Muscles + Ligaments
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
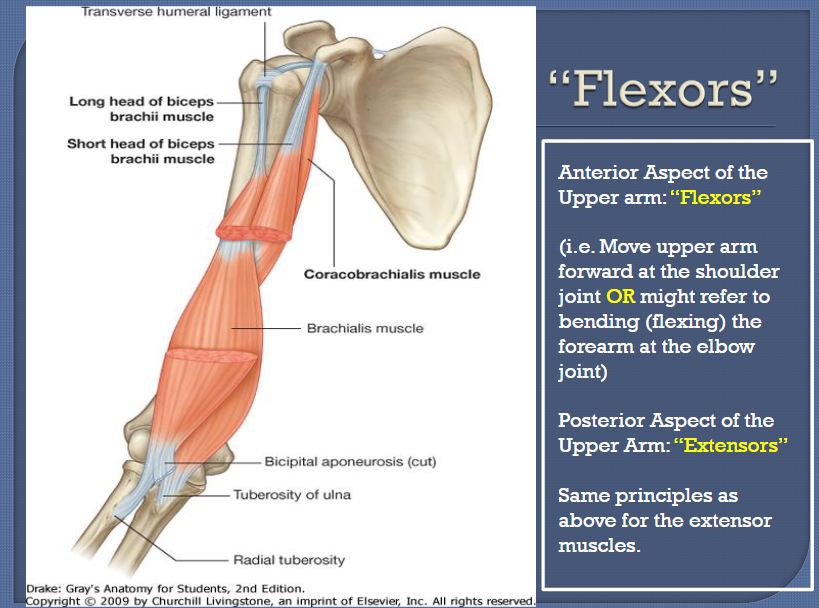
Flexors of the upper arm and forearm
Flexors = muscles that cause flexion
Extensors = muscles that cause extension
Upper arm flexors:
Coracobrachialis
Anterior deltoid
Biceps brachii
Pectoralis major
Elbow flexors:
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
Pronator teres (weak flexor)
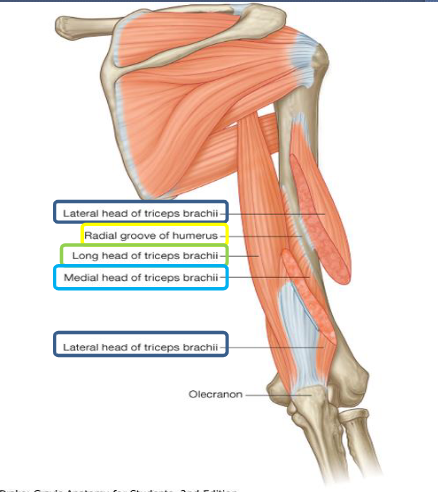
Extensors of the upper arm and forearm
Extensors = muscles that cause extension
Extensors of upper arm:
Latissimus Dorsi
Deltoid (posterior fibres)
Teres Major
Long head of biceps brachii
Extensors of forearm:
Triceps brachii
Anconeus
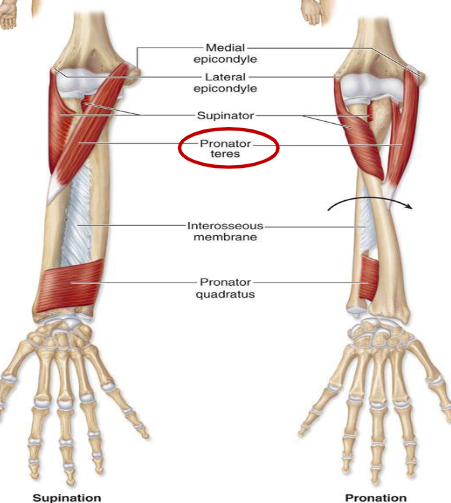
Muscles that pronate and supinate the forearm
The two muscles located on the anterior forearm that pronate the forearm are:
Pronator teres
Pronator quadratus
The one muscle located on the posterior forearm that supinates the forearm is:
Supinator
Main concepts of supination vs flexion muscles
The supinator muscle’s main function is to supinate the forearm. This can be actioned with the elbow in any position of flexion or extension. The supinator can also work synergistically with the biceps brachii to produce powerful supination if required. However, the biceps brachii muscle cannot supinate the forearm when the elbow is extended, only when it is flexed
Elbow joint classification + articulation surfaces
Classification:
Synovial Hinge
Articulation Surfaces:
Trochlea of humerus with the trochlear notch of ulna
Capitulum of humerus with head of radius
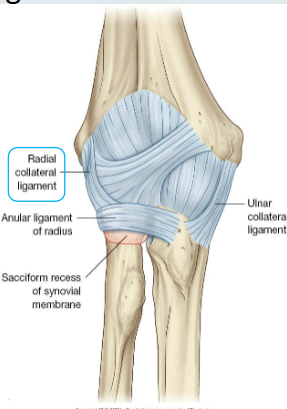
