Indirect Lec 11 - Delivery of Bonded Restos
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Cementing vs Bonding of restos
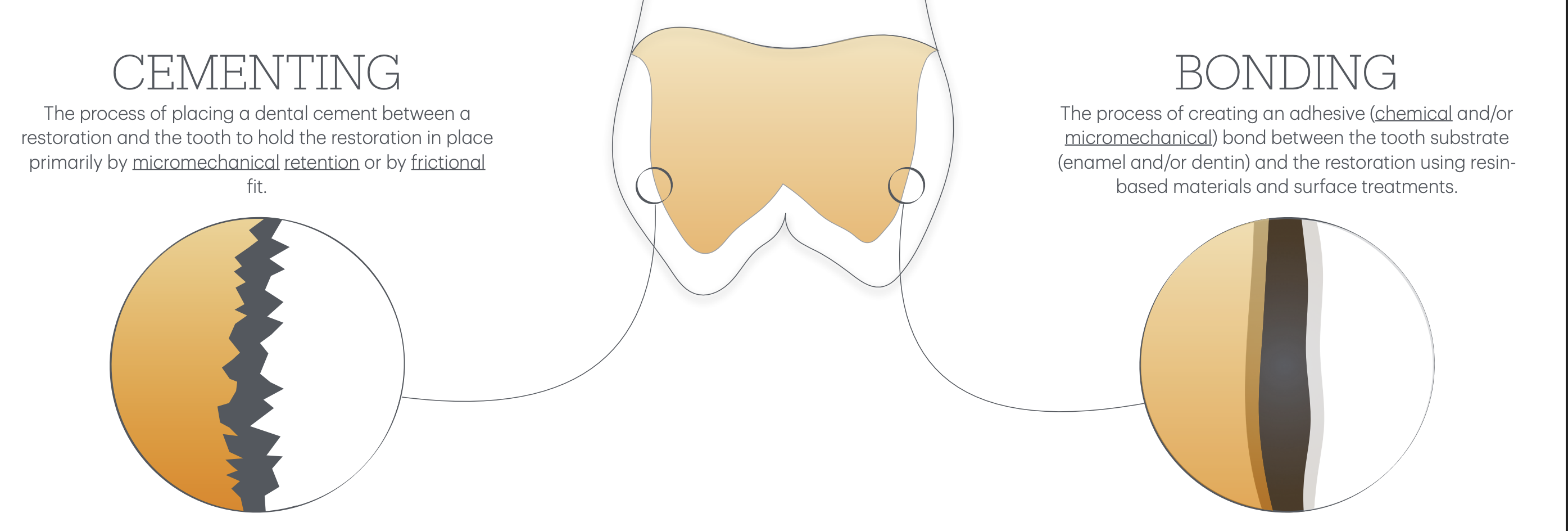
Cementing
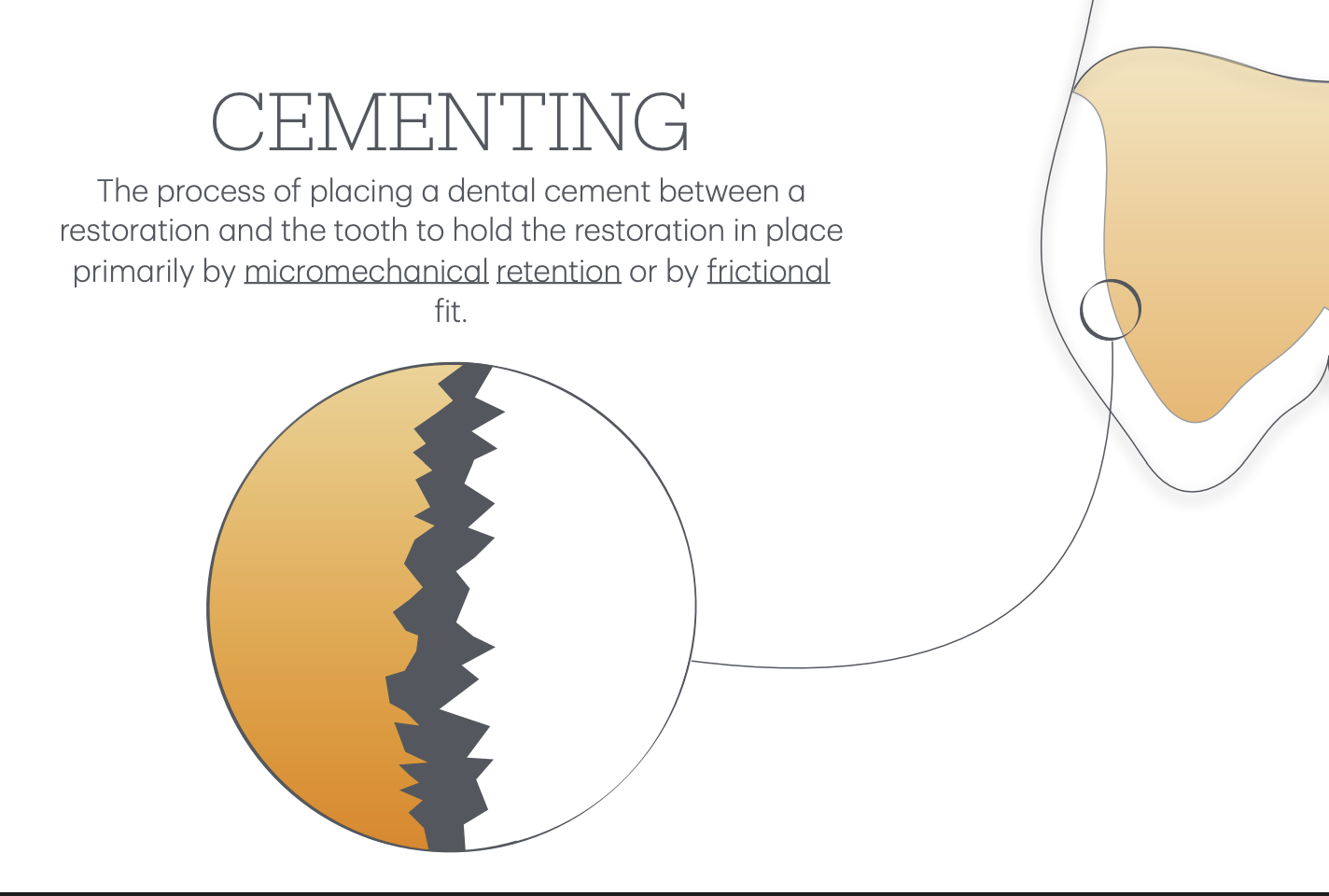
process of placing a dental cement btwn a resto and tooth, to hold resto in place by:
micromechanical retention
frictional fit
Bonding
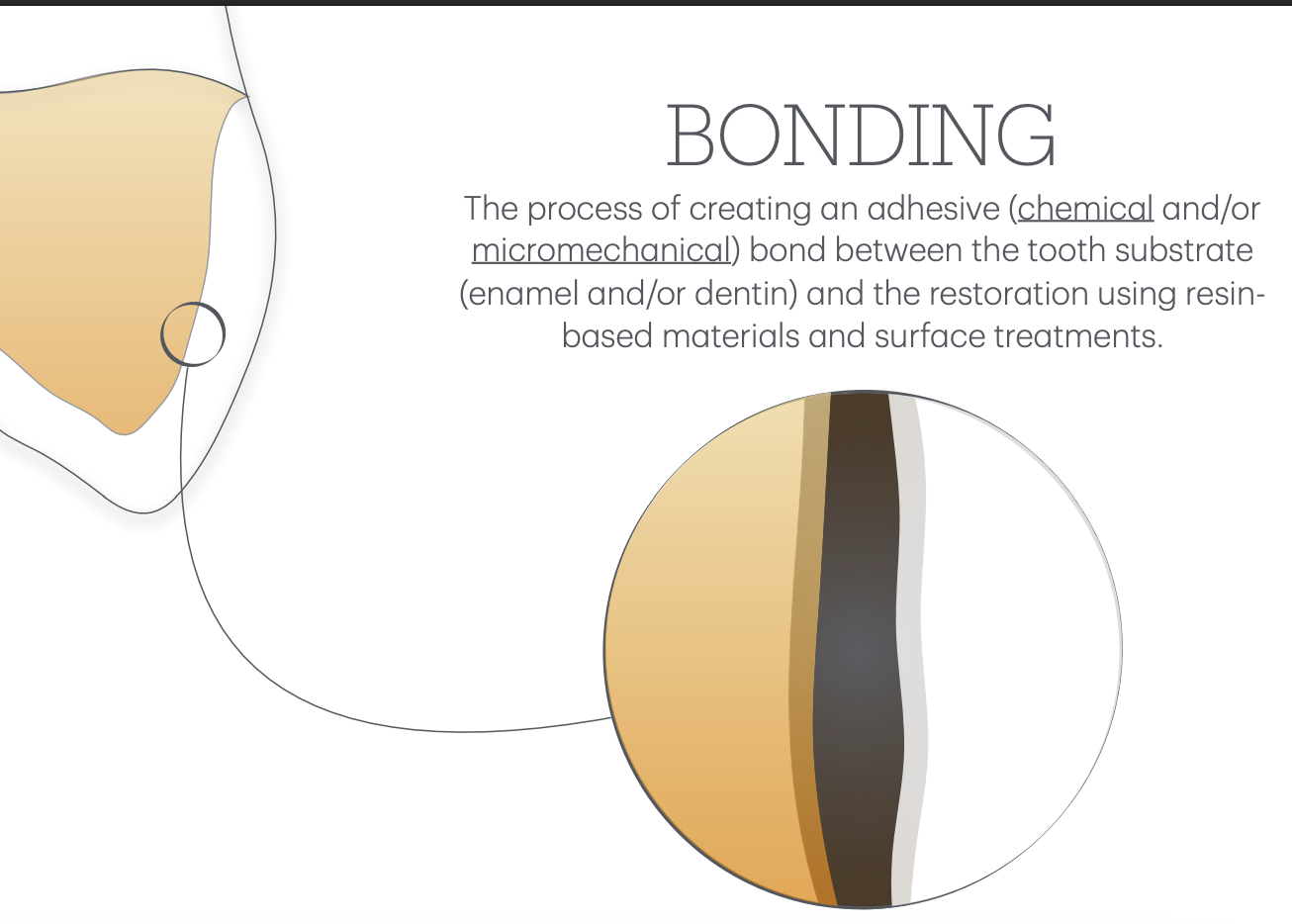
Process of creating an adhesive, which holds the resto by:
chemical
and
micromechanical
bond btw tooth matrix (enamel/dentin) and resto. using resin-based materials / surface treatments
Steps of delivering bonded restos
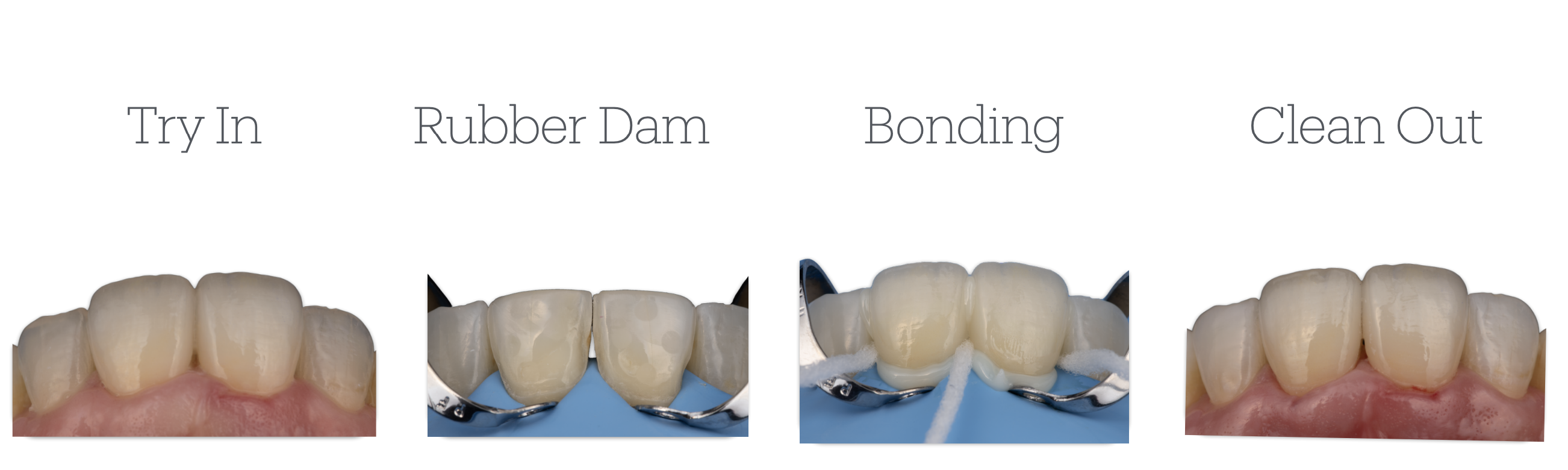
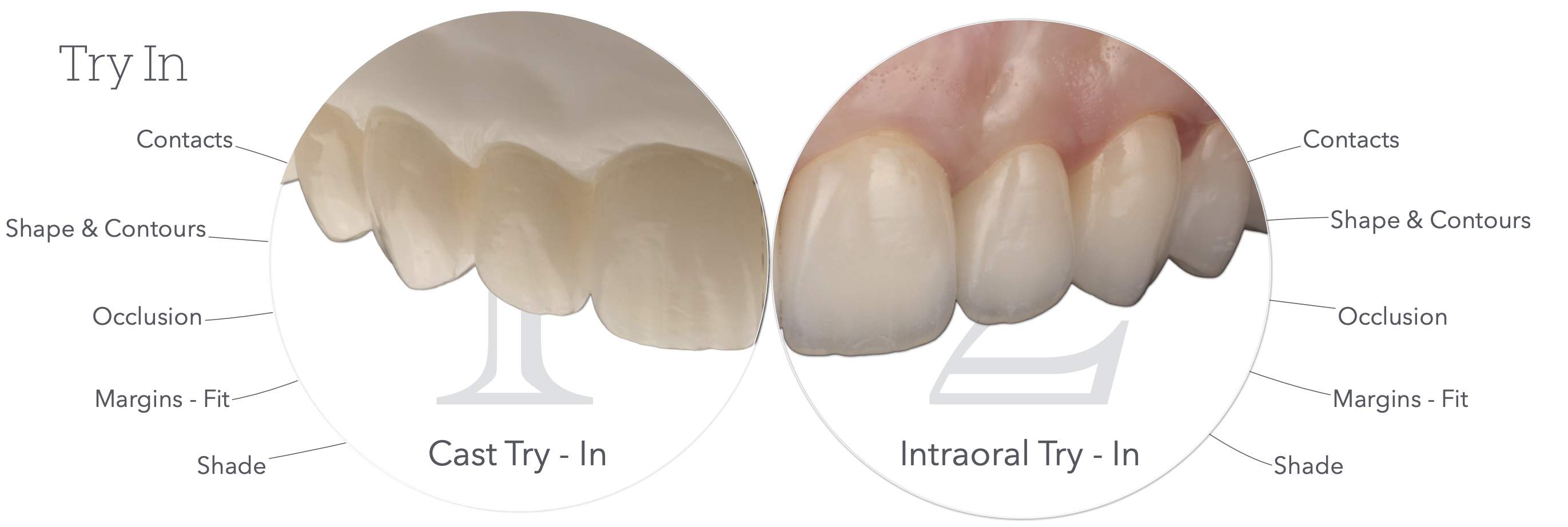
How many try-ins do we do, what are they called?
2
Cast try in
&
Intraoral Try in
What aspects do we check during these try-ins? (5)
Contacts
Shape & Contour
Occlusion
Margins - Fit
Shade
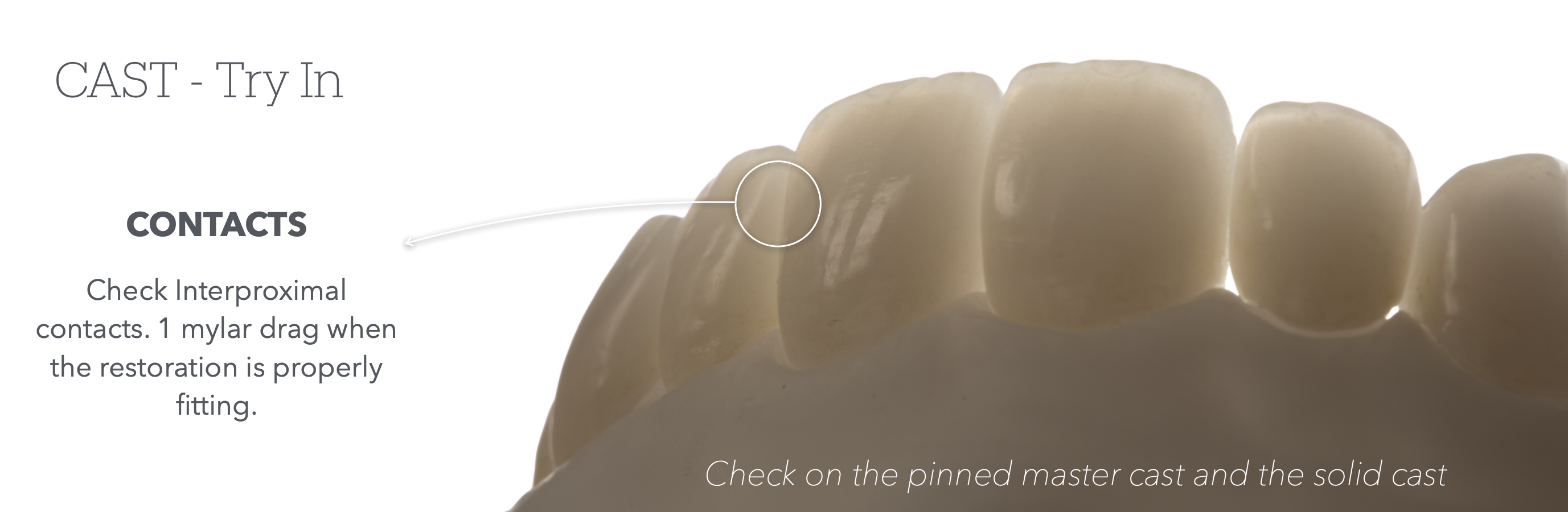
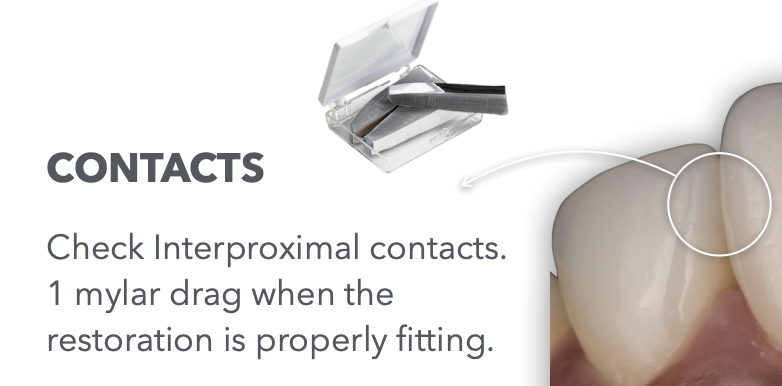
How do we check interproximal contacts on Cast Try-in? using ____,
Using the tool you answered above,
What indicates the contacts ensure proper resto fit?
mylar
1 mylar drag = proper resto fit

