Research psychology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
Gestalt Psychology
* Emphasizes understanding psychological phenomena as a whole that cannot be broken down into smaller parts.
\
* A whole is different than a sum of parts
\
* Some important quality is lost when the parts are considered alone
\
* no longer a sperate perspective
\
* A whole is different than a sum of parts
\
* Some important quality is lost when the parts are considered alone
\
* no longer a sperate perspective
2
New cards
Cultural psychology
* Emphasizes that thoughts and behvaior are shaped by social and cultural context
\
* Cultures and Societes differ in terms of what behavior is acceptable and what roles people may assume.
\
* Cultures and Societes differ in terms of what behavior is acceptable and what roles people may assume.
3
New cards
In order to be scientfiic a science like psychologicy must be:
Systematic and Objective
4
New cards
The scientific method is used by all fields of science including
Psychology
5
New cards
Scientific method
A general set of procedures for gathering and interpreting informations that limits sources errors and yields dependable results.
6
New cards
Componets include;
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
1 literature review
2 research quetsion
3 hypothesis
4 Procedure / methods
5 results
6 discusion validaty and reliablity
7 conclusion
2 research quetsion
3 hypothesis
4 Procedure / methods
5 results
6 discusion validaty and reliablity
7 conclusion
7
New cards
Hypotheisis
A tentative explanation for a set of facts or observations
It is a specific or educated guess
\
The more correct hypothesis the more you strengthen your theory
It is a specific or educated guess
\
The more correct hypothesis the more you strengthen your theory
8
New cards
Theory
A group of principles and hypotheses that combined explain some Phenomenon
\
* generak principles that explain area of inquiry
* not absoulte truth
\
* generak principles that explain area of inquiry
* not absoulte truth
9
New cards
What are three ways or types of measurements that psychologists use to collect data?
\
\
Direct naturalistic and mediated
10
New cards
Direct observation
Observation with the naked eye
Can intervene with behavior if deemed necessary
Can intervene with behavior if deemed necessary
11
New cards
Naturalistic observation
observation of naturally occurring behavior without changing the behavior
12
New cards
Mediated observation
Requires the use of special equipment or instrumentation IE EGG
13
New cards
Verbal reports
Survey or questionaires
Interviews
Interviews
14
New cards
Psychological tests
\-Asses an individual’s standing relative to others on some mental or behavioral characteristics
\-IQ tests, social readjustment and Rating scale SRRS for stress
\-IQ tests, social readjustment and Rating scale SRRS for stress
15
New cards
What are the four major types of research?
Historical, descriptive, correlational, experimental
16
New cards
Historical research
Use of previously published findings to study psychological issues.
17
New cards
Descriptive reasearch
Involves collecting data about conditions, attitudes, or characteristics of one subject or a group of subjects
\
\
18
New cards
Case study
An in depth investigation pf an individual
19
New cards
Cross sectional design
One group at one point in time
20
New cards
Longitudinal design
One group at multiple points in time
Come back after years to look at same group
Come back after years to look at same group
21
New cards
Sequential design
Combination of cross sectional and longitudinal designs
22
New cards
Correlational research
Attempts to determine whether a relationship exists between two or more quantifiable or measurable variables
Mathematically defined by correlation coefficient ( r) which ranges from. -1.00 to+1.00
Mathematically defined by correlation coefficient ( r) which ranges from. -1.00 to+1.00
23
New cards
ABC CORRELATIONAL RESEARCH
A Degree of the relationship. ( strong weak or no relationship )
B direction of the relationship (positive negative no relationship)
C cannot establish cause and effect
B direction of the relationship (positive negative no relationship)
C cannot establish cause and effect
24
New cards
Experimental research
Attempted ti define a cause and effect relationship through group comparisions
25
New cards
Independent variable
The cause or treatment
26
New cards
Dependent variable
Outcome being measured
27
New cards
Single blind desgin
Only the PARTICIPANTS are UNAWARE. Of the purpose lf the research
28
New cards
Double blind design
Both PARTICIPANTS and the RESEARCHERS assistanting the study are UNAWARE of the research conditions
29
New cards
Validity
The degree to which an instrument (equiment of test) measures what it is intended to measure
30
New cards
Reliability
Refers to consistency
31
New cards
InteRRater reliability
2 or more independent psychologists obtains ghe same resukt of diagnosis
32
New cards
IntraRater reliablity
1 psychologists consistently obtains the same result or diagnosis
33
New cards
4 main ethical safe guards
1 informed consent
2subjects can leave at anytime
3 debriefing must tell what happened
4response kept confidential
2subjects can leave at anytime
3 debriefing must tell what happened
4response kept confidential
34
New cards
What is the function of the nervous system?
