early pregnancy
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
where does fertilization typically occur?
in the ampulla of the oviduct
acrosomal reaction
sperm releases hydrolytic enzymes to penetrate zona pellucida
zona reaction
“hardening” of zona pellucida prevents binding of new sperm
what processes must be triggered in order to complete fertilization?
zona reaction (block entry of additional sperm)
completion of oocyte meiosis
fusion of sperm + egg pronuclei to form zygote
initiate developmental program of embryo
inner cell mass
cell population that will become the embryo
trophoblast
cell population that will become the outer layer of the fetal membranes (contributes to the placenta)
produce maternal recognition hormone/factors
cells play key roles in fetal-maternal communication
what conditions must be present in order for implantation to occur?
activated embryo (blastocyst stage) + receptive uterus: progesterone-dominant environment with a little bit of estrogen (ratio important; diestrus)
timing is extremely important
blastocyst hatching
destruction of zona pellucida allows for increased growth, access to uterine nutrients, and adhesion to uterine lining
results from cooperation between embryo + proteases secreted by the endometrium
what two challenges must a developing embryo overcome after hatching?
maintaining progesterone-dominant environment
obtaining nutrients
what are different strategies for maintaining progesterone?
maintain the corpus luteum (maternal recognition of pregnancy)
placental progesterone production
what are the different strategies for obtaining nutrients?
(early) implantation
development of extra-embryonic membranes (late implanters)
what is maternal recognition of pregnancy?
embryo-induced prolongation of CL lifespan
typically occurs a few days before luteolysis, except in the dog
in dogs: CL lasts length of gestation
how can an embryo prevent production of PGF2a?
embryonic products
ruminants: interferon-τ (tau)
pigs: estrogen
horses: unidentified compound that promotes uterine PGE2 synthesis over PGF2a
how can an embryo provide gonadotropic support (to CL)?
LH support
primates: “human” chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
equids: equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG) after day 36
prolactin
rodents: placental lactogen to supplement pituitary prolactin
what is unique about horses’ maternal recognition of pregnancy?
horses have 2 recognition mechanisms: prevent PGF2a production + luteotrophic support (eCG)
are maternal recognition of pregnancy and implantation dependent processes?
no: they are two distinct (independent) processes
hormonal signal (progesterone) can persist without implantation
how do late implanters obtain nutrients?
absorb histotroph (nutrition derived from maternal tissue other than blood) secreted by uterus
develop extra-embyronic membranes → high surface area for nutrient absorption
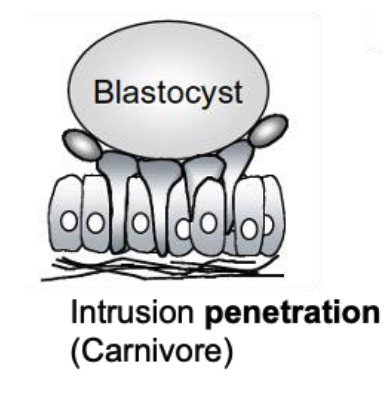
where do invasive blastocysts end up after implantation?
embedded in uterine stroma
where do non-invasive blastocysts end up after implantation?
adhered to uterine epithelium
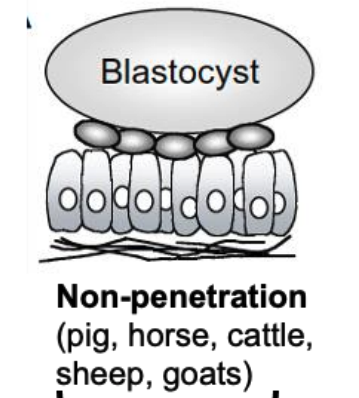
displacement penetration
trophoblast induces apoptosis of uterine epithelium
invasive implantation
rodents, some primates
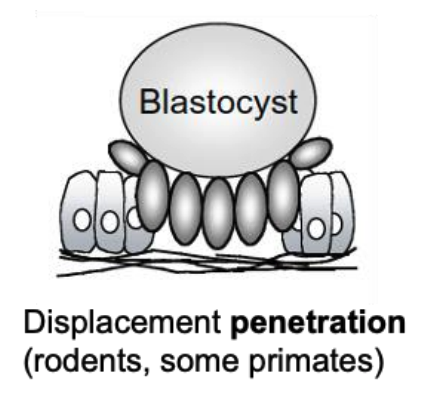
intrusion penetration
trophoblast invades between uterine epithelial cells
invasive implantation
carnivores
fusion penetration
trophoblast fuses with uterine epithelium
invasive implantation
rabbit