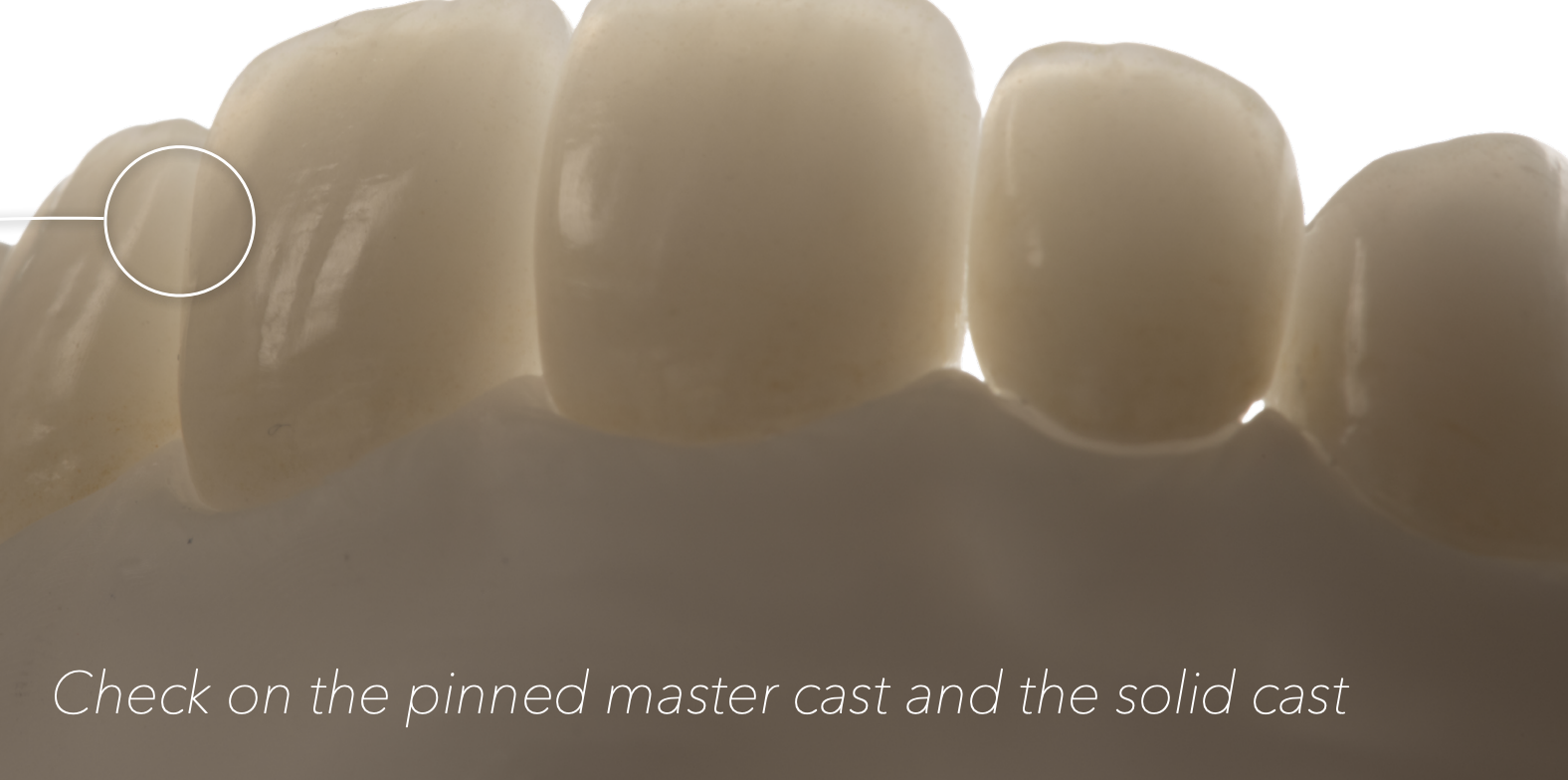
What casts will you check the contacts on when doing cast try in?
check on:
pinned master cast
solid cast

Once we have adjusted the interproximal contacts, we must check for accurate _____ ___ of the entire resto, Making sure to check that the ____ are sealed all around the resto.
We do this by ____ _____ using an _____.
marginal fit
margins
visual inspection
explorer

What casts will you check the marginal fit on when doing this during cast try in?
check on:
pinned master cast
single die

