Lab 10: The Brain and Spinal Cord
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
What are the three parts of a neuron and their functions?
Soma:
Axon:
Dendrite:
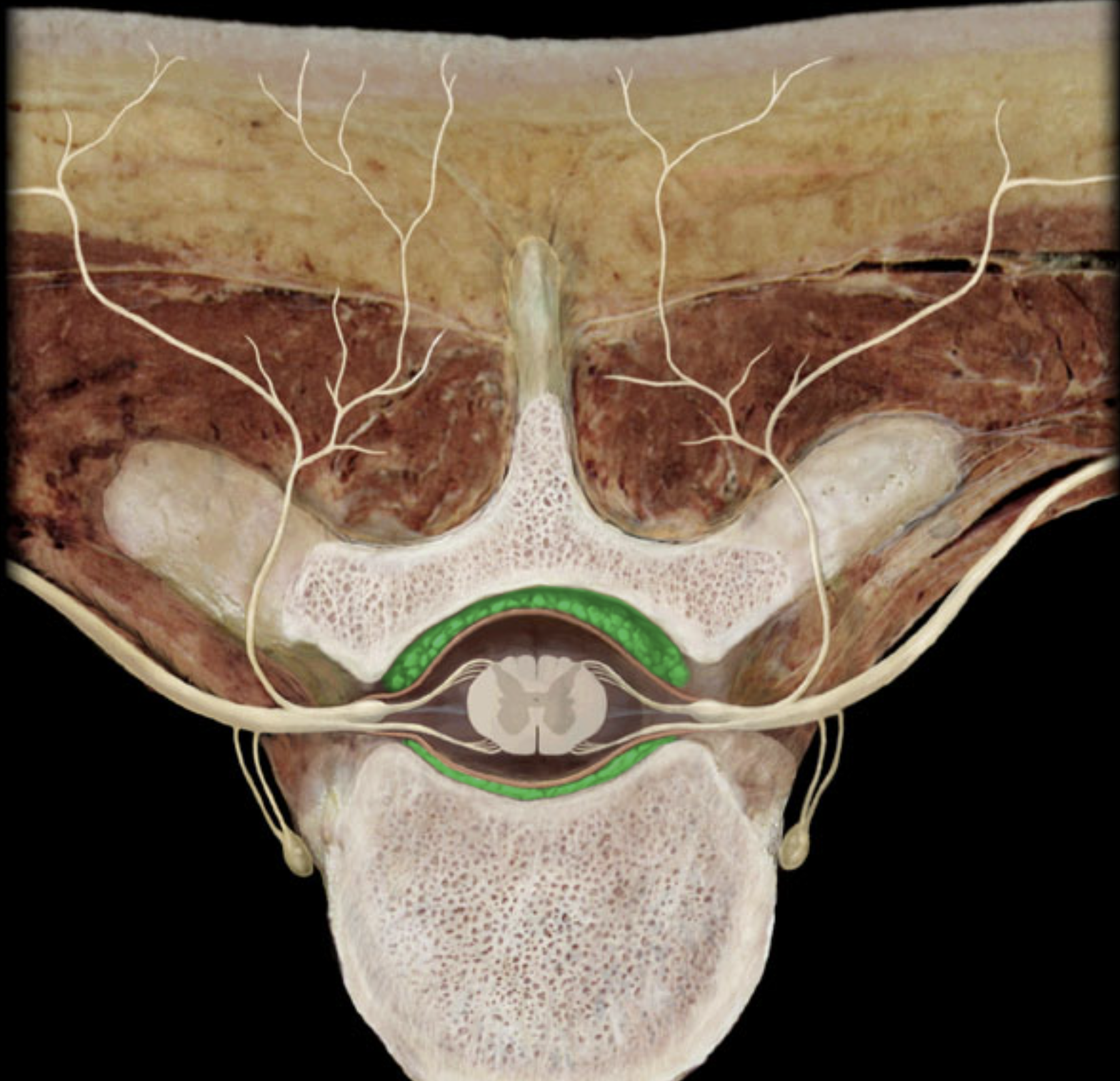
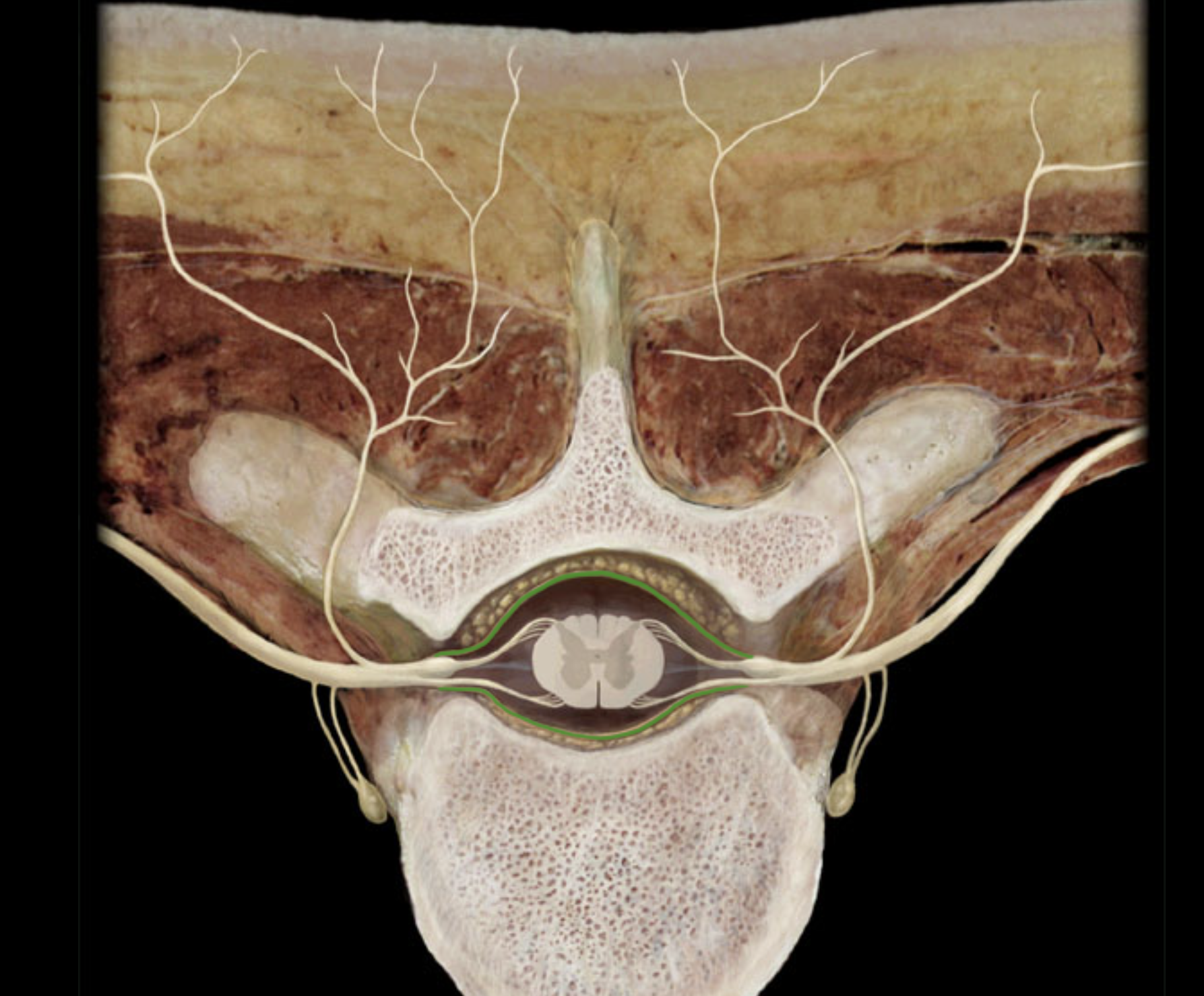
