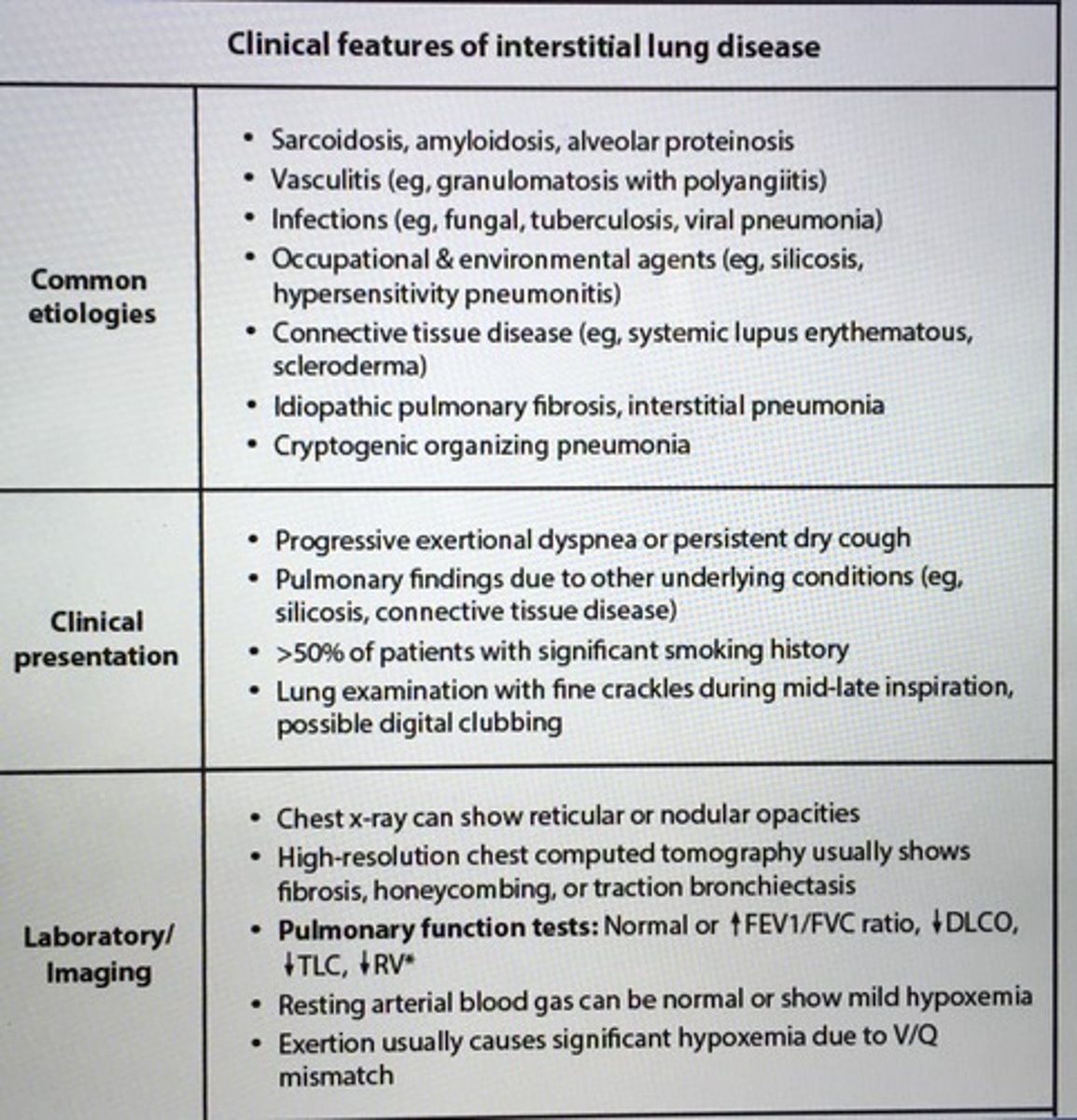
Clinical features of interstitial lung disease
Pt presents with pleuritic chest pain in setting of prolonged immobility, hemoptysis, dyspnea, tachypnea, tachy, and OCP use.
Concern PE
- 10% pt with PE have occlusion of peripheral pulmonary artery by thrombus causing pulmonary infarction
- CT pulmonary angiography is typically used for dx most pts
___ usually due to a crush injury crushing > 3 adjacent rib fractures that break in 2 places.
Flail chest
- tachypnea, shallow breaths
- intubation with mechanical positive-pressure ventilation required severe case
Recurrent bacterial infections in an adult patient may indicated ___.
Humoral immunity defect
- quantitative measurement of serum Ig feels help to establish the dx
- Selective deficiency IgA or IgG
- IgG3 alone more common females associated recurrent sinopulmonary as well as GI infections
Pt presents with a highly likely PE what should be done next?
PE likely -> start anticoagulation -> then can perform other diagnostic test for PE
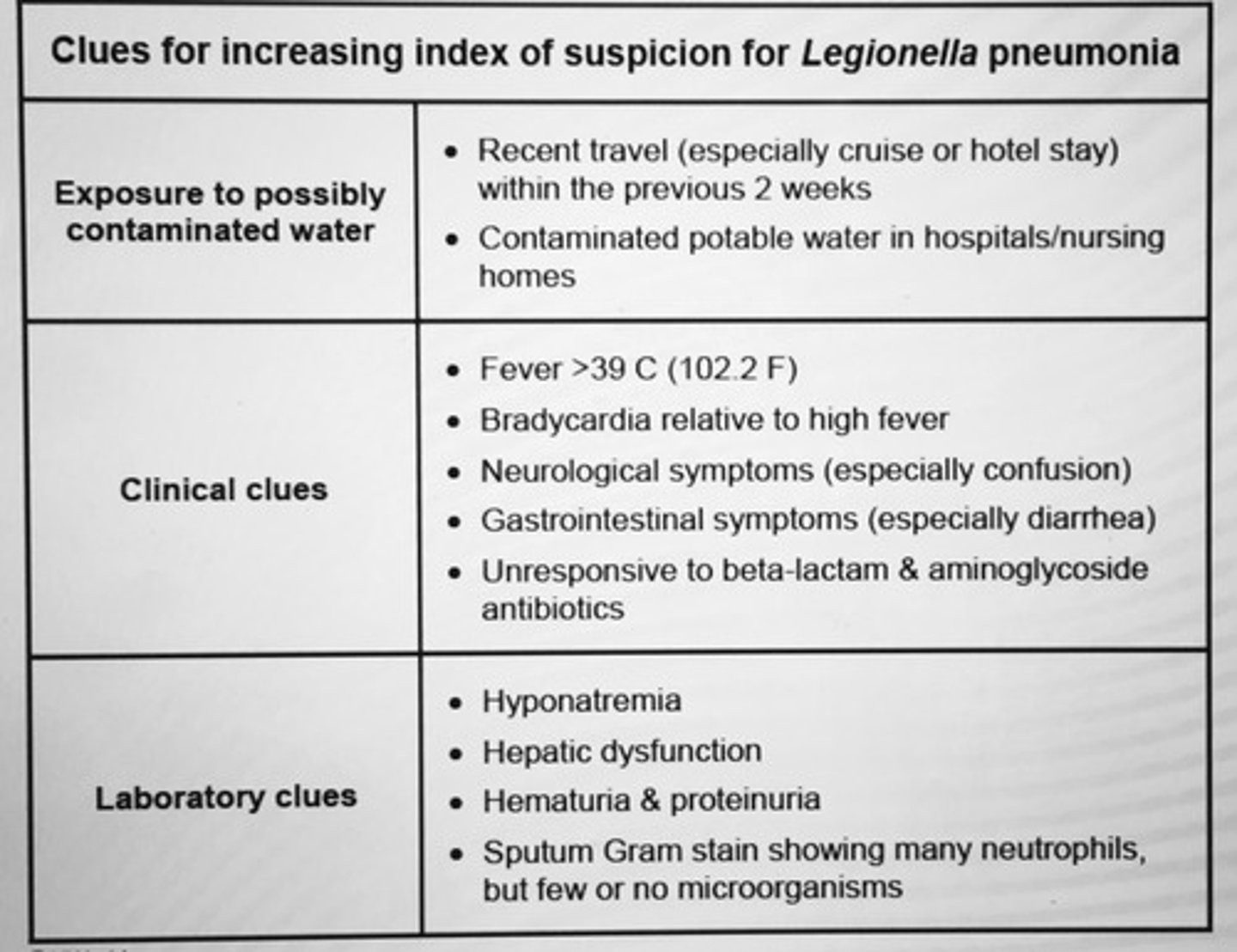
Clues for INC index of suspicion for Legionella pneumonia.
Grow on buffered charcoal yeast
Urine antigen testing rapid, highly specific
Tx: Macrolide or Fluoroquinolone
Pts with impaired consciousness, advanced dementia, and other neurologic disorder are predisposed to aspiration pneumonia due to impaired ___.