Once contacts and marginal fit/adaptation of resto is confirmed, what do we check next during the Cast try-in?
Occlusion
How do we check occlusion?
What indicates that the occlusion is good?
Using mylar
Posterior teeth, 1 mylar hold
Anterior teeth, 1 mylar drag
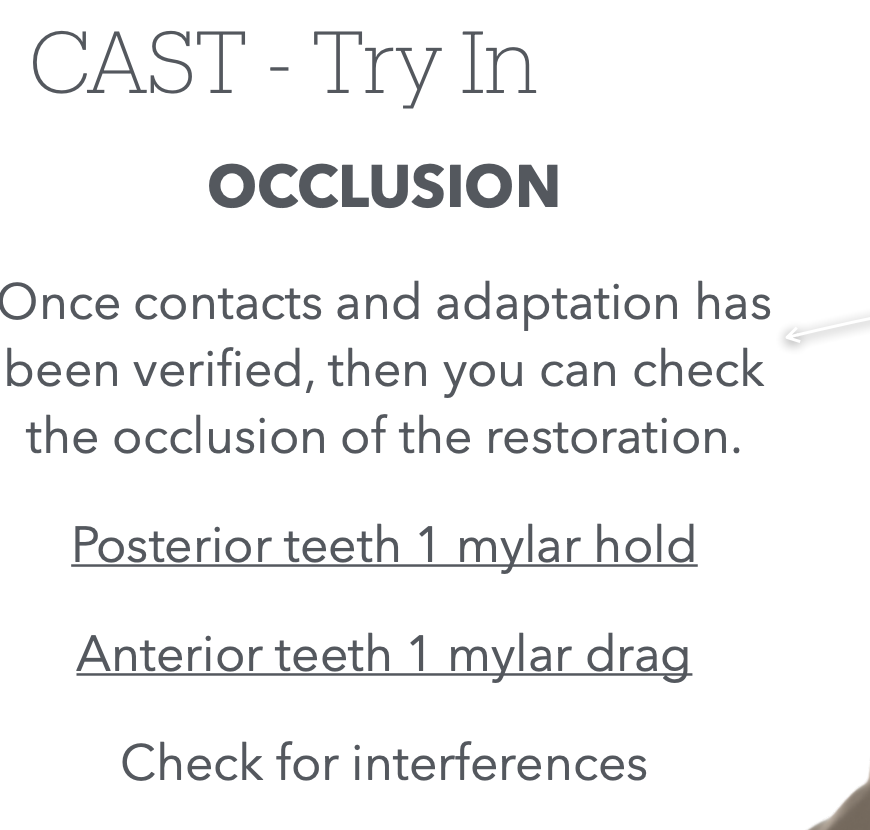
What else do we check for during the occlusion check?
interferences
What cast(s) will you check the occlusion on when doing this during cast try in?
Only on Pinned Master Cast
Next on the steps of Cast-Try in, we check _____
shape/contour of the resto
definition of checking shape/contour of the resto
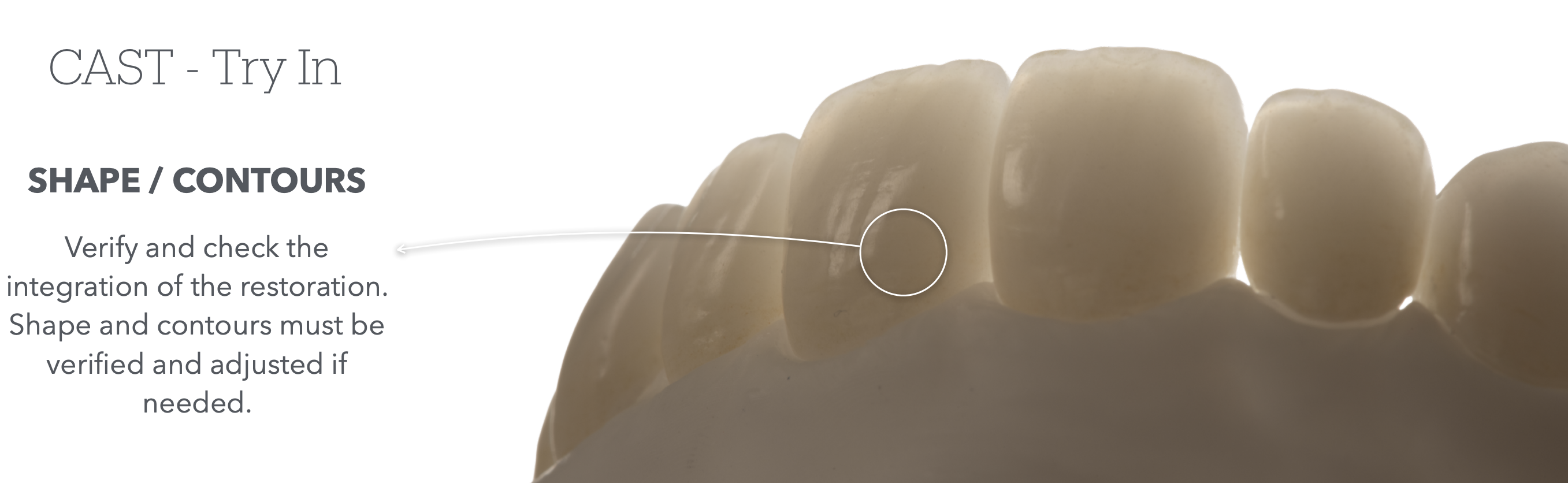
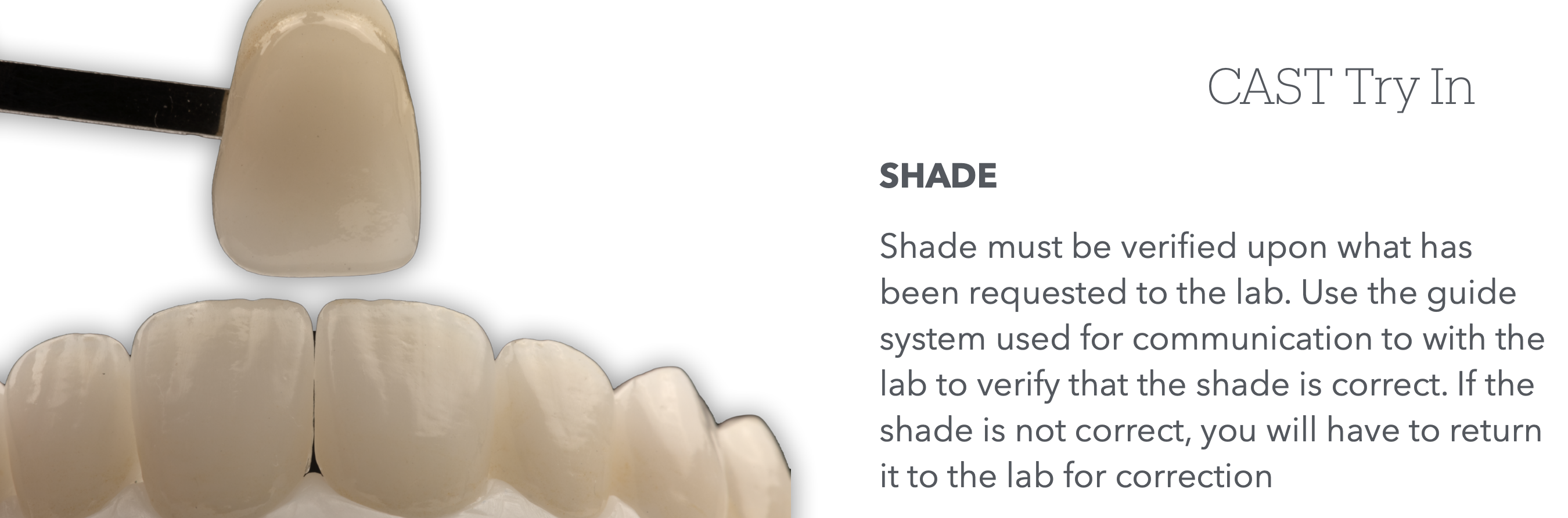
Next on the steps of Cast-Try in, we check _____
Shade
_____ must be verified upon what was requested by the lab.
Use the ___ ____ to communicate with the lab to verify correctness.
if incorrect you will have to…
Shade
guide system
return it to lab for correction
After doing the cast try in and checking all of those aspects,
what must we do if any of those aspects is off/ not good?
modify, adjust, fix it lol
Any modifications must be done using ____ ___ ____, in order to avoid _____ on the surface of the ceramics.
For zirconia we must use profuse _____ _____ to avoid _____-____ of the material.
Fine Diamond Burs
Cracks
Water Cooling
over-heating

What removes microcracks from the surface of restos?
Polishing
Polishing is also important in order to avoid ________ between the ceramic and the teeth
abrasiveness

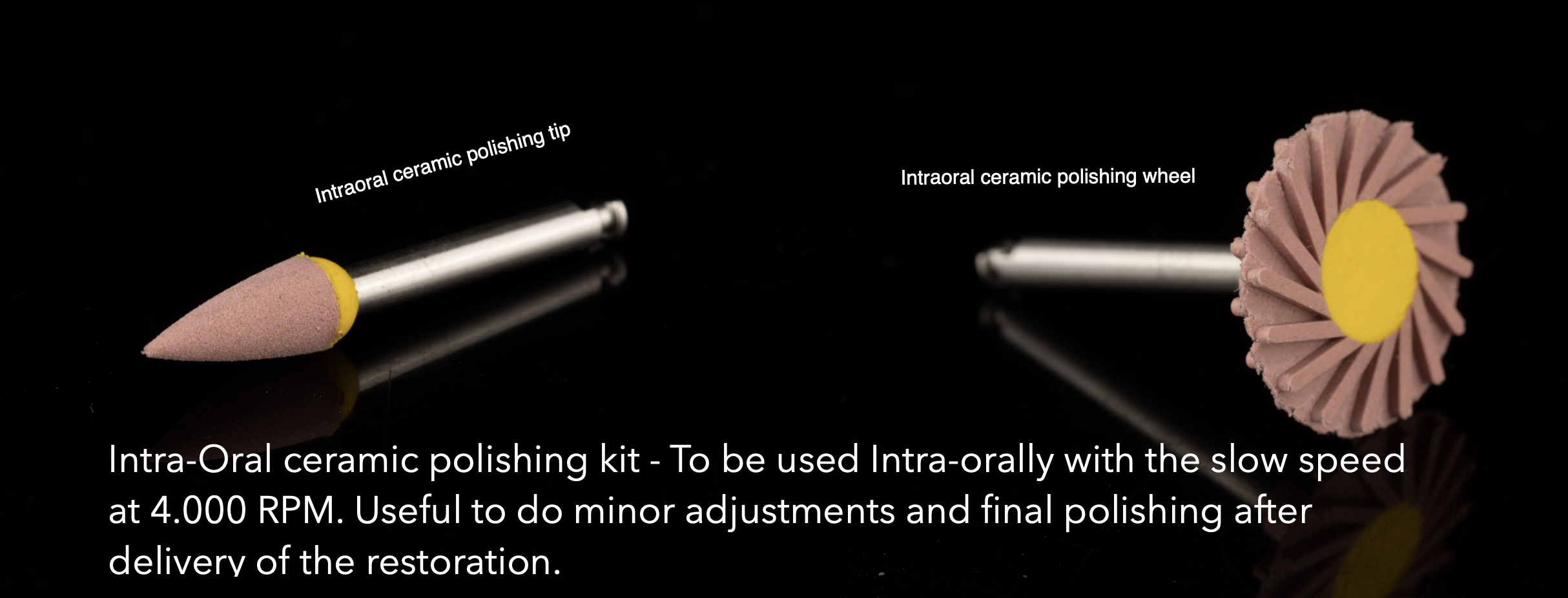
What polishing kit do we use to polish restos outside of the pt’s mouth?
What is included in this kit?
What handpiece do we use with them?
What RPM speed do we use on them?
What are they additionally useful for?

What polishing kit do we use to polish restos inside of the pt’s mouth?
What is included in this kit?
What handpiece do we use with them?
What RPM speed do we use on them?
What are they additionally useful for?
What is another polishing kit that can be used both intra-orally, and extra-orally?
What is included in this kit?
What is important to remember about this kit?

