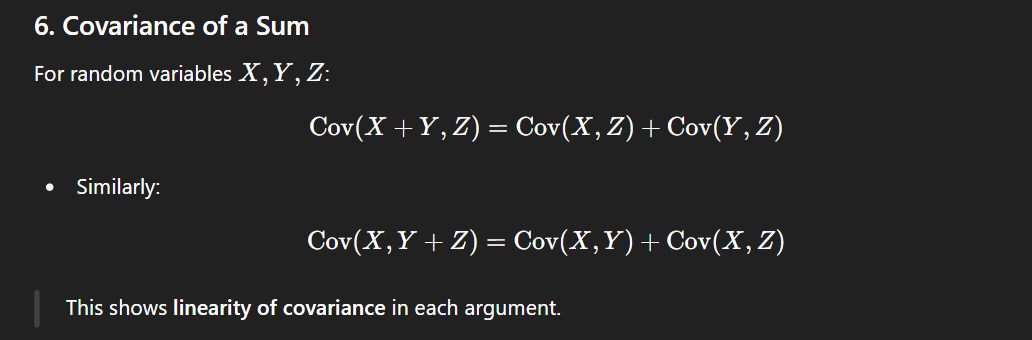Expected value and variance rules ML1
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the expected value of a discrete X? so E[X] when discrete
See image

What is the expected value of a continuous X? so E[X] when continuous
See image, and it would be the PDF over the max and min range of the function.

split up E[aX + bY]
where a and b are constants
a*E[X] + b*E[Y]
so keep in mind
E[X + Y] = E[X] + E[Y]
and
E[X*5] = 5 * E[X]
Can you take a sum out of the expected value?
Yes you can.

Can you always perform
E[X*Y] = E[X] * E[Y]
No you can not, this has to be when X and Y are independent from each other.

![<p>How to express E[X] in form of E[X|Y]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7d988cdb-ba92-472e-90aa-1b6e16ce4d33.png)
How to express E[X] in form of E[X|Y]
E[X] = E[E[X|Y]]
![<p>E[X] = E[E[X|Y]]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d904411e-3626-43ef-ae5d-335809eb6767.png)
Write the variance in terms of Expectation
So VAR[X] = …
using only E[X]
VAR[X] = E[(X-E[X])²]= E[X²] - (E[X])²
The proof is in the image.
![<p>VAR[X] = E[(X-E[X])²]= E[X²] - (E[X])²</p><p>The proof is in the image.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e7eb46ac-2e54-4246-ba6e-7d3760743d10.png)
What is VAR[c] where c is a constant
VAR[c] = 0
Rewrite VAR[aX] where a is a constant
a² * VAR[x]
pay attention, that the constant is now squared
Rewrite VAR[X+b] where b is a constant
VAR[X+b] = VAR[X]
Adding a constant shifts the distribution but does not change the spread.
Rewrite Var[X+Y]
Var[X+Y] = Var[X] + Var[Y] + 2Cov[X,Y]
![<p>Var[X+Y] = Var[X] + Var[Y] + 2Cov[X,Y]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/df7fc687-2fb0-4091-a085-532dc0451e75.png)
Write Cov[X,Y] in terms of E[X] and E[Y]
Cov[X,Y] = E[(X−E[X])(Y−E[Y])] = E[XY]−E[X]E[Y]
Positive covariance → Xand Y tend to increase together.
Negative covariance → one tends to increase while the other decreases.
![<p>Cov[X,Y] = E[(X−E[X])(Y−E[Y])] = E[XY]−E[X]E[Y]</p><p></p><ul><li><p>Positive covariance → Xand Y tend to increase together.</p></li><li><p>Negative covariance → one tends to increase while the other decreases.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c3e84052-3d85-46a6-a585-5d9a4367c4e6.png)
What is COV[X,X]
Cov[X,X] = Var[X]
Is covariance symmetric?
Yes, Cov[X,Y] = Cov[Y,X]
Rewrite Cov[aX,bY]
where a and b are constants
a*b*cov[X,Y]
![<p>a*b*cov[X,Y]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fa117c77-0da3-458d-843a-6b6b905d332b.png)
Rewrite
Cov(X+Y,Z)
and
Cov(X,Y+Z)
Cov(X+Y,Z)=Cov(X,Z)+Cov(Y,Z)
and
Cov(X,Y+Z)=Cov(X,Y)+Cov(X,Z)