EPIGLOTTIC function
=> aspiration of oropharyngeal secretions (anaerobes)
tx: clindamycin, amoxicillin-clavulanate
CHF commonly causes ___ effusion. pH is usually?
Transudative (B/L 61%, uni R sided 27%)
Normal pleural fluid = 7.60
Transudative fluid = 7.4-7.55
___ is a non-IgE mediated reaction that is seen in pts with a Hx of asthma or chronic rhino sinusitis with nasal polyposis. Bronchospasm and nasal congestion following __ ingestion.
Aspirin induced respiratory distress (AERD)
- aspirin induced prostaglandin/leukotriene misbalanc
- tx: avoid NSAIDs, desensitization is NSAIDs are required, use of leukotriene receptor antagonists (monteleukast)
Massive PE is defined as PE complicated by?
Hypotension and/or acute R heart strain (RBBB, JVD)
__ presents with dullness to percussion, bronchial breath sounds (louder and have more prominent expiratory component), and egophony.
A consolidation of the lung
Complications of ventilation with a high PEEP?
Alveolar damage
Tension pneumothorax
Hypotension
Endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation is recommended for patient who fail?
2 hour trial of NPPV
- noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NPPV) in pts with acute exacerbation of COPD has been shown to DEC mortality, rate of intubation, hospital length of stay, and incidence of nosocomial infections
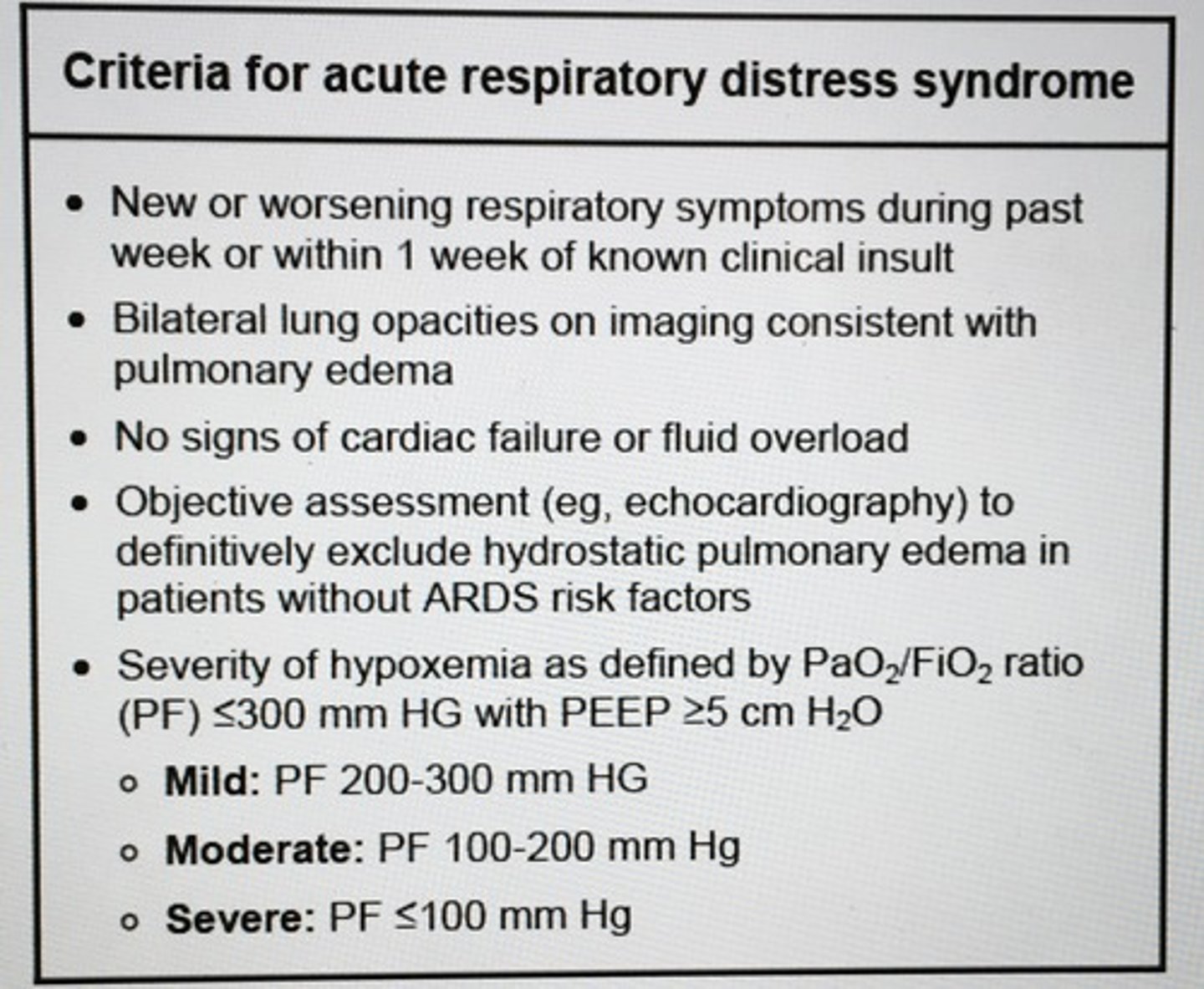
Criteria for ARDS
Longstanding ___ can cause severe LA enlargement leading to an elevation of the L main bronchus on CXR. A.fib common complication. Pt presents with gradual and progressive worsening dyspnea or orthopnea.
MS -> rheumatic HD
- opening snap after S2 (best heard at the apex), low pitched diastolic rumble at cardiac apex (pt on L side in held expiration)
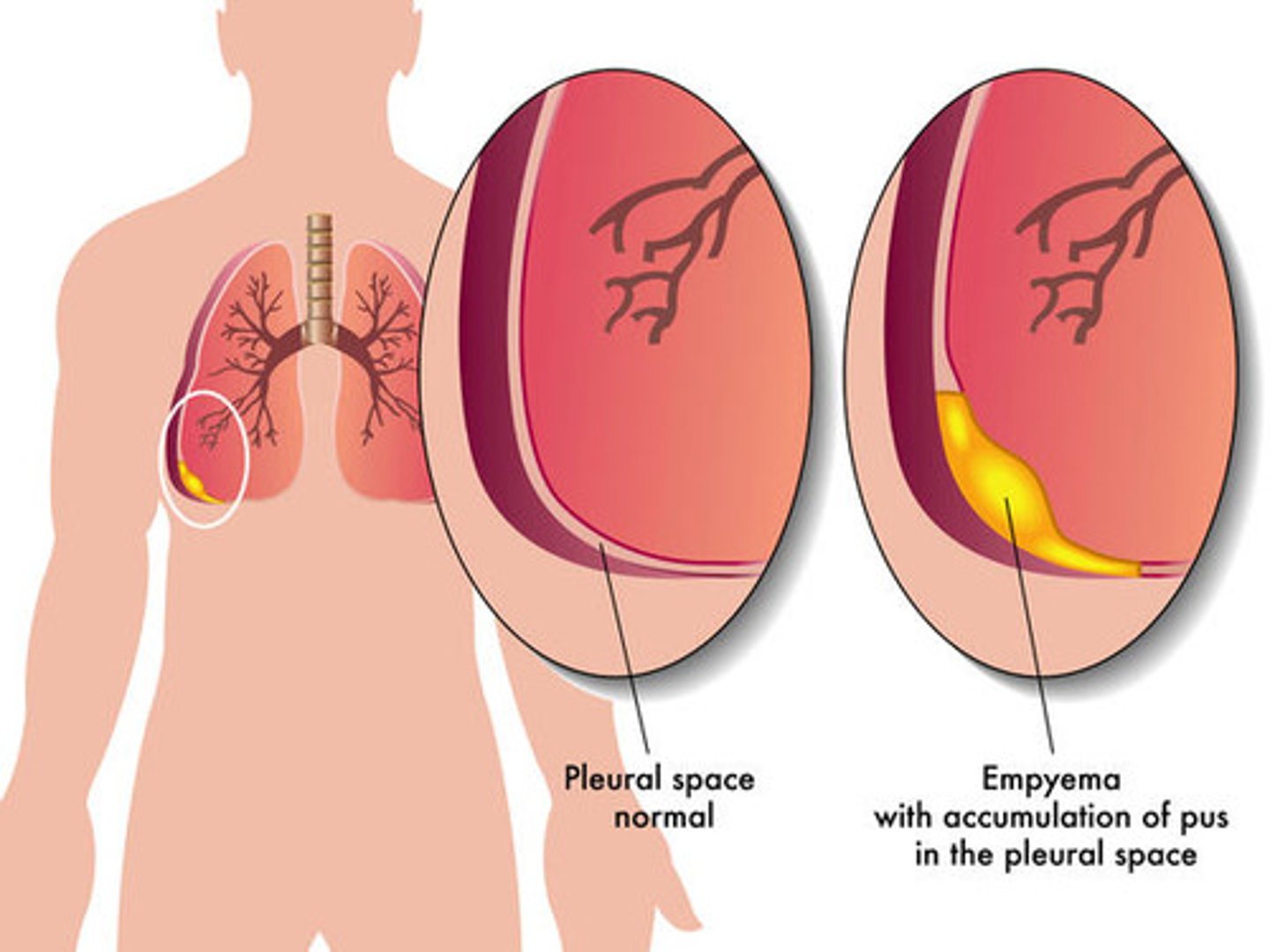
Pt has a hemothorax and developed an empyema dx by CT scan. When the empyema is localized, complex, and has a thick rim, only ___ is the answer.
