Psychological Assessment Exam 2
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
practicality: things to think about
-cost effective
-does it make sense to use it in this setting?
-worth the time and energy?
-are there better ways?
valid
-meaningful
-accurate
reliable
-consistent
-repeatable scores
are valid test reliable?
always
are reliable test practical?
not always
correlation
tells you about relationships between variables. once you know patterns you can make predictions for missing values
restricted range
causes issues because in that certain area the information could be more random (weakier)
what happens when there is variability across the range?
there is a strong correlation in the beginning of the line and a weak correlation at the end or vice versa.
if something contains both face validity and objectivity who likes it?
everybody!
-IQ test
-clinical symptoms based test
if something contains niether face validity and objectivity who likes it?
nobody:(
-projective test like the inkblot test
-incomplete sentence test
if something contains face validity but not objectivity who likes it?
test takers
-buzzfeed quizzes
-MBII
-horoscopes
-magazine test
if something contains objectivity but not face validity who likes it?
Clinicians (bc they prefer for you to not know what they are testing, harder to fake)
-MMPI
-Neuropsych Test
why is correlation coefficient so important?
they are used to determine reliability +validity. they form the basis of interpretations. stronger correlation mean less error variance (reliability) and more accurate prediction interpretations (validity)
what is a correlation coefficient?
Statistical measure of relationship between two variables. aka (-1) - (1)
how would you describe a correlation?
-positive or negative
-strong, moderate, or weak
- and be able to describe in words
what is another word for r^2?
shared variance
what is r^2?
percentage of variance accounted for by the treatment
describe this scatterplot on paper for practice.
-how would you use one to help make predictions + how far off are you likely to be?(related to the standard error of estimate)
-scatterplots also reveal curvilinear relationships and the problems they pose for prediction
-how do restricted ranges impact correlations? Outliers? Variability across the range? (scatterplots can also help identify these situations)
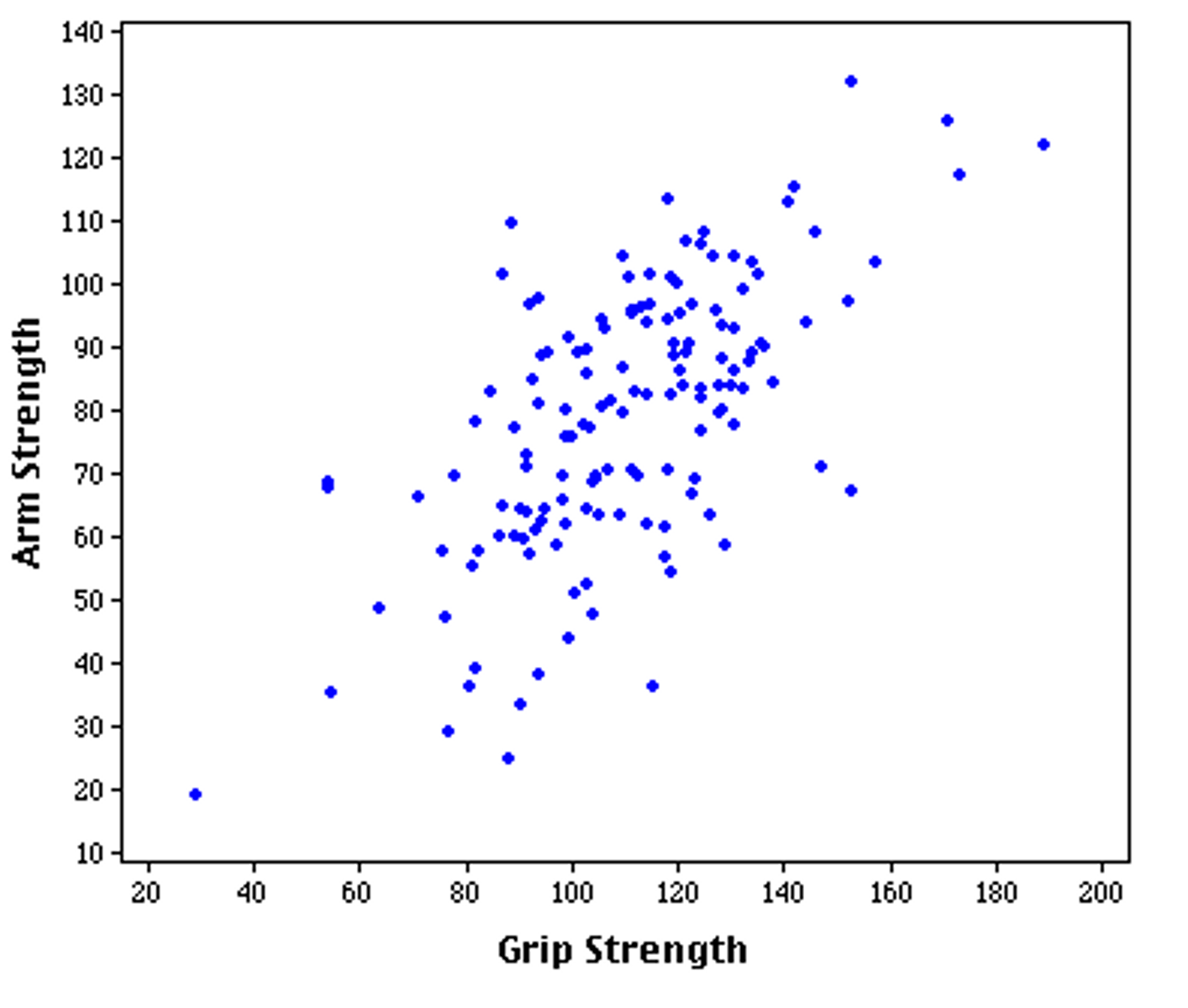
high verse low r
high- strong relationship between measure (test score) and what you are predicting- nobody is that far off, predicted (low error)
low- weka relationship between measure (test score) and what you are predicting- people are spread out, predict score on line and you will be more likely off (high error)
what is a multiple regression?
-allows for multiple predictor variables- simultaneously
-can rank order by amount of variance accounted for
-hoping predictions get better as you add more predictors (incremental validity)
how does multiple regression help with predictions?
if there are more than one predictor than there are more chances the predictions will be better
What is factor analysis?
-used to explain covariation in set of variables
-data reduction method, attempts to simplify info available
-useful for understanding the structure of constructs which will be helpful in determining some types of validity