epidural space
gray matter of the spinal cord
anterior horn
white matter of spinal cord
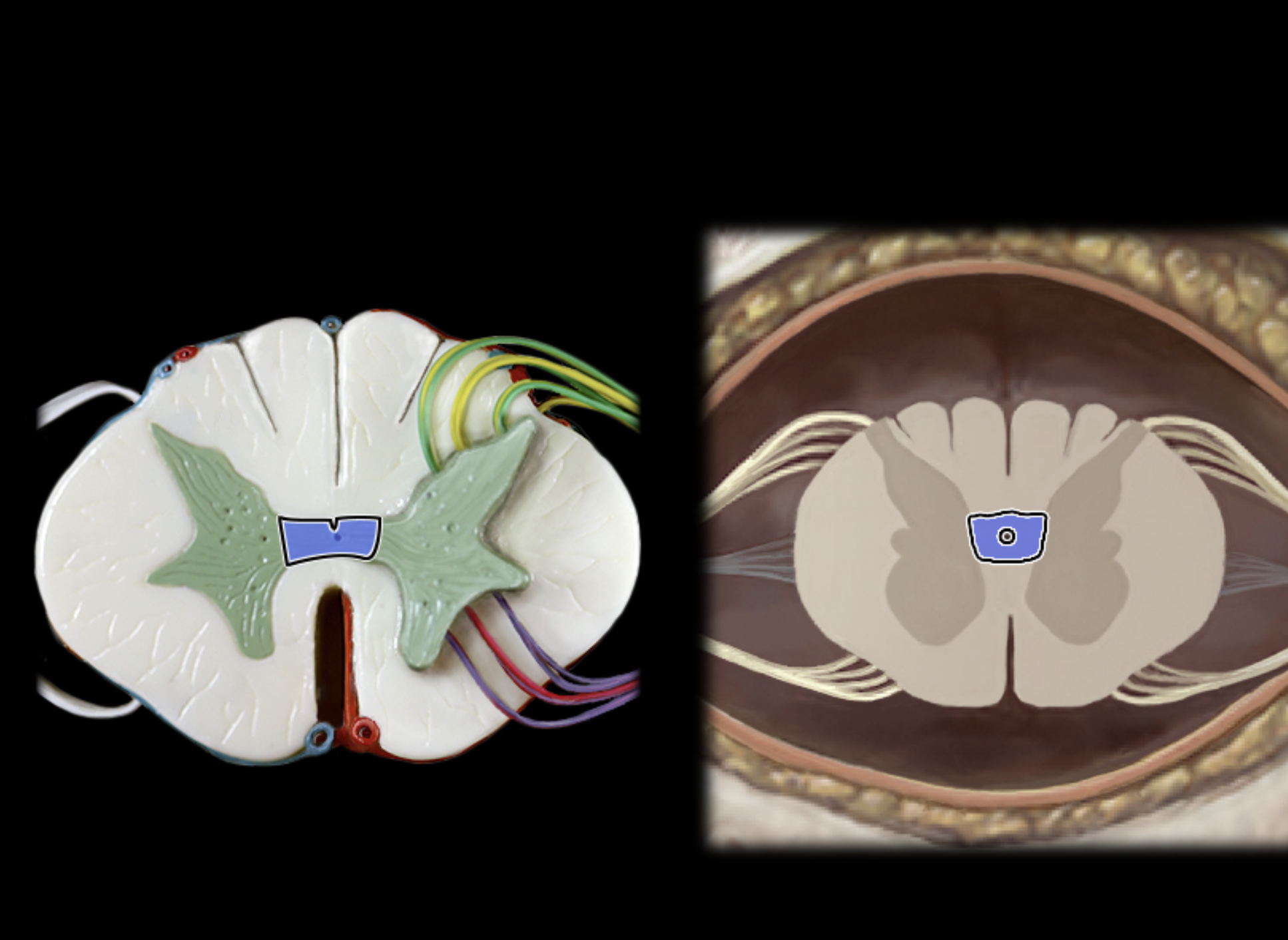
gray commisure

anterior root
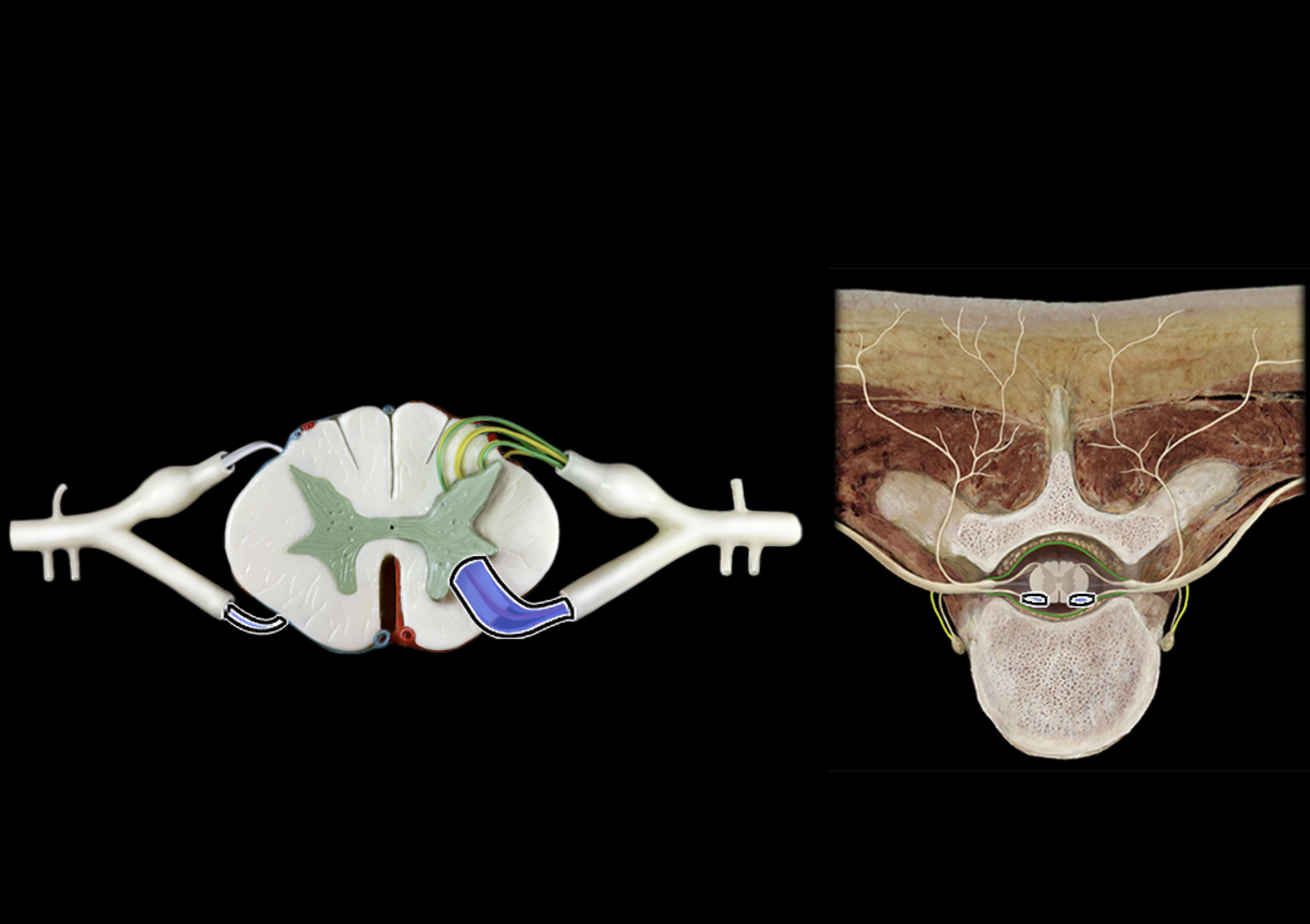
anterior rootless
