Lab 6 A Phys, Diagnosing Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
True
True or False: Elevated blood cholesterol has been established as a serious risk factor for coronary heart disease and stroke which are leading causes of death in the United States
Receptors
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder where individuals possess mutations in the gene for the LDL _________________ and thus are unable to efficiently remove LDL from the circulation resulting increased blood cholesterol..
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH)
A genetic disorder known as _____________________________________ causes an increase in blood levels of the "bad" form of cholesterol, known as low density lipoproteins (LDLs).. Give the complete name and abbreviation in parentheses.
Cholesterol
_______________________ is a complex lipid essential for the survival of all animal cells. Its primary function is the stabilization of cellular membranes and is the parent molecule for the synthesis of steroid hormones such as testosterone and estrogen.
Cellular membranes
Cholesterol is a complex lipid essential for the survival of all animal cells. Its primary function is the stabilization of _______________________________ and is the parent molecule for the synthesis of steroid hormones such as testosterone and estrogen
Steroid
Cholesterol is a complex lipid essential for the survival of all animal cells. Its primary function is the stabilization of cellular membranes and is the parent molecule for the synthesis of _______________________ hormones such as testosterone and estrogen
Cholesterol
____________________________ is also a precursor for vitamin D and for bile salts, which facilitate the digestion of lipids in the intestine.
Liver
Cholesterol is synthesized in the organ known as the ___________ and is absorbed in the intestine from ingested food.
Lipoproteins
Cholesterol and other lipids are not water soluble and thus are circulated in body fluids in spherical bodies known as ______________________.
Receptors
The proteins of the lipoproteins can serve as ligands (binding groups) to specific cell _____________________ that help move the lipoprotein into the cell. If the cells do not make the receptors or have a reduced number of receptors on their surface then the lipid containing lipoproteins are not transported into the cell very well and remain in the blood stream.
Low density lipoproteins (LDLs)
Cholesterol processed by the liver is packaged into particles known as very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs), which are processed in the
blood stream to form __________________________. Give the complete name and abbreviation in parentheses.
High density lipoproteins (HDLs)
Name the type of lipoproteins take up cholesterol from LDLs and peripheral tissues and transport it back to the liver for repackaging or excretion. Give the complete name and abbreviation in parentheses.
Good
Because HDL removes cholesterol from the circulation, this is often referred to as "______________ cholesterol". LDL, in contrast, transport cholesterol from the liver to arteries and is often termed "bad cholesterol". The naming is based on the destination of the cholesterol and realize that cholesterol is a just a molecule and is not technically bad or good.
Bad
Because HDL removes cholesterol from the circulation, this is often referred to as "good cholesterol". LDL, in contrast, transport cholesterol from the liver to arteries and is often termed "_______ cholesterol". The naming is based on the destination of the cholesterol and realize that cholesterol is a just a molecule and is not technically bad or good.
Low density lipoproteins (LDLs)
While cholesterol is essential for life, excess serum cholesterol can have serious negative consequences. The role of elevated blood cholesterol in cardiovascular disease is well established. _____________________________ can accumulate on arterial walls; stimulate inflammation and the formation of plaque which eventually can lead to occlusions that restrict blood flow to the heart or brain, resulting in heart attack or stroke.
Give the complete name and abbreviation in parentheses.
Low density lipoproteins (LDLs)
FH is characterized by very high levels of _______________________________, in the blood and early cardiovascular disease.
Give the complete name and abbreviation in parentheses.
Dominant
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) follows an autosomal ________________________ (dominant or recessive) pattern of inheritance meaning that one copy of an altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder.
One
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance meaning that ______________________ copy of an altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder.
Heterozygous
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance meaning that one copy of an altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. However this type of expression is considered to be an incomplete dominant or a semidominant trait, which means there are two forms of the disease - the disease exhibits a gene dosage effect. Patients who are _______________________ (1 bad gene copy) for the mutation still have one functional gene and therefore possess 50% of the normal level of receptors of unaffected individuals and higher-than-normal levels of blood cholesterol. Although they are at increased risk for atherosclerosis and heart disease, symptoms may not develop at all, or not until later in life.
Homozygous
Patients who are _______________________ (2 bad gene copies) for the Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) mutation completely lack the LDL receptor and therefore possess extremely elevated levels of serum cholesterol and if untreated, usually die in childhood of coronary artery disease.
500
Heterozygotes for FH occur with a frequency of 1 in ______________ which makes this disease one of the most common inherited disorders in metabolism.
