Histo Exam 3
1/479
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
480 Terms
components of saliva
glycoproteins (mucin), proteins (gustin and enzymes), ions, immunoglobulins

Which of the following sensory mechanoreceptors can be seen in the histological image?
pacinian corpuscle

what type of burn is this?
3rd degree, full thickness

which of the following skin regions has been infiltrated by inflammatory cells (lymphocytes)?

which junctional complex of the epidermis has been impacted?
desmosomes

what is the pathological condition? on A
basal cell carcinoma

what do the numbers represent?
1) Corneum 2) Lucidum 3) Granulosum 4) Spinosum 5) Basale

where is this tissue located?
esophagus

where is this tissue located?
middle of esophagus. notice presence of skeletal and smooth muscle

what do the letters represent?
A: mucosa B: submucosa C: muscularis externa D: adventita/serosa
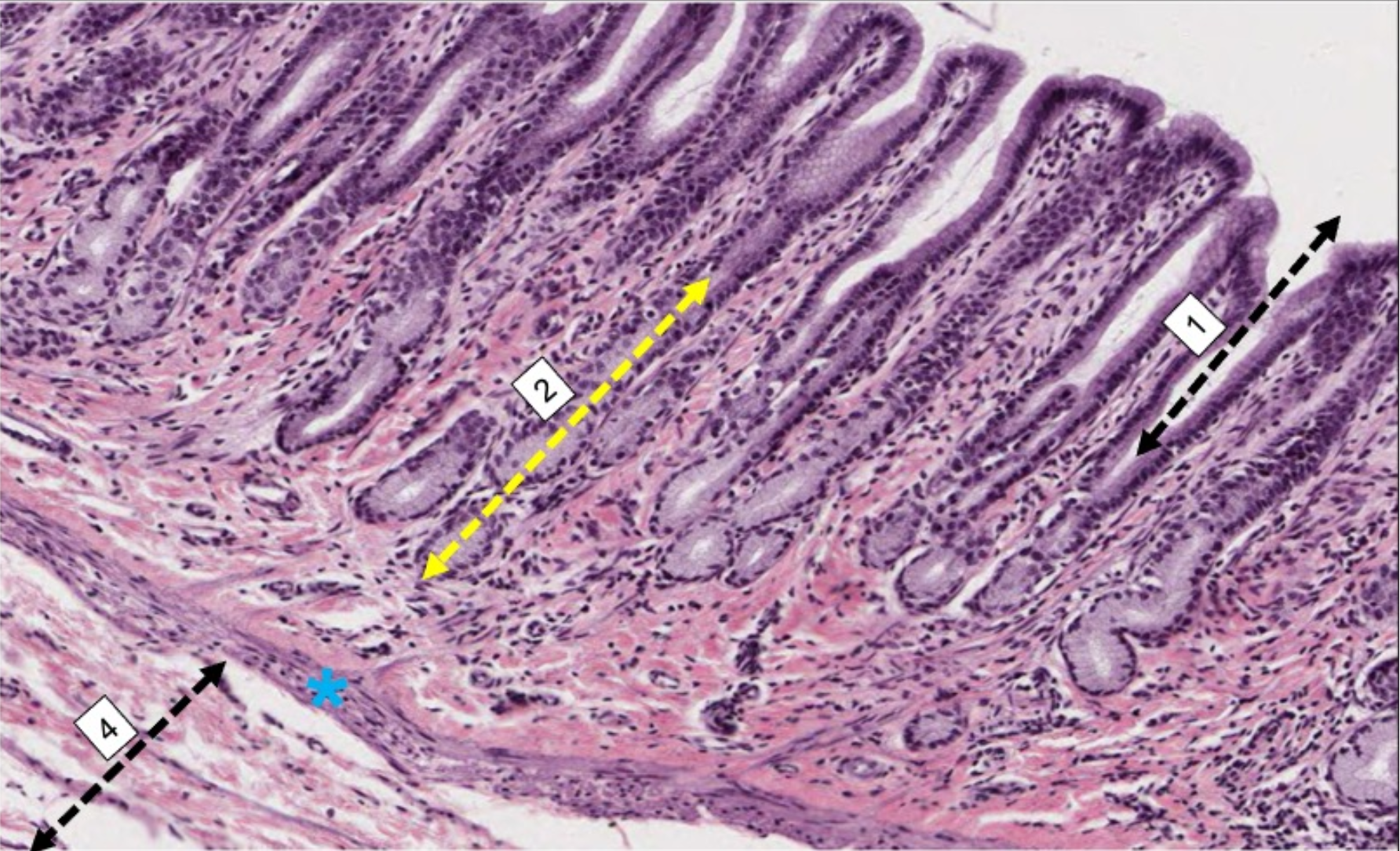
what organ is this from? and what are the numbers
stomach. 1) gastric pit 2) gastric gland star is the muscularis mucosa, 4) submucosa