Surgery
- thick pleural peel is removed, the pus is removed, the the chest is drained
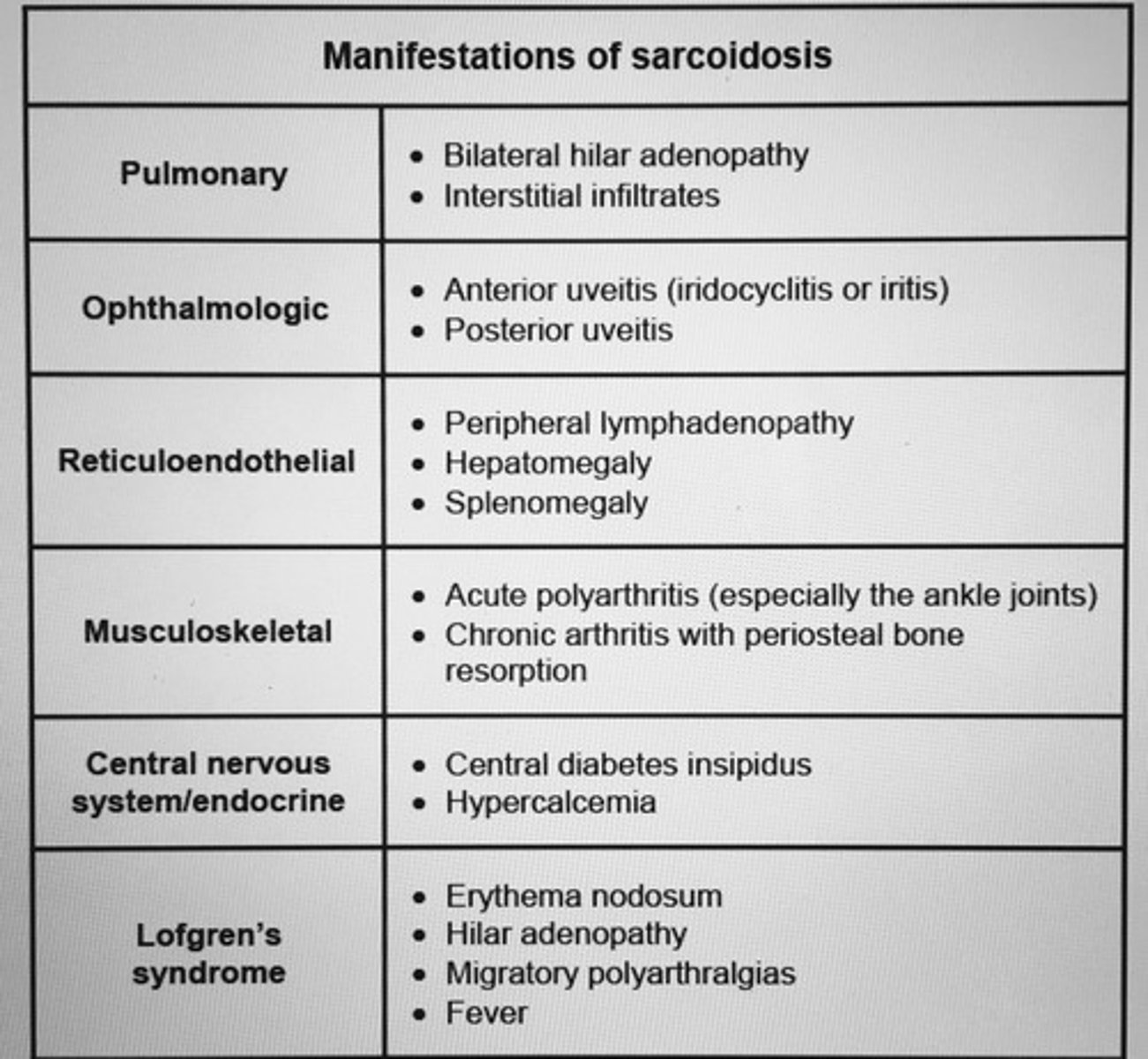
Manifestations of sarcoidosis
___ is the most common medical cause of excessive daytime sleepiness in the US.
Obstructive sleep apnea
- poor oropharyngeal tone and results in daytime sleepiness, morning HA, and depression
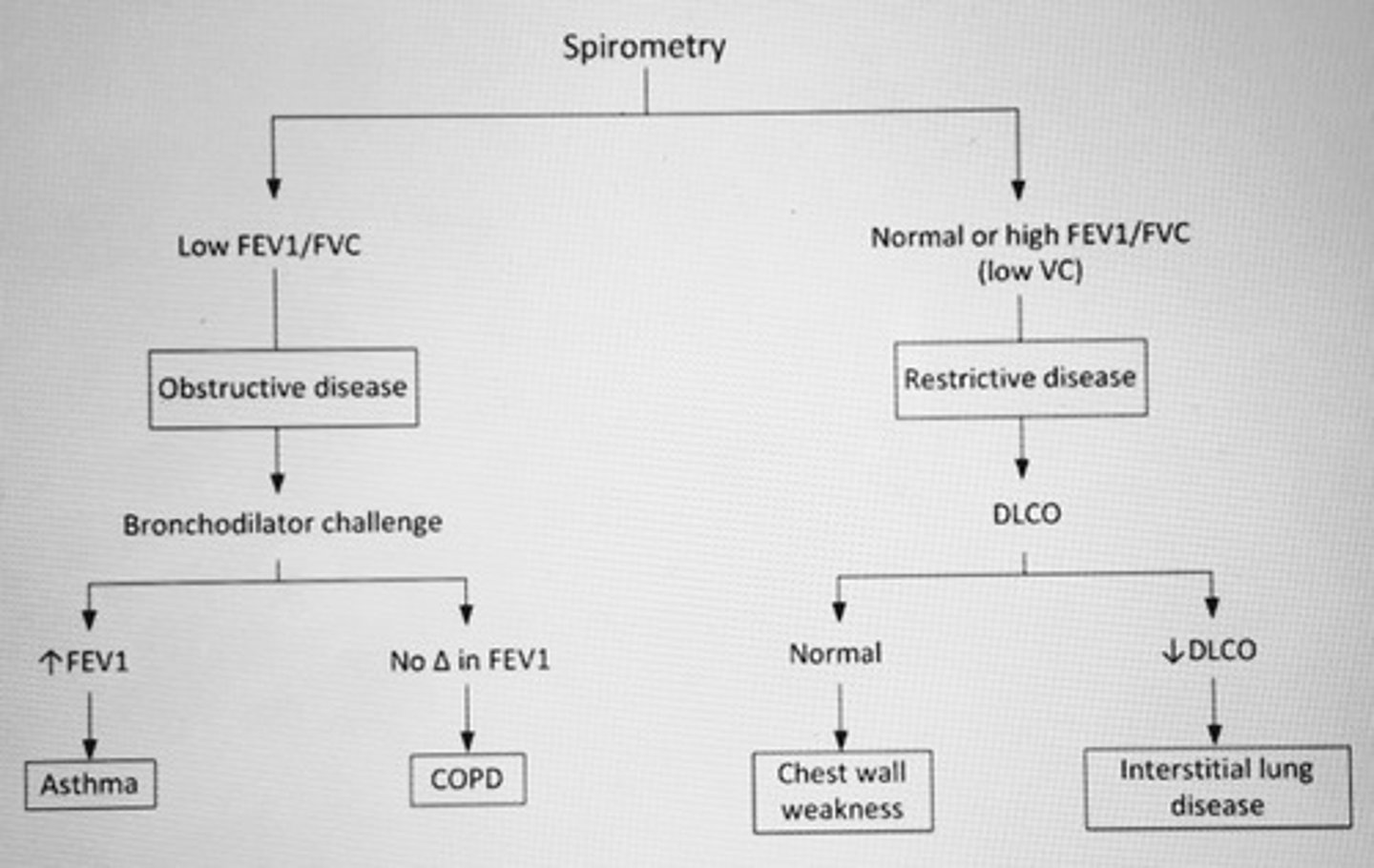
Spirometry in lung dz algorithm
Pts with chronic hypoventilation due to COPD, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, or neuromuscular causes have gradual INC in the __ that results in respiratory acidosis. To compensate, the ___ INC bicarb retention.
