Morin The Brain
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
1
New cards
Brain lesion
naturally/experimentally destroyed brain tissue to study animal behaviors after such destruction
2
New cards
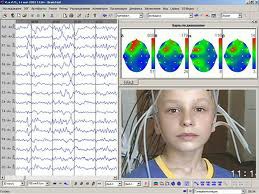
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Amplified recording of electrical waves across brains surface - measured by electrodes on scalp
non intrusive and painless
non intrusive and painless
3
New cards
different colors of EEG
Blue is non-active area
Red/orange shows activity
Red/orange shows activity
4
New cards
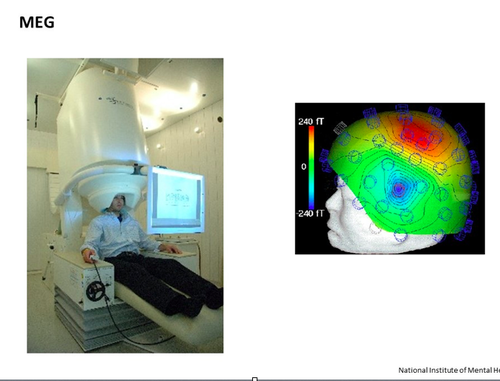
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
a patient completes tasks and thousands of neurons create electrical pulses which create magnetic fields
speed and strength helps researchers understand how tasks influence brain activity
speed and strength helps researchers understand how tasks influence brain activity
5
New cards
What are MEGs used for
surgical brain mapping
6
New cards
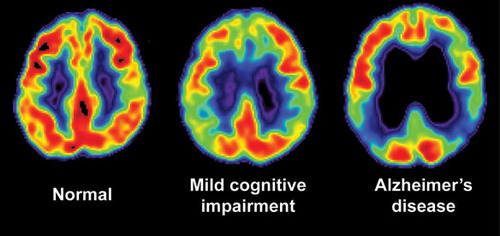
PET scan
you drink a sugary glucose liquid beforehand -- active neurons gobble glucose
visual display of brain activity that detects a radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a task
visual display of brain activity that detects a radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a task
7
New cards
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of brain tissue
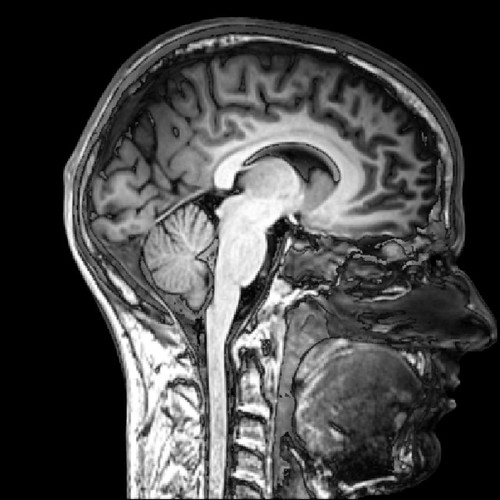
8
New cards
fMRI
uses magnetic fields and radio waves that distinguish brain tissue and shows the structures that are functioning
9
New cards
MRI vs fMRI
fMRI is a video it shows which structures are working
MRI is a picture
MRI is a picture
10
New cards
MRI vs X-Rays
MRI shows ligaments, x-rays show bones
11
New cards
CT Scans
x-ray photos from 180 angles that create a cross-sectional image
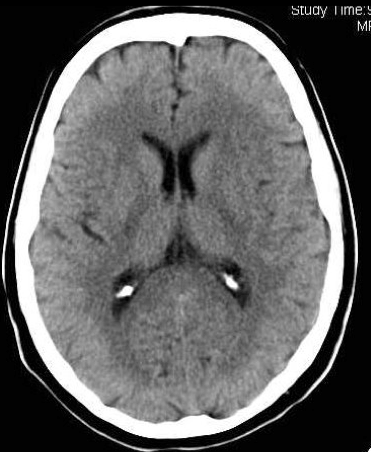
12
New cards
Brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
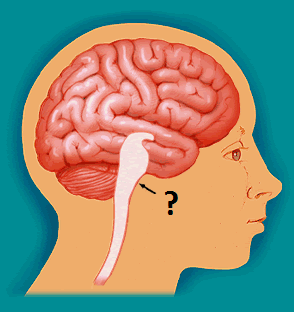
13
New cards
Medulla
base of brainstem - controls heartbeat and breathing
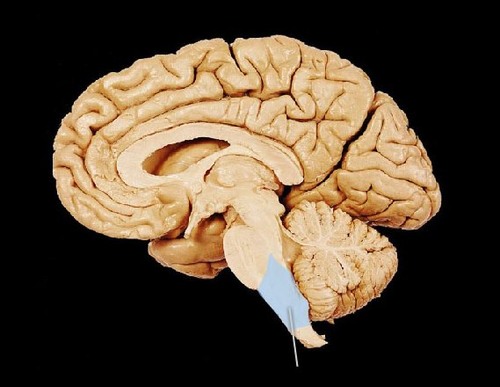
14
New cards