What are some COOL additional products/things we can use to really let us end with a beautiful gloss and surface of the ceramics?
the GOAT polishing brush lol 🐐
coarse grit diamond paste

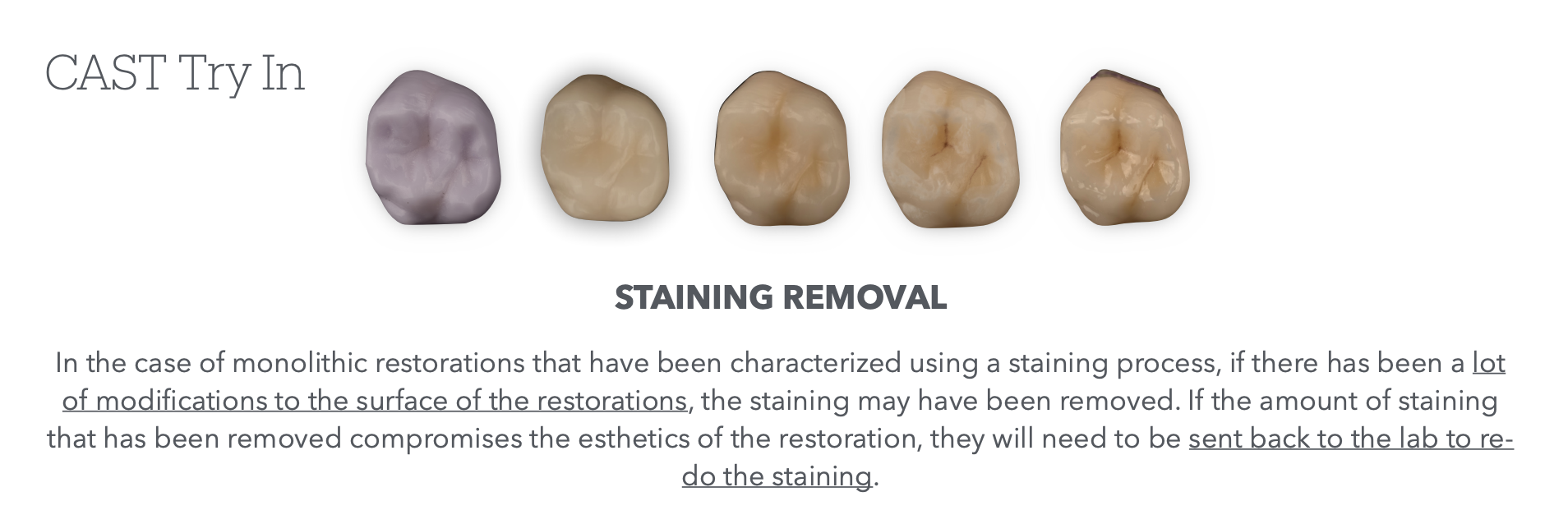
In the case of _____ _____ that have been purposely stained for shade match purposes, what can happen to them after we do a bunch of modifications/work to the surface of them?
What will we need to do if that happens excessively to the point where it ruins the esthetic?
monolithic restos
The staining can be removed
send them back to the lab to be restained
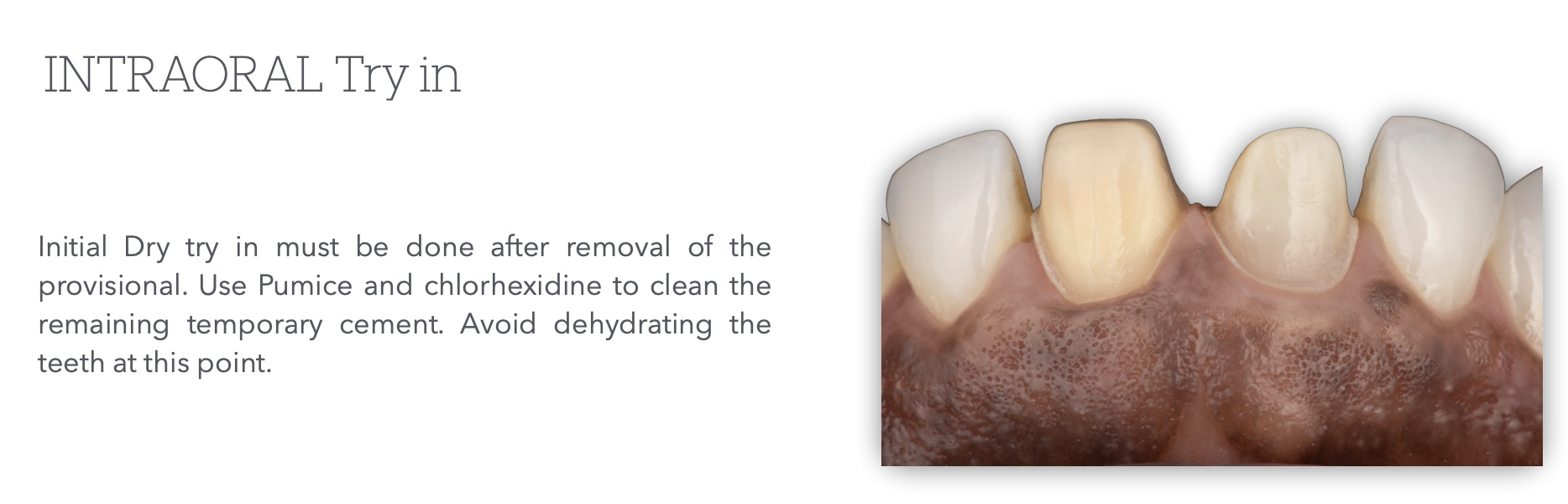
What is the first step of intra-oral try-in that must be done after removal of the provisional?
Initial Dry Try-in
Use _____ and _____ to clean the remaining ____ _____.
Avoid _____ the teeth at this point.
Pumice & Chlorhexidine
Temporary cement
dehydrating
We must keep the teeth as hydrated as possible during the ___ ___ ___ in order to avoid changes in _____.
Having the resto ready from the cast will ____ the time it takes, and avoid excessive ___ _____.
dry try-in
shade
reduce
intraoral modifications
What aspects are we going to check during the dry try-in? (4)
Contacts
Fit
Occlusion
Shape/Contour
How do we check interproximal contacts in intraoral / try-in?
bruh, same as the cast try in i guess:
What do we do if the resto still doesn’t fit even after adjusting the contacts?
Use “fit checker” to check for any internal interferences
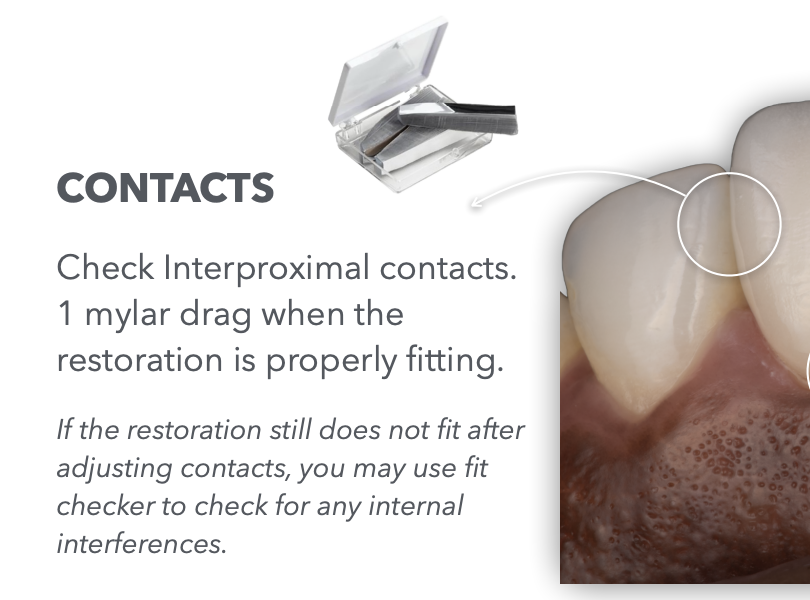
Once we finish adjusting the interproximal contacts we must check for ….
accurate fit of the resto… aka Marginal fit
AGAIN lol
How do we check for marginal fit?
What tool do we use?
What are we looking for when checking for marginal fit?
Visual inspection
using Explorer
Check to make sure that we have sealed margins all around the tooth
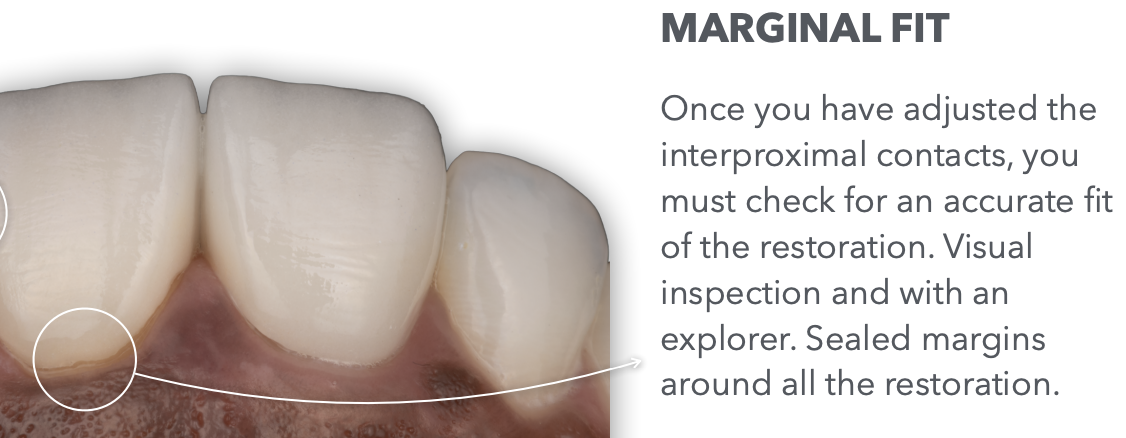
What’s an additional step we can take during intraoral try-in, to help check marginal fit and sealed margins?
We can take X-Ray to radiographically check the fit of the resto
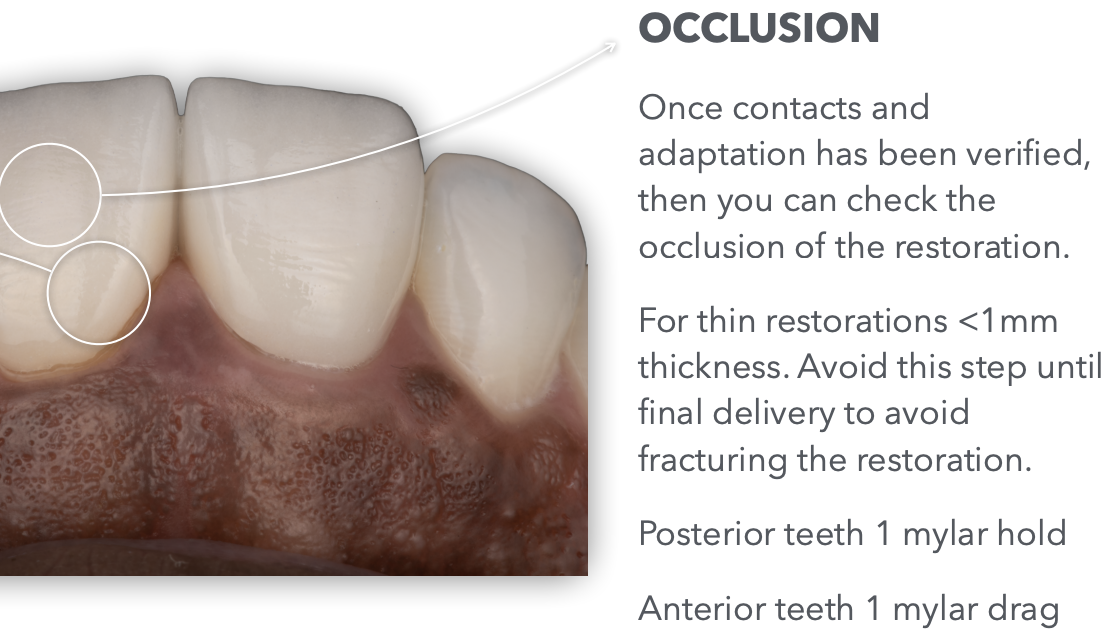
Once Contacts and adaptation has been verified in intraoral try-in, we shall check the
occlusion
How do we check occlusion during intraoral try-in?
What do we use? What indicates good occlusion?
What is an important note to remember specifically for checking occlusion intraorally?
Use mylar
posterior teeth 1 hold
anterior teeth 1 drag
For thin restos thinner than 1 mm, avoid this occlusion checking step until final delivery to avoid breakage of the resto
Lastly, during intraoral try-in we shall verify/confirm…?
Shape/contour
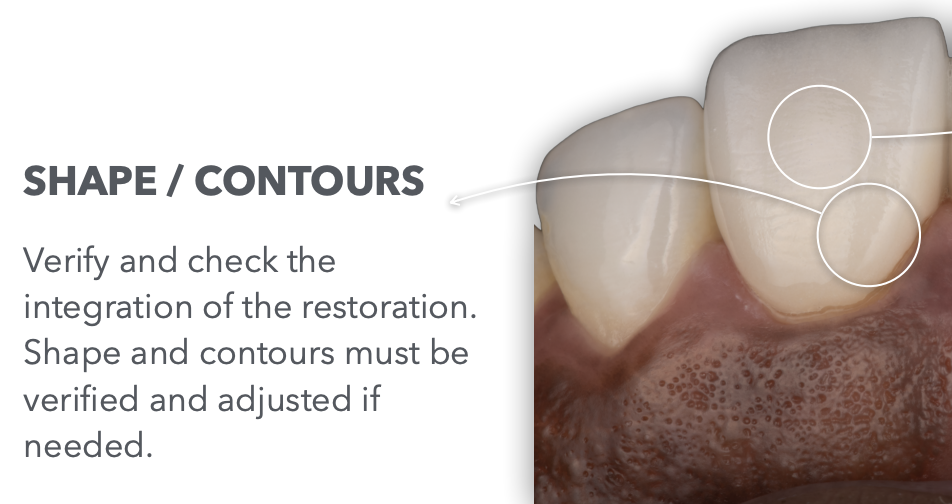
What is the next thing to do after completing dry-try in and all of its aspects?
Wet try-in
What aspects does Wet try-in involve?
Wet shade confirmation
Cement Selection

