Articulation and Prosody
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is the segmental aspect of speech?
A) speech sound production
B) prosody (pitch, duration, loudness, rhythm, stress patterns, etc.)
speech sound production
What is the suprasegmental aspect of speech?
A) speech sound production
B) prosody (pitch, duration, loudness, rhythm, stress patterns, etc.)
prosody (pitch, duration, loudness, rhythm, stress patterns, etc.)
What are the most prevalent characteristics of patients with dysarthria?
A) imprecise consonants and distorted vowels
B) equal pitch and stress
C) fast rate and monoloudness
imprecise consonants and distorted vowels
True or False
Traditional artic tx is seldom effective for speakers with dysarthria
True
What is the sequence of training for the segmental aspects of speech?
A) optimize other subsystems of speech first before focusing on the artic performance.
B) optimize articulation first before focusing on the other subsystems of speech.
optimize other subsystems of speech first before focusing on the artic performance.
Which of the following is correct about perceptual ratings of speech component?
A) Perceptual measurements are widely used for clinical assessment.
B) Overall perception of articulatory performance, and how it compares to performance of the other speech subsystems.
C) AMRs and SMRs used to assess articulation rates and regularity of movement.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
All of the above
Perceptual measurements are widely used for clinical assessment. Overall perception of articulatory performance, and how it compares to performance of the other speech subsystems. AMRs and SMRs used to assess articulation rates and regularity of movement.
Why have traditional artic inventories such as Fisher-Logemann and word lists thay sample all speech sounds have not been accepted as part of clinical assesssment?
A) The clinicians’ perceptual judgements are not always true.
B) Distorted but recognizable vs distorted but no longer within phoneme boundaries.
C) Overestimation of the accuracy of productions
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
All of the above
The clinicians’ perceptual judgements are not always true. Distorted but recognizable vs distorted but no longer within phoneme boundaries. Overestimation of the accuracy of productions
Which of the following are considered better assessment tools for articulation inventories for those with dysarthria?
A) Speech Intelligibility Test (SIT) - word and sentence level
B) Fisher-Logemann/word lists
C) Kent et. al. protocol - looks at 19 acoustic-phonetic contrasts
D) A and B
E) A and C
F) B and C
G) All of the above
Speech Intelligibility Test (SIT) - word and sentence level
Kent et. al. protocol - looks at 19 acoustic-phonetic contrasts
What are Restoration-Normalizing Function treatment approaches?
A) Medical Management, Biofeedback training, Strengthening exercises
B) Prosthetic, Behavioral
Medical Management, Biofeedback training, Strengthening exercises
What are compensation treatment approaches?
A) Medical Management, Biofeedback training, Strengthening exercises
B) Prosthetic, Behavioral
Prosthetic, Behavioral
Which of the following is correct about medical management restoration approach?
A) May have some spontaneous recovery as with Guillain-Barre, stroke.
B) Some symptoms of Parkinson’s are managed with medication,
C) Reducing tone: Antispasticity meds for spastic dysarthria, botox for hyperkinetic dysarthria
D) Surgery may restore function –anastomosis, CN VII is linked to CN XII to restore Fx
E) All of the above
F) None of the above
All of the above
May have some spontaneous recovery as with Guillain-Barre, stroke.
Some symptoms of Parkinson’s are managed with medication,
Reducing tone: Antispasticity meds for spastic dysarthria, botox for hyperkinetic dysarthria
Surgery may restore function –anastomosis, CN VII is linked to CN XII to restore Fx
Which of the following is correct about stretching and relaxing restoration approach?
A) Most applicable for patients with spasticity and rigidity – no evidence for or against this practice
B) Jaw – sustained max jaw opening, Lip – retraction, pursing, and puffing, Tongue – protrusion, retraction or lateralization
C) Caution: Because the lips and tongue do not demonstrate a typical pattern of stretch reflexes, stretching of those structures may not be beneficial.
D) All of the above
All of the above
Most applicable for patients with spasticity and rigidity – no evidence for or against this practice
Jaw – sustained max jaw opening, Lip – retraction, pursing, and puffing, Tongue – protrusion, retraction or lateralization
Caution: Because the lips and tongue do not demonstrate a typical pattern of stretch reflexes, stretching of those structures may not be beneficial.
Which of the following is correct about biofeedback restoration approach?
A) Usually used to reduce abnormally high muscle tone
B) sEMG: Electrodes placed on lips, jaw, forehead, etc. and an alert signals pt when muscle has too much tone.