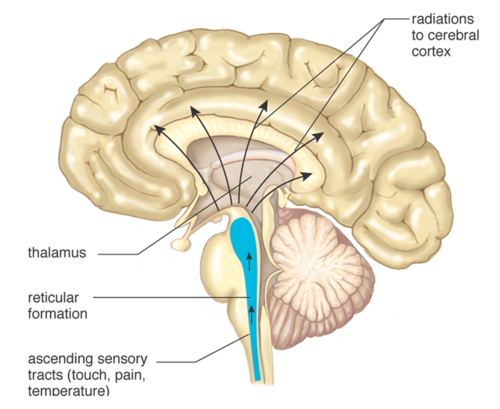
Reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal
15
New cards
Pons
Sits directly above medulla
Connects upper and lower part of the brain, controls dreams during REM stage
Connects upper and lower part of the brain, controls dreams during REM stage
16
New cards
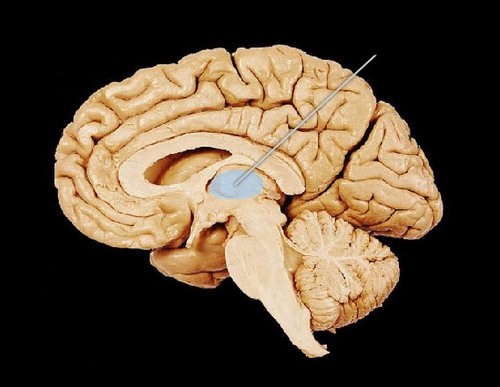
Thalamus
Sensory switchboard - directs messages to sensory areas in cortex, sends replies to cerebellum and medulla
at top of brainstem
at top of brainstem
17
New cards
What sense does the thalamus not process
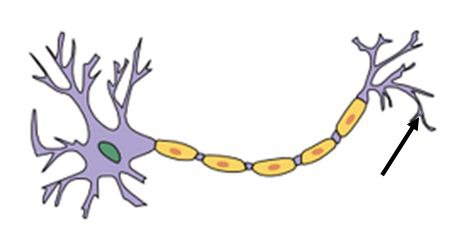
Smell
18
New cards
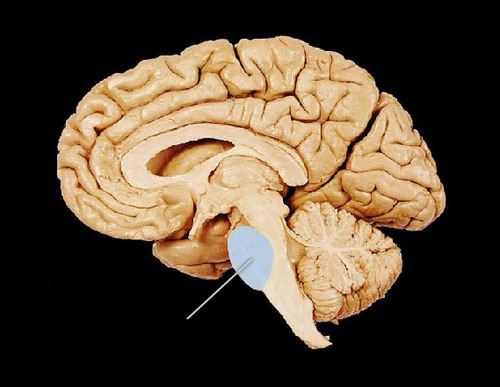
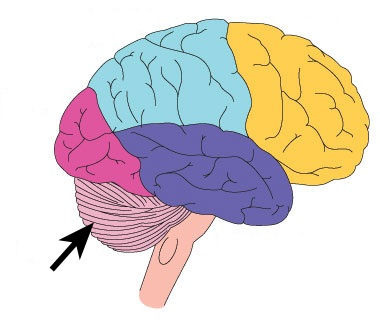
Cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem
coordinates voluntary movements and balance
coordinates voluntary movements and balance
19
New cards
limbic system
System of neural structures at border of brainstem and cerebrum
associated with fear, aggression, hunger, sex
associated with fear, aggression, hunger, sex
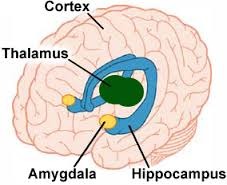
20
New cards
Amygdala
Part of the limbic system - two almond-shaped neural clusters linked to fear and anger
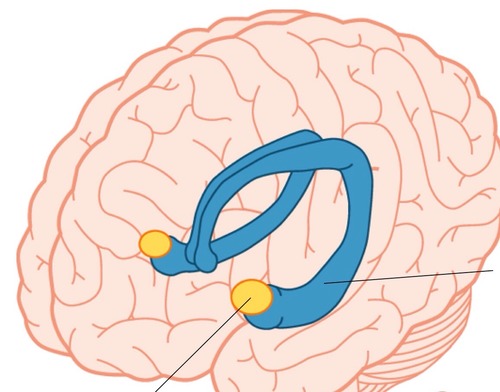
21
New cards
Hypothalamus
Part of the limbic system, under thalamus
directs maintenance activities (eating, drinking, temperature, emotion), helps govern endocrine system w pituitary gland
directs maintenance activities (eating, drinking, temperature, emotion), helps govern endocrine system w pituitary gland
22
New cards
4 F's Hypothalamus is responsible for...
Food, fight, flight, fornication
23
New cards
Two parts of hypothalamus
lateral hypothalamus and ventromedial hypothalamus
24
New cards
Hippocampus
forms, stores, processes memory
part of limbic system, (looks like a seahorse)
part of limbic system, (looks like a seahorse)
25
New cards
parts of the limbic system
Hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus
26
New cards
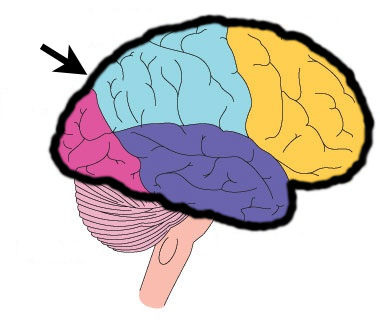
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres
the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
27
New cards
Four lobes of cerebral cortex