INC pCO2
KIDNEYs INC bicarb retention
* Pt able to contain normal pH but typically do not normalize or overcorrect their pH
Pt has a large anterior mediastinal mass with elevated levels of B-hCG and AFP consistent with a ___ tumor.
Nonseminomatous germ cell tumor
- confirm by biopsy
- testicular US exclude small primary tumor
- almost all germ cell tumors in the anterior mediastinum are primary than metastatic
__ is a neoplasm that is associated with systemic syndromes, including myasthenia gravis and pemphigus.
Thymoma, neoplasm thymus
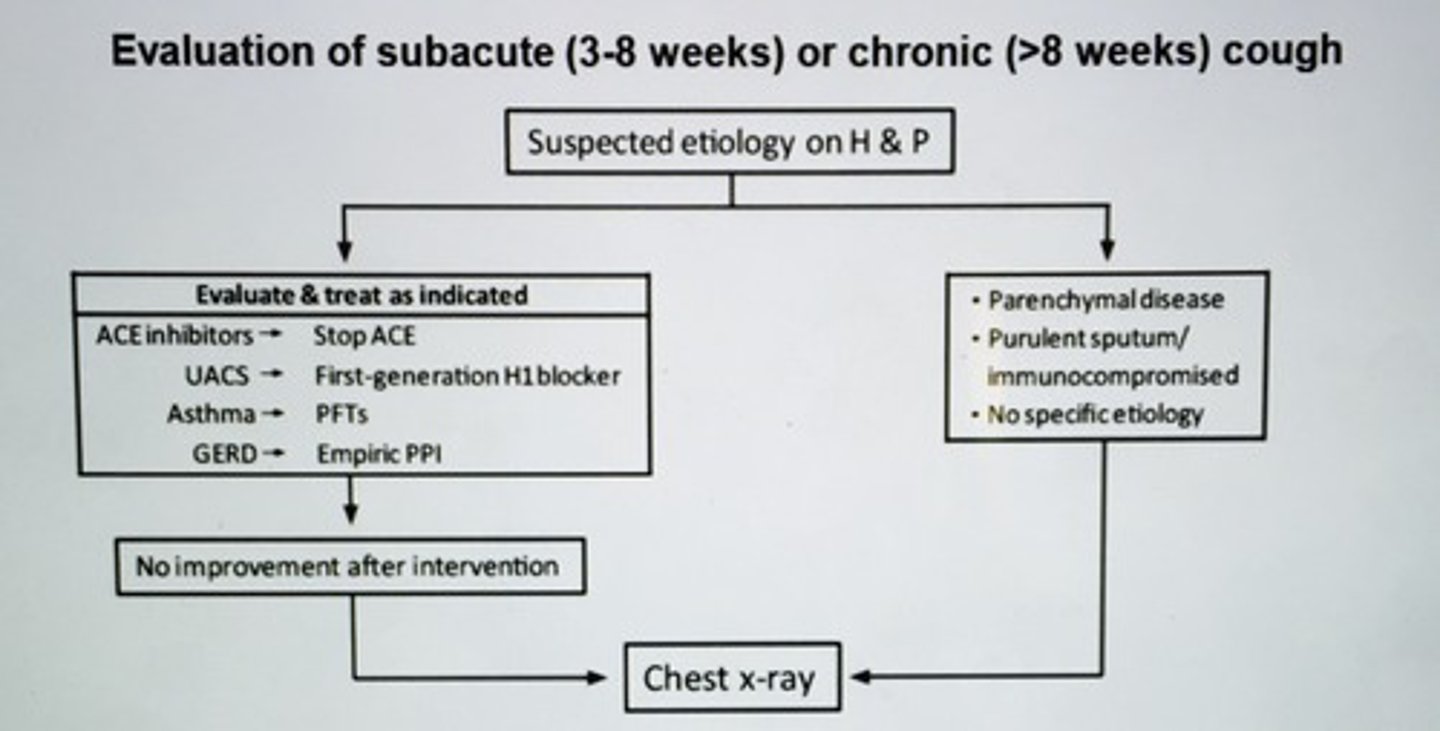
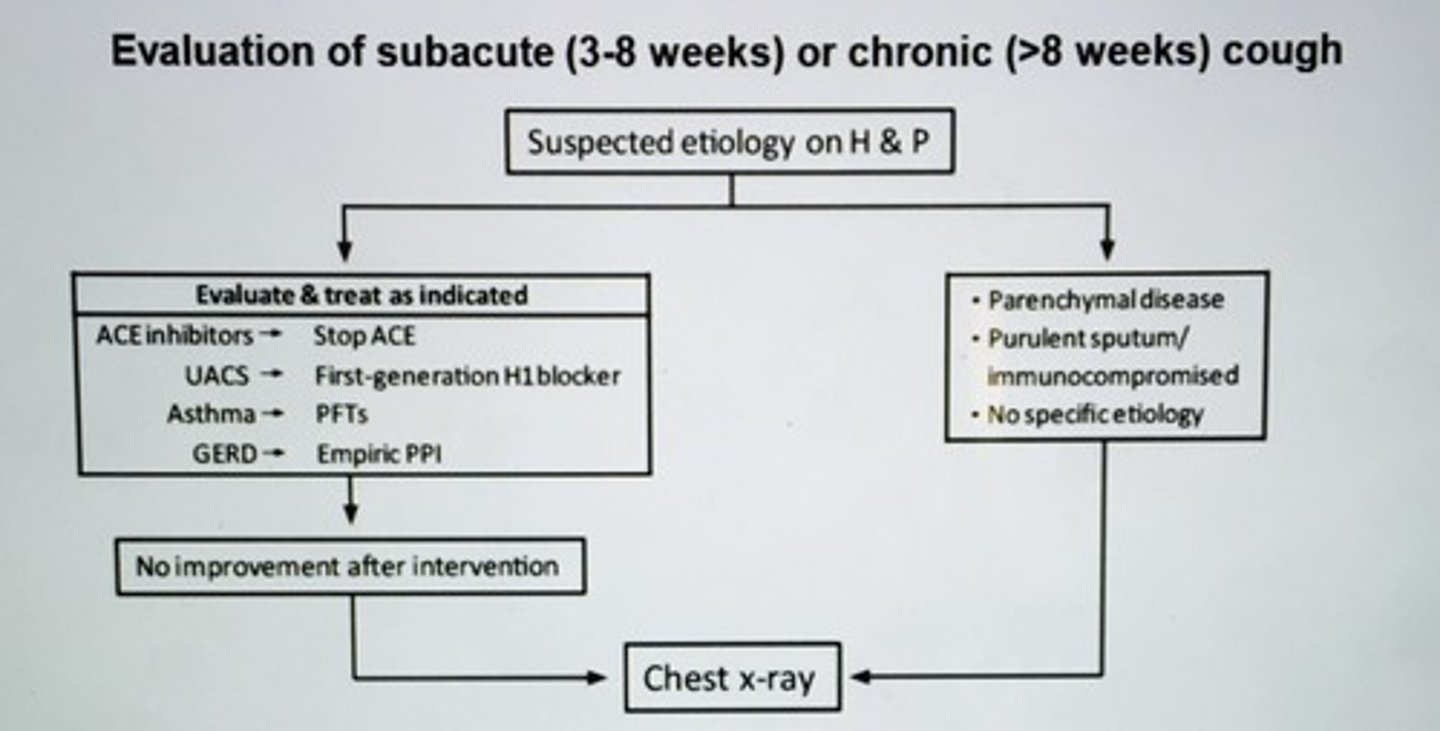
Evaluation of subacute (3-8 weeks) or chronic (>8 weeks) cough algorithm
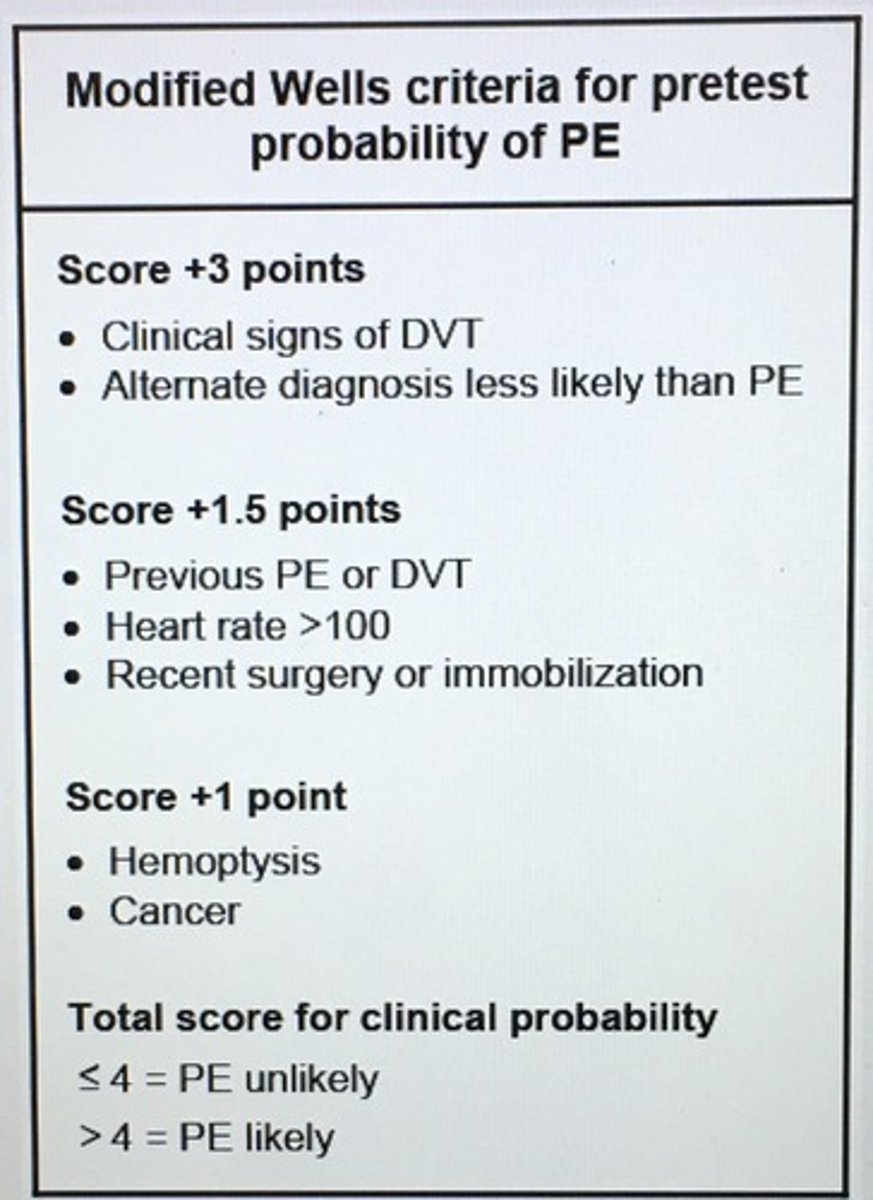
Modified Wells criteria for pretest probability of PE.