C) Must be evidence that the spasm or hypertonicity is contributing to degraded speech and is amenable to treatment (can be changed)
D) Can work to increase general relaxation – monitoring frontalis tension
E) Electropalatography – evidence of positive effects on intelligibility
F) All of the above
All of the above
Usually used to reduce abnormally high muscle tone
sEMG: Electrodes placed on lips, jaw, forehead, etc. and an alert signals pt when muscle has too much tone.
Must be evidence that the spasm or hypertonicity is contributing to degraded speech and is amenable to treatment (can be changed)
Can work to increase general relaxation – monitoring frontalis tension
Electropalatography – evidence of positive effects on intelligibility
Which of the following is correct about strengthening restoration approach?
A) OME’s can be beneficial when weakness is present and interferes with speech production e.g., flaccid dysarthrias
B) OMEs have been shown to improve function of cranial nerves V, VII, and XII
C) May need to start with physical assist, but goal is to move against resistance
D) OMEs contraindicated for myasthenia gravis, ALS
E) Non-speech OME’s do not have good support in research (Do not use if Pt is not willing to do regularly to gain benefit. Do not delay other intervention until the Pt “is strong enough”. Iowa Oral Performance Instrument)
F) All of the above
G) None of the above
All of the above
OME’s can be beneficial when weakness is present and interferes with speech production e.g., flaccid dysarthrias
OMEs have been shown to improve function of cranial nerves V, VII, and XII
May need to start with physical assist, but goal is to move against resistance
OMEs contraindicated for myasthenia gravis, ALS
Non-speech OME’s do not have good support in research (Do not use if Pt is not willing to do regularly to gain benefit. Do not delay other intervention until the Pt “is strong enough”. Iowa Oral Performance Instrument)
What is a prosthetic compensation approach for articulation?
A) bite block
B) palatal lift
C) Nasal obturator
bite block
WHat are behavioral compensation approaches?
A) bite block
B) Contrastive Production
C) Intelligibility Drills
D) A and B
E) A and C
F) B and C
Contrastive Production and Intelligibility Drills
What are contrastive production drills?
A) Drills with minimal pairs - direct client to make the salient sounds as different as possible
B) word sets - client is prompted for best production of sets of words that are produced without the clinician seeing the visual
Drills with minimal pairs - direct client to make the salient sounds as different as possible
What are Intelligibility drills?
A) Drills with minimal pairs - direct client to make the salient sounds as different as possible
B) word sets - client is prompted for best production of sets of words that are produced without the clinician seeing the visual
word sets - client is prompted for best production of sets of words that are produced without the clinician seeing the visual
What is the order of the steps of Intelligibility Drills?
A) The speaker attempts a word or phrase (consider how you would use carrier phrases); The listener makes a guess; If the listener is incorrect, the speaker tries again. If wrong again, this necessitates another means of repair, can build in time for supplementation. Caregivers and other comm. partners need to help, even Siri
B) The speaker attempts a word or phrase (consider how you would use carrier phrases); If wrong again, this necessitates another means of repair, can build in time for supplementation. The listener makes a guess; If the listener is incorrect, the speaker tries again. Caregivers and other comm. partners need to help, even Siri
The speaker attempts a word or phrase (consider how you would use carrier phrases); The listener makes a guess; If the listener is incorrect, the speaker tries again. If wrong again, this necessitates another means of repair, can build in time for supplementation. Caregivers and other comm. partners need to help, even Siri
Which of the following is incorrect about prosody and suprasegmental aspects of speech?
A) •A Greek word that means “to add song”
B) The melodic aspect of speech that signal linguistic and emotional features
C) Prosody can make a marked impact on intelligibility- serves many functions in speech
D) The role of the prosodic code is not understood as well as the phonemic code
E) Don’t discount work on prosody or save it for last in Tx
F) Optimize other subsystems of speech first before focusing on the prosody performance.
Optimize other subsystems of speech first before focusing on the prosody performance.
What is stress patterning perceptually?
A) timing pattern
B) changes in pitch
C) emphasis on a particular syllable
emphasis on a particular syllable
What is intonation perceptually?
A) timing pattern
B) changes in pitch
C) emphasis on a particular syllable
changes in pitch
What is rate-rhythm perceptually?
A) timing pattern
B) changes in pitch
C) emphasis on a particular syllable
timing pattern
What is stress patterning acoustically?