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
separated by prominent fissures
separated by prominent fissures
28
New cards
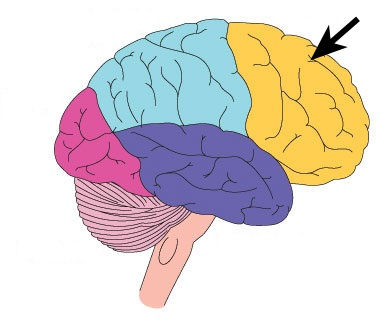
Frontal lobe
functions include planning, organizing, problem solving, "higher cognitive functions" - behavior and emotions
fully mature at 25
fully mature at 25
29
New cards
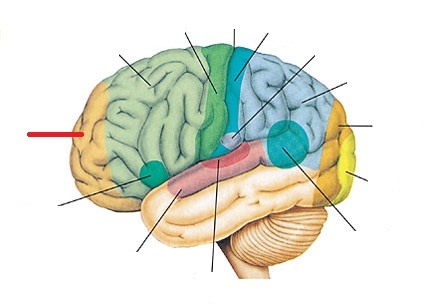
Prefrontal cortex
the frontmost portion of the frontal lobes - especially important for decision making
30
New cards
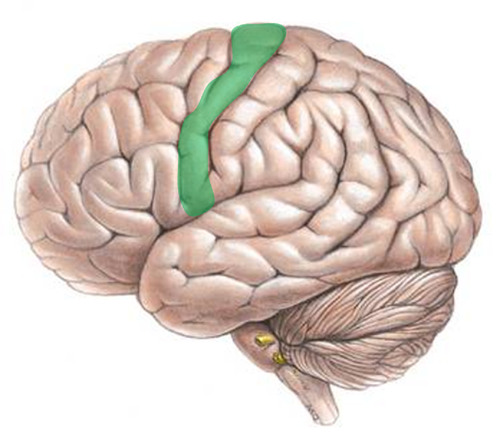
Back of the frontal lobe
pre-motor/motor areas -- motor cortex
31
New cards
Damage to the frontal lobe
Change in talking, mood, mental flexibility, socialization and behavior
IQ does not get impactd
IQ does not get impactd
32
New cards
Parietal lobe
processes sensory input/discrimination, body orientation
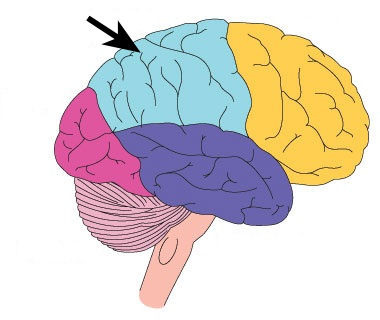
33
New cards
somatosensory cortex
registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
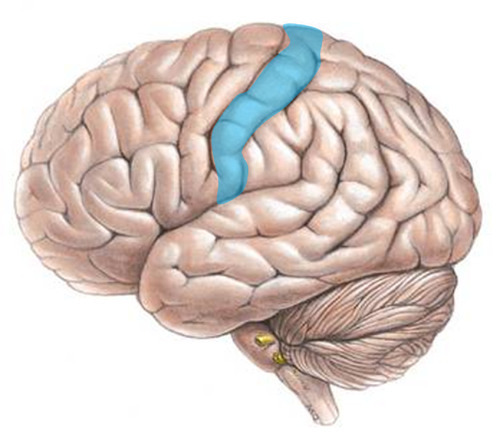
34
New cards
primary somatosensory cortex
area of the parietal lobe where messages from the sense receptors are registered
35
New cards
secondary somatosensory cortex
Region of cerebral cortex that analyzes information from the primary somatosensory cortex and thalamus;
36
New cards
Damage to the Parietal Lobe
disorientation of environment or parts of body, can't distinguish sensory stimuli
severe: can't recognize yourself
severe: can't recognize yourself
37
New cards
Occipital lobe
primary visual reception/association area - allows for visual interpretation
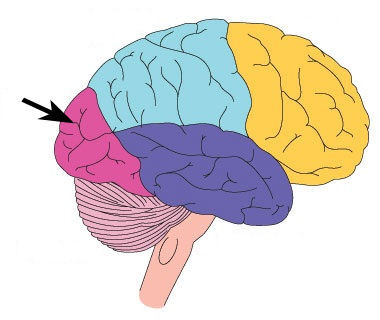
38
New cards
Damages to occipital lobe
hallucinations
39
New cards
temporal lobe
hearing and auditory interpretation -- damages cause hearing deficits
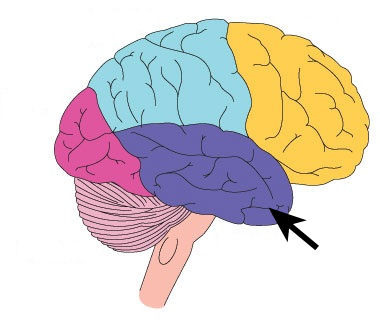
40
New cards
Homunculus
a maplike representation of regions of the body in the brain
shows how a person would look if it was proportionate to the amount of the brain that goes towards it -- lips would be biggest
shows how a person would look if it was proportionate to the amount of the brain that goes towards it -- lips would be biggest
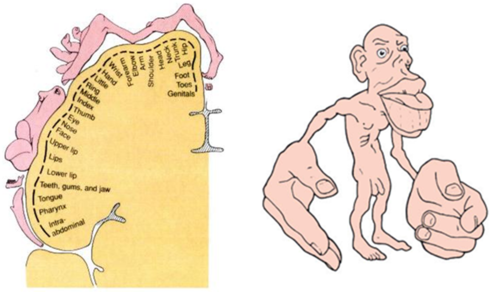