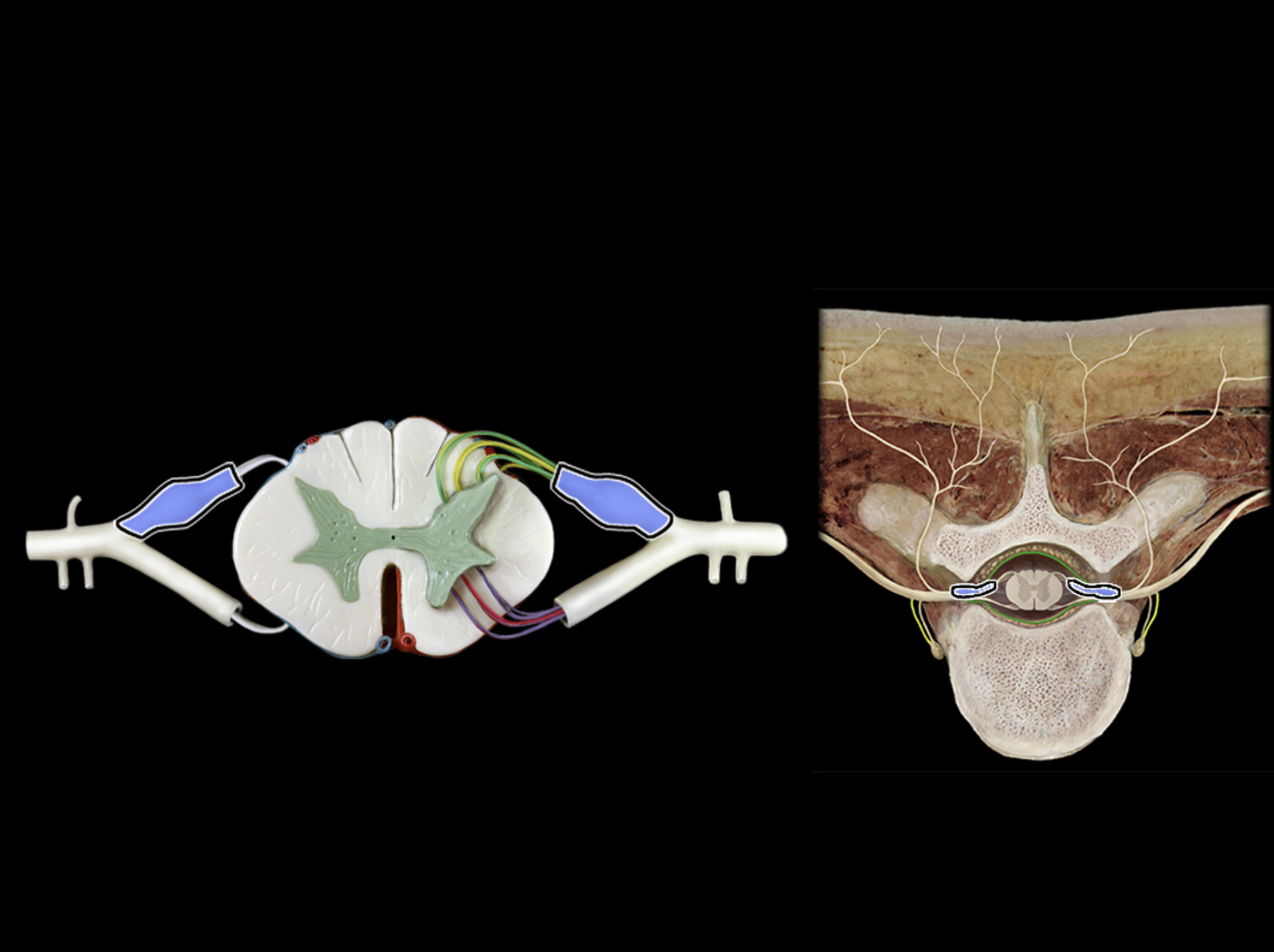
posterior root
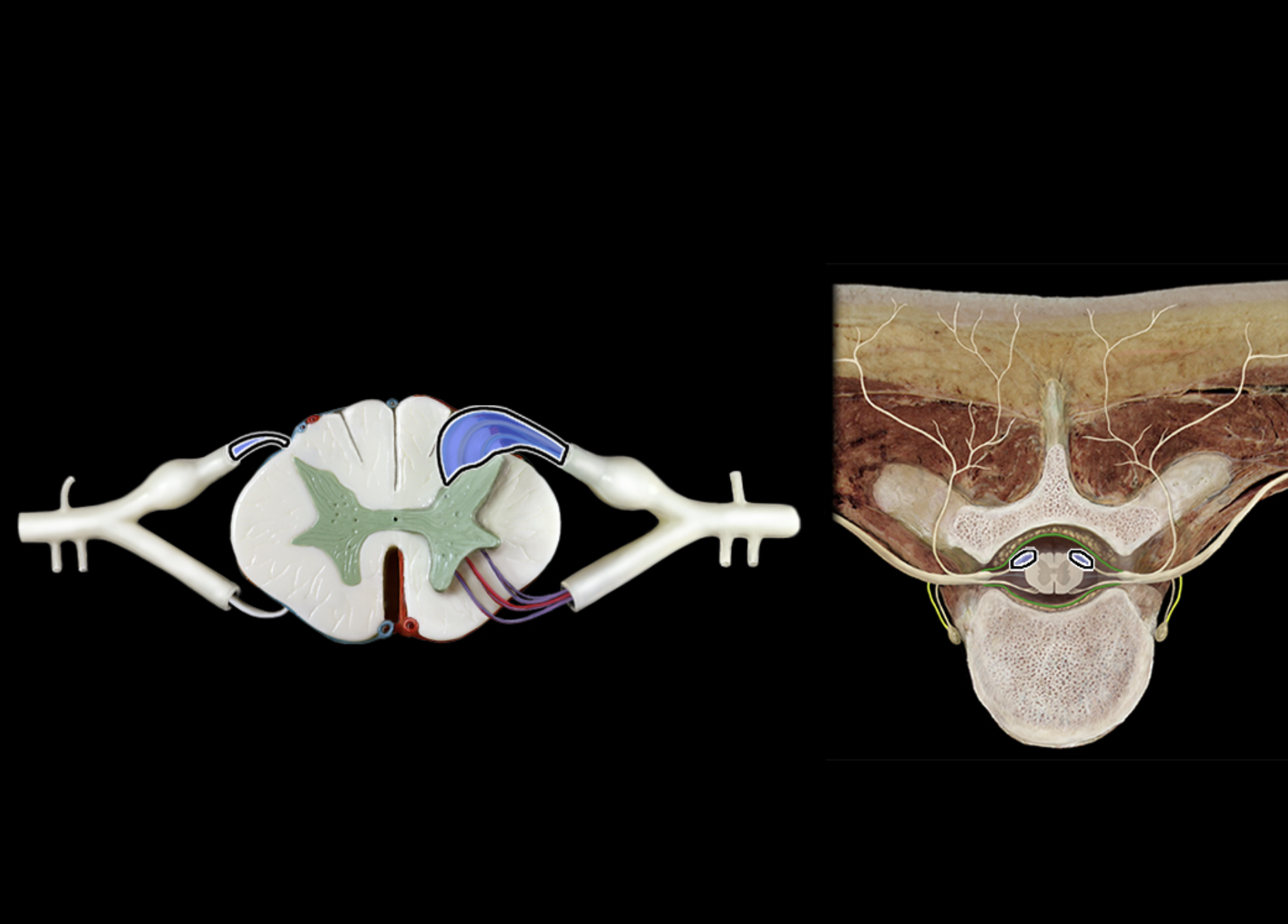
posterior rootless
dura matter
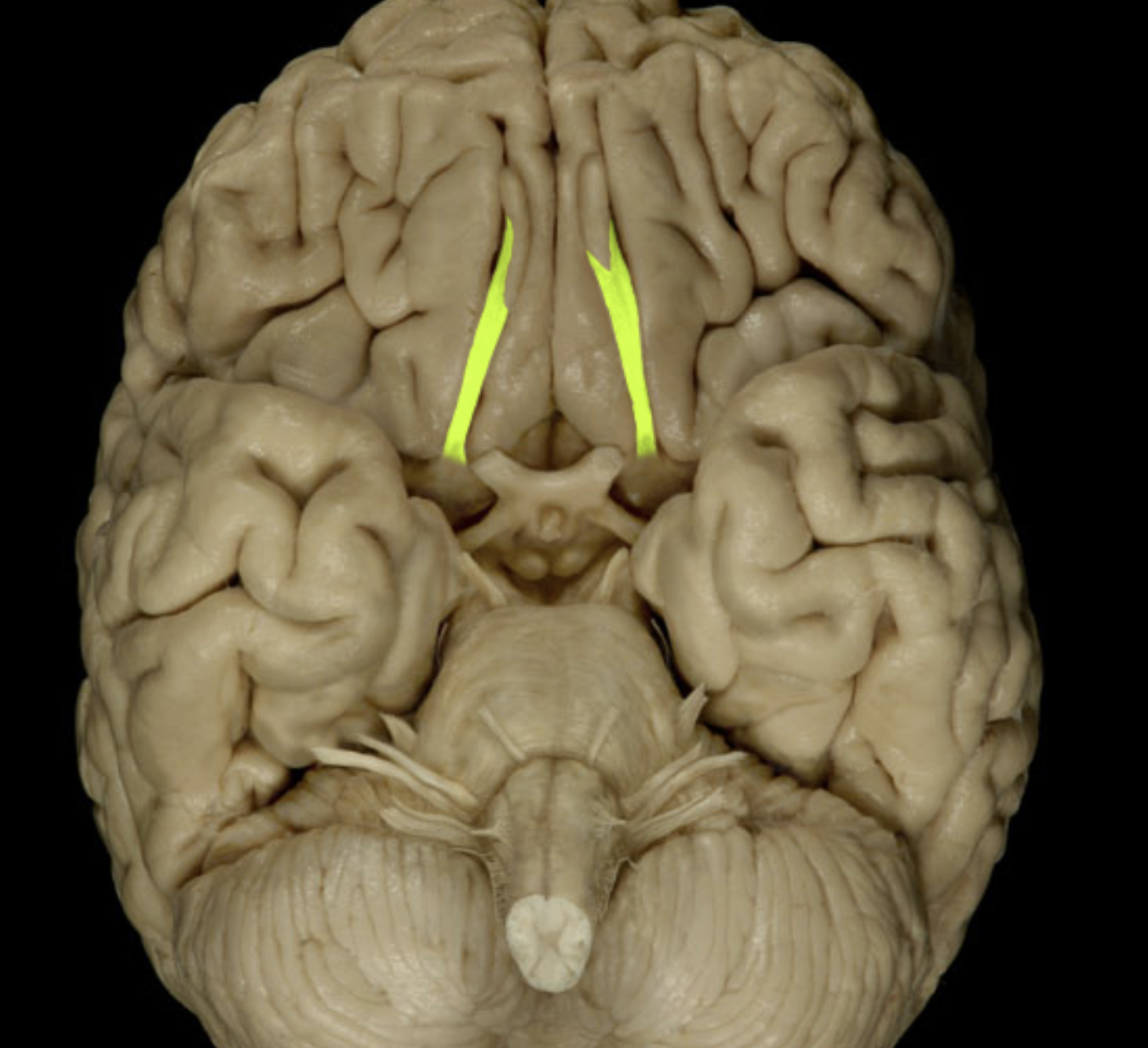
olfactory tracts
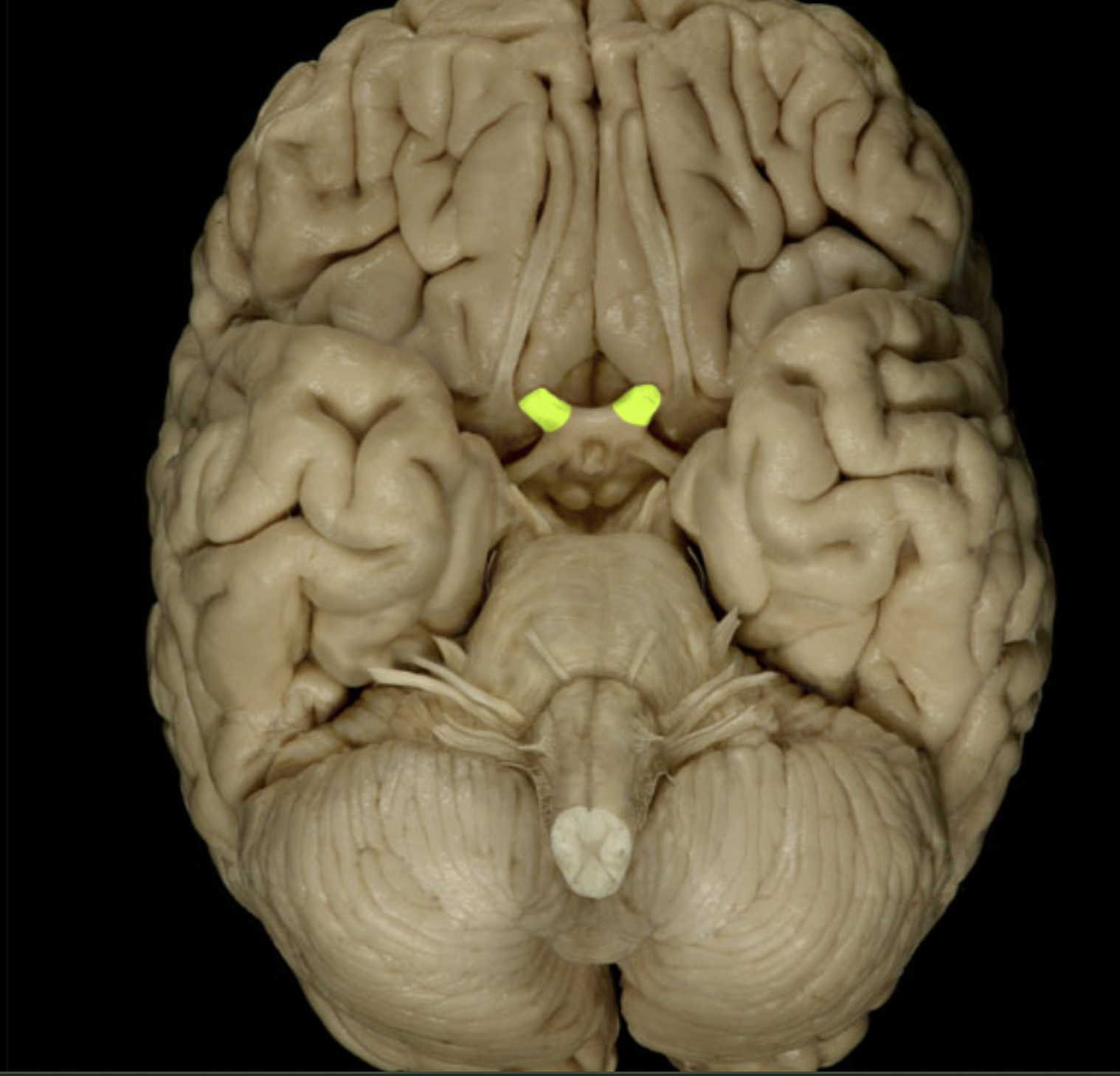