What model is used to assess risk in community acquired pneumonia and need to inpatient therapy?
CURB-65
Confusion
Uremia (BUN>20 mg/dL)
Tachycardia (Respiration > 30/min)
Hypotension (Blood pressure < 90/60 mm Hg)
Age > 65
2 or more benefit inpatient tx
> 4 need ICU admission
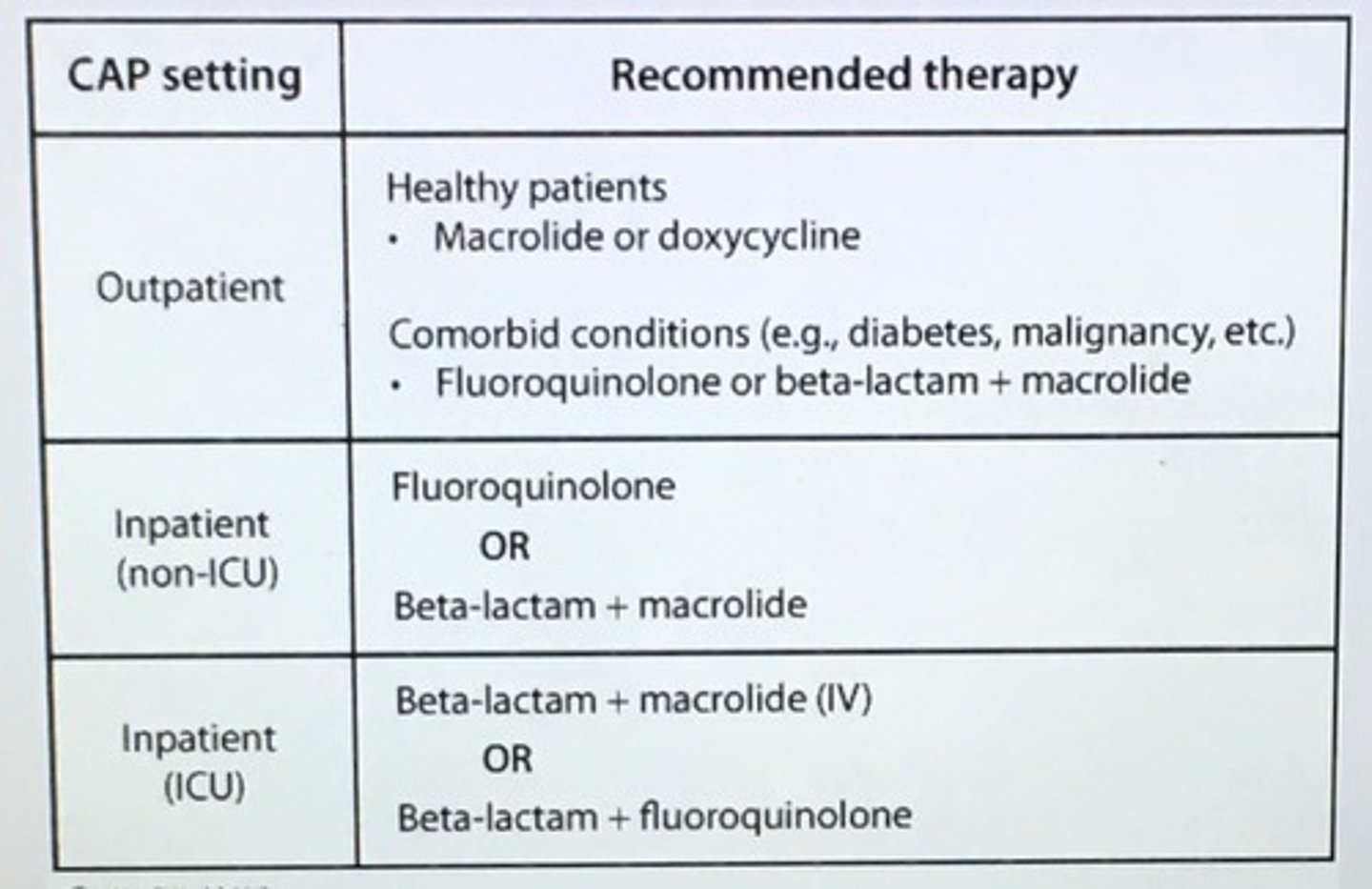
Community acquired pneumonia setting and abx treatment choice.
Evaluation of subacute (3-8 weeks) or chronic (> 8 weeks) cough.