41
New cards
aphasia
inability to speak
caused by damage to Broca's area or wernicke's area (both in left hemisphere)
caused by damage to Broca's area or wernicke's area (both in left hemisphere)
42
New cards
Broca's area
left frontal lobe -- impairs speaking
specialized strip of neurons used for speech production
specialized strip of neurons used for speech production
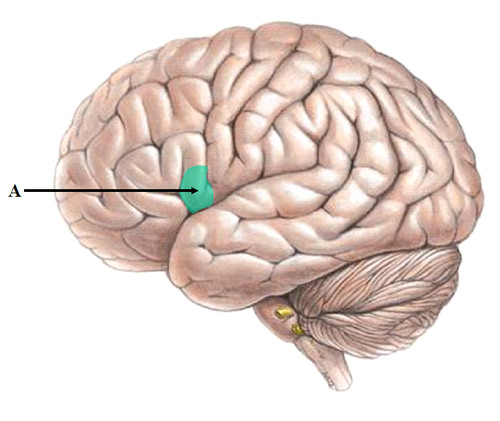
43
New cards
wernicke's area
left parietal/temporal lobe - impairs understanding
this typically allows you to comprehend the words people speak
this typically allows you to comprehend the words people speak
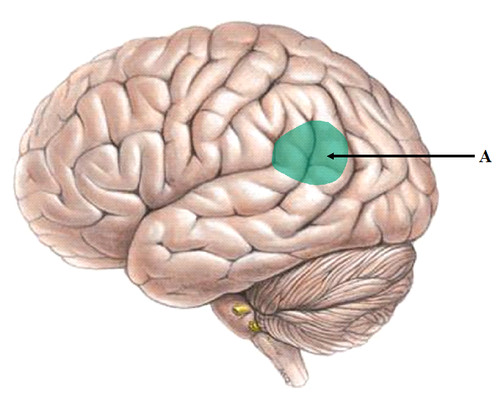
44
New cards
angular gyrus
transforms visual representations into an auditory code - helps with reading
on temporal, parietal and frontal (TPF)
on temporal, parietal and frontal (TPF)
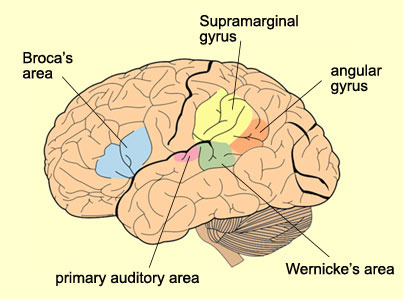
45
New cards
visual cortex
The visual processing areas of cortex in the occipital and temporal lobes.
receives written words as visual stimulation
receives written words as visual stimulation
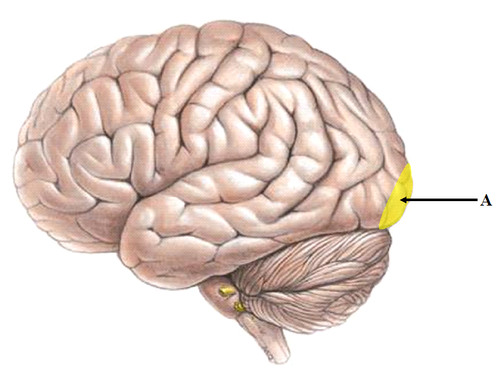
46
New cards
Do you want an EEG to show brain activity
no because you can't isolate the different parts being used
47
New cards
which parts are used to hear words
auditory cortex and wernicke's area
48
New cards
Which parts are used to see words
visual cortex and angular gyrus
49
New cards
which parts are used to speak words
Broca's and motor cortex
50
New cards
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are composed of neurons that help provide sense and meaning to information registered in the cortex -- they're multitaskers that have a lot of different info but aren't highly specialized
51
New cards
plasticity
the brain's ability to change -- decreases with age
52
New cards
what is the brain sculpted by
genes and experiences
53
New cards
Plasticity in sensory deficits
if there's a deficit neurons can go from one place to the other to help the body
EX: If you're blind neurons go to other senses
EX: If you're blind neurons go to other senses
54
New cards
Plasticity with repeated behaviors
