Chem Unit 2 - Kim (WIP)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Empedocles (c. 490 BC-c. 430 BC)
Believed that the world was made of fire, earth, air, and water (popularized by Aristotle).
Alchemists (in general)
Forerunners to modern day chemists who did experiments with their developed equipment (that's still used today) and used techniques in hopes of creating gold and the elixir of life (immortality).
Jabir ibn Hayyan (721-815)
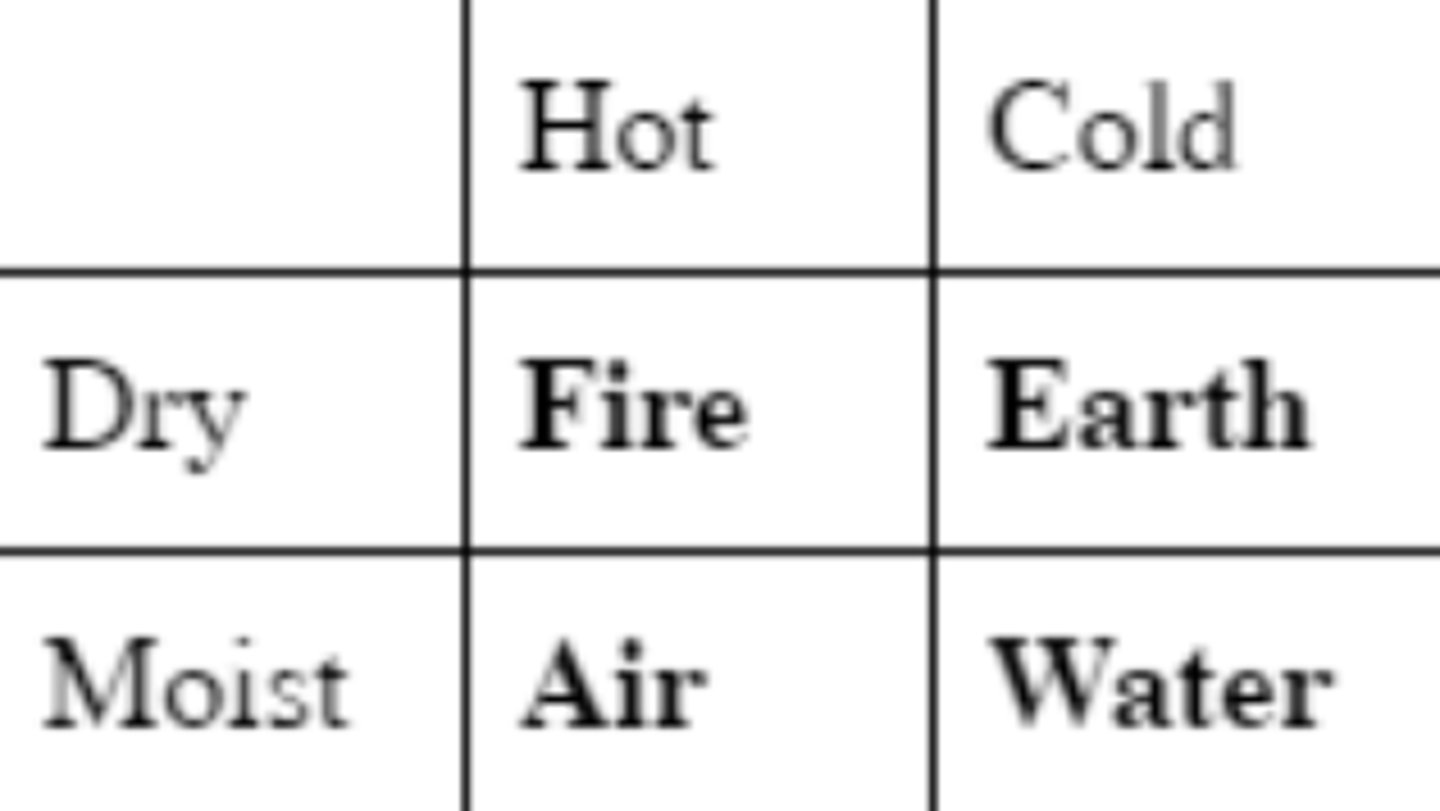
One of the many Islamic alchemists that organized the Aristotelian elements (fire, earth, air, water) on the basis of hot/cold and dry/moist.