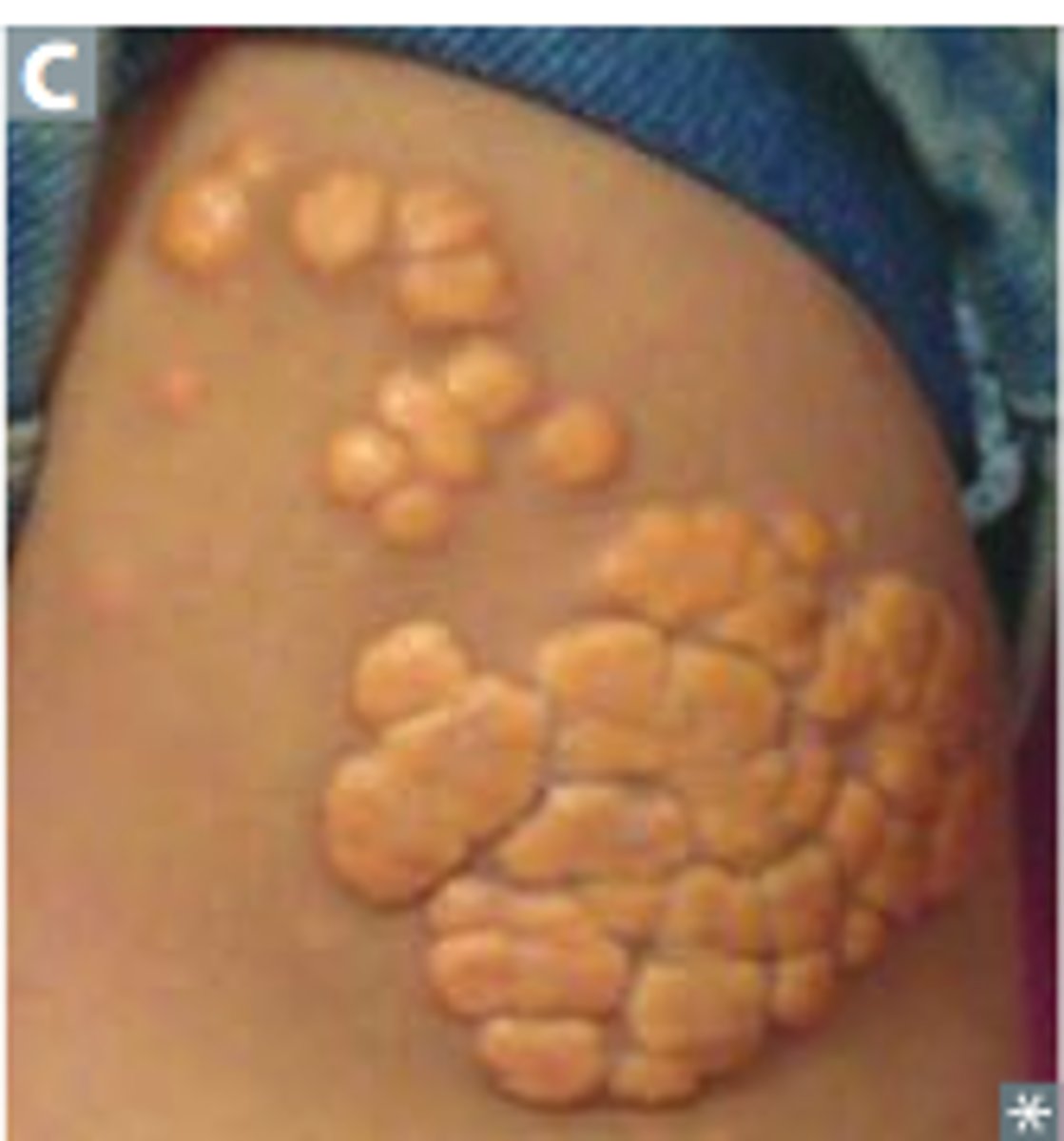
Xanthoma
Term for the yellow colored raised growths due to excess lipids (lipidosis) mainly due to high LDL levels. They are often associated with inherited disorders of lipid metabolism (inherited problems with the way that fats are broken down and used), such as in familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). The growths are caused by accumulations of lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells). The excess LDLs containing fat/cholesterol-rich material are taken up by macrophages and become foam cells. Accumulations of these cells cause the growth and can appear anywhere in the body.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Give the complete name and abbreviation in parentheses of the technique used to "amplify" segments of DNA.