How do we do the Wet try-in shade confirmation?
Use water / glycerin to stimulate a neutral environment without shade interaction of the cement
To check shade of final resto, they must be tried in a ____ environment in order to achieve proper ____ ____ through the resto and tooth substrate
wet
light transmission
What can we use to test how the cement will affect the overall shade of the final resto?
____ and ____ tones of cements can modify the _____//____ of the restos for ____ restos
try-in cements
lighter & warmer
shade/value
thinner
Next:
The bonding protocols are very ______ sensitive.
_____ _____ / isolation is fundamental to achieve appropriate bonding of resto so the use of ___ ___ is fundamental
Lack of use of ___ ___ will jeopardizze the longevity of the bond.
technique
Moisture Control / isolation
rubber dam
rubber dam
Using rubber dam, How many adjacent teeth do we isolate that are adjacent to the tooth we are delivering bond to?
Why do we do this?
Isolate at least 2 adjacent teeth from the tooth that will be delivered. This will allow us proper access to the interproximal area to clean excess cement.
using rubber dam, what can further help us isolate the teeth and more clearly separate the gingiva from the finish line

what are the steps for going about bonding the actual thing? like the adhesive procedures?

what are all the layers of things that will be present in the final bonded resto in between the actual tooth and the resto.
draw a picture or list in order from inside to out
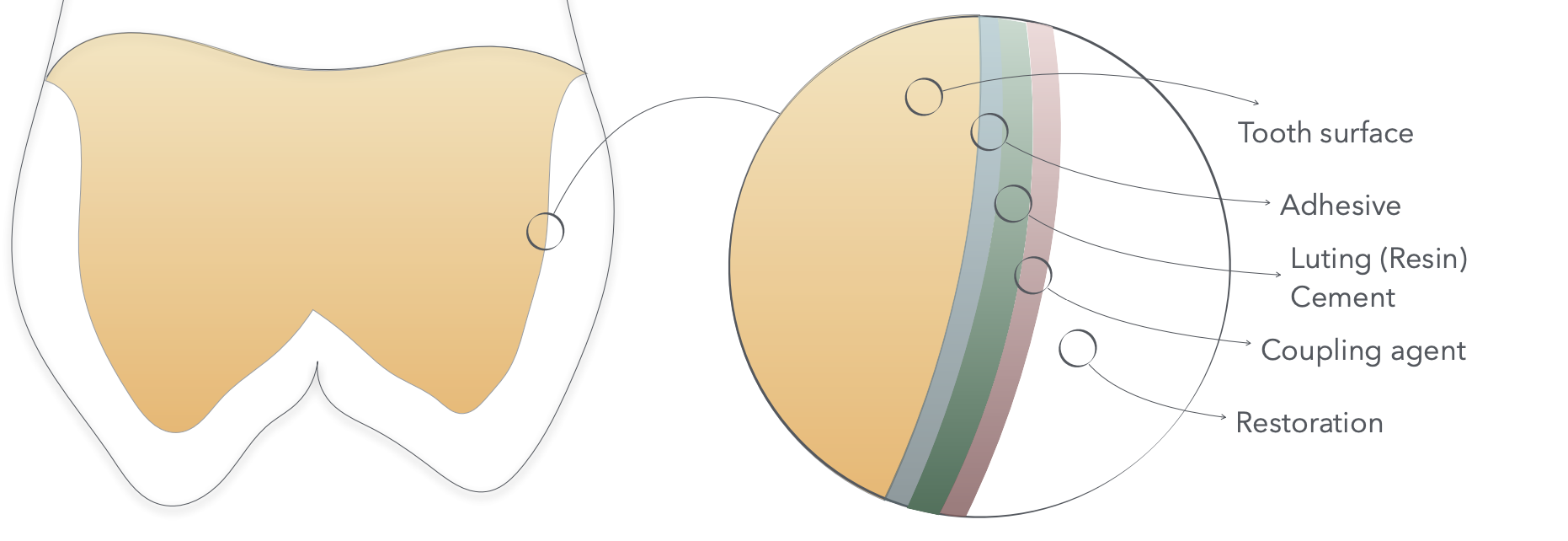
The bonding on the surface of the resto will depend on 2 aspects, a _______ and a _____. The way we will achive these will depend on the ______.

So once again, what are the retention types?
Micromechanical
Chemical
Micromechanical Retention:
What are the methods one can achieve michromechanical retention on the surface of the resto
(memorize this chart rly well, i will be asking u lots of questions about it below)
(ik its confusing, but remember here are methods to reach end goal of MICROMECHANICAL Retention) don’t mix up with the general chemical retention mentioned in the previous flashcard!!! That “chemical retention” section will come later
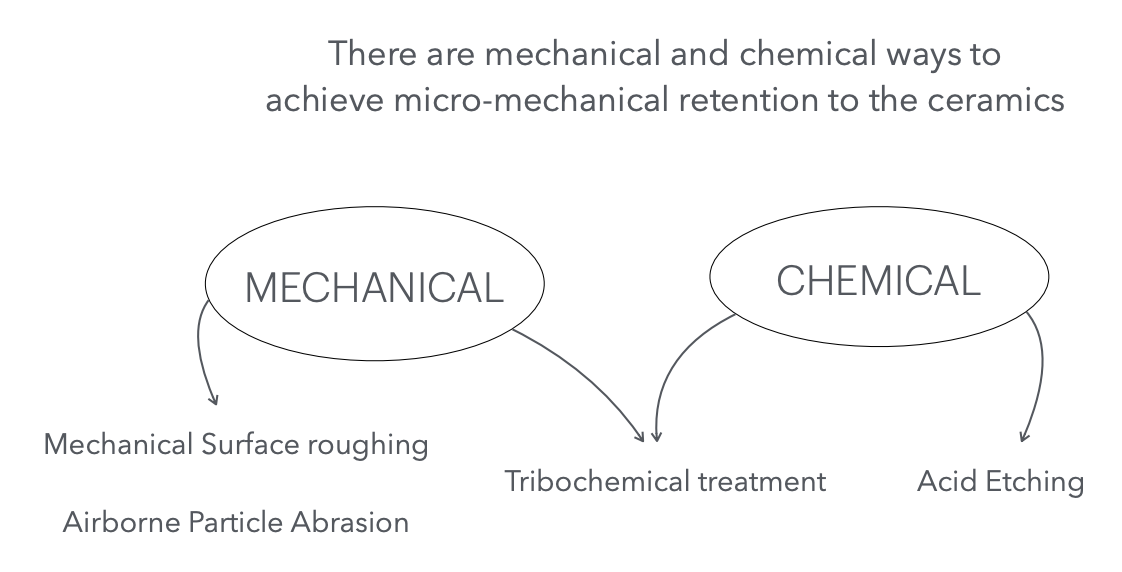
summary of All the ways we can achieve MICROMECHANICAL:
mechanical → micromechanical (2)
mechanical + Chemical → micromechanical (1)
chemical → micromechanical (1)
Airborne Particle Abrasion:
what chemical is used?
size of particles?
blasting pressure?
how long do we blast for?
Al2O3
30-50 (um) micrometers
0.5-2.5 bar
10-20 sec @ distance of 10 mm at area of 10 mm
What is something important we must remember in terms of having a higher blasting pressure?
useless hint:
higher sandblasting pressure…. (increases) / (decreases) ? the ____ ______ on ______

What material can NOT be used with particle abrasion?
Glass ceramics
What is something important we must remember in terms of having a bigger particle size?
useless hint:
bigger particle size…. (increases) / (decreases) ? the ____ of ______ ______ which increases/ decreases resistance