A) changes in F0
B) longer duration, high dB, higher F0
C) segmental and pause durations
longer duration, high dB, higher F0
What is intonation acoustically?
A) changes in F0
B) longer duration, high dB, higher F0
C) segmental and pause durations
changes in F0
What is rate-rhythm acoustically?
A) changes in F0
B) longer duration, high dB, higher F0
C) segmental and pause durations
segmental and pause durations
WHat are the most common features of prosody in dysarthria?
A) imprecise consonants and distorted vowels
B) monopitch and monoloudness
monopitch and monoloudness
Which characteristics of prosody best match Ataxic dysarthria?
A) Excess and equal stress (scanning speech) especially in cerebellar lesions.
B) Variable rate, prolonged intervals, and monopitch in chorea.
C) Overly fast rate in Parkinson’s
Excess and equal stress (scanning speech) especially in cerebellar lesions.
Which characteristics of prosody best match Hyperkinetic dysarthria?
A) Excess and equal stress (scanning speech) especially in cerebellar lesions.
B) Variable rate, prolonged intervals, and monopitch in chorea.
C) Overly fast rate in Parkinson’s
Variable rate, prolonged intervals, and monopitch in chorea.
Which characteristics of prosody best match Hypokinetic dysarthria?
A) Excess and equal stress (scanning speech) especially in cerebellar lesions.
B) Variable rate, prolonged intervals, and monopitch in chorea.
C) Overly fast rate in Parkinson’s
Overly fast rate in Parkinson’s
What are ways we can assess prosody?
A) Overall Rating of Naturalness
B) Assessment of Communicative Function
C) Speaker’s Understanding of the task
D) Analysis of Intonation and Stress Patterning
E) Perceptual Assessment of Accuracy and Naturalness
F) Acoustic Analysis of Habitual Prosodic Patterning
G) All of the above
All of the above
Overall Rating of Naturalness, Assessment of Communicative Function, Speaker’s Understanding of the task, Analysis of Intonation and Stress Patterning, Perceptual Assessment of Accuracy and Naturalness, Acoustic Analysis of Habitual Prosodic Patterning
What is overall rating of naturalness?
A) Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
B) Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
C) Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
D) Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
E) Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
F) Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
What is Assessment of Communicative function?
A) Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
B) Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
C) Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
D) Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
E) Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
F) Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
What is Speaker’s Understanding of the task?
A) Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
B) Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
C) Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
D) Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
E) Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
F) Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
What is Analysis of intonation and stress patterning?
A) Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
B) Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
C) Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
D) Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
E) Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
F) Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
What is perceptual assessment of accuracy and naturalness?
A) Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
B) Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
C) Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
D) Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
E) Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
F) Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
What is Acoustic analysis of habitual prosodic patterning?
A) Scale of 1-7, 1 = “natural speech”, & 7 = “highly unnatural”
B) Can the client successfully signal emotion, emphatic stress, and syntactic junctures when reading a sentence.
C) Verify that the speaker intended to emphasize the target word. Need to be certain that the patient understands the demands of the task. Asked questions where they need to put stress on a certain word in their response.
D) Habitual and Max breath group length, examination of individual breath groups
E) Is there a match between targeted stress and perceived stress? Unsuccessful due to lack of signal OR misleading or multiple signals? If there is a match, how close is it to what is anticipated or natural?
F) Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
Augments perceptual info and can help to tease out what is unnatural, what suprasegmental feature is being used.
What is stress patterning physiologically?
A) effort
B) respiration and vocal fold activity
C) movement rates
effort
What is intonation perceptually?
A) effort
B) respiration and vocal fold activity
C) movement rates
respiration and vocal fold activity
What is rate-rhythm physiologically?
A) effort
B) respiration and vocal fold activity
C) movement rates
movement rates
Which of the following speech dimensions relate to stress patterning?
A) monoloudness, monopitch, excessive loudness variation, loudness decay, alternating loudness, reduced stress, excess and equal stress
B) pitch level, monopitch, short phrases
C) rate, increased rate in segments, increased overall rate, variable rate, prolonged intervals, inappropriate silences, short rushes of speech
monoloudness, monopitch, excessive loudness variation, loudness decay, alternating loudness, reduced stress, excess and equal stress
Which of the following speech dimensions relate to intonation?
A) monoloudness, monopitch, excessive loudness variation, loudness decay, alternating loudness, reduced stress, excess and equal stress
B) pitch level, monopitch, short phrases
C) rate, increased rate in segments, increased overall rate, variable rate, prolonged intervals, inappropriate silences, short rushes of speech
pitch level, monopitch, short phrases
Which of the following speech dimensions relate to rate-rhythm?