how does factor analysis help with assessment?
it helps because when it comes to mental health issues there is typically more than one issue going on and with a factor analysis you can see if any of them are related
what is validity?
a judgment about how well a test measure what it says it measures
how is validity establish?
by gathering evidence to show a measurement tool accurately measures what it intends to
what is incremental validity?
-adding this improves predictions
-accounts for variation not measured by the other measures you are already using for predictions
what is an example of incremental validity?
GPA and ACT scores predicting college GPA
what is content validity?
evidence that the test developer adequately surveyed the domain (field) the test covers, that the test items match the domain, and that the test items are accurately being weighted for relative importance
what is test blue print?
a plan regarding types of information to be covered, number of items tapping each area, and the organization of the test
What is face validity?
does it look like it the test is measuring what it should be measuring. Is it covering the correct content or domain? this is not an actual form of validity since appearance doesn’t = accuracy
what is criterion-related validity?
a measure of validity based on showing a substantial correlation between test scores and performance scores
What is concurrent validity?
can predict scores now
-IQ, depression test
what is predictive validity?
can it predict scores/performance in the future
-classic high school GPA and college GPA
what is standard error of estimate?
gives us a confidence interval around a predicted score. Based on the scores receive on a variable. ex: SAT’s allows us to predict the range of scores a person may get on a second variable (ex: first year of college)
do you want a high standard error of estimate?
no you want a low one
do you want a high or low r?
high r bc that means less standard error of estimate
what do we mean by hit rate?
the hit rate is the rate at which the prediction are hitting the line of regression (line of best fit)
what is a false negative?
says you do not have something but you do
What is a false positive?
says you have something but you don't
what happens if you move the cutoff score up or down?
if you move the cutoff score down the you are increasing your risk of a false positive. if you move it up then you are increasing your risk of a false negative.
what is construct validity?
the degree to which test scores are consistent with theoretical constructs, concepts or expectations.
-heavily used in psych because it accounts for the mental illnesses since they are intangible
what is a construct?
theoretical, intangible quality people vary on
what are the factors that help show evidence for construct validity?
factor analysis and multiple regression
what is convergent validity?
scores correlate highly as expected with other tests
-older established test have the same measures as newer test
what is discriminant validity?
scores show little (or no) relationship to those that the theory predicts they should not be related to
-if mental health is not related to intelligence then the test should not correlate the two
what are the two types of experimental design validity?