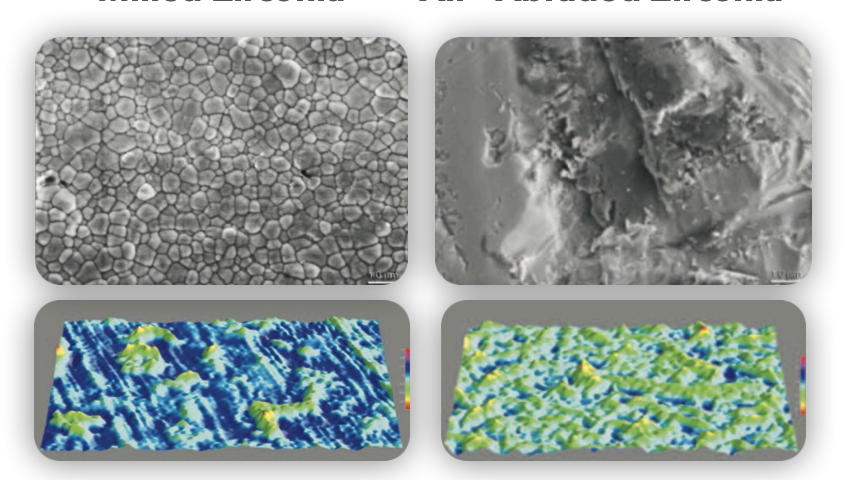
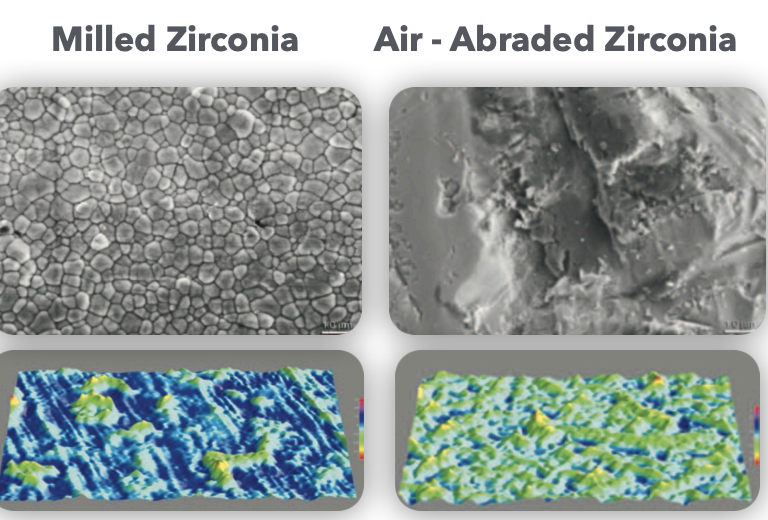
What method has both mechanical and chemical ways to reach micromechanical retention?
basically, Chemical + mechanical → micromechanical in this case, which material does this?
Tribochemical treatment
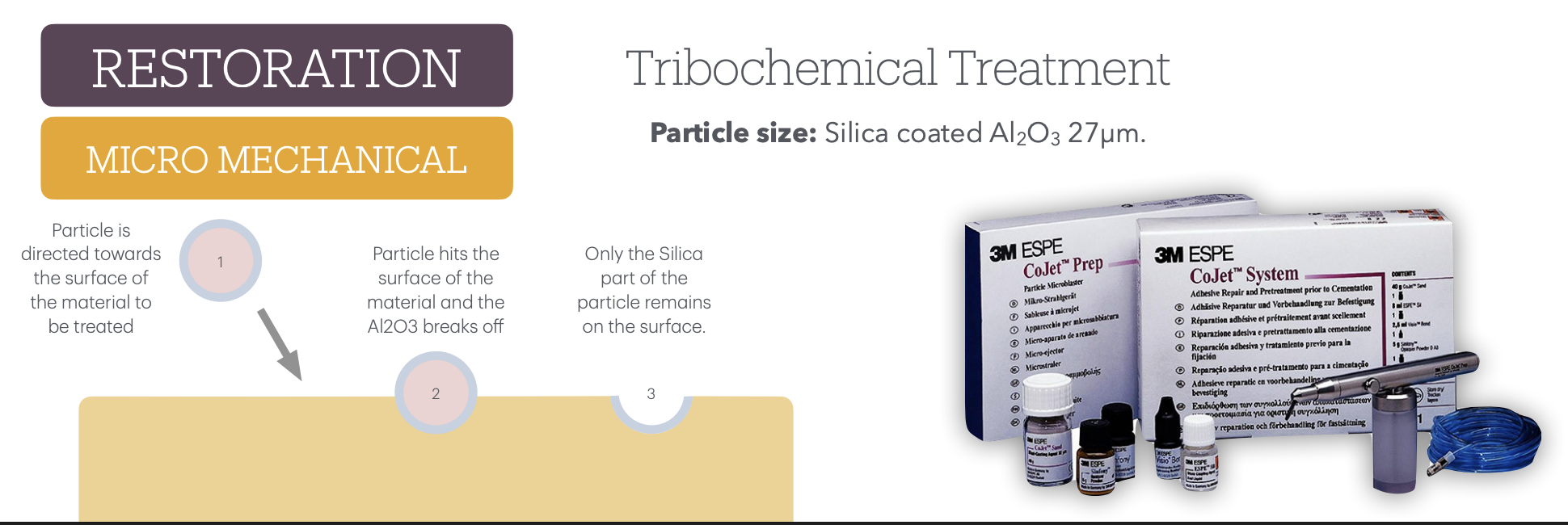
Tribochemical Treatment:
What is it made of
particle size
mechanism of action
draw a pic of the steps (3)
What can hydrofluoric acid etching only be used with?
Only with glass containing ceramics
HF acid etching is an example of a ______ method to reach the end goal of ___ ___ retention

chemical → micromechanical
5% HF used with what materials?

9% HF used with what materials?

The higher content of glassy phase in requires _____ concentration of ____.
higher
HF
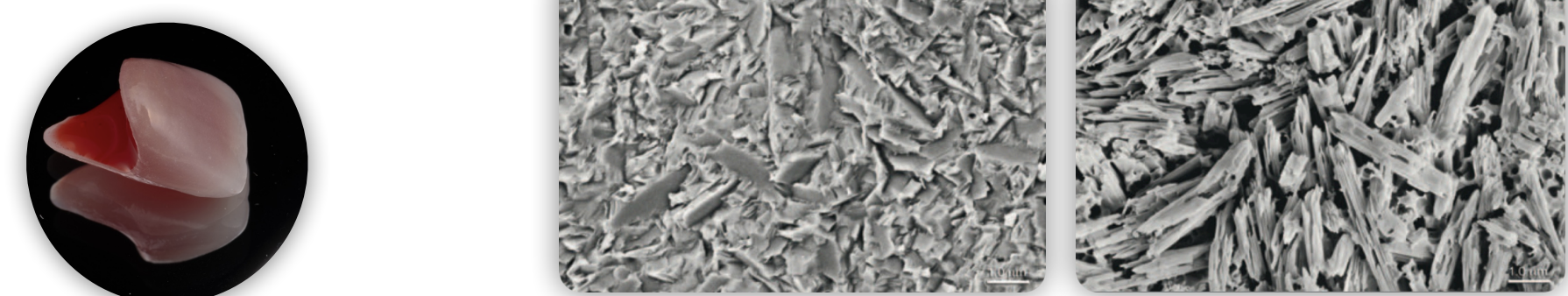

Give a summary of all the ways to achieve micromechanical retention!
mechanical → micromechanical (2):
airborne particle abrasion
mechanical surface roughening (idk soflex?)
mechanical + Chemical → micromechanical (1) ; Tribochemical
chemical → micromechanical (1)
HF acid
5% and 9%
Chemical Retention! yay
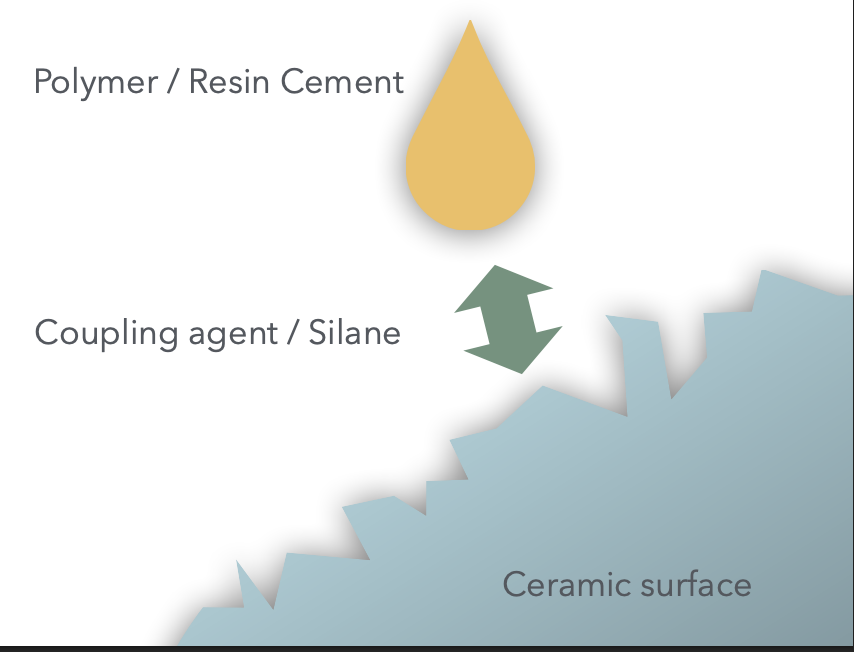
Chemical treatments enhance bonding by applying ____ _____ which are ____ _____ that allow a chemical reaction btwn the inorganic _____ and the organic _____.
The most commonly used coupling agents are __________
coupling agents
bifunctional molecules
ceramic
resin cement
organosilanes


Ochem steps of bonding to Silicate Surface (glass ceramics)
Step 1:
reactant?
product?
Their _____ group (_____) is _____ in the presence of water, to a ____ group (-Si-OH), which subsequently can bond with the _____ groups on the surface of the ceramic, forming a _____ bond (-Si-O-Si-)
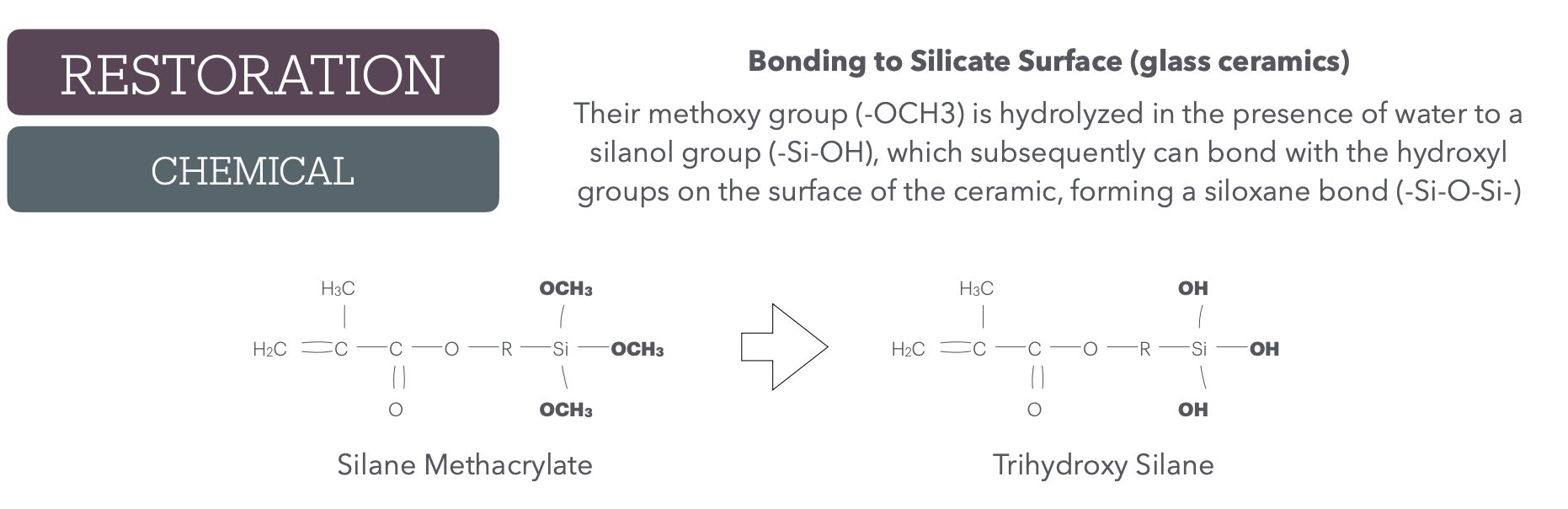
methoxy
-OCH3
hydrolyzed
silanol
hydroxyl
siloxane
Step 2 of bonding to Silicate Surface (glass ceramics)?
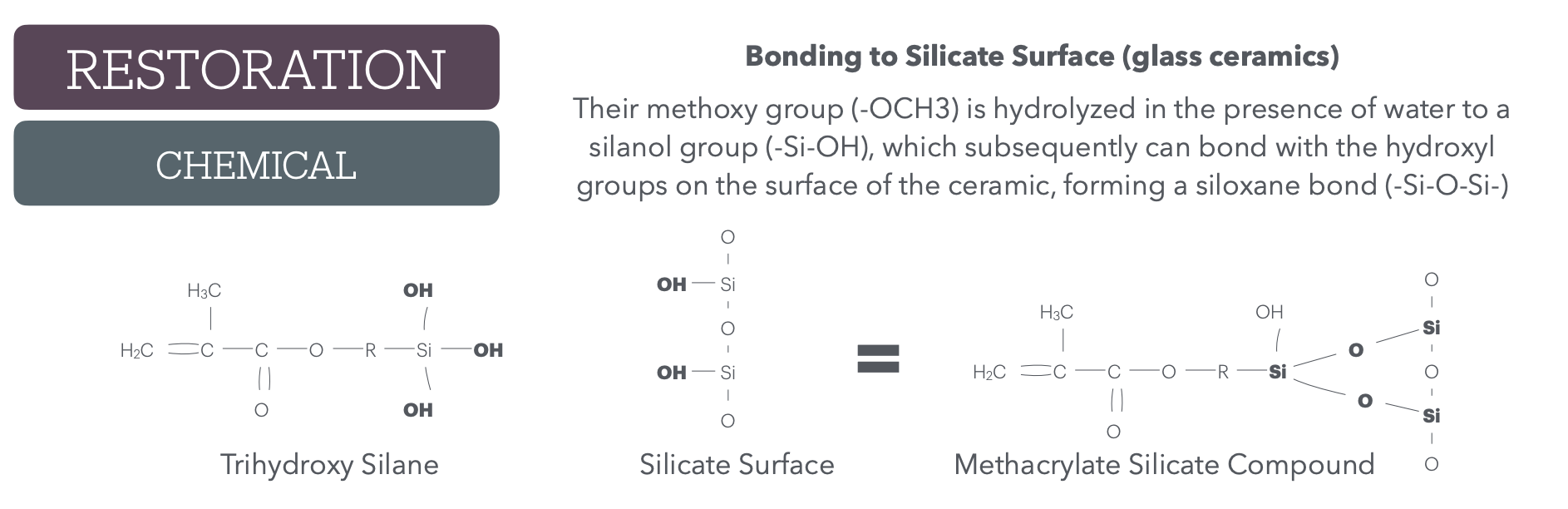
basically end result of this whole chemical rxn for bonding to Silicate Surface (glass ceramics)?
methacrylate silicate compound w/ Si-O-Si bonds
Ochem formula for bonding to Zirconia, alumina and base metals?
The _____ monomer promoting chemical bonding to oxide ceramics is _____. This ______ molecule contains a __ ___ group which bonds directly to surface ____ and a _____ group which bonds to the resin matrix of the ___ ____.
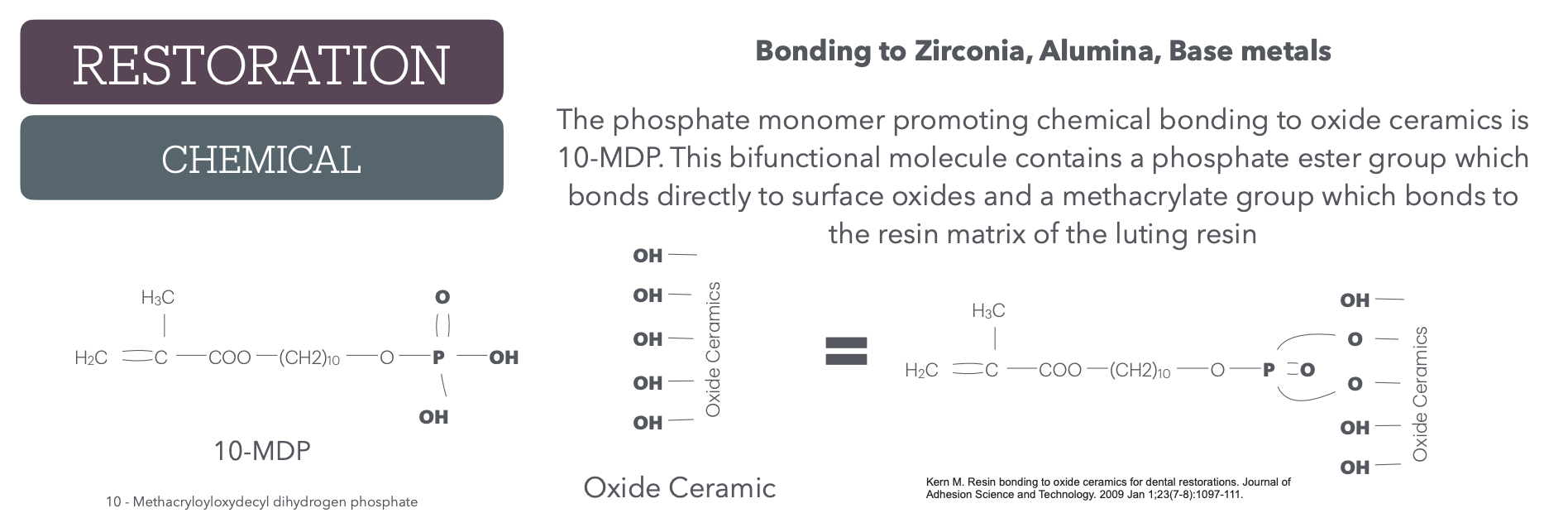
phosphate
10-MDP
bifunctional
phosphate ester
oxides
methacrylate
luting resin
Different conditioning for surface of resto depending on type of material