A) monoloudness, monopitch, excessive loudness variation, loudness decay, alternating loudness, reduced stress, excess and equal stress
B) pitch level, monopitch, short phrases
C) rate, increased rate in segments, increased overall rate, variable rate, prolonged intervals, inappropriate silences, short rushes of speech
rate, increased rate in segments, increased overall rate, variable rate, prolonged intervals, inappropriate silences, short rushes of speech
What are some interventions for prosody
A) Generalization to spontaneous speech
B) indirect treatment of naturalness
C) All of the above
All of the above
Generalization to spontaneous speech & indirect treatment of naturalness
What is generalization to spontaneous speech?
A) sentence reading, paragraph reading, create short dialogues, scripts or even read plays if it is of interest, fade feedback, increase self-assessment and modification
B) monitor the multidimensional influences of intervention (pacing board vs LSVT)
sentence reading, paragraph reading, create short dialogues, scripts or even read plays if it is of interest, fade feedback, increase self-assessment and modification
What is indirect treatment of naturalness?
A) sentence reading, paragraph reading, create short dialogues, scripts or even read plays if it is of interest, fade feedback, increase self-assessment and modification
B) monitor the multidimensional influences of intervention (pacing board vs LSVT)
monitor the multidimensional influences of intervention (pacing board vs LSVT)
What is the general pattern for declarative?
A) low- high - reset - rising intonation
B) high - low - reset - falling intonation
C) low - reset - high - rising intonation
D) high - reset - low - falling intonation
high - low - reset - falling intonation
Which of the following is NOT part of the suprasegmental speech?
A) pitch
B) rhythm
C) stress patterns
D) articulation
articulation
True or False
Optimize artic performance first before focusing on the other subsystems of speech
False
Which of the following can stabilize the jaw and remove its impact on other articulators during perceptual assessment
A) tongue depressor
B) surface electromyography
C) bite block
D) electropalatography
bite block
You most likely do not use this test to evaluate articulation in a patient with dysarthria
A) AMRs and SMRs
B) Kent et al. protocol
C) Speech Intelligibility Test
D) Fisher-Logemann
Fisher-Logemann
Stretching of this structure may not be beneficial because it does not have a typical stretch reflexes?
A) Lip
B) tongue
C) jaw
D) A and B
E) A and C
F) B and C
A and B