1. theory consistent group differences
2. theory consistent intervention effects
what are theory-consistent group differences?
- creating research studies that show instrument works as expected
-groups that are more hostile act more agressive
what are theory- consistent intervention effects?
does treatment reduce score of depression?
what is reliability?
measure of consistency
tells you how close you are to the true score
how is reliability determined?
variance of T/ variance of T + error of variance
where does error come from?
random sampling error and systematic error
What is random error?
-unpredictable fluctuations of other variables in the measurement process
-should cancel each other out over time but larger the amount lower the reliability
what is systematic error?
-measuring something else
-consistently off in same direction (raising or lowering scores.
what are the sources of random error?
item selection, test administration, test scoring
what is standardization and how does it help?
specific criteria on what qualifies a scores meaning. If multiple different clinicians are giving different scores this could be due to lack of this. it helps bc it sets a base line
what is test-retest?
-correlates scores from same test given at different times
-possible issues include practice effects, look up answer, etc)
-gold standard
what is alternate forms?
-same content tapped differently but equally
-correlate people's scores on both versions
what is interscorer (interrater)?
-same people different administration
what does it mean if a test has high internal consistency?
it is reliable
What is standard error of measurement (SEM)?
knowing reliability coefficient allows you to calc the likely precision of observed scores based estimated error- SEM tells you how confident you can be that the observed score is close to the true score.