what is the pathological condition?
stomach ulcer
main function of saliva
facilitates swallowing, moisten oral epithelium, neutralize plaque acid, oral immunity
exocrine glands
transport via ducts
serous cells
high protein, low carb. stain deeply
serous cells appearance
triangle profile, eosinophilic secretory granules at apex. basophilic nucleus

mucous cells

what type of cells are shown?
mucous cells

serous cells

serous cells
mucous cells
low protein, high carb. greater emphasis on lubrication
mucous cells appearance
pale and eosinophilic. pyramidal, wide base w/ nucleus
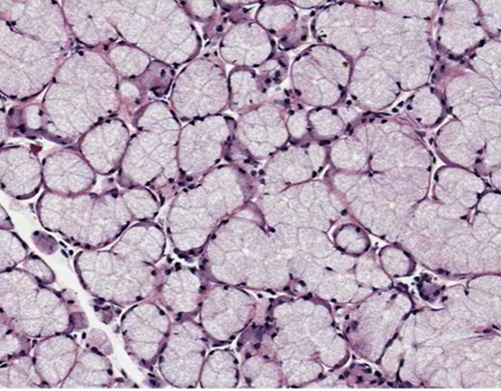
mucous cells
endpieces
collection of salivary cells with just the saliva producing cells in aggregates
acinus
group of serous cells. resembles a raspberry. apical surfaces of cells face lumen. where acinus ends, exocrine ducts begin
tubules
group of mucous cells
outer layer of acinus
basal membrane that secludes from surrounding tissues

serous acini

mucous tubules

serous acini
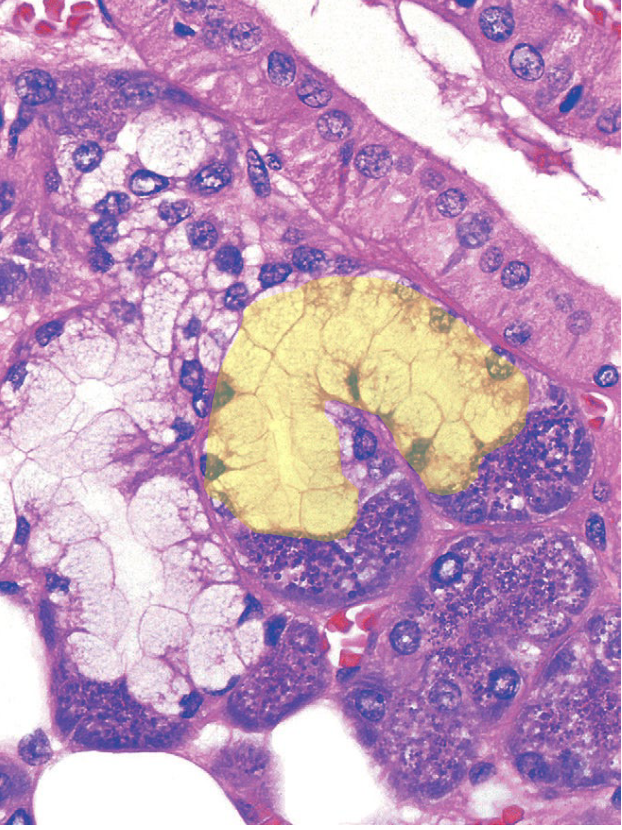
what is the structure?
mixed mucous and serous