Post-nasal drip (upper airway cough syndrome) give first generation antihistamine (chlorpheniramine) or combo antihistamine-decongestant (bropheniramine and pseudo ephedrine)
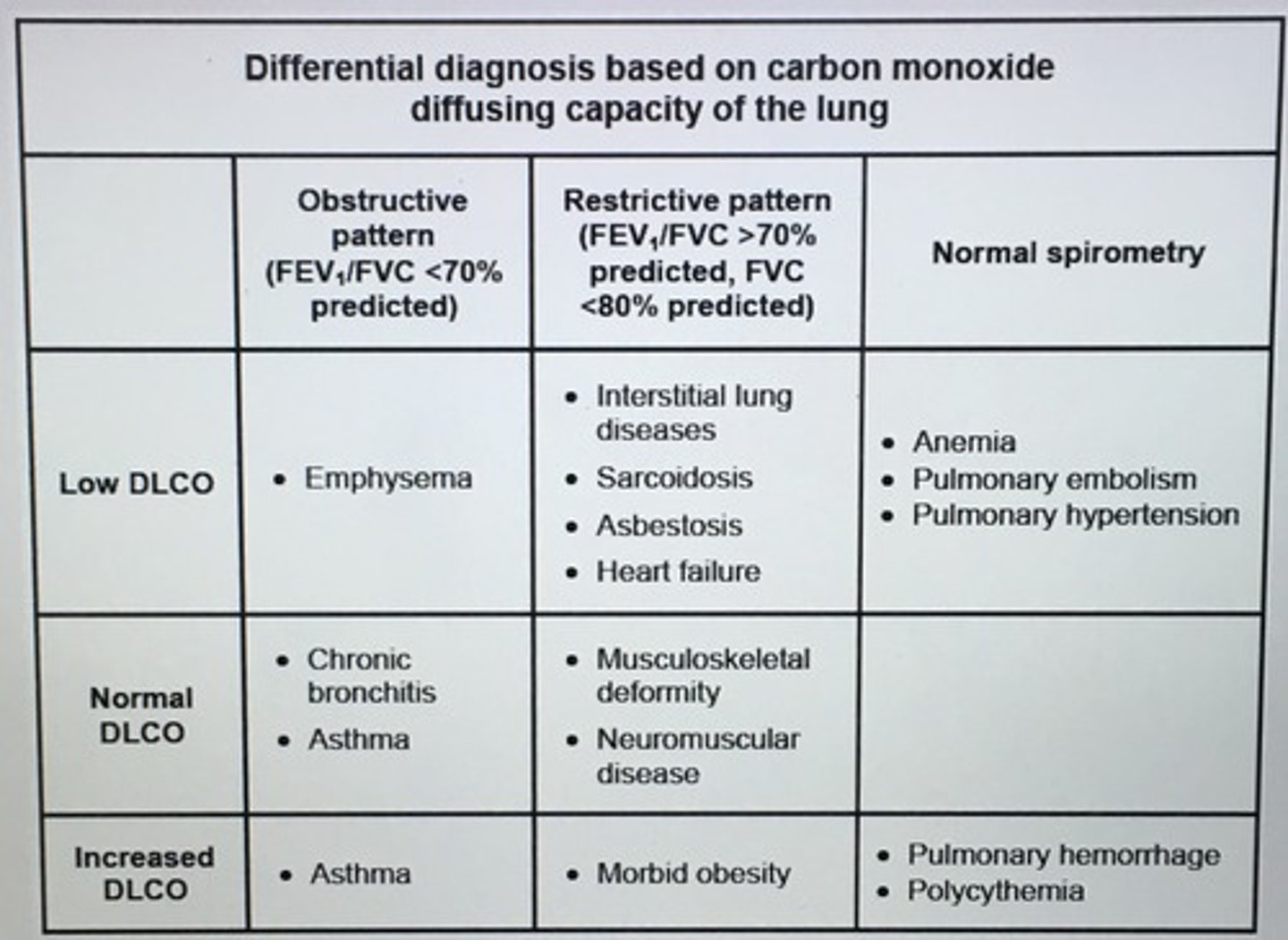
Clinical features of asbestosis

___ pattern with decreased lung volume, decreased diffusion lung capacity, and normal FEV1/FVC ratio.
Restrictive lung disease
Differential diagnosis based on carbon monoxide diffusing capacity of the lung.
Suspect ___ of the lung in patient with a significant smoking history, hypercalcemia, and a hilar mass.
Squamous cell carcinoma
(sCa++mous)
- PTHrP
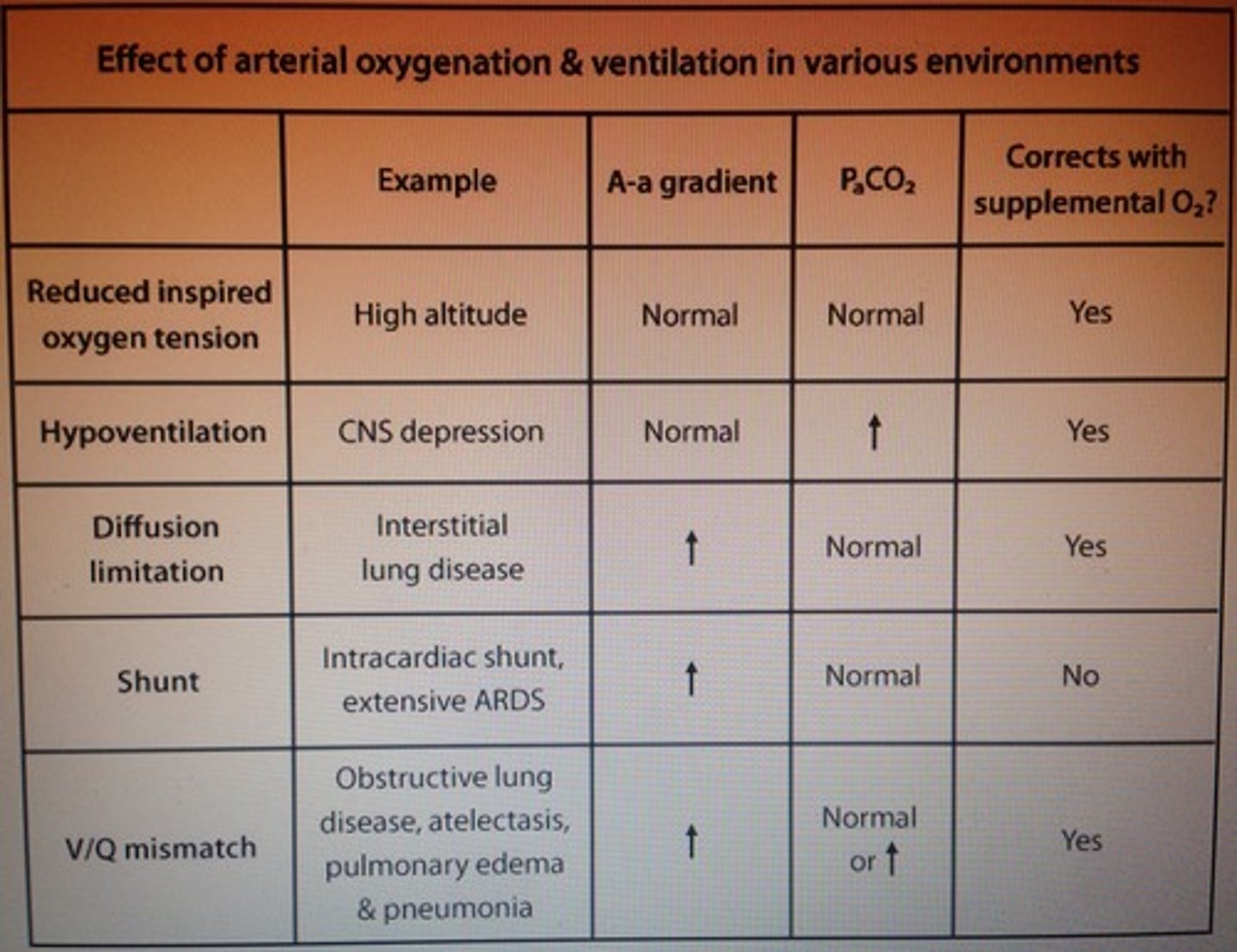
Effect of arterial oxygenation & ventilation in various environments
Pts with severe asthma exacerbation should received?
Inhaled SABA
Inhaled ipratropium
Systemic steroids
*Endotracheal intubation as needed
___ isolated right sided heart failure (RHF) from pulmonary HTN most commonly 2/2 COPD.
Cor pulmonale
- JVD
- INC intensity P2 (pulmonic component 2nd heart sound)
- RV heave
- Hepatomegaly
- Dependent pitting edema
- Possible ascites
Gold standard dx: Right heart catheterization
This organism is endemic in the Mississippi and Ohio river valleys and Central America. Bird or bat guano droppings. Inhalation of spores.
Histoplasa capsulatum
___ classically presents with sudden-onset pleuritic chest pain, cough, dyspnea, and hemoptysis. CT shows wedge-shaped infarction.
Pulmonary emboli
Which arrhythmia is associated with PE?
A.fib (irregular RR intervals, absent P waves, narrow QRS complexes) caused by atrial strain from INC RA pressure
What factors are associated with a poor prognosis in PE?
Low O2 saturation
A.fib
Most common causes of secondary digital clubbing.
