8.1 Structure of the Immune System Diagram | Quizlet
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Group A Streptococcus, Clostridium Perfringens, and MRSA
Types of bacteria that can cause necrotizing fasciitis.
Superantigen
An antigen that activates many different T-cells, thereby eliciting a large immune response.
Superinfection
Infection on top of an infection.
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Dangerous not only because of the bacteria and subsequent inflammatory response, but also because the nonspecific immune defense that destroys the skin leaves the body susceptible to superinfection.
TERM
Innate Immune System
DEFINITION
Composed of defenses that are always active against infection, but lack the ability to target specific invaders over others.
TERM
Adaptive Immune System
DEFINITION
Refers to the defenses that target a specific pathogen. It can maintain a memory of pathogens it has previously been exposed to.
Bone Marrow
Site of production for all leukocytes.
Spleen
A location of blood storage and activation of B-cells, which turn into plasma cells to produce antibodies as part of adaptive immunity.
B-Cells
Turn into plasma cells in the spleen and they then produce antibodies for the adaptive immune system.
Humoral Immunity
The plasma cells secrete antibodies as part of adaptive immunity and the antibodies dissolve and act in the blood.
T-Cells
Another class of adaptive immune cells which mature in the thymus.
Thymus
A small gland just in front of the pericardium where T-cells mature.
Cell-Mediated Immunity
T-cells are agents of this because they coordinate the immune system and directly kill virally infected cells.
Lymph Nodes
Provide a place for immune cells to communicate and coordinate an attack.
Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
An additional type of immune tissue found near the gut, which is a common site of invasion.
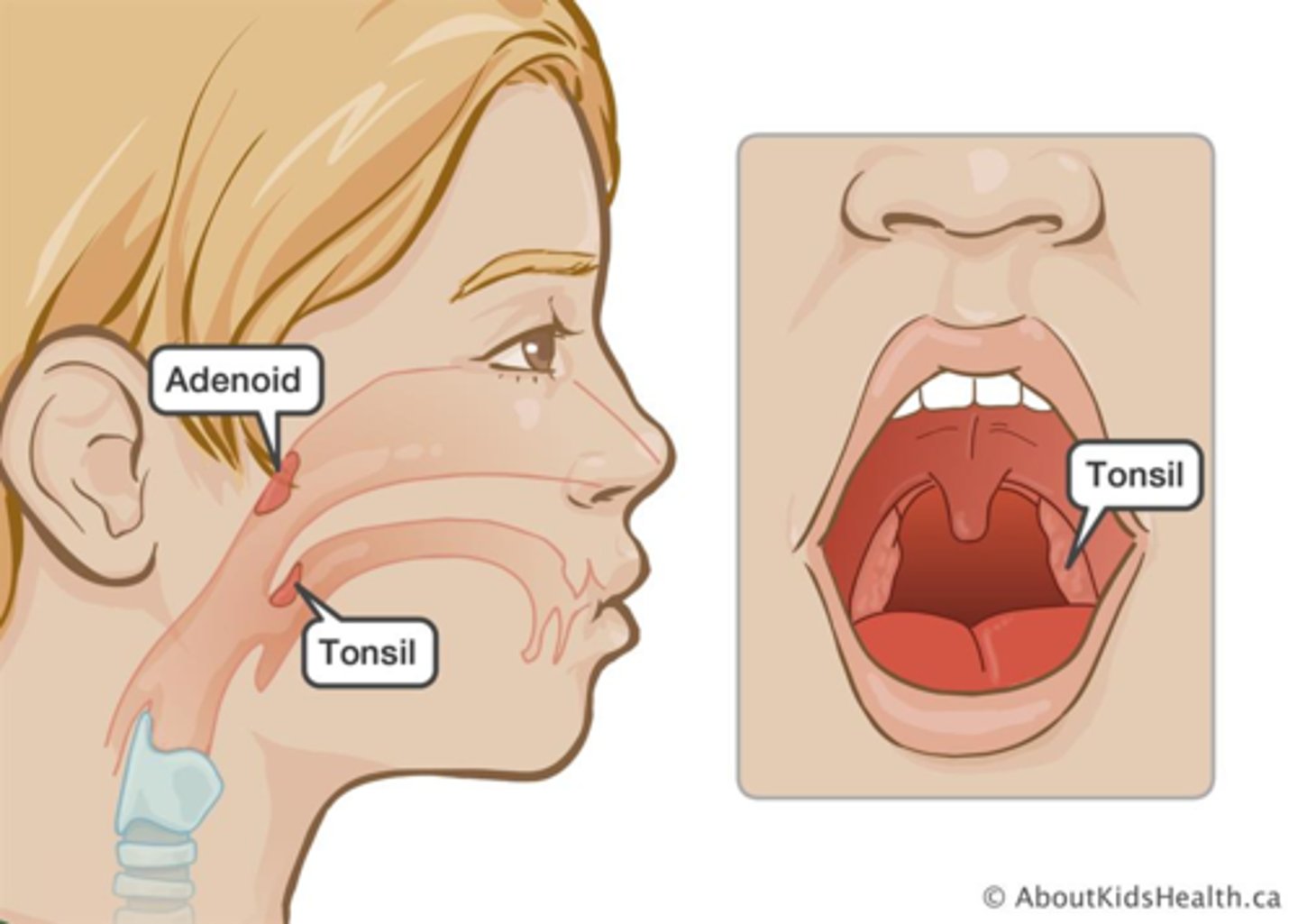
Tonsils and Adenoids
Another type of excess immune tissue found in the head to fight off infection.