Taq DNA polymerase
Name of the enzyme used in PCR that is purified from a bacterium found in hot springs, It is used because it is stable at high temperatures.
Denaturation
In the fist step of PCR, DNA is heated to about 95°C and the DNA complimentary strands separate in a process called ____________________
Primers
In the second step of PCR, the sample is cooled to around 50°C. This "cooling" allows the attachment (annealing) of a set of two small synthetic oligonucleotides, known as _________________ to the target region to be amplified.
Nucleotides
In the third step known as elongation, the temperature is raised to about 72°C and the Taq DNA polymerase then adds _________________________ to the primers to complete each new complimentary strand of the target DNA.
Restriction enzyme
Typically, following PCR the amplified DNA is digested with a specific enzyme known as a _____________________. If the patient possesses a mutation in the LDL receptor gene, the digestion pattern will differ from the pattern obtained from unaffected individuals.
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
Term for a variation in the length of restriction fragments produced by a given restriction enzyme in a sample of DNA.
Gel electrophoresis
__________________________ is a laboratory procedure used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to molecular size and charge. In this procedure the molecules to be separated are pushed by an electrical field through a gel that contains small pores.
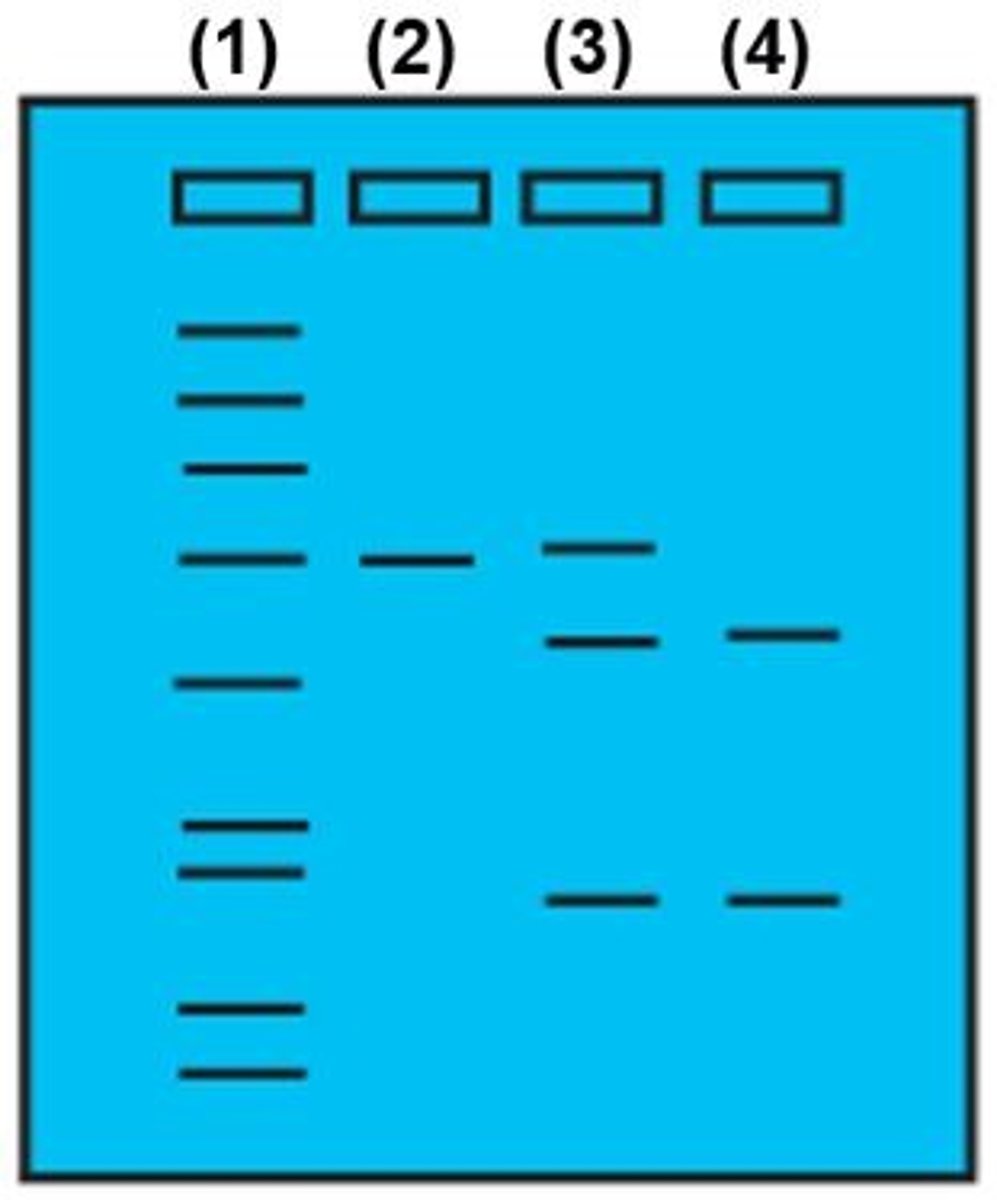
Standard marker
Name for lane (1) is the DNA _______________________________ or DNA ladder.