if you do something often enough (typically at a young age) association area neurons can become specialized
55
New cards
how is the brain controlled
contra-laterally
left hem controls right side
right hem controls left side
left hem controls right side
right hem controls left side
56
New cards
left hemisphere
reading, writing, speaking, math and comprehension skills
(Broca's and wernicke's are here)
(Broca's and wernicke's are here)
57
New cards
right hemisphere
spatial abilities, face recognition, visual imagery, music
58
New cards
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
59
New cards
How to split the brain and why
cut the corpus callosum
if you have an epilepsy or a stroke or some storm in the brain cutting this protects it from spreading
if you have an epilepsy or a stroke or some storm in the brain cutting this protects it from spreading
60
New cards
how a severed corpus callosum impacts seeing objects
objects in the right visual sphere (processed by left) can be named but in the left they can't
61
New cards
optic nerves
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
don't get severed when corpus is cut
don't get severed when corpus is cut
62
New cards
divided consciousness post severed corpus callosum
the two sides of the brain have processed two different things
if you see heart the person would verbalize they saw "art" but with their left hand point to "he"
if you see heart the person would verbalize they saw "art" but with their left hand point to "he"
63
New cards
chimeric figures test
constructed of two half pictures arranged so that patients fixate upon the vertical division between the two half stimuli
tests which hemisphere is dominant & how a split brain patient processes things
tests which hemisphere is dominant & how a split brain patient processes things
64
New cards
how information is processed in non-split brains
two hemispheres share information through corpus callosum - work together
65
New cards
what factors influence handedness
genes/prenatal factors
66
New cards
what professions are lefties more prominent in
musicians, mathematicians, baseball players, architects, artists
67
New cards
how percentage of left handers is impacted by age