optic nerves (II)
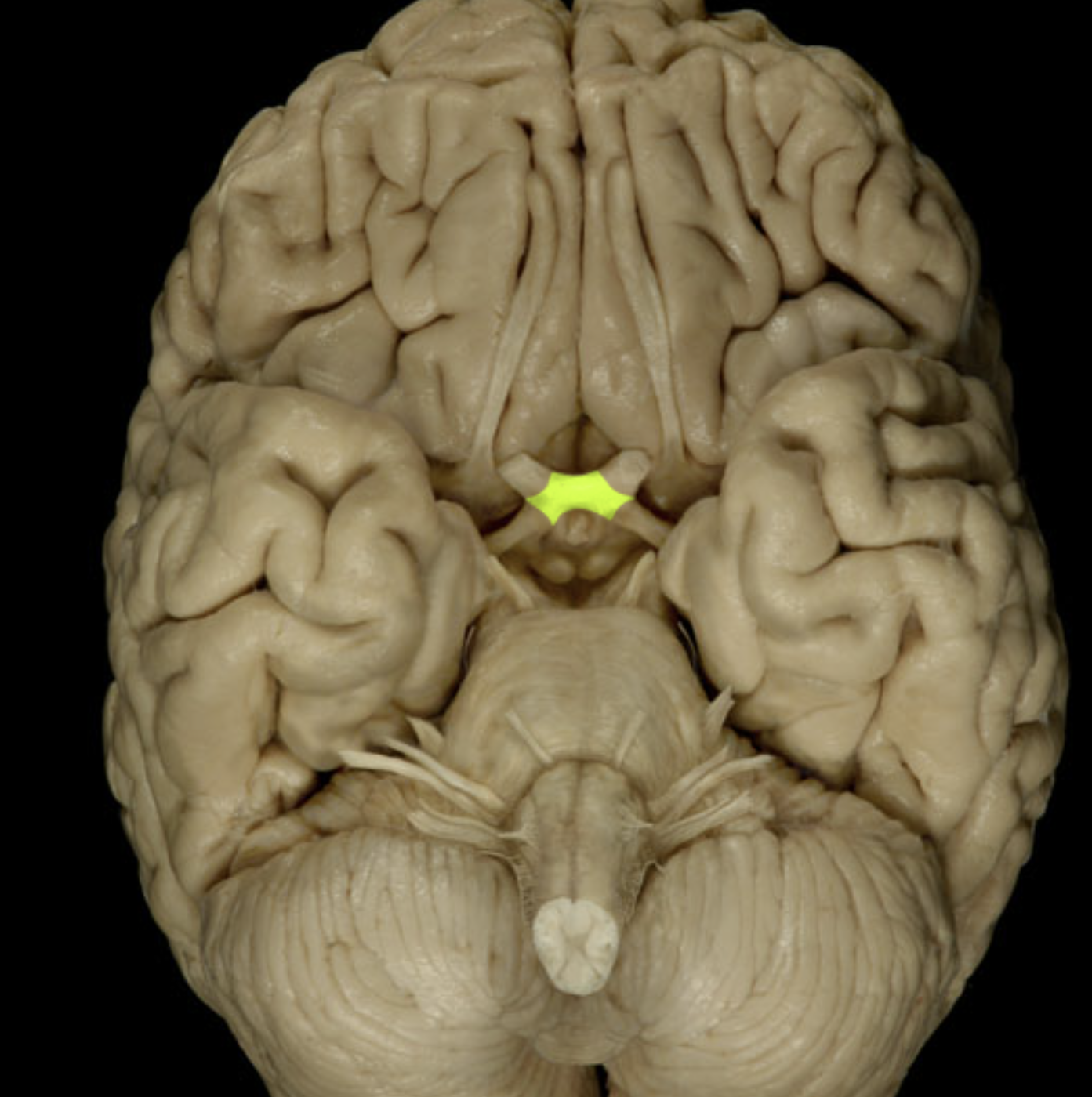
optic chiasm
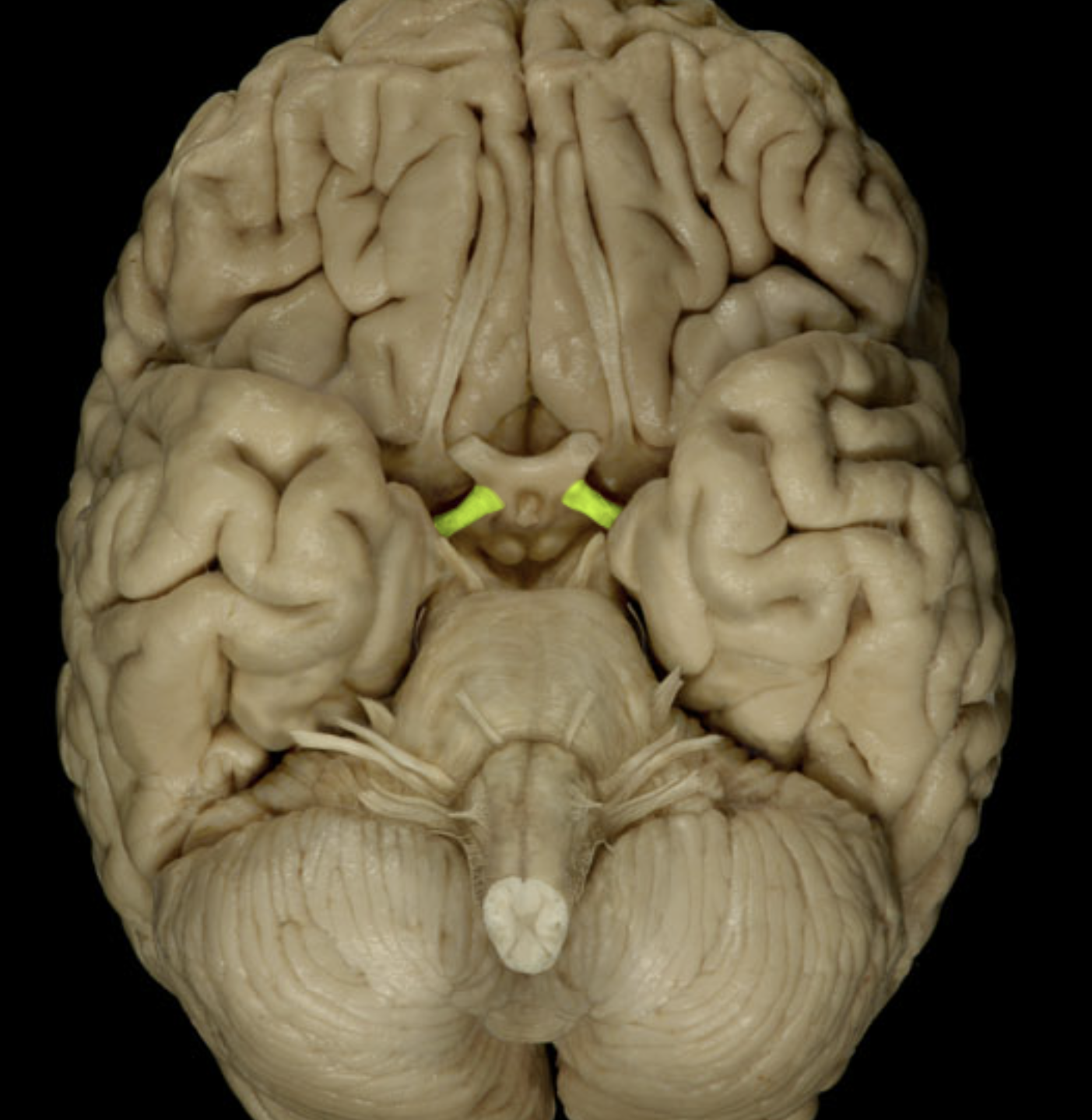
optic tract
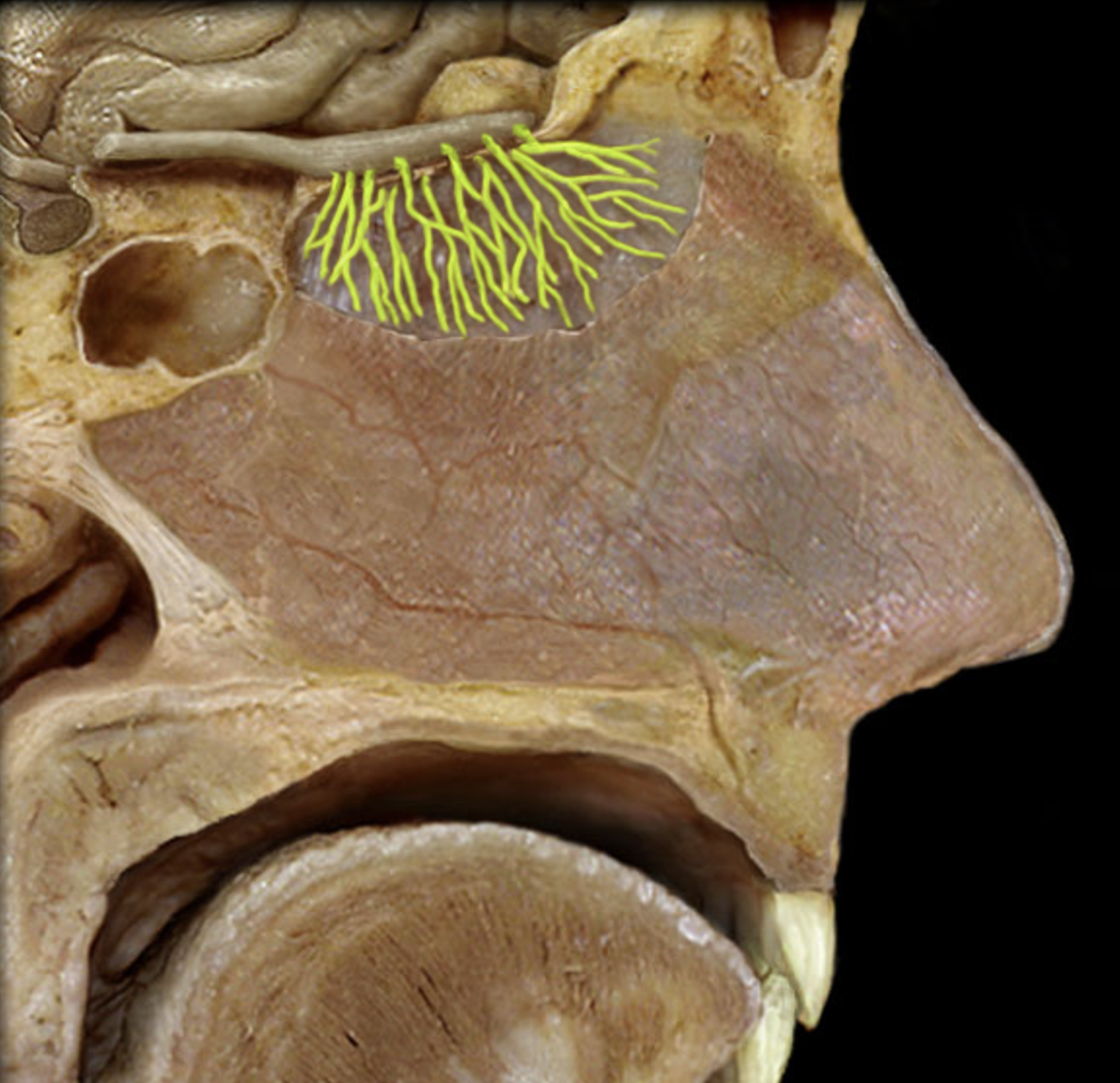
olfactory nerve (I)
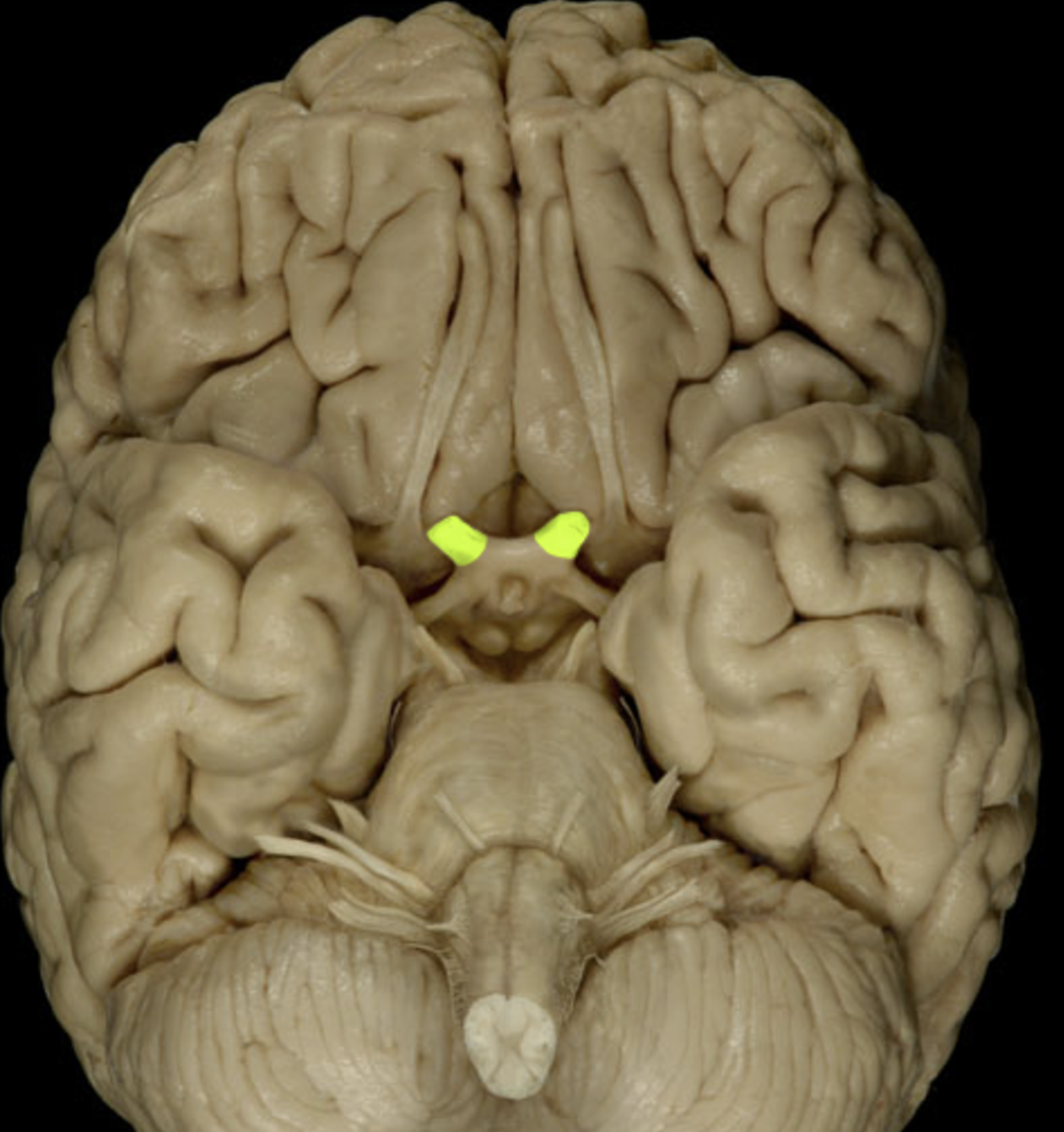
optic nerve (II)