Lung malignancies
CF
R to L cardiac shunts
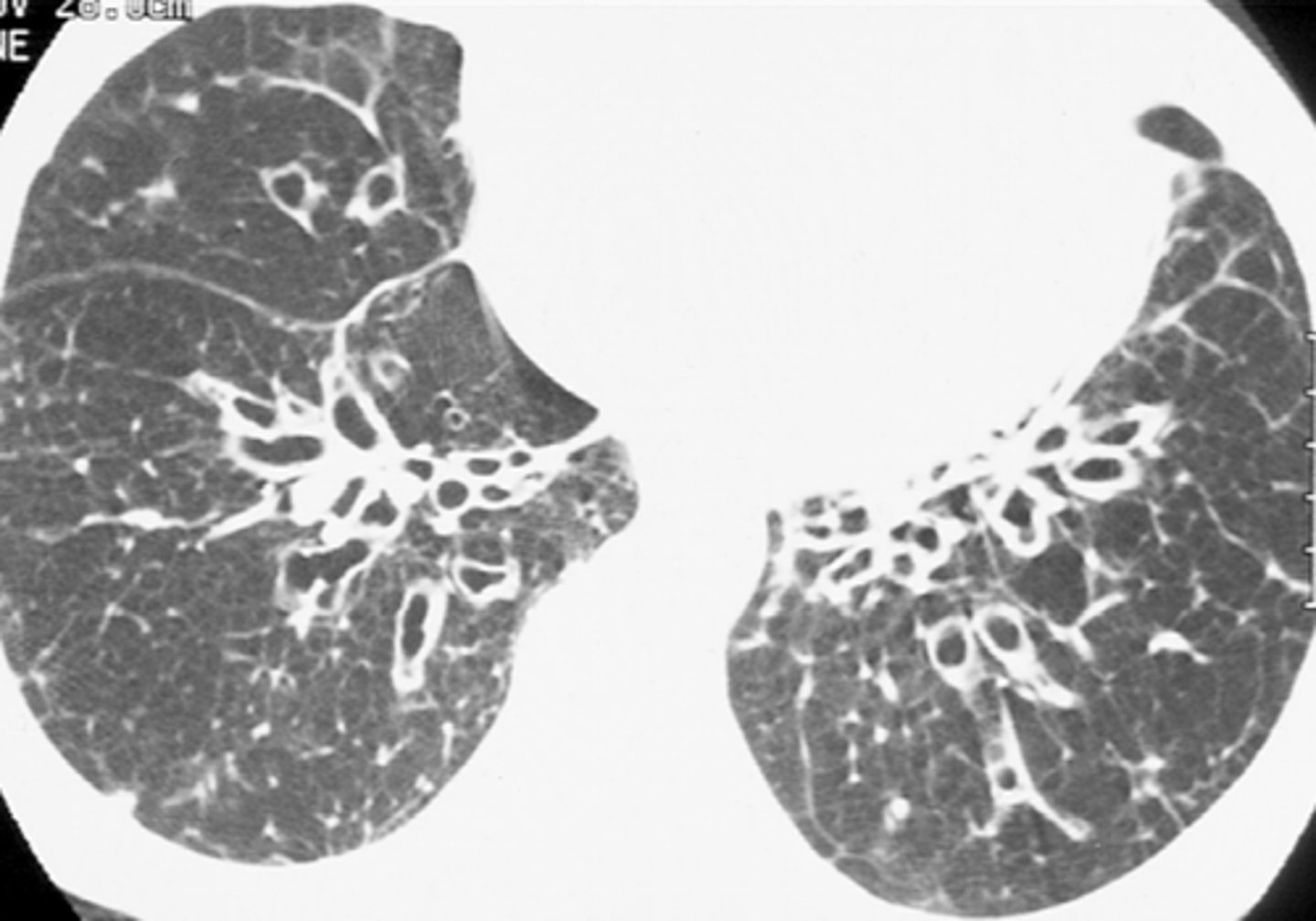
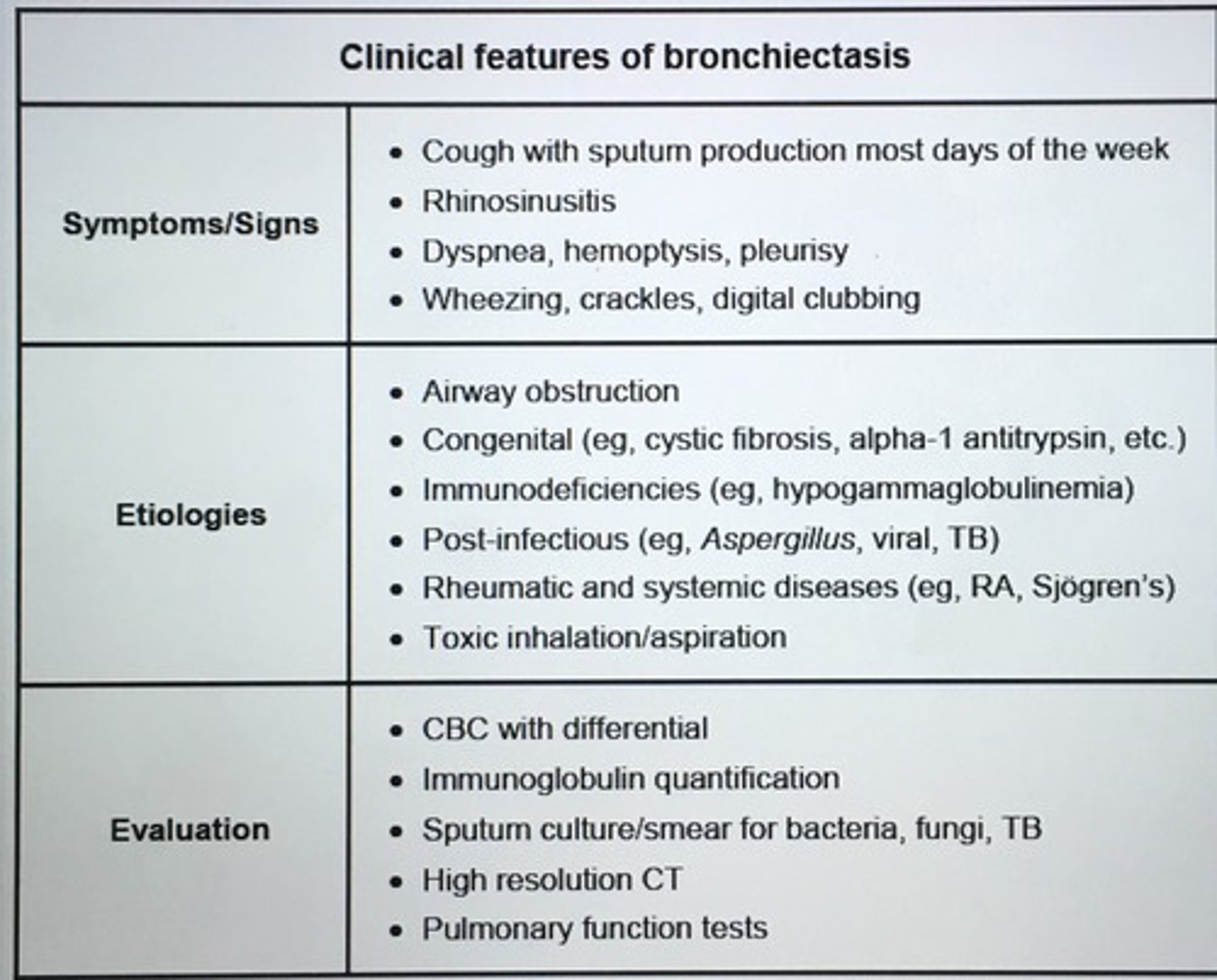
___ can be ID on CT by the presence of dilated bronchi with thickened walls. It can occur in any patient where there is pulmonary infection accompanied by either decreased airway drainage or impaired immune defense. ___ is a potential complication.
Bronchiectasis
Hemoptysis
Secondary pneumothorax should be suspected in COPD patients presenting with catastrophic worsening of their respiratory sxs and is usually due to ___.
Dilated alveolar blebs that rupture air into the pleural space
___ are exudative effusions with a low glucose concentration due to the high metabolic activity of leukocytes and bacteria within the pleural fluid.
Empyema
___ intubation is relatively common complication of endotracheal intubation. It causes symmetrical chest expansion during inspiration and marked decreased or absent breath sounds on the L side on auscultation.
Right mainstem bronchus
- repositioning the ET tube by pulling back slightly will move the tip between the carina and vocal cords and solve the problem
FiO2 should be reduced as soon as possible below levels that predispose to O2 toxicity. Which level?
FiO2 < 60%
- mechanical ventilation improves oxygenation by providing an increased fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) and PEEP
- O2 can lead to oxygen toxicity pro inflammatory oxygen free radicals predispose to atelectasis as alveoli nitrogen is displaced
Inhaled albuterol and systemic steroids are appropriate treatment for acute asthma attacks. Patients on high dose beta-2 agonists may develop ___ which may presents with muscle weakness, arrhythmias, and EKG abnormalities. Tremor, palpitations, HA.
Hypokalemia
- driving K+ into the cells via beta-2 agonists
___ is inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by antigen exposure. Acute episodes present with cough, breathlessness, fever, and malaise that occur within 4-6 hours of antigenic exposure. Chronic exposure may cause weight loss, clubbing, and honeycombing of the lung.
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP)
- tx is avoidance of the responsible antigen
The development of clubbing and sudden-onset joint arthropathy in a chronic smoker is suggestive of ___.