lip and tongue
All the following statements are correct regarding using OME for artic treatment in dysarthria except
A) Can be specifically beneficial for patients with flaccid dysarthria
B) Shown to improve function of cranial nerves V, VII, and XII
C) Strong evidence exists regarding the effectiveness of non-speech OME’s on improving artic
D) Contraindicated for myasthenia gravis and ALS
Strong evidence exists regarding the effectiveness of non-speech OME’s on improving artic
One technique to modify production to improve intelligibility is overarticulation, during which we
A) increase word boundaries
B) contrast minimal pairs
C) changing the pitch
D) correct the articulation placement
increase word boundaries
What is the F0 contour within a breath unit in an interrogative sentence?
A) Reset -> high -> low
B) low -> high -> reset
C) High -> low -> reset
D) High -> reset -> low
low -> high -> reset
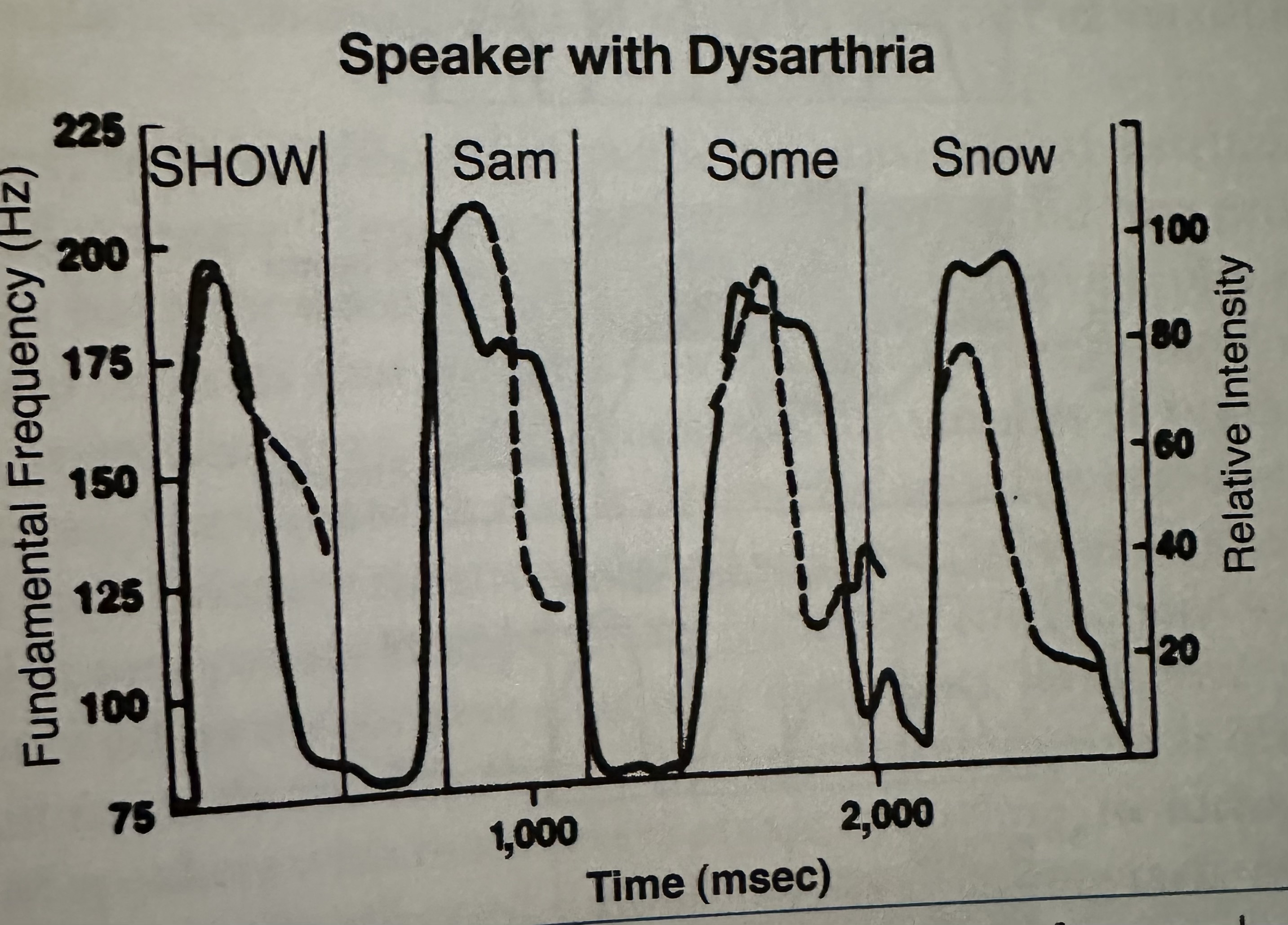
The following shows you an acoustic graph of a patient’s voice that should have stressed on the term “show” in a sentence. This acoustic profile likely belongs to patient with _____ dysarthria
A) hypokinetic
B) hyperkinetic
C) ataxic
D) flaccid
ataxic
Which of the following is an intervention designed to improve prosody in ataxic dysarthria?
A) Finger tapping for every syllable spoken
B) Reducing the loudness
C) Limiting variation in syllable durations
D) Prolongation of stressed syllables and use of pauses
Prolongation of stressed syllables and use of pauses
Video of woman with short hair, glasses, and dark lipstick on
What is the most prominent speech abnormality?
A) Scanning speech
B) Imprecise or distorted articulation
C) Strain-strangled voice
D) Monopitch & monoloudness
Imprecise or distorted articulation
Video of woman with short hair, glasses, and dark lipstick on
How was MPT?
A) Short
B) WNL
WNL
Video of woman with short hair, glasses, and dark lipstick on
How were the AMRs?
A) slow
B) WNL
C) /PA/ and /TA/ WNL but /KA/ was a bit slow
D) /PA/ was WNL but both /TA/ and /KA/ were slow
WNL
Video of woman with short hair, glasses, and dark lipstick on
How were the SMRs?
A) Slow
B) WNL
WNL
Video of woman with short hair, glasses, and dark lipstick on
How were the cough and coup?
A) Neither of them was sharp
B) The cough was sharp but not the coup
C) The coup was sharp but not the cough
D) Both were normal
Neither of them was sharp
Video of woman with short hair, glasses, and dark lipstick on
Which cranial nerves were affected?
A) V, VII, X
B) V, X, XII
C) IX, X, XII
D) VII, IX, X, XII
E) V, VII, IX, X, XII
IX, X, XII