Not following appropriate protocols for the specific type of material used will result in
decreased bond btwn resin and ceramic
Glass matrix ceramics - What types of retention do we use for it? by using what?

bonding procedures for:
Glass matrtix ceramics
specific steps pls
as if dr. Phark was testing u on the bonding procedures

Polycrystalline ceramics - What types of retention do we use for it? by using what?

bonding procedure steps for:
Polycrystalline ceramics

Resin-Matrix ceramics - What types of retention do we use for it? by using what?

bonding procedure steps for:
Resin-Mattrix Ceramics

Luting Material / Cement Selection:
Water based vs resin based?
Water based for cemented restos
Resin based for bonded restos
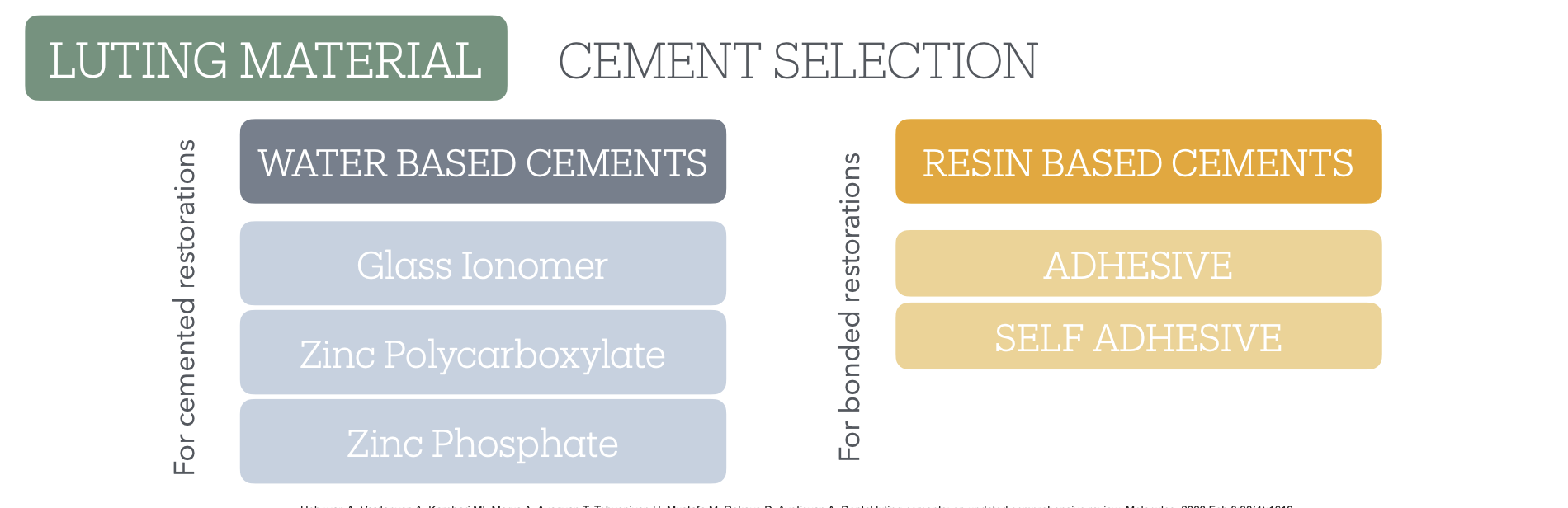
What are all the water-based cements?
What are all the resin-based cements?

Which water based cements are used for the cementation of full-metalic and metal-ceramic crowns and _____ apparently
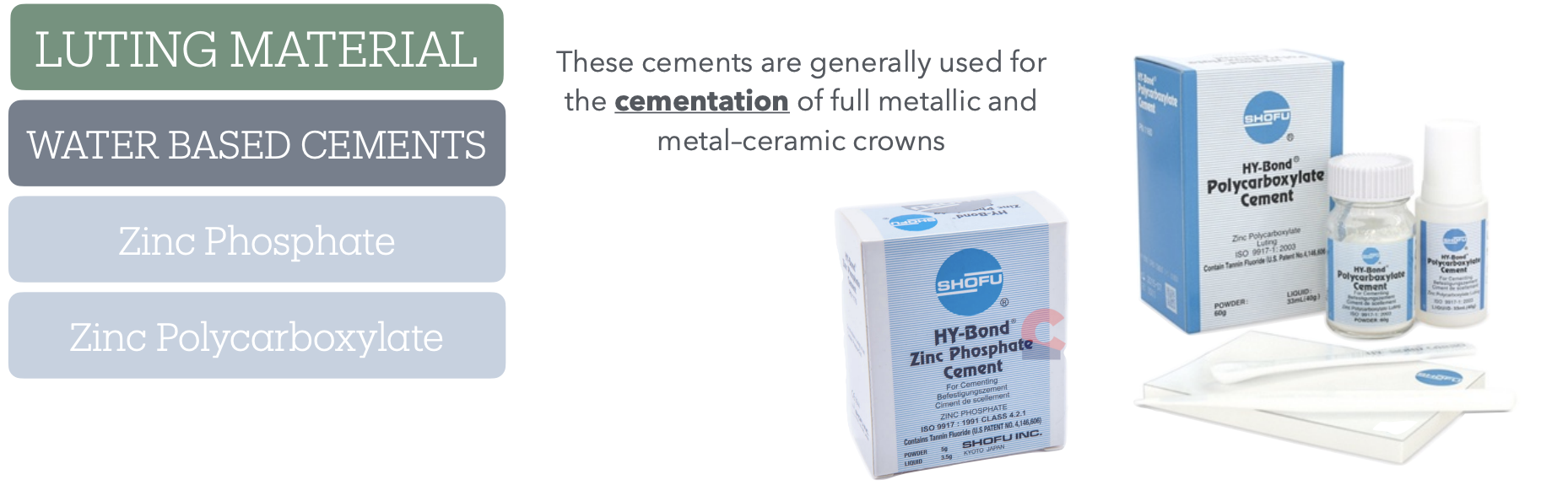
GIC’s too?
GIC’s are used for
cementation of:
full-metalic
metal-ceramic
Partial FDP
MCC w/ porcelain margins
slip cast alumina
metal posts
inlays
implant supported crowns/bridges
anesthetic postcore/core fiber ceramic
LITERALLY EVERYTHING
What are RMGIC’s used for
indicated to retain:
total crowns/bridges
metal ceramic crowns/bridges
Zirconia frameworks/restos
metal posts
metal inlays
ortho appliances
postcore, core fiber ceramic
For delivery of resto w/ use of any type of Glass ionomers, a ___ ________ must be used on the tooth instead of bonding protocol.
Which one specifically do we use and steps of how?
cavity conditioner
20% polyacrylic acid