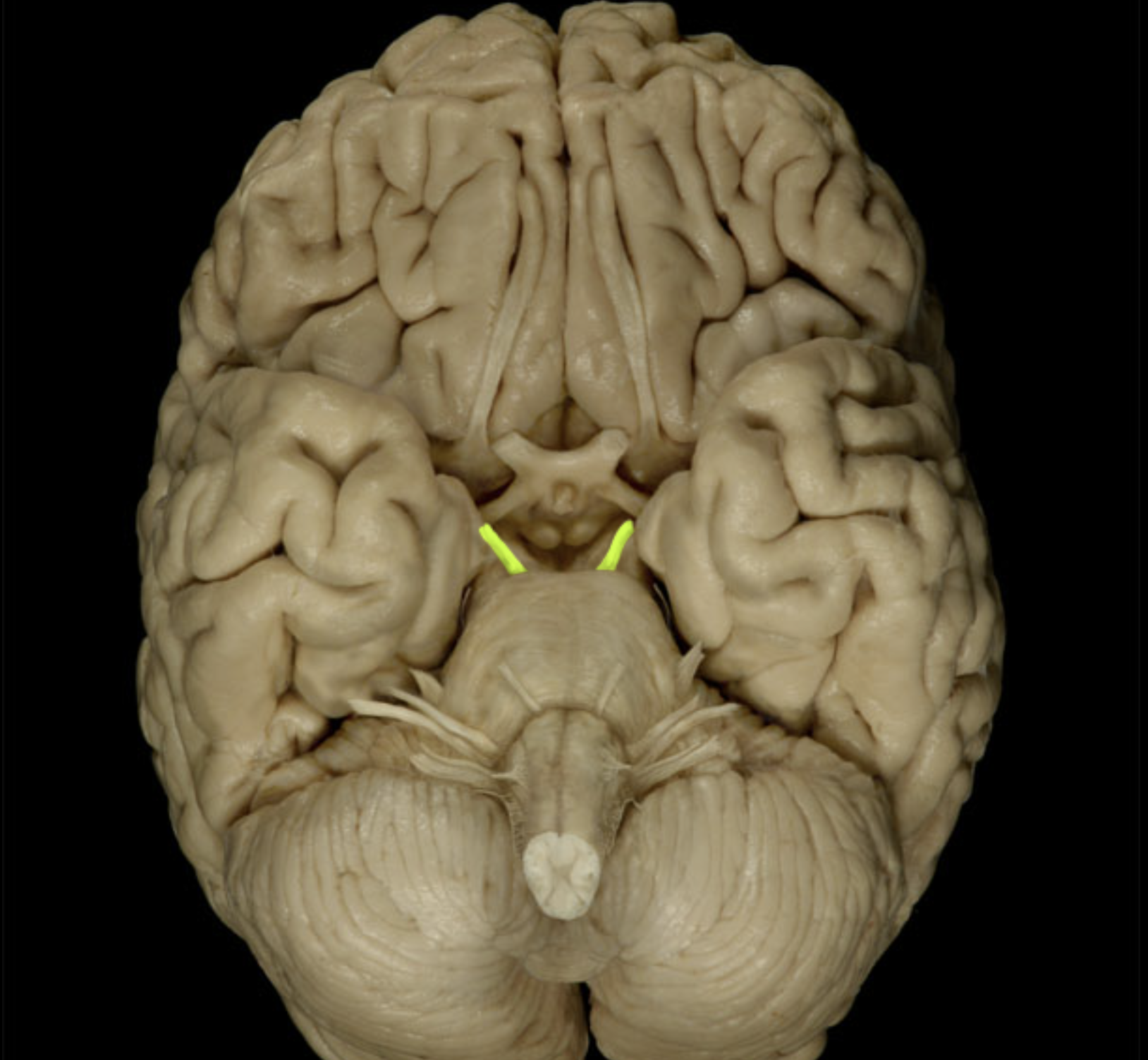
oculomotor nerve (III)
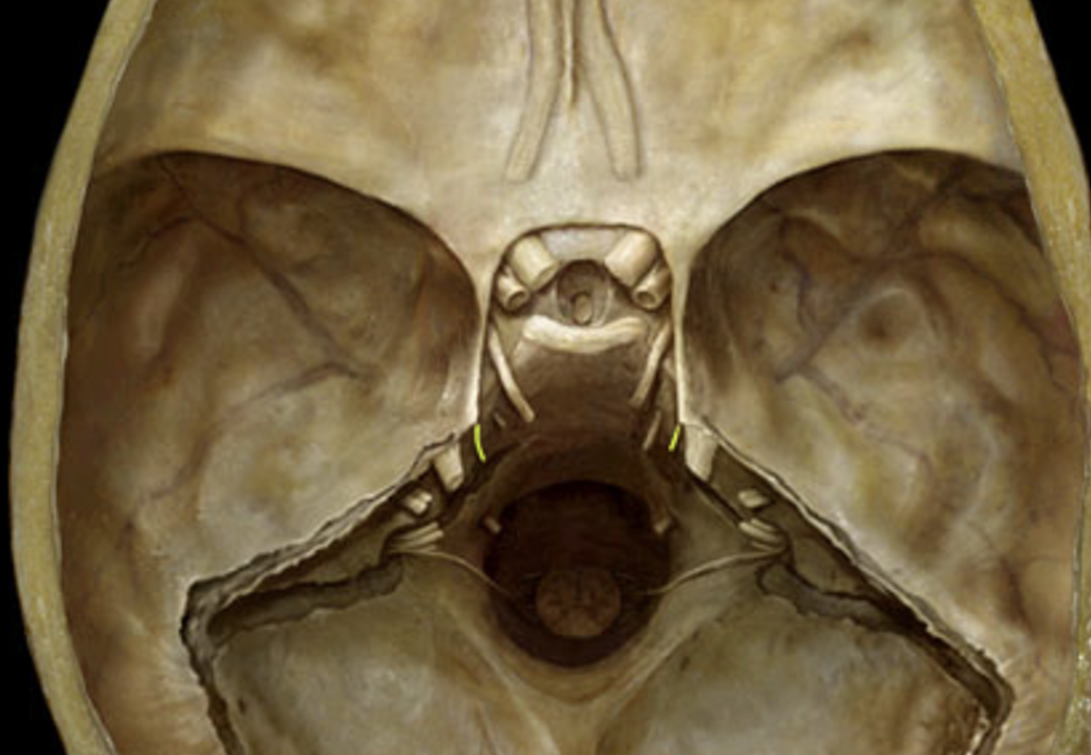
trochlear nerve (IV)
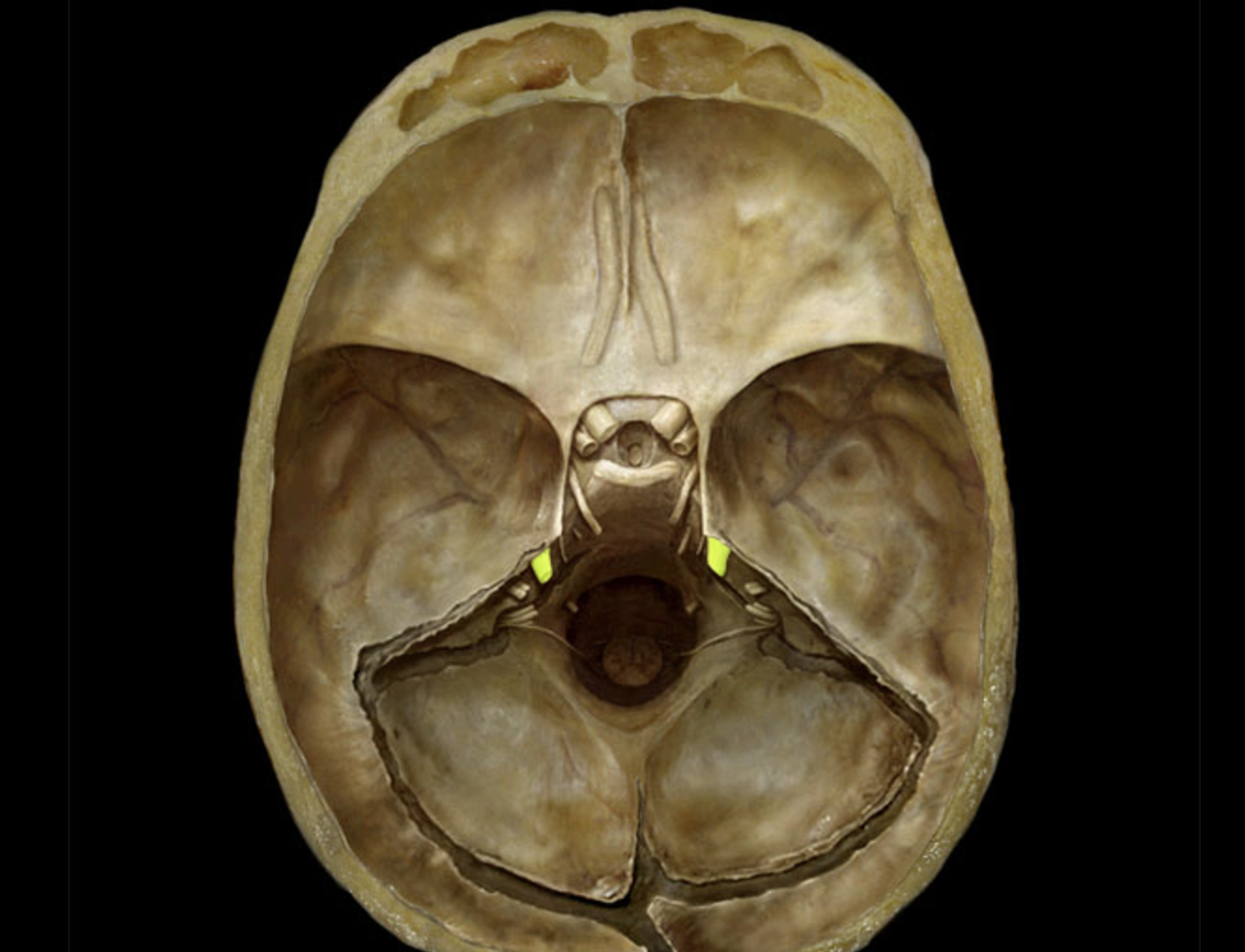
trigeminal nerve (V)
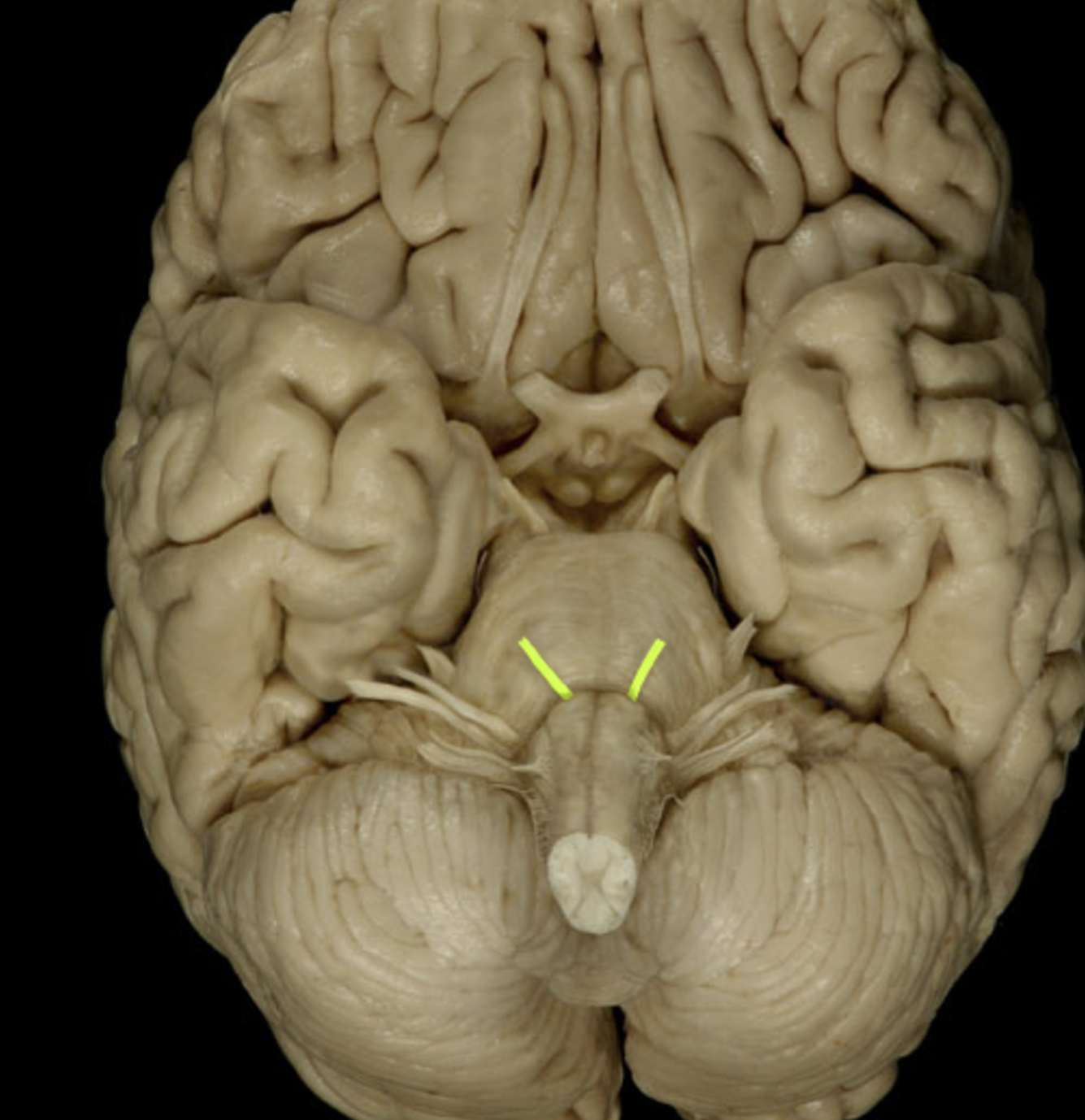