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
- associated with lung cancer
- CXR r/o malignancy
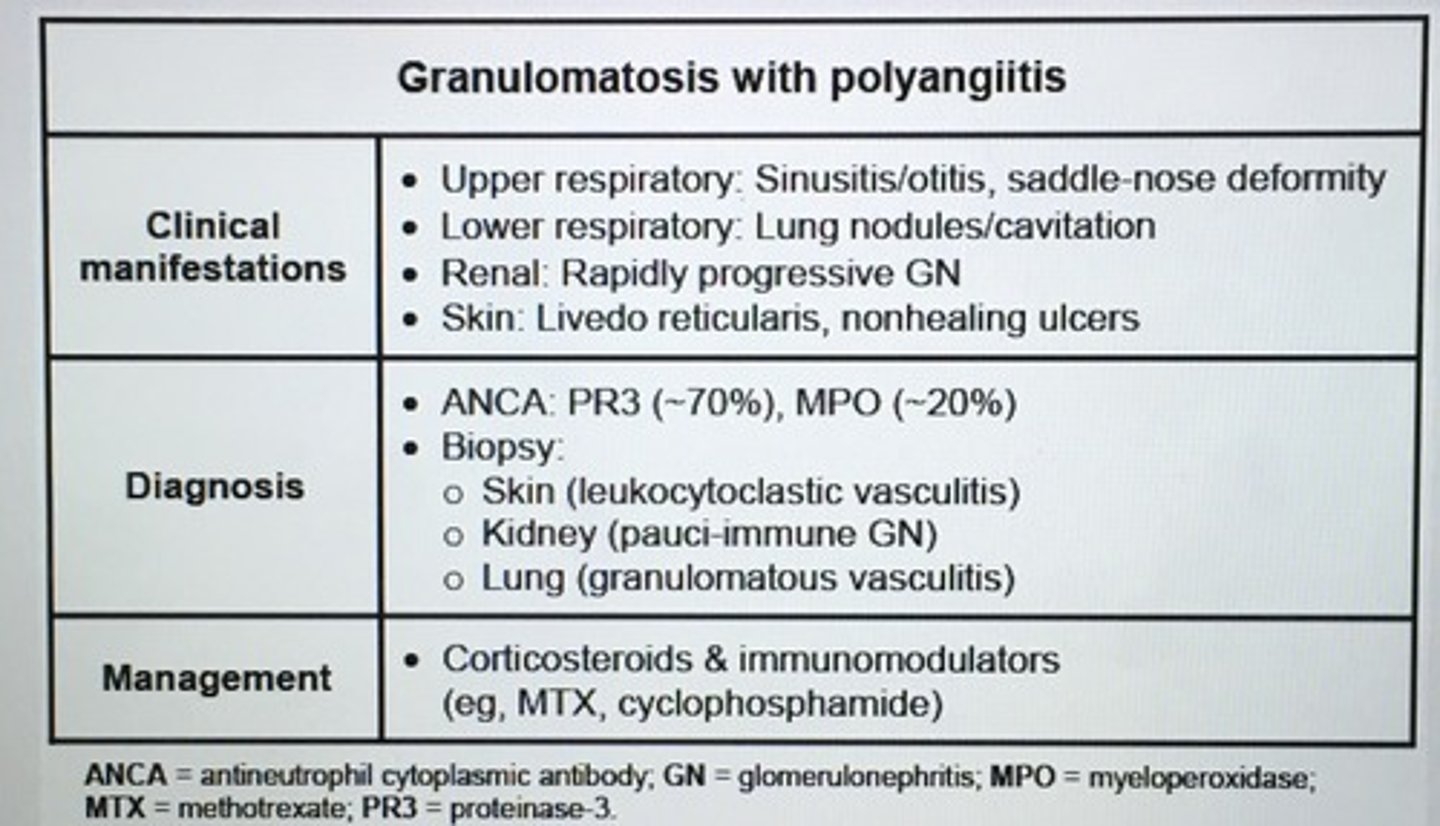
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis clinical features, dx, management.
For anticoagulation ___ is preferred over LMWH, fondaparinux, and rivaroriban in patient with severe renal insufficient (eGFR < 30 mL/1.73m2) as reduced renal clearance INC anti-Xa activity levels and bleeding risk.
unfractioned heparin
- aPTT
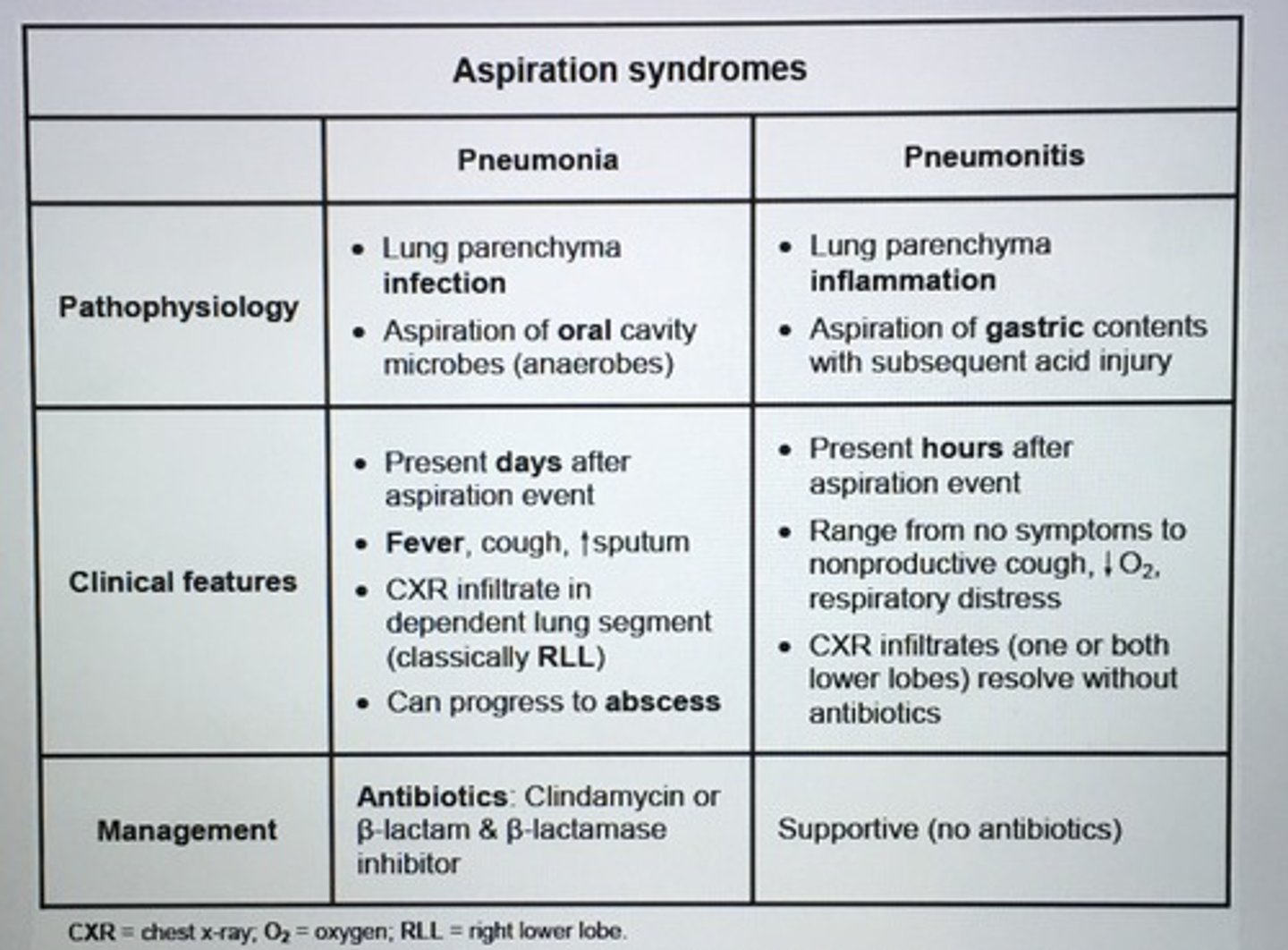
Aspiration syndromes pneumonia vs pneumonitis.
Pathophysiology of ARDS.
Lung injury -> fluid/cytokine leakage into alveoli
Impaired gas exchange, DEC lung compliance, PHTN, INC elastic recoil of edematous lungs, loss surfactant
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency should be considered in a number of situations including patients with?
1. COPD at a young age (<45)
2. COPD with minimal or no smoking history
3. Basilar-predominant COPD
4. Hx of unexplained liver disease
dx: measure AAT levels, and PFT
tx: IV supplementation with pooled human AAT
___ presents with cough, mucopurulent sputum, and hemoptysis that often responds to antibiotics.
Bronchiectasis
> 100mL/day sputum, fever, Pseudomonas infections
- crackles, rhonchi, and wheezes on lung exam
- high resolution CT preferred for dx
Asthma name the 4 categories.
1. Intermittent
2. Mild persistent
3. Moderate persistent
4. Severe persistent
HIGH YIELD: Undiagnosed pleural effusion is best evaluated with ___, except in patients with clear-cut evidence of CHF.
Thoracentesis
__ cause neutrophilic by increasing bone marrow release and mobilizing the marginated neutrophil pool. Eosinophils and lymphocytes are decreased.
Glucocorticoids
Which lung tumor is in the periphery, associated with gynecomastia and galactorrhea?
Large cell carcinoma
___ most common type of primary lung cancer in both smokers and nonsmokers.
Adenocarcinoma
- periphery
- stage at diagnosis is the most important prognostic factor, with survival determined primarily by resectability