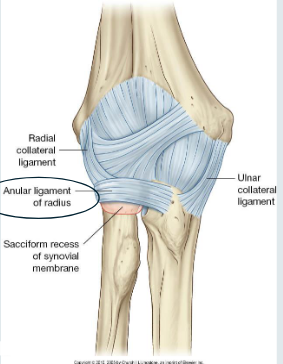
Ligaments of the elbow
Function of elbow ligaments: Stabilisation
Primarily 3 ligaments:
Medial (ulnar) collateral (MCL)
Lateral (radial) collateral (LCL)
Annular ligament
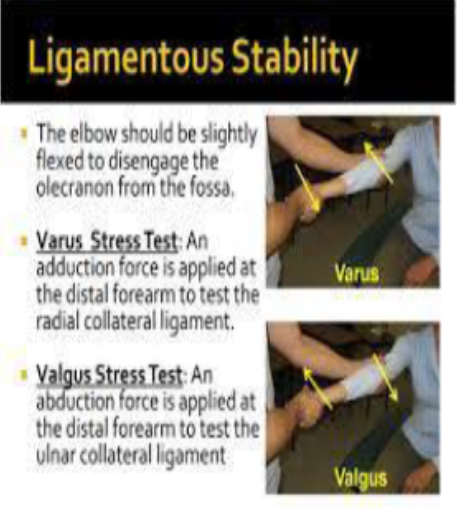
MCL & LCL provides:
Varus and valgus stability
Enable rotation
Annular ligament = stabilises radial head in radial notch
(Varus and valgus stability refer to the ability of a joint, like the knee or elbow, t resist forces that push it inward (valgus) or outward (varus)
Ulnar collateral ligament
From: Medial epicondyle of humerus
To: Coranoid process of the ulna (anteriorly) and olecranon (posteriorly)
Action: enables rotation
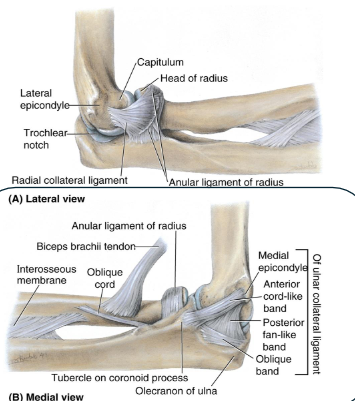
Radial collateral ligament
From: Lateral epicondyle
To: Annular ligament
Valgus and Varus stresses at the elbow
Annular ligament
Stabilises radial head in radial notch
Both ends attach to the anterior and posterior margins of the radial notch of the ulna- hereby surrounding the radial head and neck
Fibrous joint capsule also attaches as well as radial collateral ligament
Quadrate ligament
Olecranon and elbow bursa’s
Thin, fluid-filled sac- located at olecranon (elbow bony tip).
Function: Helps reduce friction between bone and soft tissue e.g. skin etc
Olecranan bursitis = inflammation of a bursa
Borders of the antecubital fossa
BORDERS of ANTECUBITAL FOSSA:
Lateral: brachioradialis muscle
Medial: pronator teres muscle
Superior: Imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus
Roof: Skin & Fascia
Base: proximally by the brachialis, and distally by the supinator muscle.
Apex: Where the lateral and medial