what are the structures?
lobe and lobule
the stroma
outer connective tissue capsule (beige). surrounds and penetrates salivary tissues. divides gland into lobes and lobules
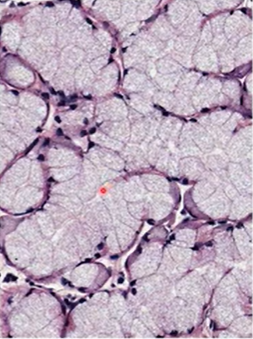
what is the structure?
mucous tubules

what is the structure?
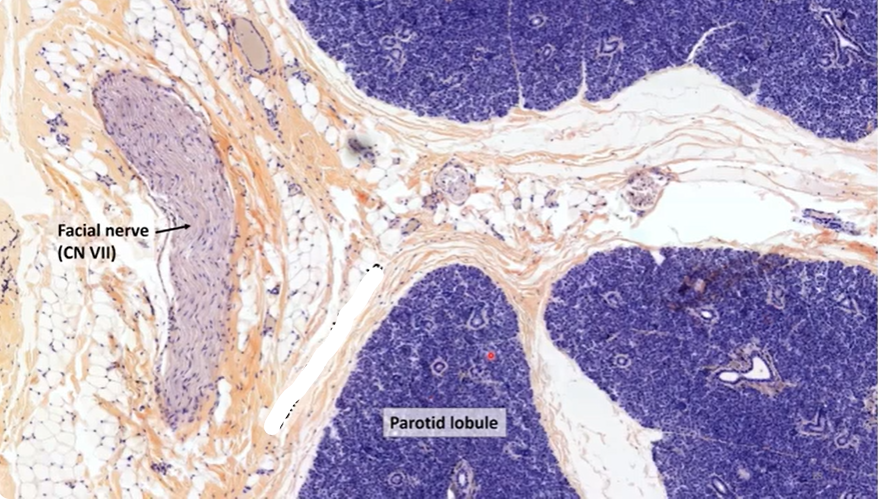
parotid lobule
what is the structure?
dense ct parotid capsule
intralobular
ducts found within lobules, within parenchyma. can be intercalated or striated
interlobular
leaves parenchyma. excretory duct aka collecting duct
order of duct movement
intercalated disk → striated duct → excretory duct
intercalated disk
smaller than acinus/tubule. short cuboidal cells. nuclei fill cells. narrow lumen
striated duct
tall columnar cells. bands of mitochondria. central nuclei, wide lumen

what is the structure?
intercalated duct
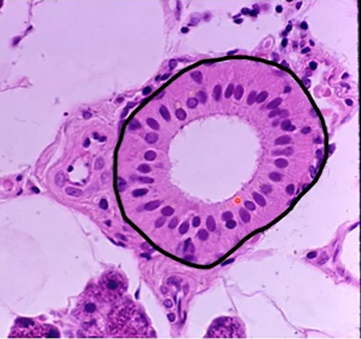
what is the structure?
striated duct
saliva initially _____ to blood plasma, then becomes _______
isotonic, hypertonic
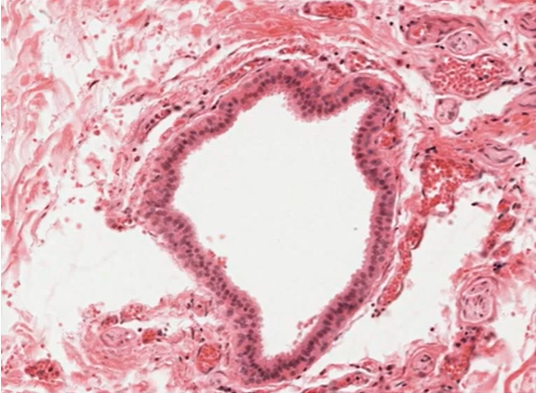
what is the structure?
excretory ducts
excretory ducts
within CT, outside of lobes. distinct columnar epithelium. sometimes stratified, sometimes pseudostratified