Peyer's Patches
Structures in the small intestine that are considered additional immune tissue. They are involved in the response against invaders to the digestive tract.
Appendix
Anatomical structure that houses lymphoid aggregates and counts as additional immune tissue for the digestive tract.
Granulocytes and Agranulocytes
The two groups of leukocytes.
Granules
Presence indicates if a leukocyte is granular or not. These contain toxic enzymes and chemicals which can be released by exocytosis to protect the cell from bacteria, fungi, parasites, etc.
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Precursors to all blood cells, including both types of leukocytes.
Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils
The different types of granulocytes.
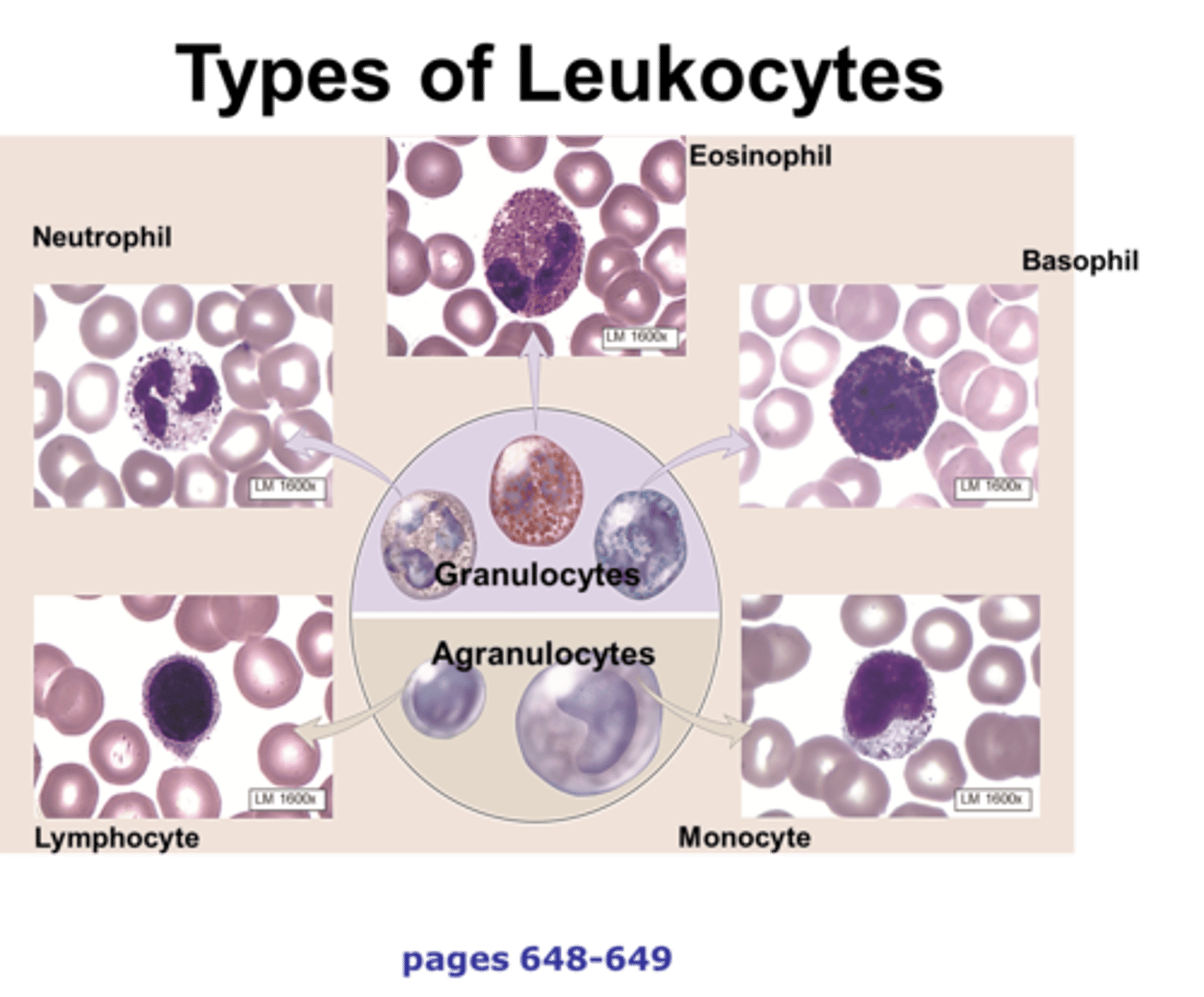
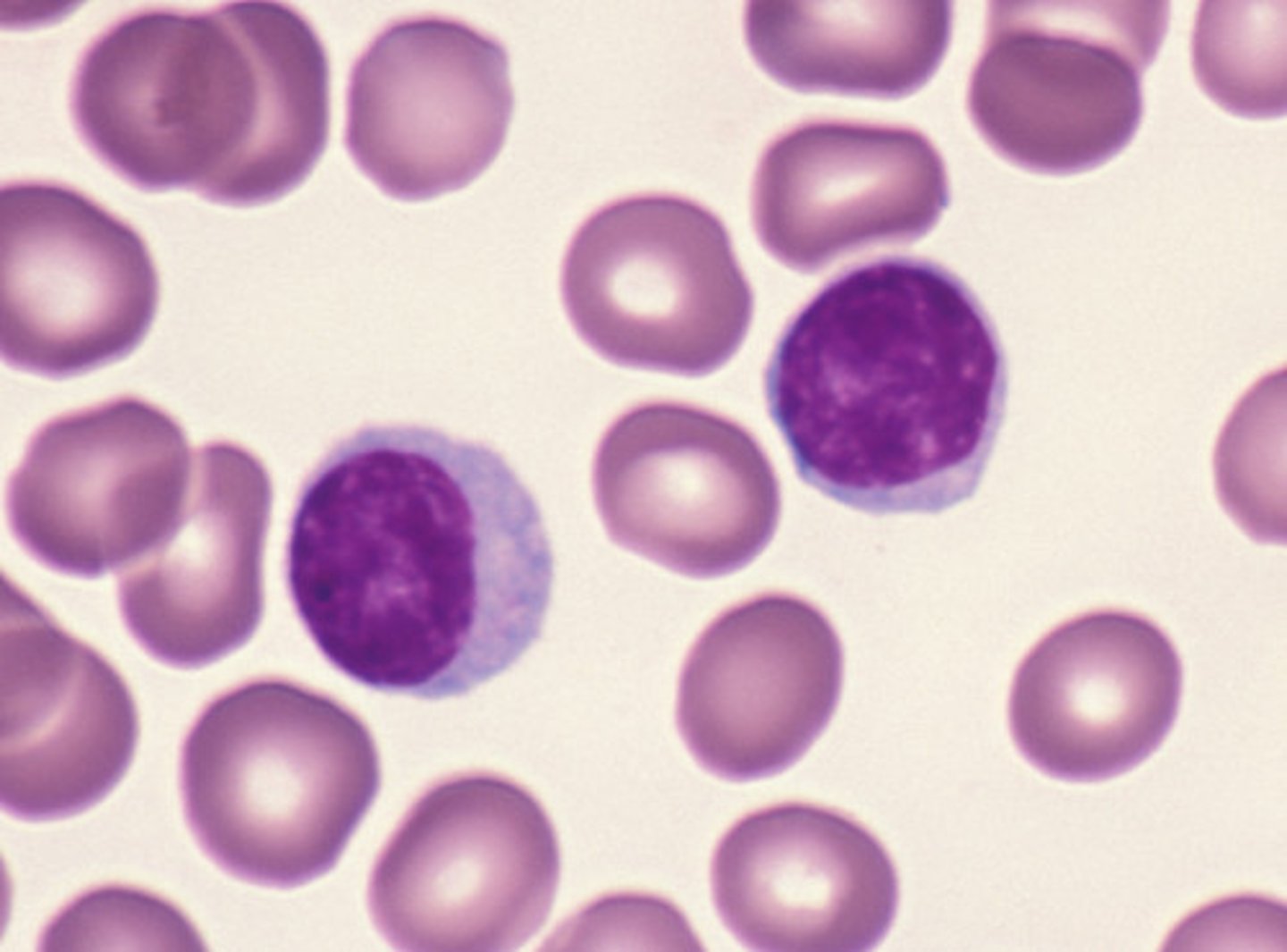
Lymphocytes and Monocytes
The different types of agranulocytes.