abducens nerve (VI)
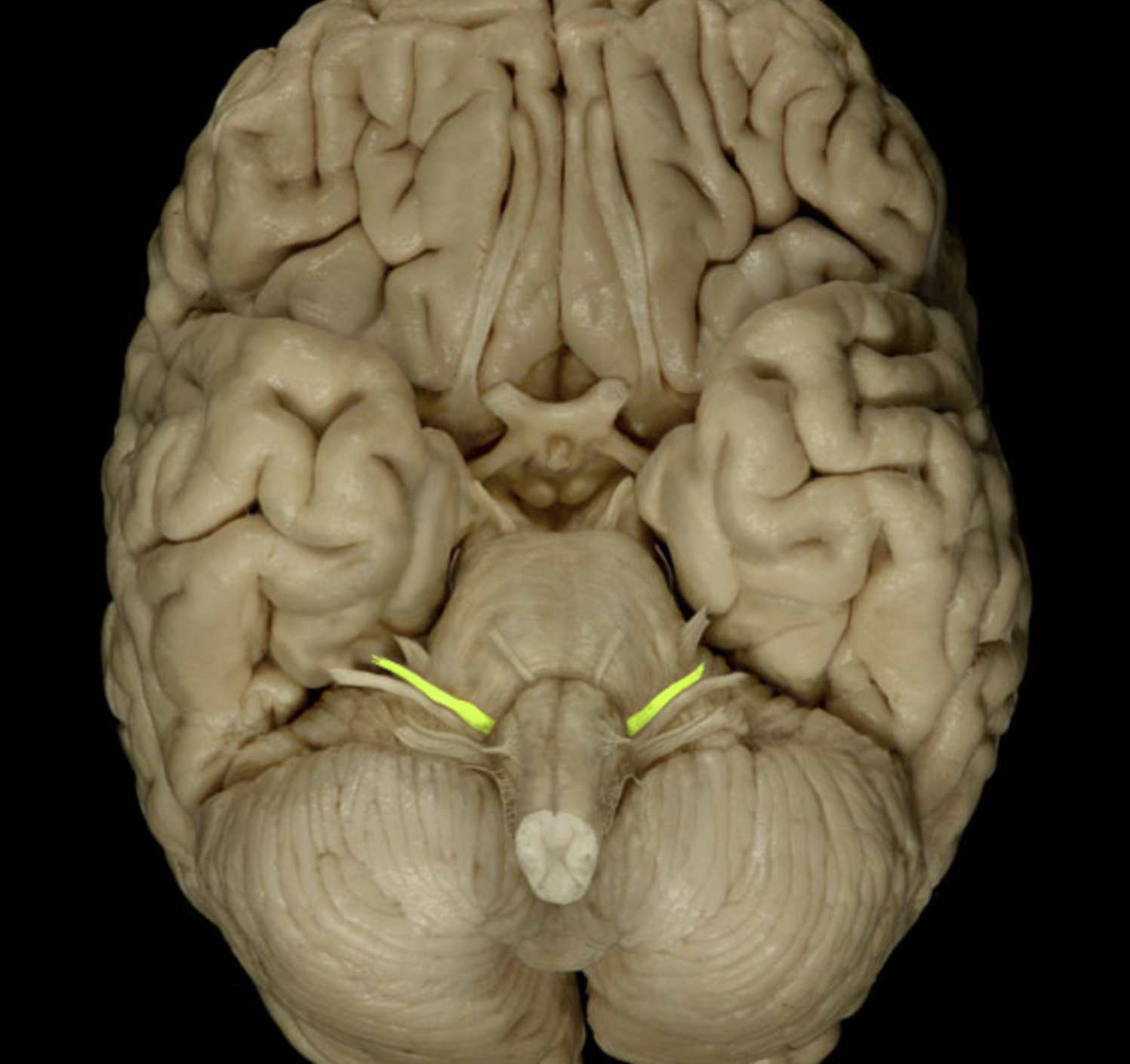
facial nerve (VII)
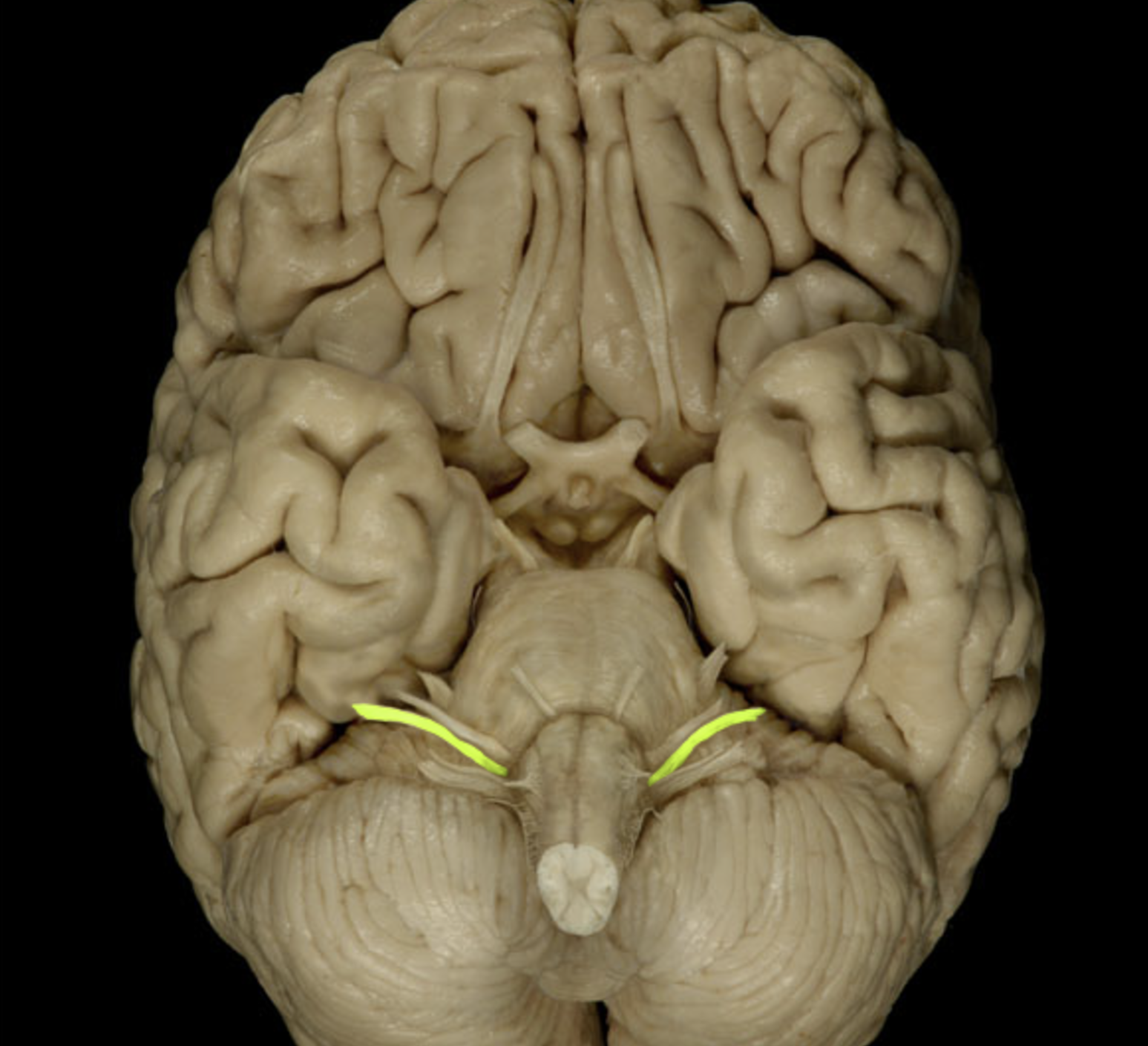
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
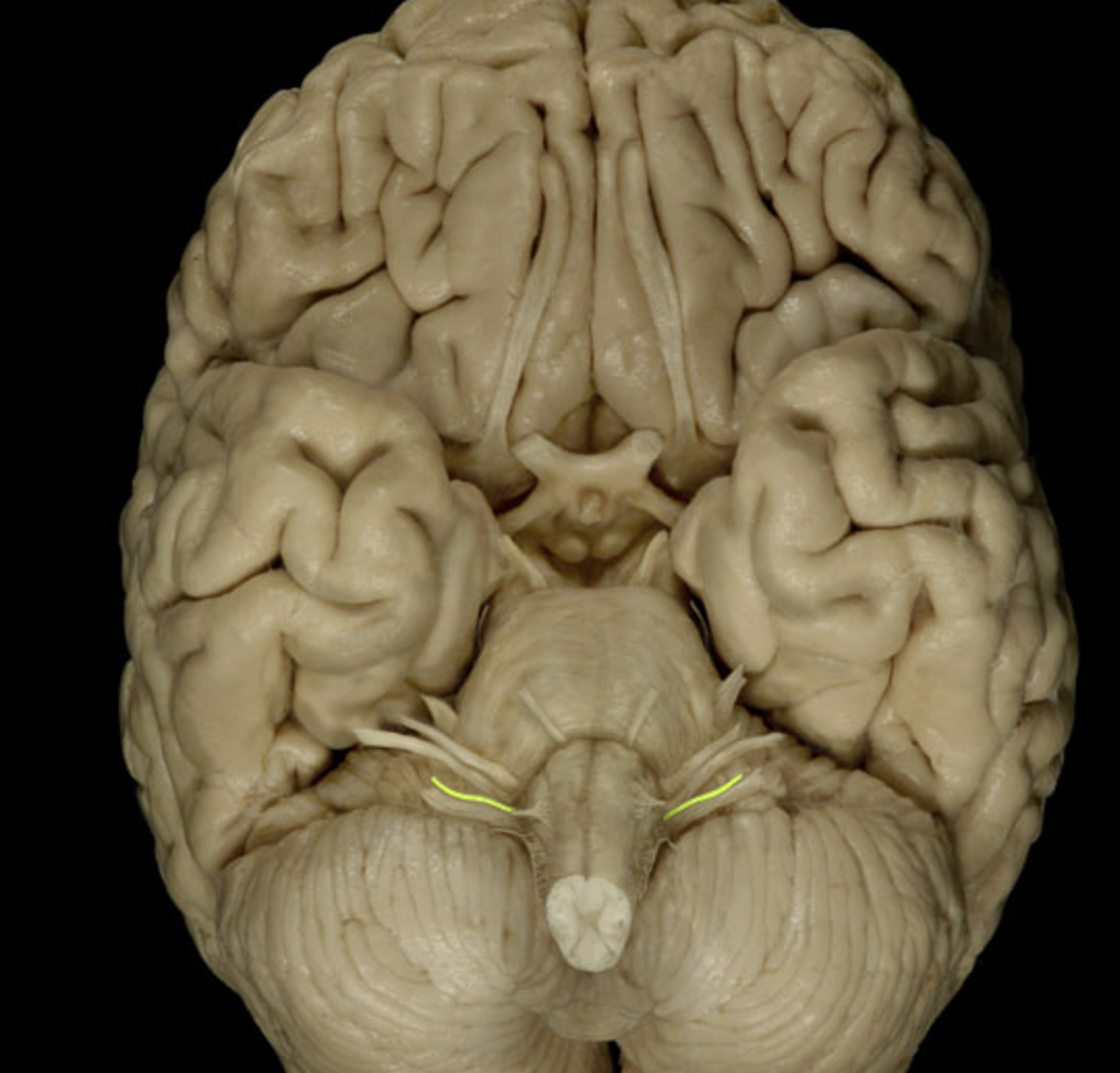