Paracelsus (1493-1541)
Applied alchemical ideas to medicine, and believed that the world was made of 3 substances (tria prima): mercury (quicksilver), sulfur, and salt, and each represented a part of the human identity.
Robert Boyle (1627-1691)
Commonly called the founder of modern chemistry, he believed that all theories must be proven with experiments (wrote "The Sceptical Chymist" in 1661). Claimed that the world was made of elements.
Hennig Brand
He boiled down urine expecting to find gold, but accidentally found phosphorus instead.
Henry Cavendish
He reacted metals with acid to produce "inflammable air", which was actually hydrogen.
Carl Wilhelm Scheele
He heated manganese dioxide to form "fire air", which is oxygen.
Joseph Priestley
He heated mercuric oxide to form "dephlogisticated air", which is oxygen.
Antoine Lavoisier
He decomposed mercuric oxide to form "eminently breathable air" (oxygen). He also created the Law of Conservation of Mass.
Daniel Rutherford
He isolated a gas that does not support combustion or life, which is nitrogen.
Humphry Davy
He used an electrical current to break down compounds into elements.
Jules Janssen and Norman Lockyer
They observed a solar eclipse and find a yellow spectral line in sunlight (helium).
Pierre and Marie Curie
Discovered Polonium and Radium, and other radioactive elements, which they term radioactivity.
Friedrich Ernst Dorn
He discovers radon as a decay product of radium.
Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner
He starts forming elements in groups of three by similar chemical properties; known as triads.
Johns Jacob Berzelius
He created a list of known elements from lightest to heaviest and developed a modern chemical formula notation with one or two letter symbols for elements. Associated with atomic weight.
John Newlands
He proposed the Law of Octaves: every 8th element has similar chemical properties (think of the piano). He ordered elements by atomic weight.
Dimitri Mendeleev
Made the FIRST periodic table, which ordered the elements by atomic weight, and put similar chemical properties together in groups. He even predicted future elements.
William Ramsey
Discovers noble gases (including helium, argon, krypton, neon, and xenon), which was hard to discover because they're unreactive (valence shell is full).
Henry Moseley
Developed the MODERN periodic table: elements ordered by atomic number, and Lanthanides and Actinides are placed below other elements to save space.
Democritus
He said that atoms are physically indivisible units of matter.
John Dalton
He created atomic theory, believed that elements are made up of very small particles called atoms. Believed that all atoms of an element are identical with the same size, mass, and other properties (which was untrue because of isotopes). Created Law of Multiple Proportions.
J.J. Thomson
He used a cathode ray tube to produce particles that were deflected by electric and magnetic fields. Also created the plum pudding model, where electrons are arranged in a positively-charged body.
Robert Millikan
He used the oil drop experiment to find the charge of an electron.
Ernest Rutherford (with Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden)
They shot positively-charged alpha particles at a gold foil. From the plum pudding model by J.J. Thomson, alpha particles should go straight through, but some bounce back. Concluded that there must be a central nucleus.
James Chadwick
He shot alpha particles at Beryllium to discover neutrons, which are particles with no charge.
Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassman (with Lise Meiter and Otto Frisch)
They discovered nuclear fission.
Wilhelm Rontgen
He worked with cathode rays, produces and detects a new kind of electromagnetic radiation that he calls "x-rays".
Henri Becquerel
He used uranium salts to expose photographic plates with radiation different than Rontgen's.
Ernest Rutherford (by himself)
He classified radioactivity into three types: alpha, beta, and gamma.
Hans Geiger (by himself)
He made the Geiger counter, which can be used to detect and measure ionizing radiation (clicks go brrr).
Willard Libby
He developed radiocarbon dating, useful dating for (formerly) living things.
Irene and Frederic Joliot-Curie
They produced the first artificial radioactive isotope.
Enrico Fermi
He achieved the first chain reaction.
Hermann Muller
He was the first to recognize the ability of radiation.
Ernest Lawrence
He built the first cyclotron, which is a particle accelerator.