Lymphocytes
Responsible for antibody production, immune system modulation, and targeted killing of infected cells.
Monocytes
Phagocytic cells in the bloodstream that are considered agranulocytes.
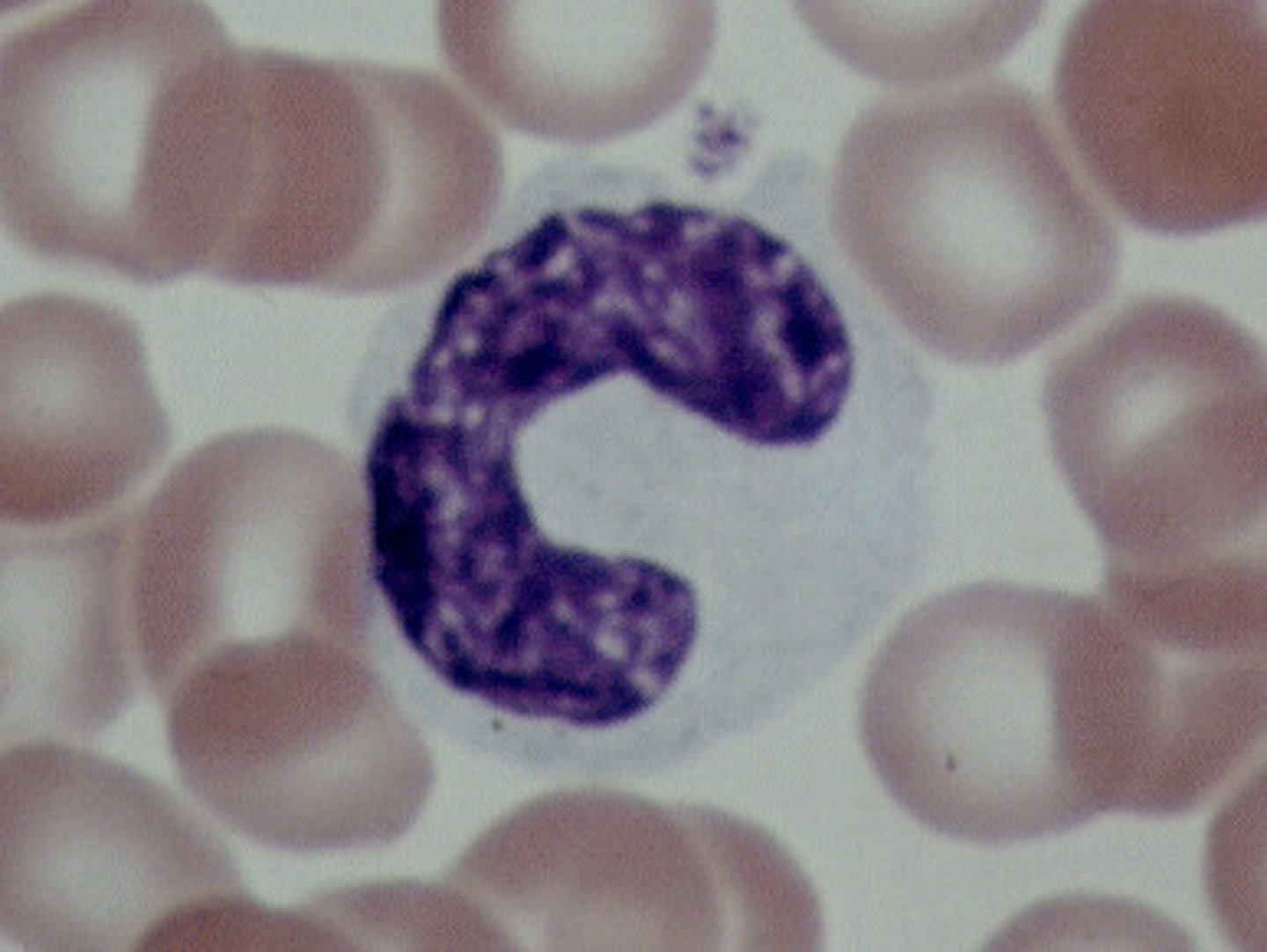
Macrophages
Monocytes are renamed this when they enter the tissue.
Microglia
Special name for macrophages in the central nervous system.
Langerhans Cells
Special name for macrophages in the skin.
Osteoclasts
Special name for macrophages in the bone.
Nonspecific Immune Response
Innate immunity, which refers to the responses cells can carry out without learning.
Specific Immune Response
Adaptive immunity, which is developed as immune cells learn to recognize and respond to particular antigens.
Divisions of the Specific Immune System
Humoral immunity is driven by B-cells, and cell-mediated immunity is provided by T-cells.