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
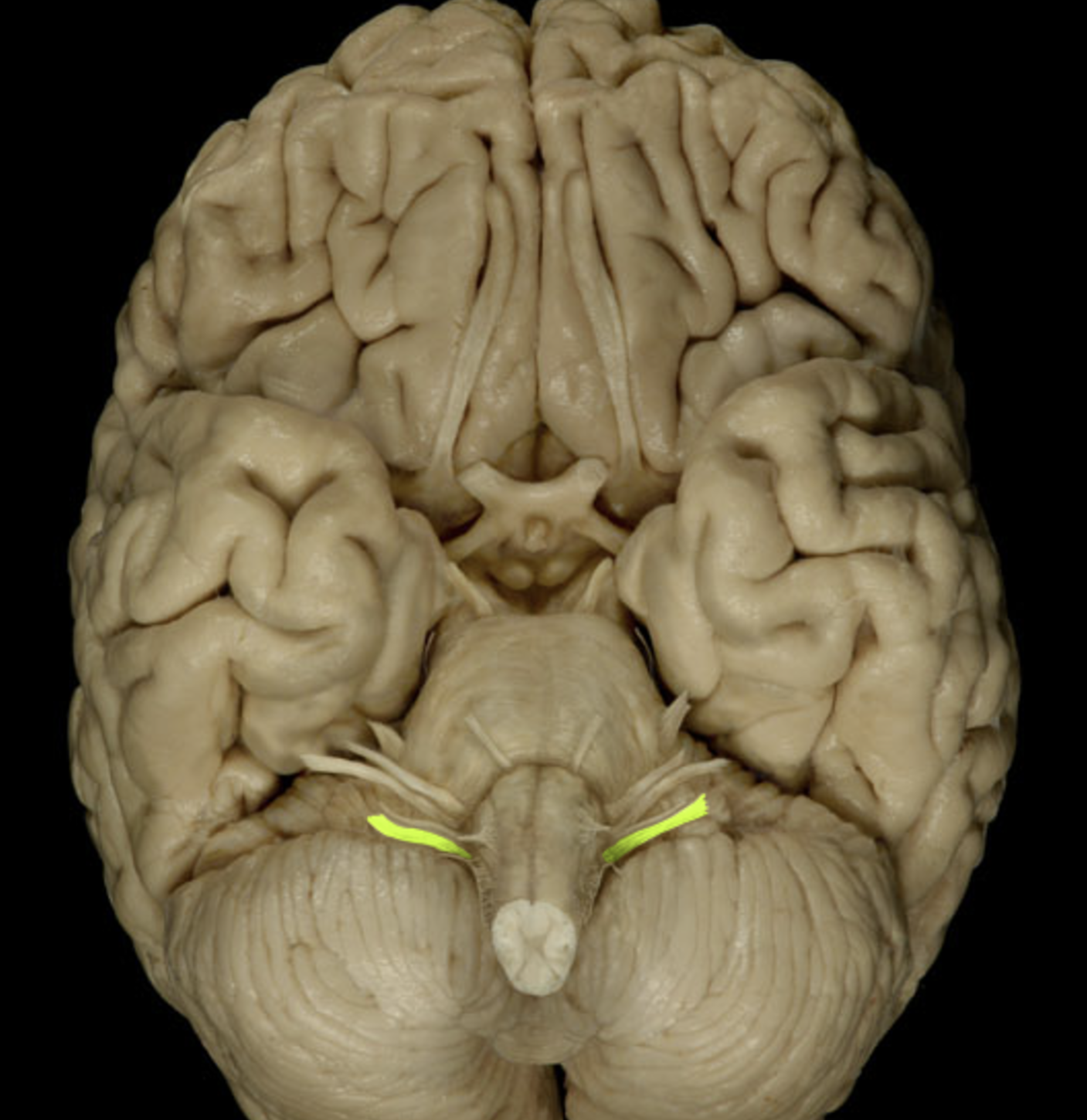
vagus nerve (X)
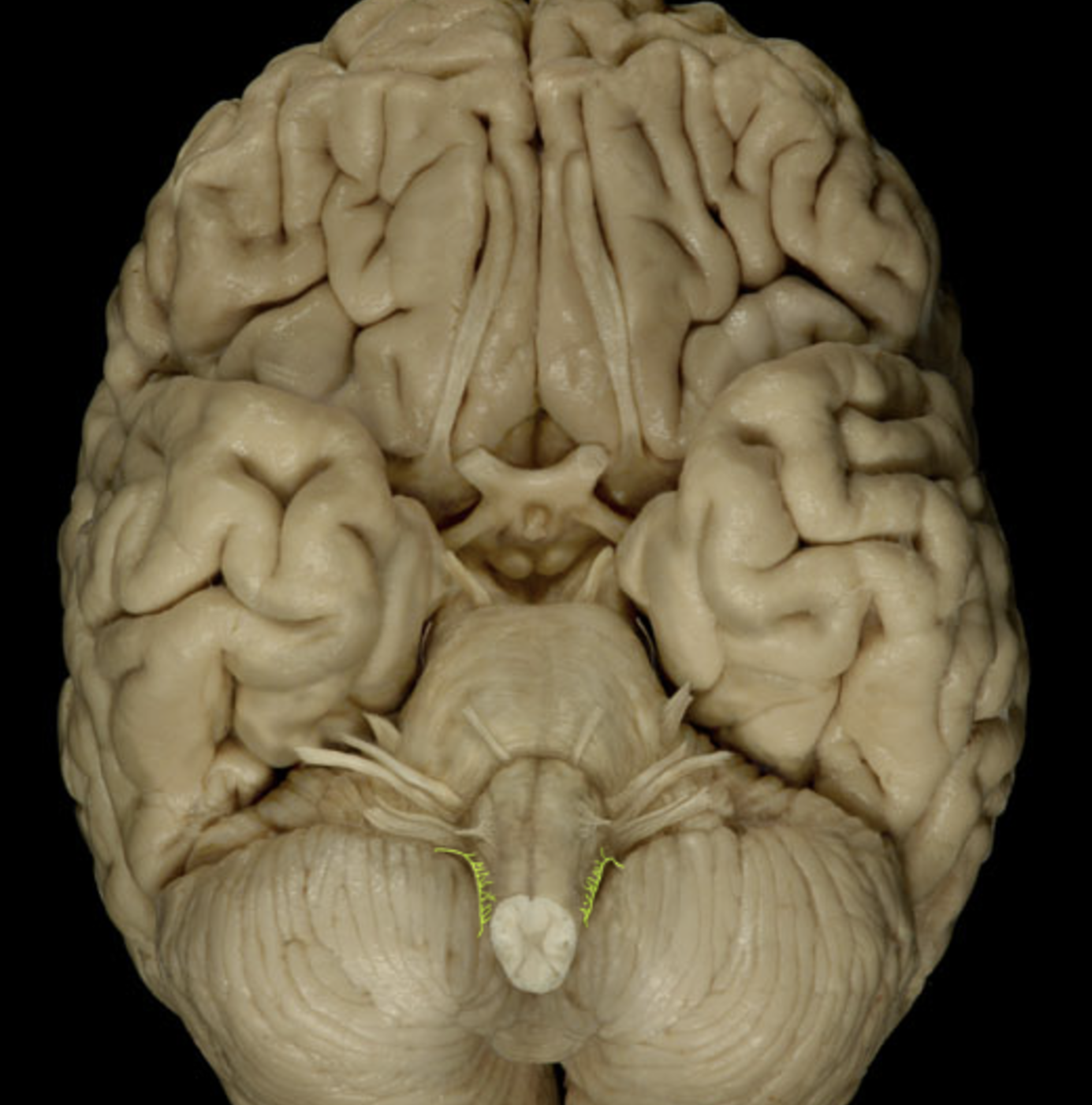
Accessory nerve (XI)
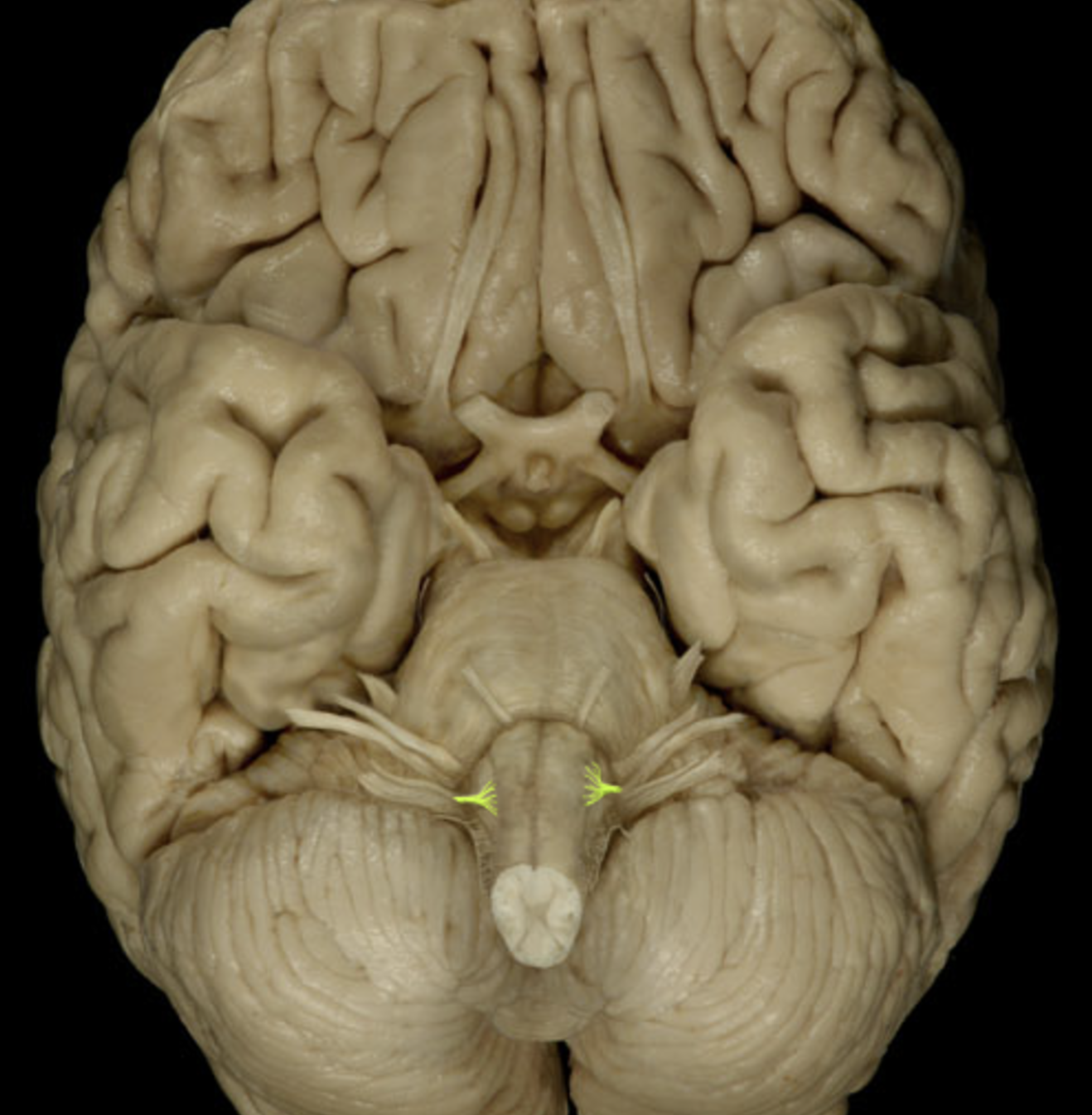
hypoglossal nerve (XII)