what is the structure?
parotid gland
parotid gland
almost completely serous
submandibular gland
serous and mucous cells. telltale indicator is demilunes which are serous crescent moons adjacent to mucous tubules

what is the structure?
demilune of submandibular gland

what is the structure?
mucous tubule
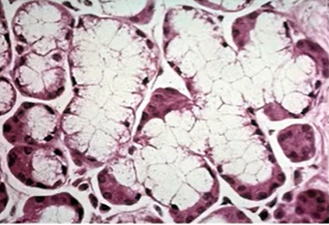
what is the structure?
mucous tubules with serous demilunes

what is the structure?
mucous tubules with serous demilunes

what is the structure?
mucous tubules with serous demilunes

what type of gland?
sublingual gland
sublingual gland
exclusively mucous cells
myoepithelial cells
surround acini and intercalated disk. stellate cells w processes. flat nuclei, stained brown. provides contractile support and innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic

what is the structure?
myoepithelial cells
what is the structure?
elongated nucleus of myoepithelial cells

what is the structure?
myoepithelial cell on a mucous tubule

what is the structure?
myoepithelial cells

what is the gland?
parotid gland

what type of duct?
striated duct

what is the structure?
striated to the left, intercalated duct on the right

identify the duct
excretory duct
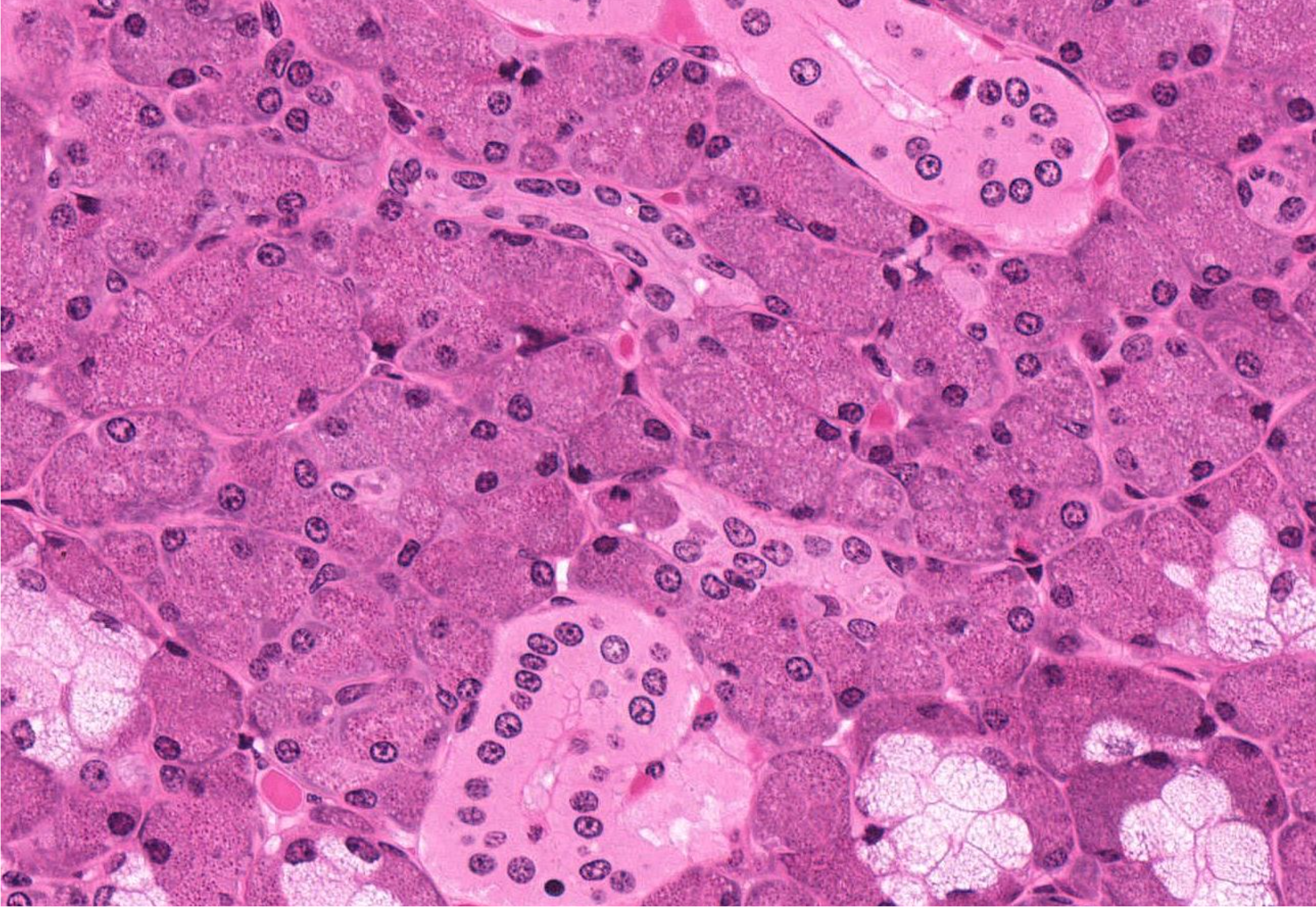
what ducts are pictured?
intercalated ducts
what is the hardest substance in the body?
teeth
enamel rods
extend from DEJ to outer surface of crown. diameter inc towards outer surface
what is bw rods?
interrod enamel
dentin
rigid (harder than bone and cementum), elastic (softer than enamel). 70% hydroxyapatite, 20% collagen, 10% water. protects the whole tooth structure unlike enamel. can regenerate
tubules
pulpal surface to dentinoenamel and DEJ. contain processes of odontoblasts and dentinal fluid. sigmoid course, aka primary curve
primary dentin
first to form. 2 subdivisions
mantle dentin
outermost later of primary. at DEJ. larger diameter collagen fibrils here
secondary dentin
borders pulp. bulk of primary dentin. more mineralized than mantle. s curve found here
predentin
innermost layer. non mineralized. adjacent to odontoblasts
tertiary dentin