percentage decreases sharply in older people
68
New cards
The two types of nervous systems
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
69
New cards
Sensory Neurons (Afferent neurons)
carry nerve impulses from receptors/sense organs to CNS
tells the CNS what's happened
tells the CNS what's happened
70
New cards
Motor Neurons (Efferent Neurons)
carry nerve impulses AWAY from CNS to muscles
tell the body what the CNS says
tell the body what the CNS says
71
New cards
Interneurons
connect sensory and motor neurons, only exist in the CNS
72
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal cord
73
New cards
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Consist of autonomic and somatic nervous system
Consist of autonomic and somatic nervous system
74
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
controls self regulated actions of internal organs
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
75
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
Arousing
Part of the autonomic nervous system (peripheral)
Part of the autonomic nervous system (peripheral)
76
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
Calming
Part of the autonomic nervous system (peripheral)
Part of the autonomic nervous system (peripheral)
77
New cards
Somatic nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system
controls voluntary movements (deals with the body)
controls voluntary movements (deals with the body)
78
New cards
Nervous System
Consists of all nerve cells -- speedy electrochemical communication system
79
New cards
Examples of what the autonomic nervous system controls
breathing, blinking, heartbeat, digestion, salivation, sweating, arousal
80
New cards
When does the sympathetic nervous system activate
in stressful situations it arouses the body and mobilizes its energy
81
New cards
When does the parasympathetic nervous system activate
in calming situations it calms the body, conserving its energyt
82
New cards
Does the spinal cord feel things (pain, pleasure, etc)
No, this all comes from the brain
83
New cards
Can the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system work together?