How does the standard error of the difference between two scores help us?
helps determine if two scores are truly different. is there actually a difference between a score of 57 and 60? how big is that difference?
what is split-half (odd-even)?
-try to divide into two equally hard halves, correlate scores
-especially useful if cost or practice effect would impact test-retest
What is coefficient alpha?
mean of all possible split halves
what is inter-item consistency?
degree of correlation among all items
Why can't we just compare scores to know if two people are different?
bc you need all the information like whether a high score or low score is better, what the mean, median, and mode of each score.
When is the median most useful?
when you have outliers that distort the mean too far from the middle
what is range?
the difference between the highest and lowest scores or that plus one
What is the interquartile?
-68% 1 SD
-95% 2SD
-99.5% 3SD
what is standard deviation?
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
when is there a large SD on a distribution? what about small?
there is a large SD when the distribution is wide and small when it is narrow
What is the difference between skew and kurtosis?
skew is an asymmetrical distribution while kurtosis is the steepness of a distribution
what does a positive skew look like?
the high point near the x-axis and the tail (skew) going towards the positive numbers

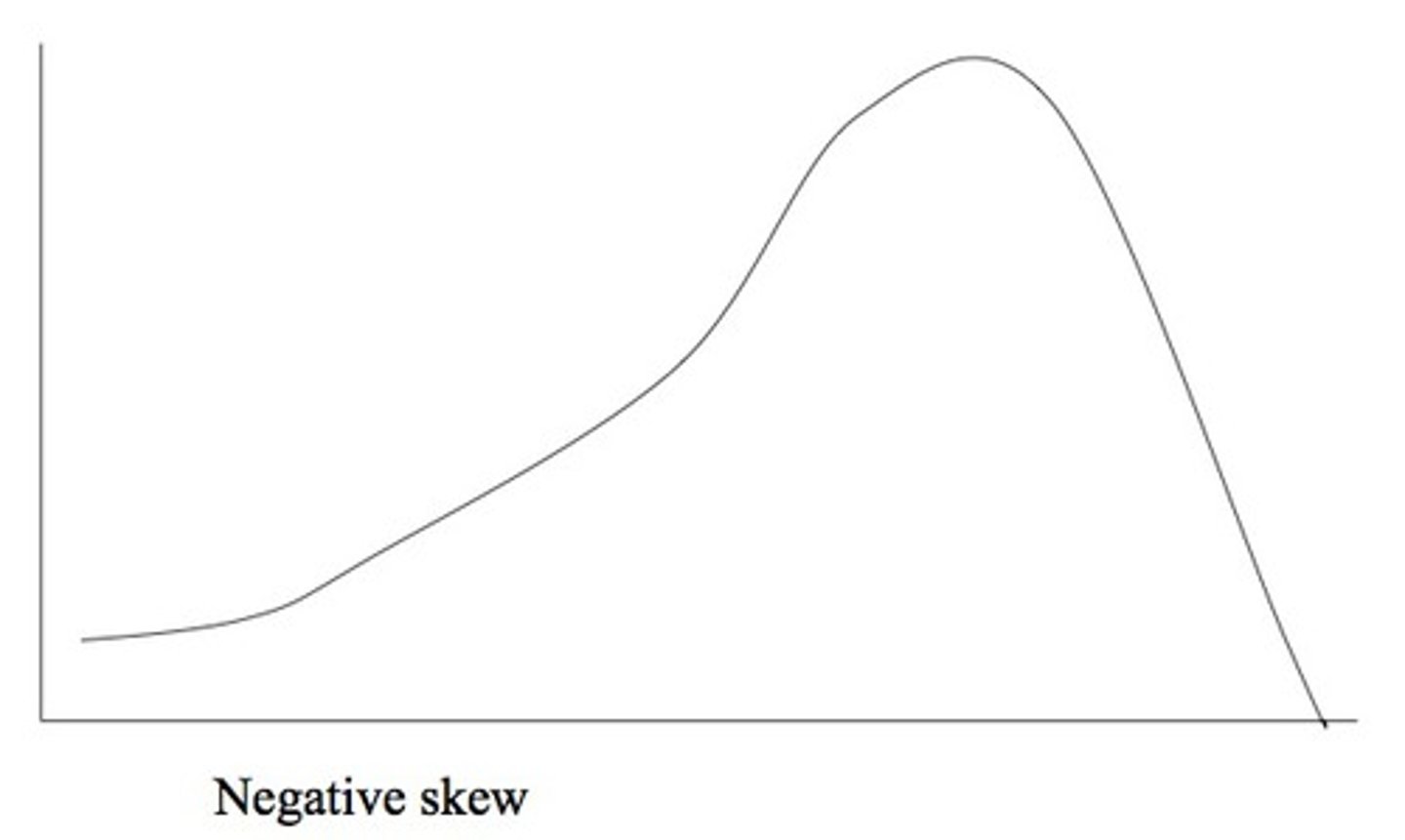
what does a negative skew look like?
the high point is on the farthest side from the x-axis and the tail (skew) is going towards the negative numbers
what does a mesokurtic distribution look like?
normal

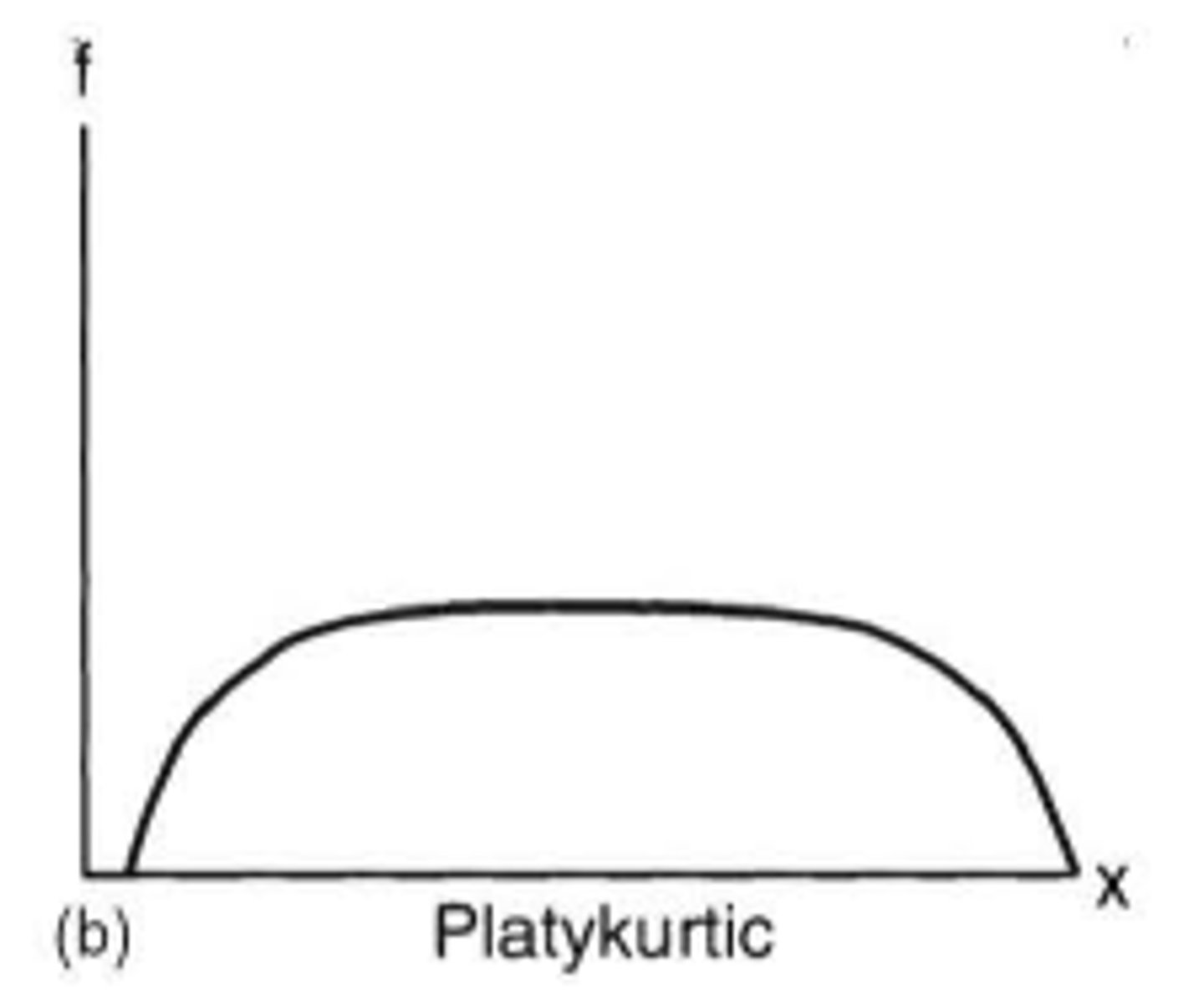
