Nomenclature (naming organic compounds)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
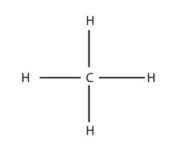
methane (1)
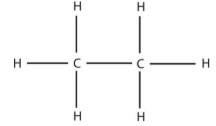
ethane (2)
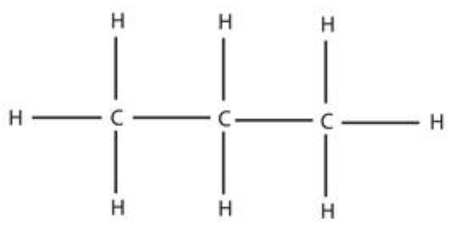
propane (3)
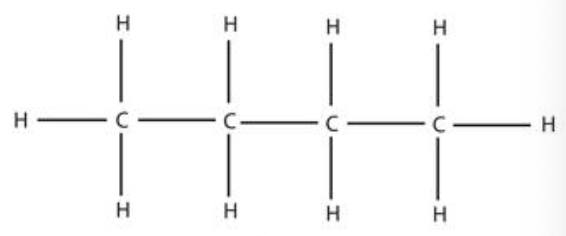
butane (4)
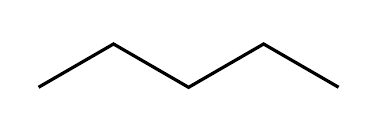
pentane (5)
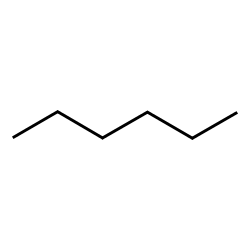
hexane (6)
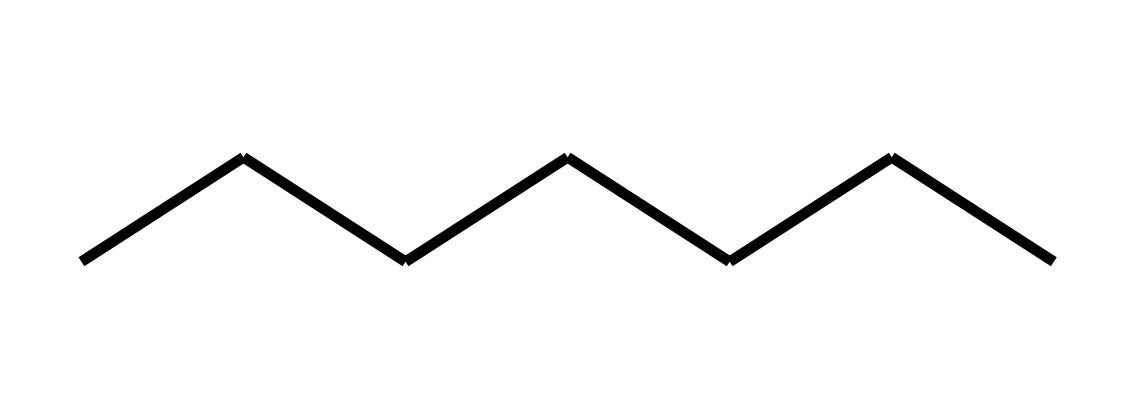
heptane (7)
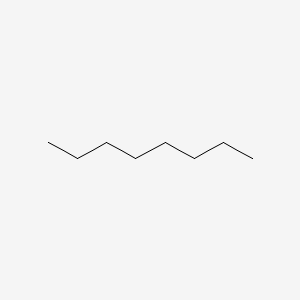
octane (8)
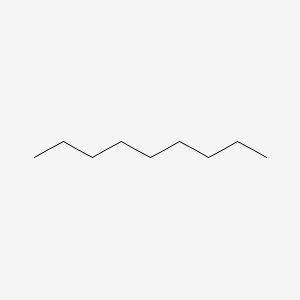
nonane (9)
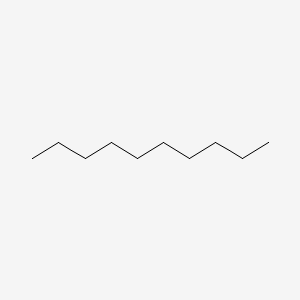
decane (10)
what is the mnemonic for Mom Eats Peanut Butter?