no, when one is on the other is off
84
New cards
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS - Lou Gehrig's disease)
"No muscle nourishment" - progressive degeneration of motor neurons affecting nerve cells in brain and spinal cord
when motor neurons die the brain can't initiate/control muscle movement -> can lead to total paralyzation
when motor neurons die the brain can't initiate/control muscle movement -> can lead to total paralyzation
85
New cards
The Endocrine System
the body's "slow" chemical communication system
86
New cards
How does the endocrine system communicate
carried out by hormones synthesized by a set of glands
87
New cards
Hormones
chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands and secreted in the bloodstream -- affect the brain and other tissues o the body
88
New cards
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, excitement during emergency situations
89
New cards
Pituitary Gland
"master" gland
has an anterior and posterior
has an anterior and posterior
90
New cards
Anterior pituitary gland
Releases hormones that regulate other glands
91
New cards
Posterior pituitary gland
Regulates water and salt balance
92
New cards
Thyroid Gland
Affects/regulates metabolism
93
New cards
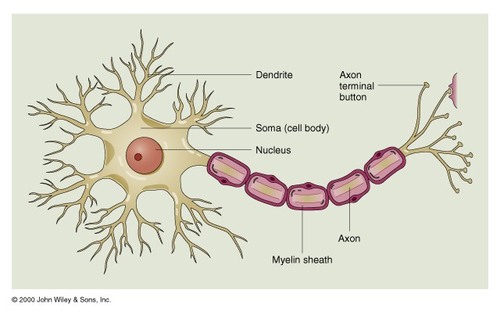
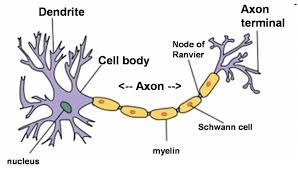
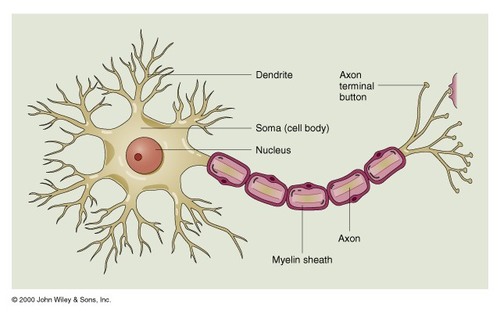
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
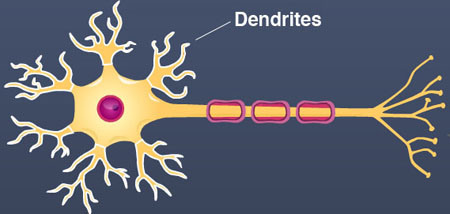
94
New cards
Soma/the cell body
contains the cell nucleus, connected to dendrites
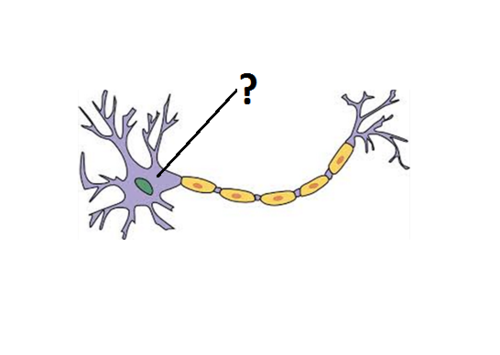
95
New cards
Nucleus
96
New cards
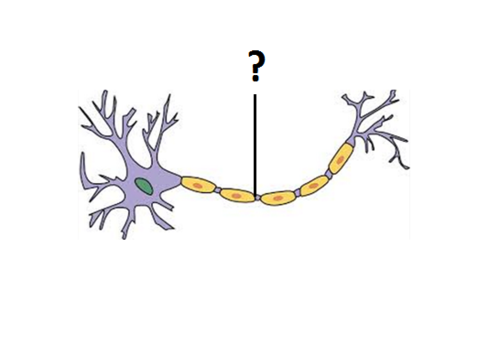
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers
97
New cards
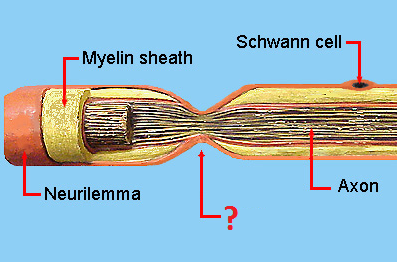
Myelin Sheath
Insulates axon, helps the speed of neural transition
98
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
99
New cards
Terminal buttons/buds
Neurotransmitters are here
100
New cards
Terminal branches