what does a platykurtic distribution look like?
relatively flat distribution
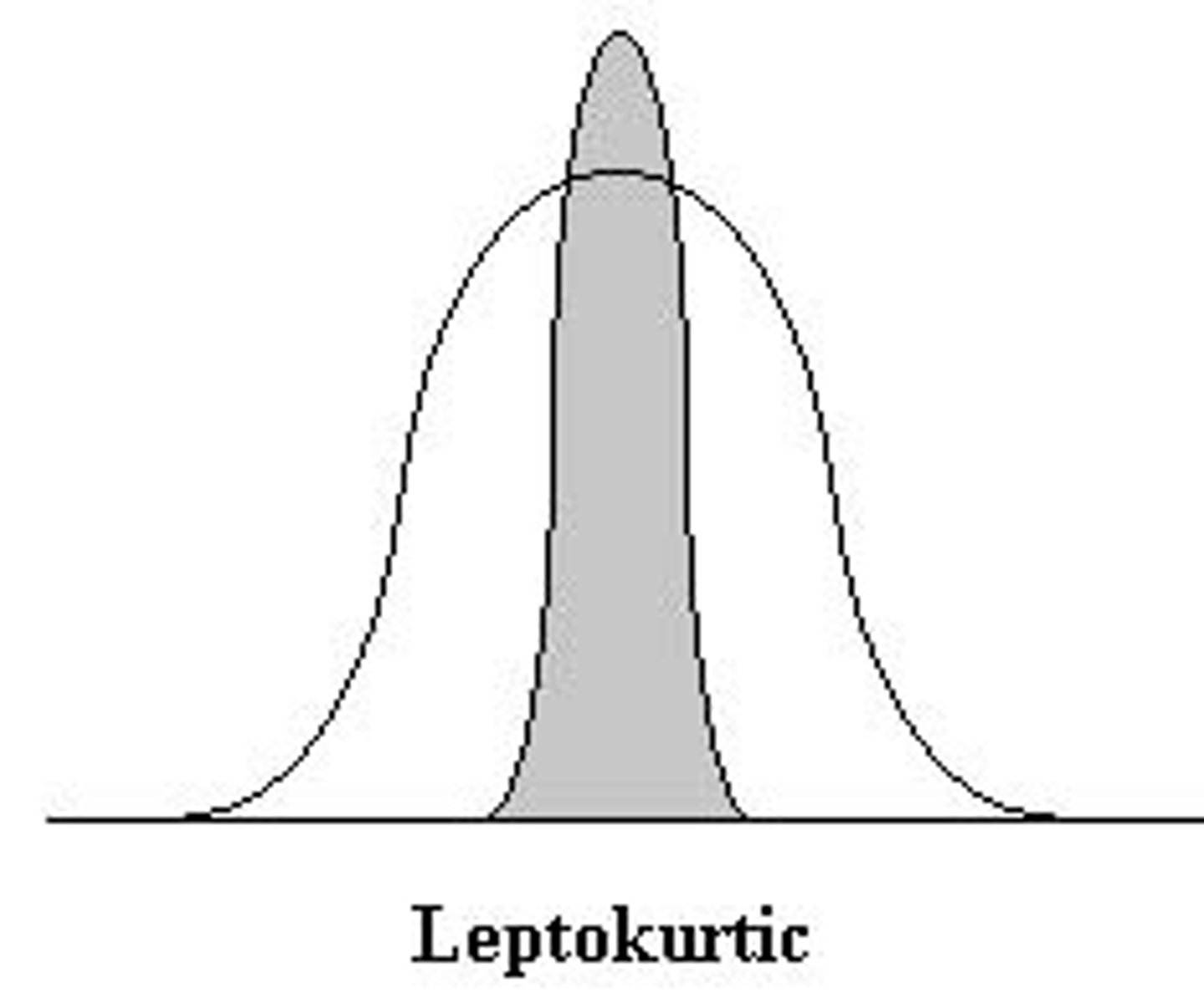
What does a leptokurtic distribution look like?
tall and skinny
What are norms?
provide additional info about the exact distribution of scores for a specific group
How are norms developed?
by collecting test scores on a large, representative sample of the desired comparison group
what do norms tell you?
they tell you what is the average score of the people in the population. age norms is the average performance of different aged samples of instructions. grade norms are the average performance of test takers in that grade
what does percentile tell you?
tells you what percent of people you did better than. if you are in the 84th percentile than you did better than 84% of people
what is random sampling?
people are randomly selected
pros- everyone in the population has an equal chance of being studied, convenience, cost effective, high chance of being representative
What is stratified random sampling?
All groups are represented based on class, ethnicity and gender and age.
However, this is complex and takes long to plan, because it is proportionate to each group. It is also biased since the researcher decides the categories used.
What is purposive sampling?
handpicking sample members
pros- get exactly what you need
cons- unintentional bias
what is convenience sampling?
Selecting sample based on whoever is convenient
pros-easy
cons- easy to not be representative
what are age norms?
average performance of different samples of testtakers who were at various ages when the test was administered
what are grade norms?
the average test performance of testtakers in a given school grade
what are national norms?
derived from a sample that was nationally representative of the population at the time