methane, ethane, propane, butane
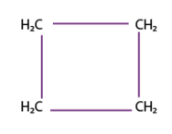
cyclobutane (4)
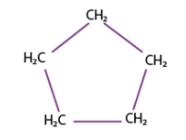
cyclopentane (5)
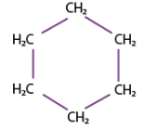
cyclohexane (6)
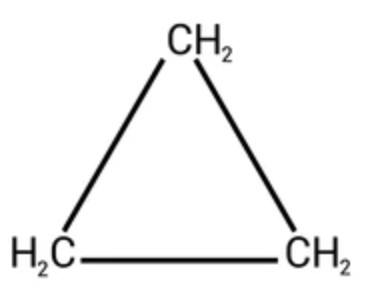
cyclopropane (3)
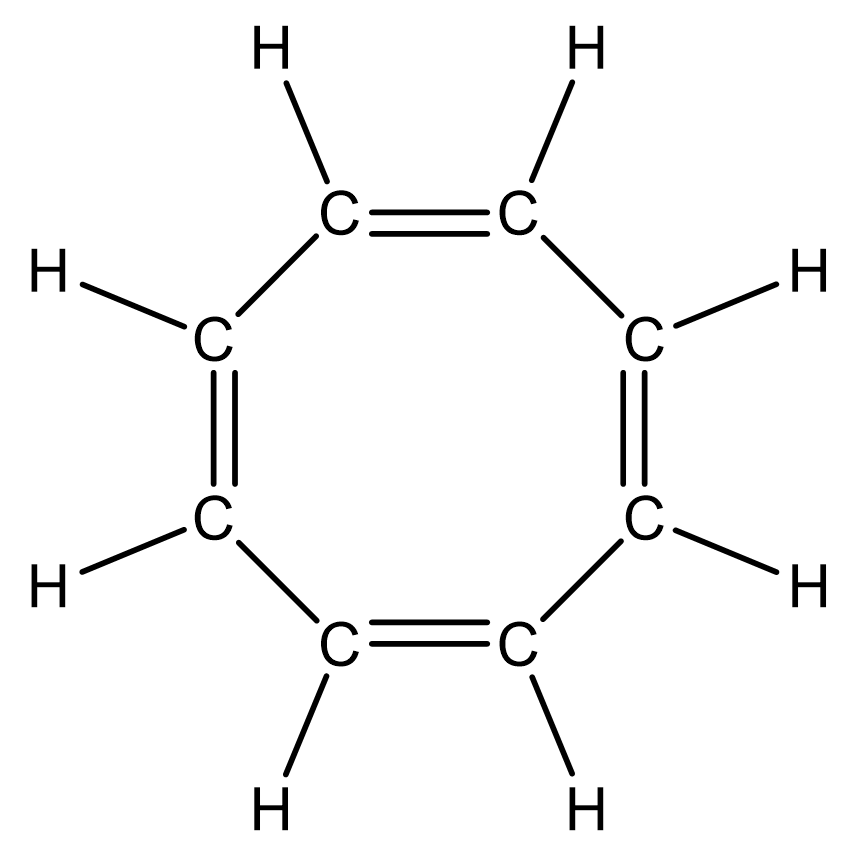
cycloctane (8)
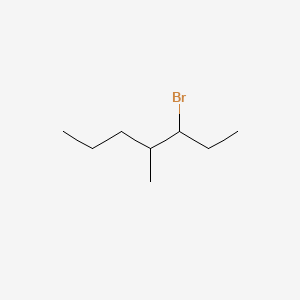
3-bromo-4-methylheptane
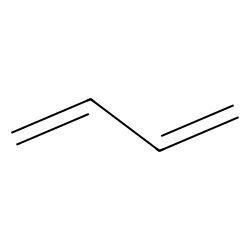
1,3-butadiene
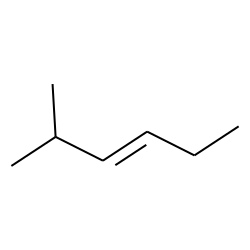
2-methyl-3-hexene
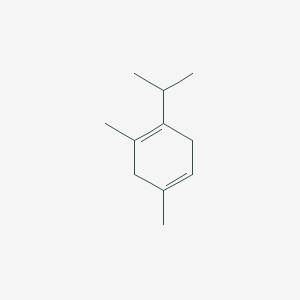
1-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylcyclohexane
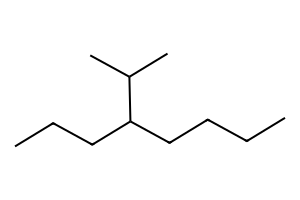
4-isopropyloctane
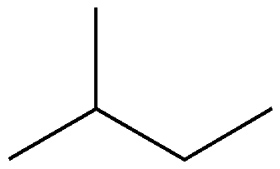
2-methylbutane
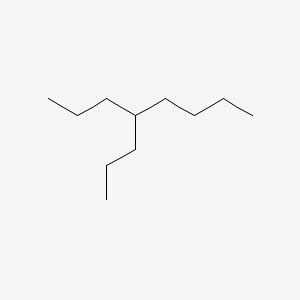
4-propyloctane
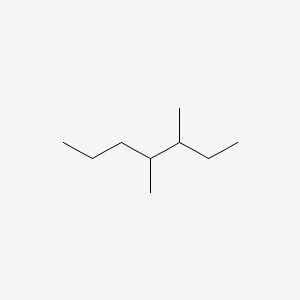
3,4-dimethylheptane
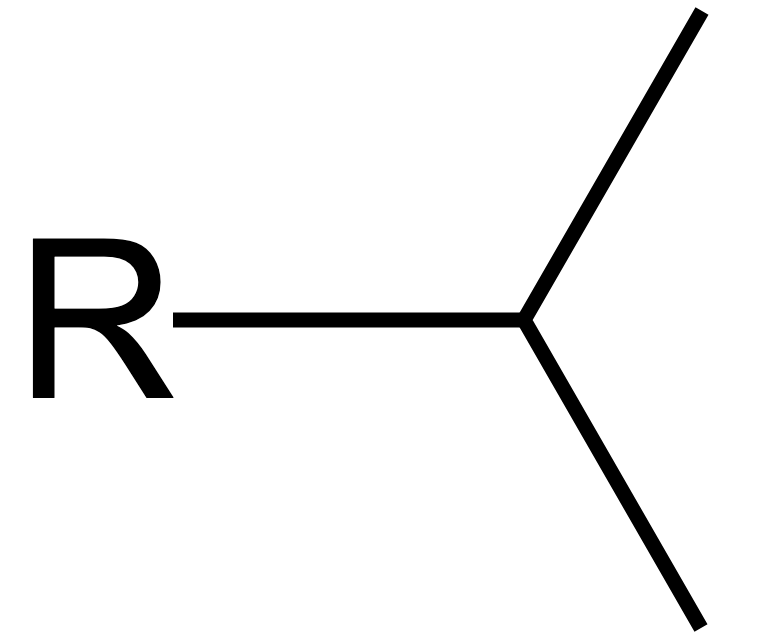
isopropyl group
sec-butyl
tert-butyl
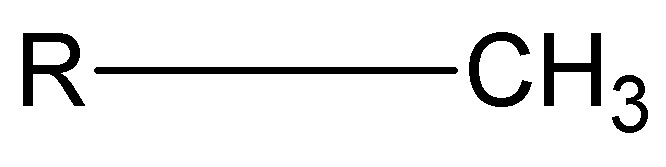
methyl group
diethyl
what does an sp hybridization indicate?
triple bond
what does an sp2 hybridization indicate?
double bond
what does an sp3 hybridization indicate?
single bonds (4)
what does hydrogen bonding have to have in order to be considered an H-bond?
O-H or N-H
what is the strongest IMF? Why?
hydrogen bonding, takes significantly more heat to break
what do dipole-dipole interactions have to have to be considered?
F, Cl, N, O
explain why the same chemical structures with a high vs low boiling point be different?
whichever bond that has a single H can form hydrogen bonds with the same structure, this structure would be harder to break because it contains hydrogen bonds with means that it will be more difficult to break the bonds
what are pi bonds?
double or triple bonds, that are weak and can be broken easily
what are sigma bonds?
single bonds, that are strong and hard to break
what does a soap molecule have to obtain?
a polar head (OH) and a non polar continuous tail
can sigma σ bonds rotate?
YES! They allow for rotation without breaking the bond, they allow for head to head overlap (head on collision)
can pi π bonds rotate?
NO! because they are like upward ballon’s they cant necessarily bend to overlap with one another
what is torsional strain?
repulsion between e- in eclipsed bonds
what is steric strain?