Resin cements are _____ materials w/ different chemical compositions. Theyre classified based on ___ ___ and ___ ___
composite
polymerization process and adhesion strategy
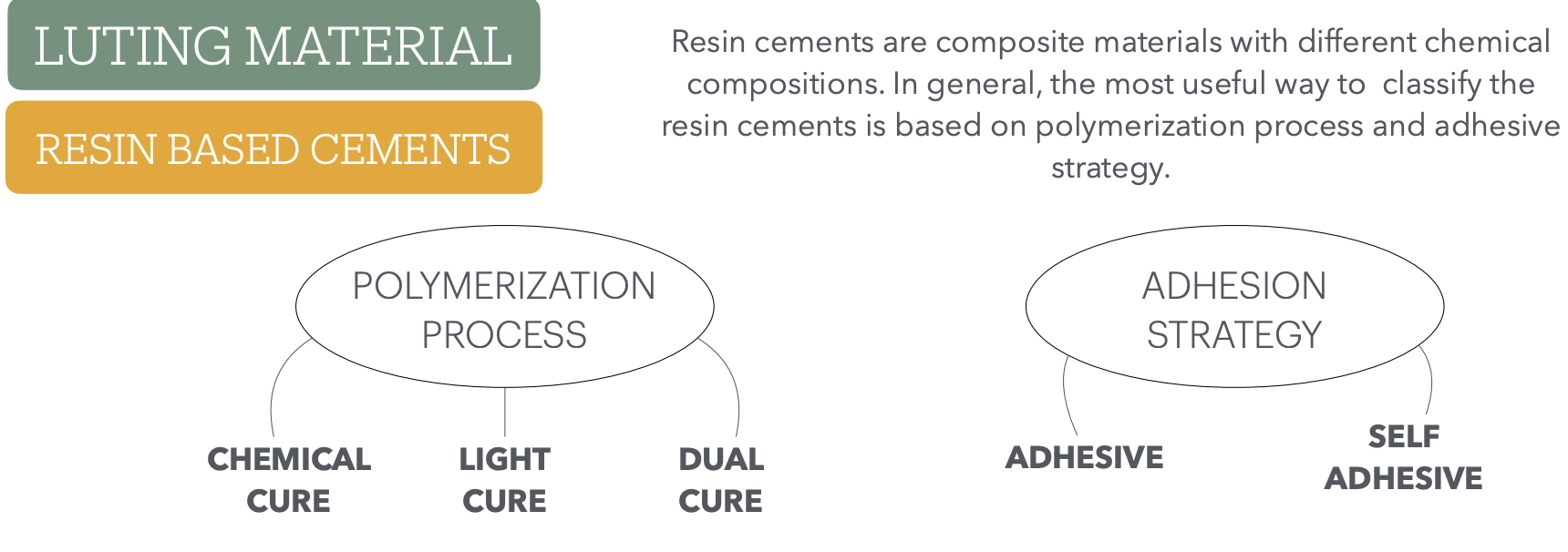
What aspects are involved in polymerization process and give a description of each
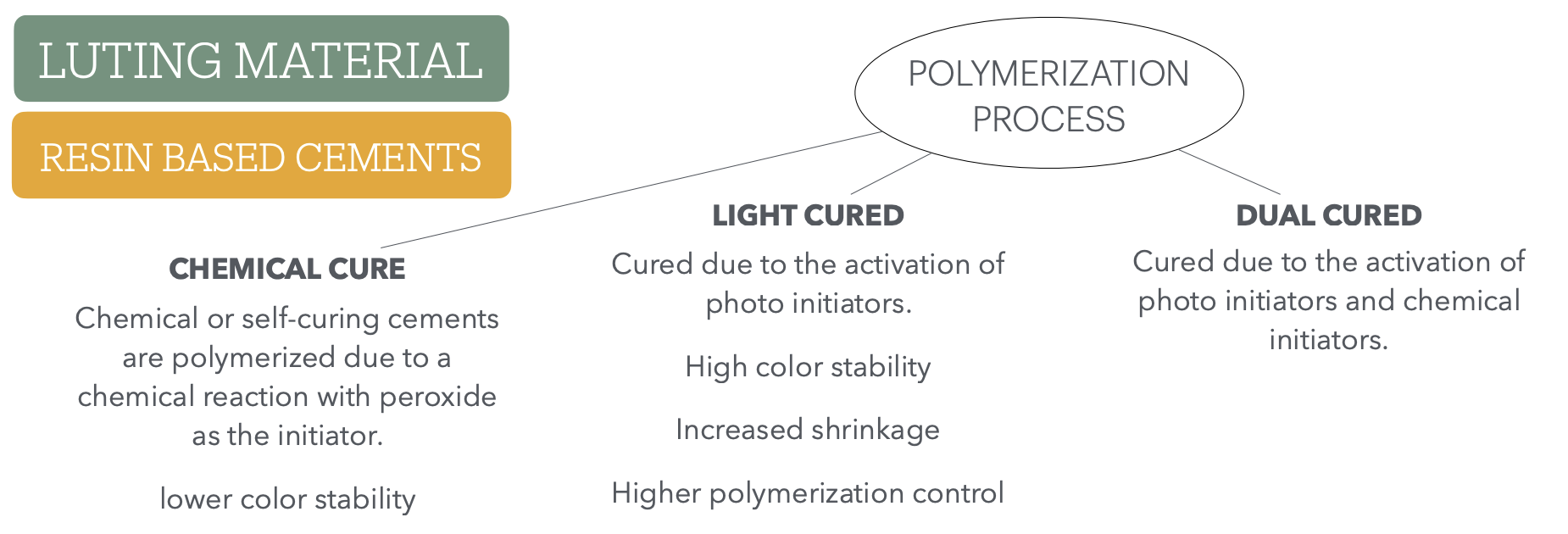
when do we use
chemical cure vs light cure vs dual cure?

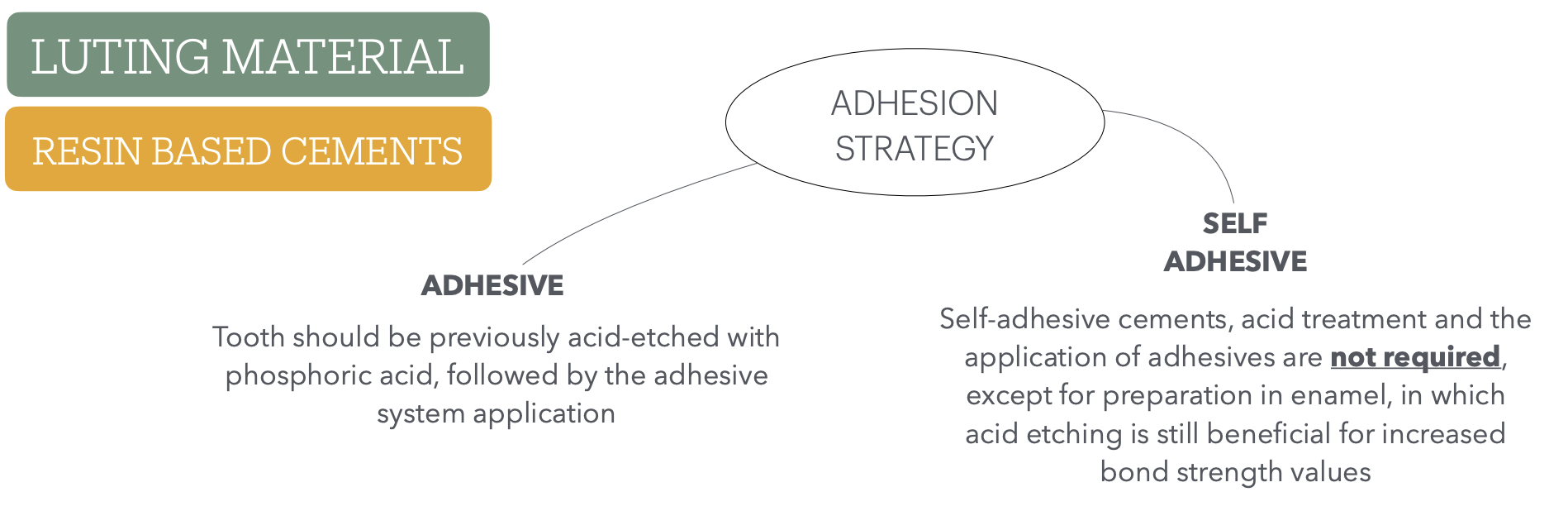
whats involved in adhesion strategy and give a description for each
Steps for standard delivery of adhesive cement - glass matrix & enamic
Steps in detail as if Dr. Phark were giving u a bonding exam!!!
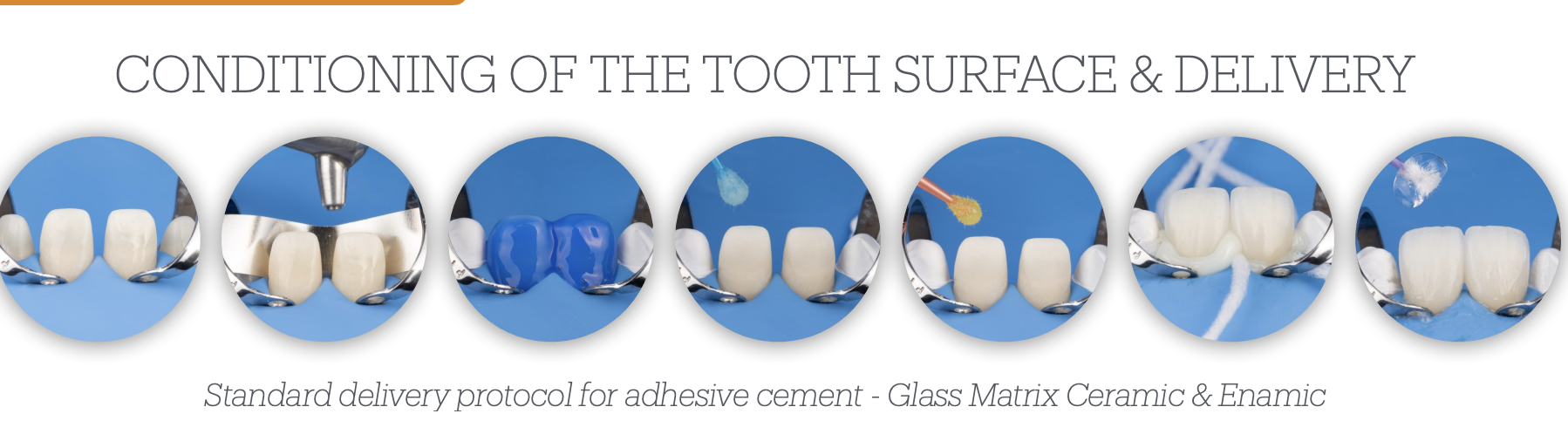
Step 1
Rubber Dam isolation for dry env

Step 2

Step 3

Step 4
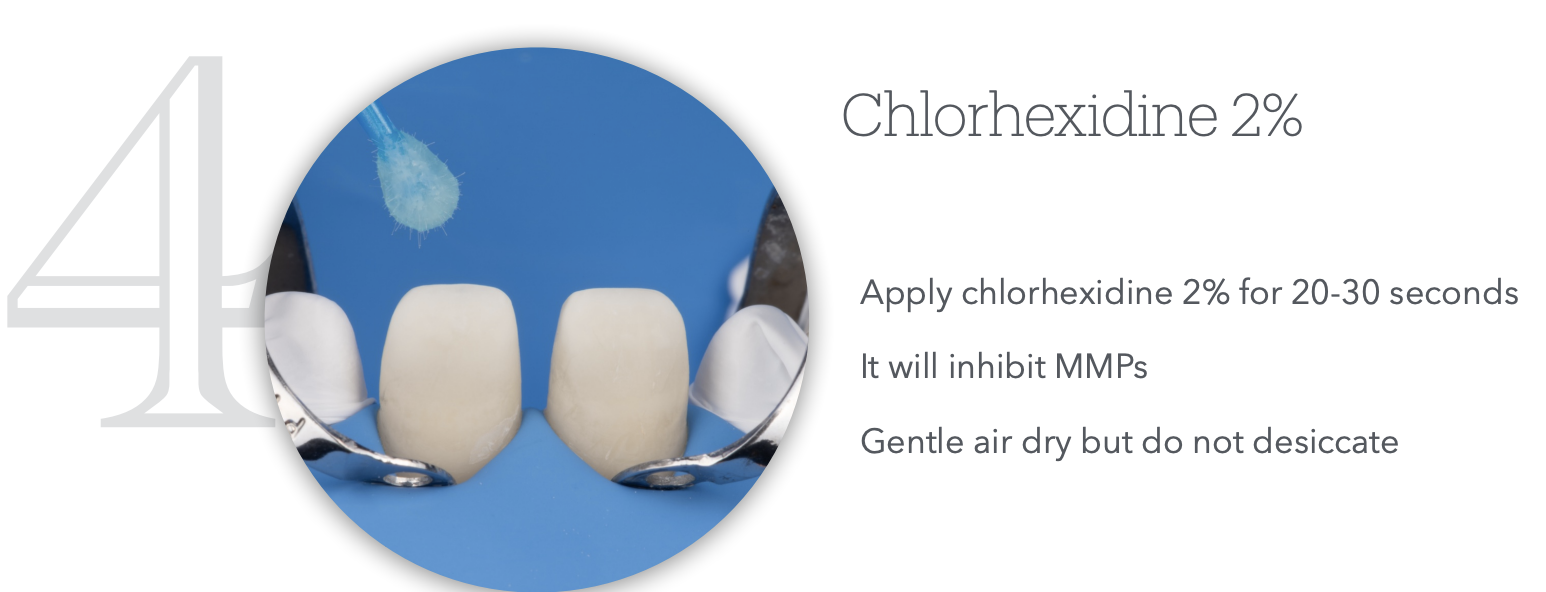
Step 5

Step 5.5?

Step 6

Step 7