DNA ladder
Name for lane (1) is the DNA standard marker or _______________________ .
Homozygous normal
Based on the gel, which of the following best describes the genetic makeup of patient number (2):
Homozygous normal
Homozygous for FH
Heterozygous for FH
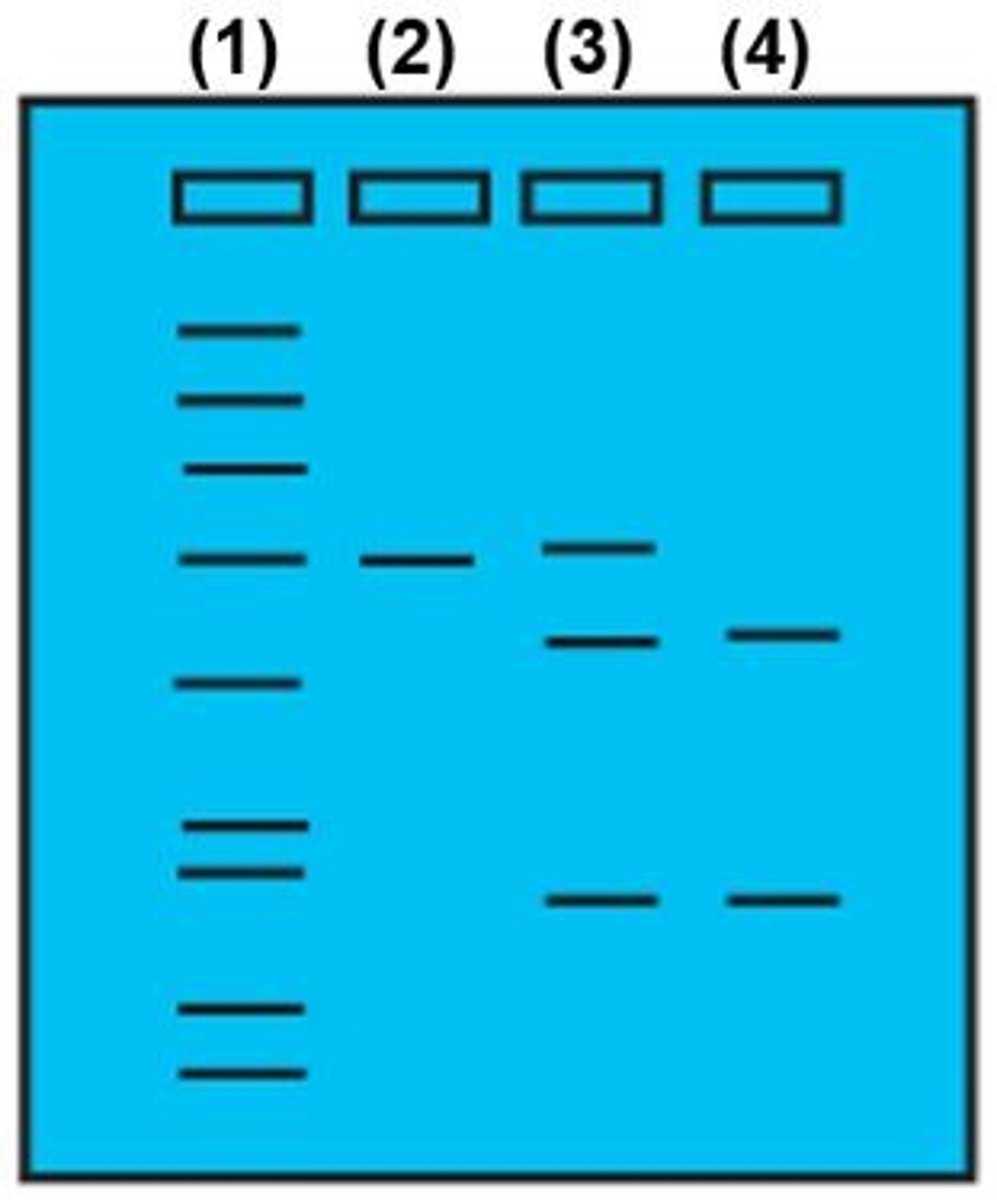
Heterozygous for FH