reparative response to damage (cavities, restorative procedures). more rapid=more irregular
pulp
specialized connective tissue. predominantly fibroblasts (GAGs, collagen fibers). support matrix for neurovasculature
cell free zone nerves
nerves, capillaries
cell rich zone
fibroblasts, leucocytes
parietal layer
nervous plexus. unmyelinated axons may terminate among odontoblasts or continue into tubules
where is there a pathway for infection?
root canals- connect pulp chamber with periodontal tissues
cementum
thin layer of calcified tissue lining root. seals surface of root dentin and open dentin tubules. softer than dentin. large collagen content
acellular cementum
adjacent to root, seems structureless
cellular cementum
found closer to root apex. resembles bone, cementoblasts are trapped in matrix then turn to cementocytes. have canaliculi
PDL
dense fibrous connective tissue. bw root and alveolus. continuous w gingiva and dental pulp
PDL functions
resists displacing forces, maintains tooth position, repairs alveolar bone and cementum, provides feedback
alveolar bone
tooth socket, hold teeth in place, respond to changes in teeth. mediate forces applied by mastication. spongy bone
cortical layer of bone
lamina dura. lines socket and is where PDL attaches
free gingiva
narrow rim of mucosa, not bound to hard tissue
free gingival groove
border structure bw attached and free
attached gingiva
directly bound to tooth and alveolar bone. masticatory mucosa: comes into contact w food. keratinized epithelium. dense, relatively avascular lamina propria. long, narrow pegs
sulcular gingiva
parakeratinized epithelium
junctional epithelium
thin, nonkeratinized
alveolar mucosa
extends from border of gingiva to buccal and labial sulci. thin, nonkeratinized epithelium
respiratory surface epithelium
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar. contain goblet cells that secrete mucous
lamina propria of respiratory surface
arteries, extensive venous plexus
masticatory epithelium
protective and masticatory function. resists abrasion, extreme temp, and laceration
epithelial layers of hard palate
basale, spinosum, granulosum, corneum