when atoms occupy the same region of space, as it causes a force in physical overlap and an increase in energy because they are too close together.
what does 4 electron groups indicate?
tetrahedral
what does 2 electron groups indicate?
linear
what does 3 electron groups indicate?
trigonal planar
which confirmation is the most stable (gauche, anti, eclipsed)?
anti is the most stable confirmation
which confirmation is the least stable (gauche, anti, eclipsed)?
eclipsed is the least stable confirmation
which confirmation is less stable and WHY?
eclipsed confirmation, because of torsional strain, the repulstion between e- in overlapping bonds
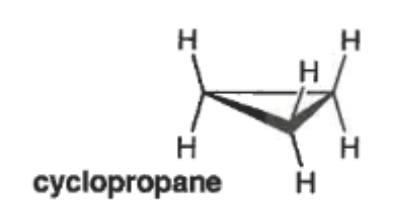
what are the two types of strain that occur in cyclopropane, what causes them?
torsional strain: from the eclipsed C-H bonds
angle strain: bond angles are 60°, which is much smaller than 109.5°
is equatorial or axial more stable?
equatorial because it minimizes steric strain caused by 1,3-diaxial interactions between the substituent and other axial atoms or groups on the ring
what is the angle of sp3 bond?
109.5°
what is the name of the 109.5° configuration?
tetrahedral (4 single bonds)
what is the angle of sp2 bond?
120°
what is the name of a 120° configuration?
trigonal planar (3)
what is the name of a 180° configuration?
linear (2)
what is the angle of the sp bond?
180°
what is the only strain for gauche conformation?
steric
what is the strain for eclipsed?
torsional strain, because e- repulsion
what is the strain for anti?
there is none, it is the most stable because it 180° and happy!
whenever you do a ring flip _____ becomes ________.
axial becomes equatorial (same with the other way around, equatorial becomes axial after a ring flip)
when drawing chair conformations, dashes are always _____ and wedges are always ______.
down, up
What is by far the most common cycloalkane?
Cyclohexane
What is forever eclipsed?
Cyclopropane, torsional strain, very high energy and good fuel
What do we want to minimize in steric strain?
1,3 diaxial interaction
What does puckering mean?
Distorts away from polarity
Is coolant colorless?
NO! Coolant is not colorless, keep away from dogs because it is highly toxic
What are isomers?
Same chemical formula, but occupy space differently