what are subgroup norms?
a norm sample can be segmented by any of the criteria used to select full sample
what are local norms?
normative information with respect to the local population's performance on some test
what is the relationship between the mean, median, and mode in a normal distribution?
the are all equal
what are z scores and how are they helpful?
the number of standard deviations units from the mean a score is. they are helpful because they standardize scores. instead of a 50,25, and a 30 they are all now z=2 meaning they are two deviations away from the mean
practicality
whether it makes sense to use a test in a particular situation
factor analysis
helps developers determine difference and similarities between subsets. Helps determine patterns and calculate which variables has a higher degree of commonality
Criterion related validity
relationships between scores and other measures. Do the scores predict the performance on a criterion? must be VALID and noncontaminated (meaning it’s independent can't share any items)
Two Types of Criterion Related Validity
Concurrent Validity and Predictive Validity
Concurrent Validity
can predict score now (very quickly) Ex: 100 clients take the Beck Depression Inventory Test (BDI). 500 people take the alcohol test
Predictive Validity:
can predict scores/performance in the future. Ex: using your current college gpa to determine your insurance claim. Basing it on potential risk of you crashing based on how low or high your gpa is. SAT scores correlated w/ college GPA. GRE correlated to graduation rate.
High r
strong relationship between measure (test score) and what you are predicting. no one is that far off, predict score on the line and you will be close
No r
no relationship between measures