Enables us to exist and interact with our environment
35
New cards
2 main divisions of central system
Central and peripheral ( BRAIN SPINE CORD)
36
New cards
Somatic
Voluntary and under your control
37
New cards
Auto nomic
Not under your control and involuntary
38
New cards
Sympathetic
Heart rate up
Blood pressure up
Breathing up pupil dilates
Digestion down
Blood pressure up
Breathing up pupil dilates
Digestion down
39
New cards
Parasympathetic
Heart rate down
Blood pressure down
Breathing down pupil constrict
Digestion up
Blood pressure down
Breathing down pupil constrict
Digestion up
40
New cards
Two major functions of the brain is
Control behavior and regulate the body’s physiologicak responses
41
New cards
Adult humanbrain weight
3-35 lbs
42
New cards
Adult human brain contains
100 billion neurons
43
New cards
\
\
\-% of total blood volume is in the brain
\
\-% of total blood volume is in the brain
20
44
New cards
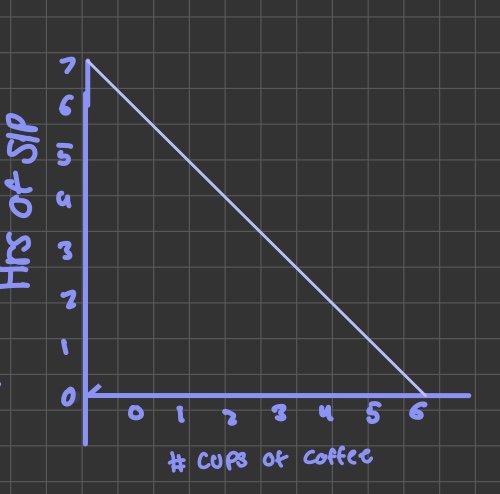
Negative
45
New cards
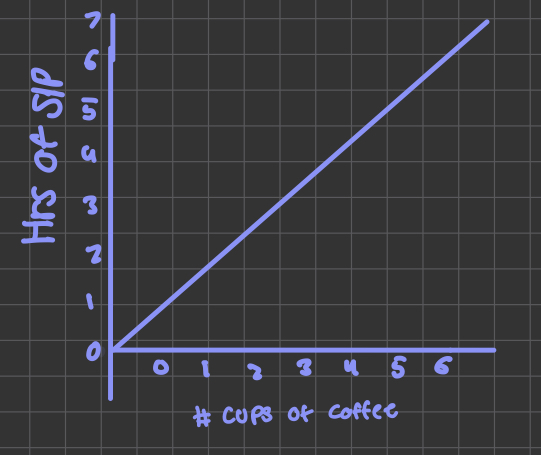
Positiven
46
New cards
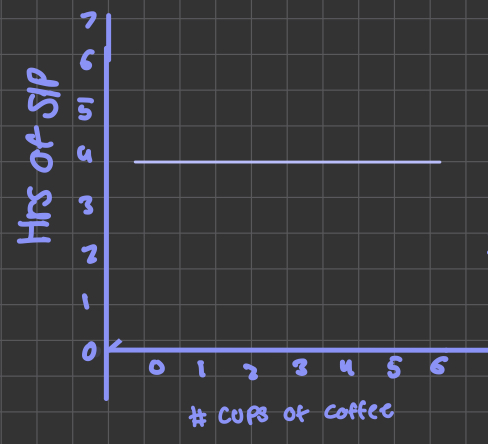
no correlation
47
New cards
PNS
Autonomic sinomic parasympathetic and sympathetic
48
New cards
Bone disc nerves
Peripheral
49
New cards
Brain and spinal cord
Central
50
New cards
2 main systems
Central peripheral