Based on the gel, which of the following best describes the genetic makeup of patient number (3):
Homozygous normal
Homozygous for FH
Heterozygous for FH
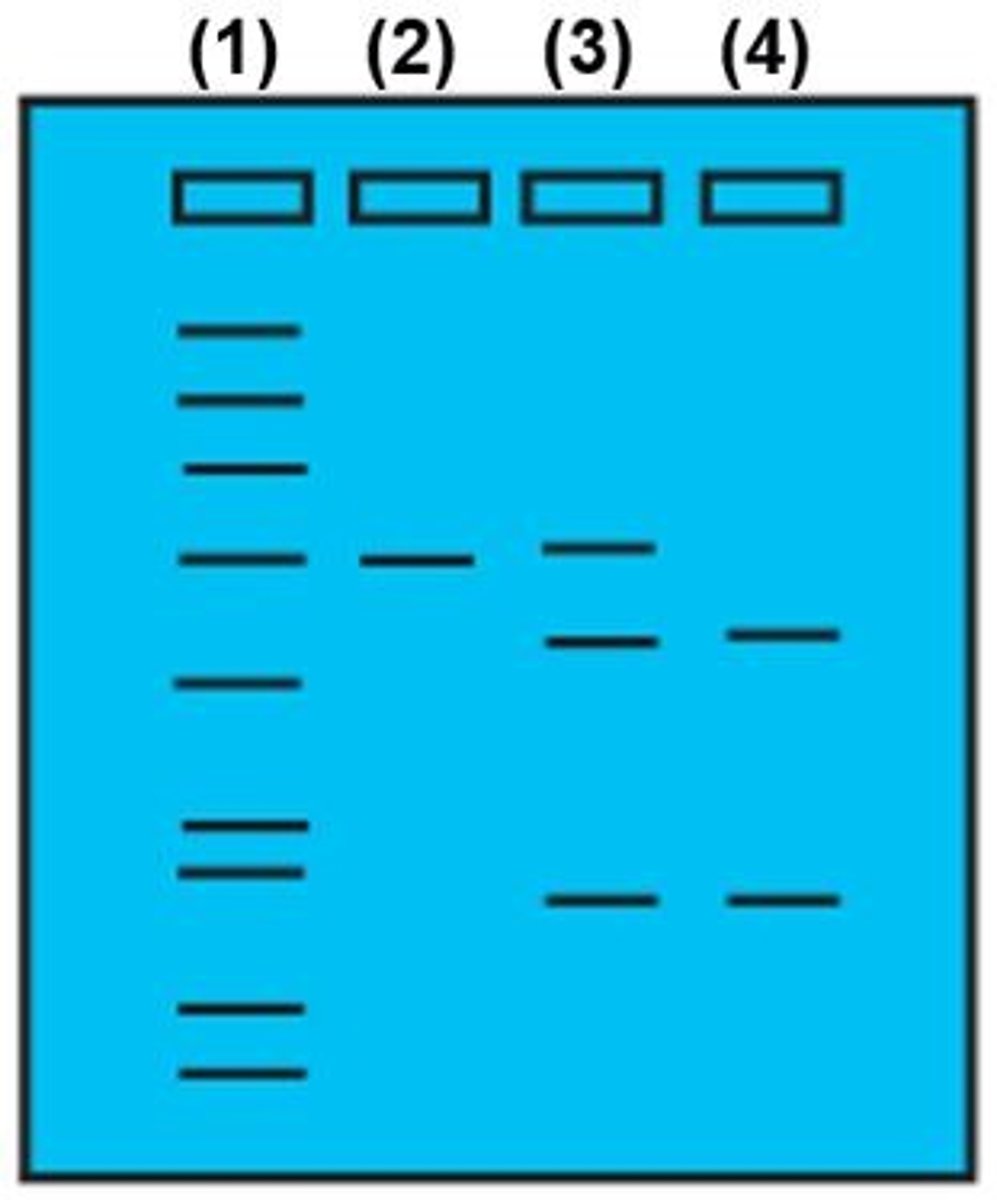
Homozygous for FH
Based on the gel, which of the following best describes the genetic makeup of patient number (4):
Homozygous normal
Homozygous for FH
Heterozygous for FH