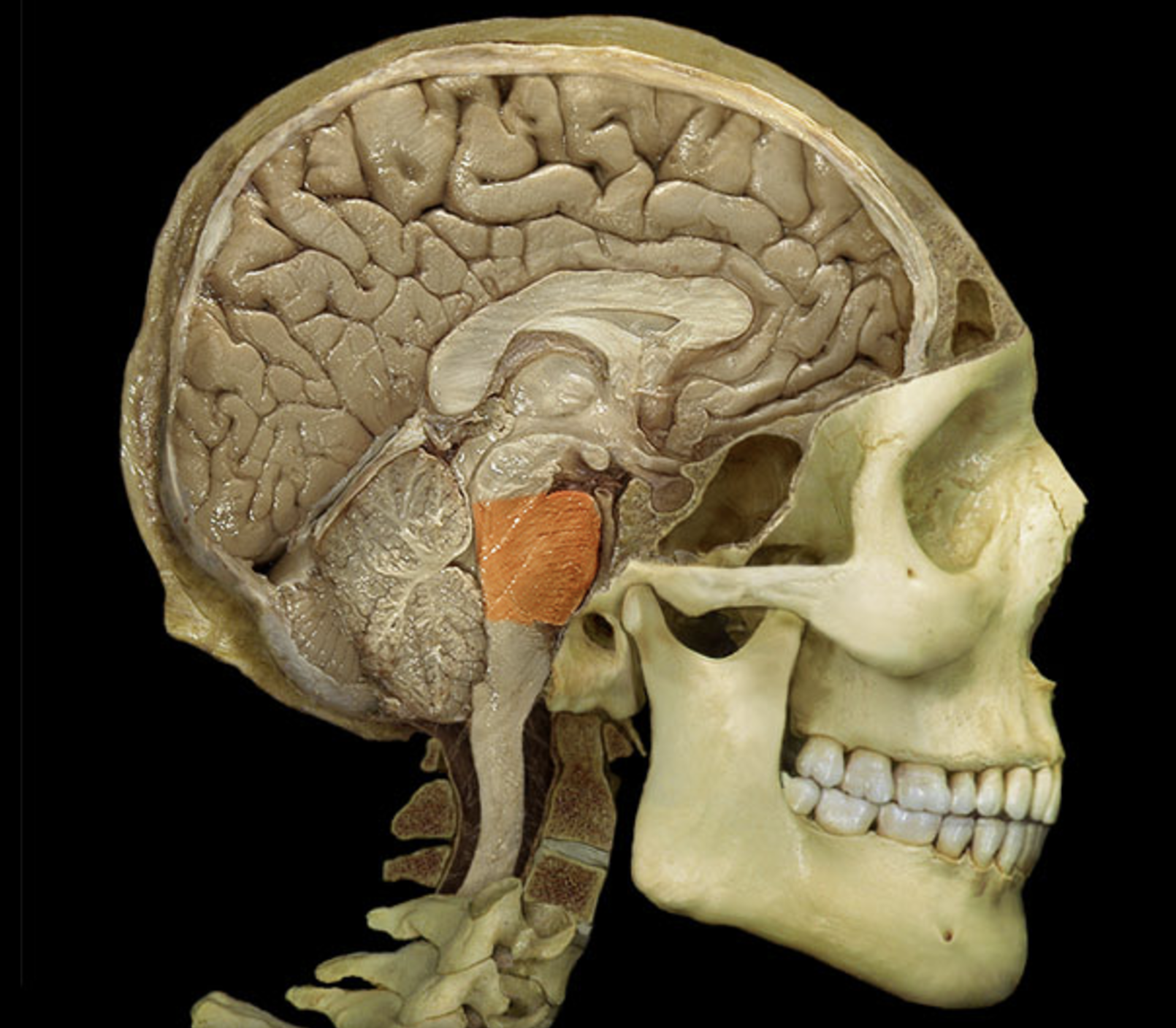
pons
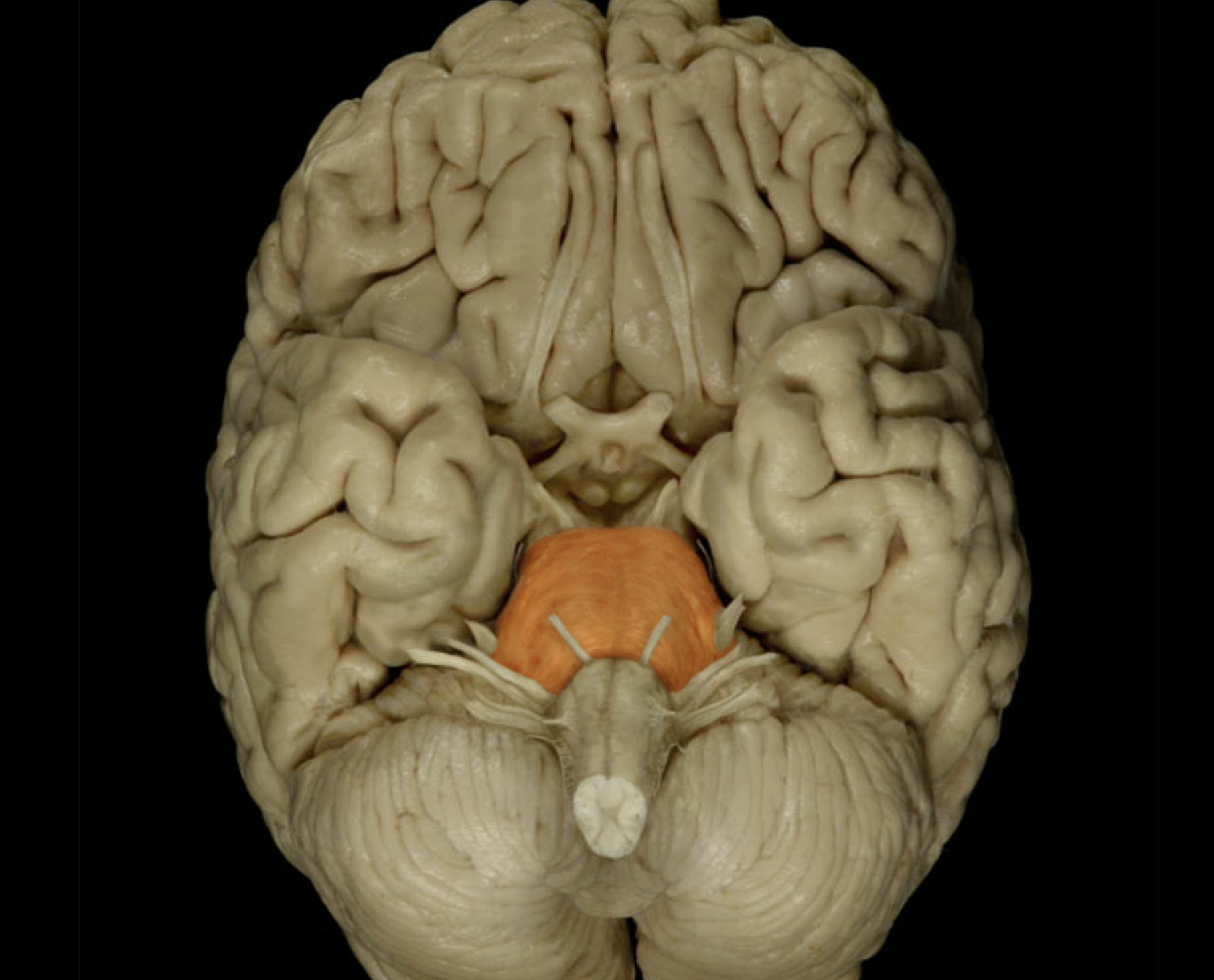
Pons
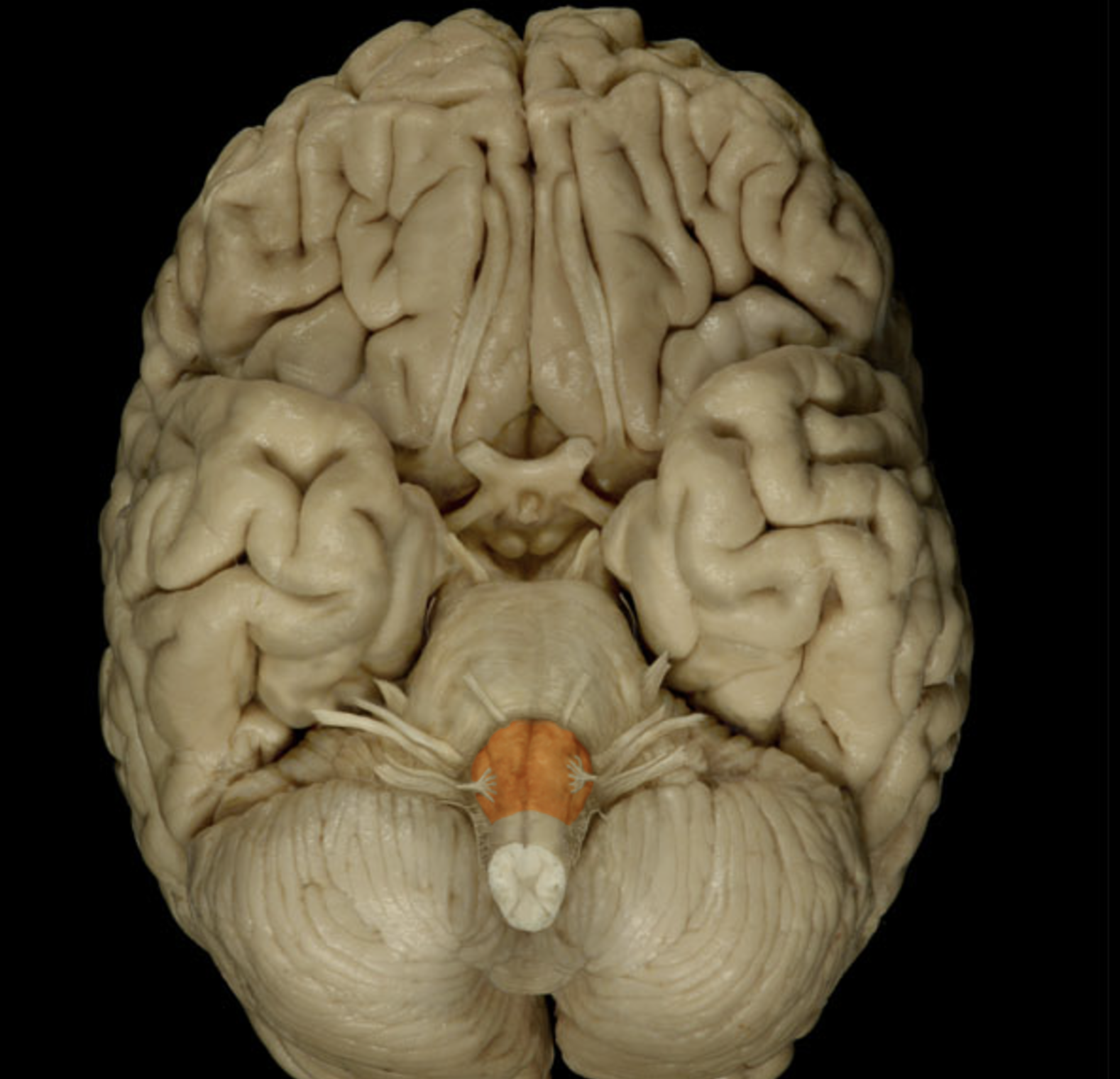
medulla oblongata
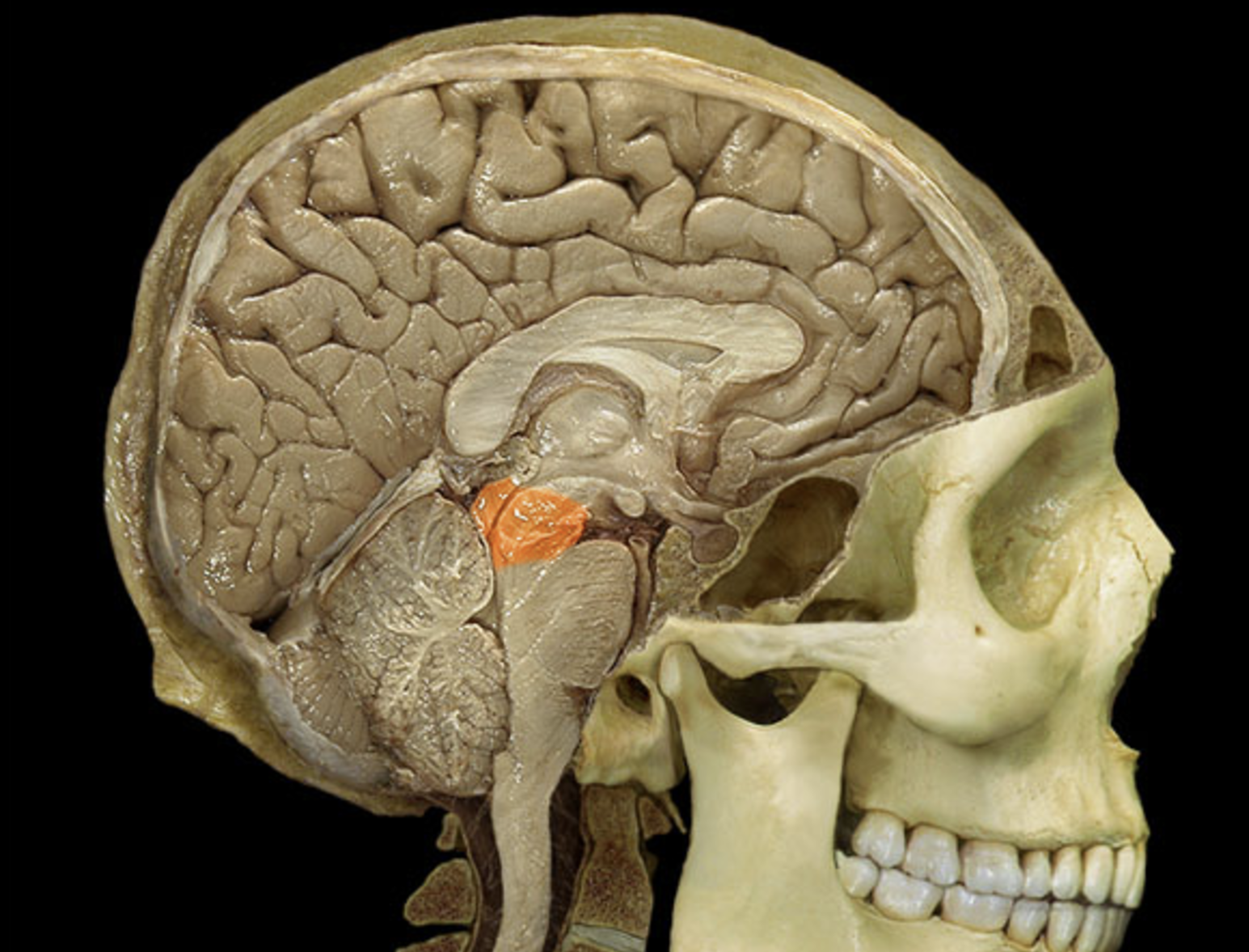
midbrain
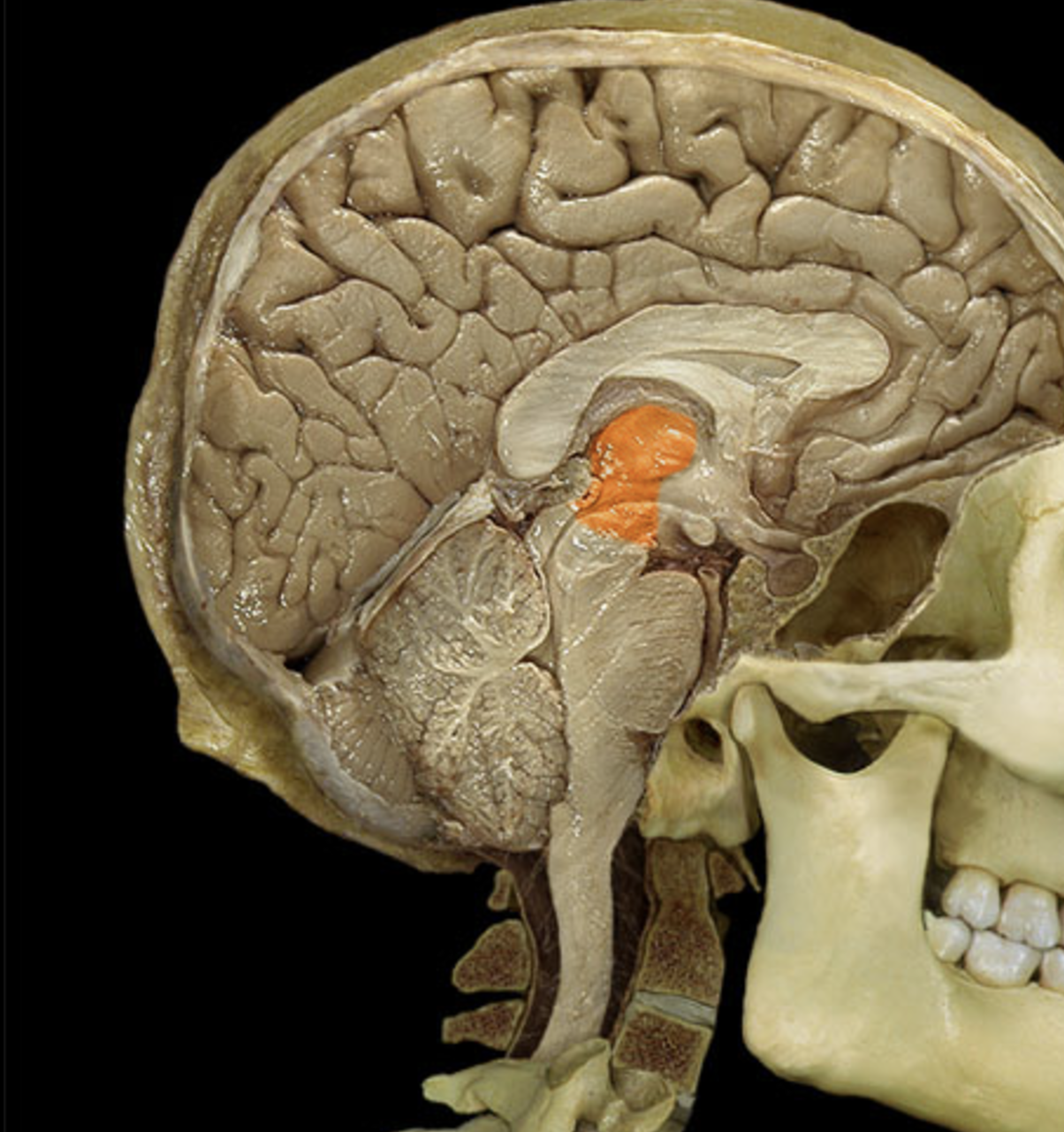
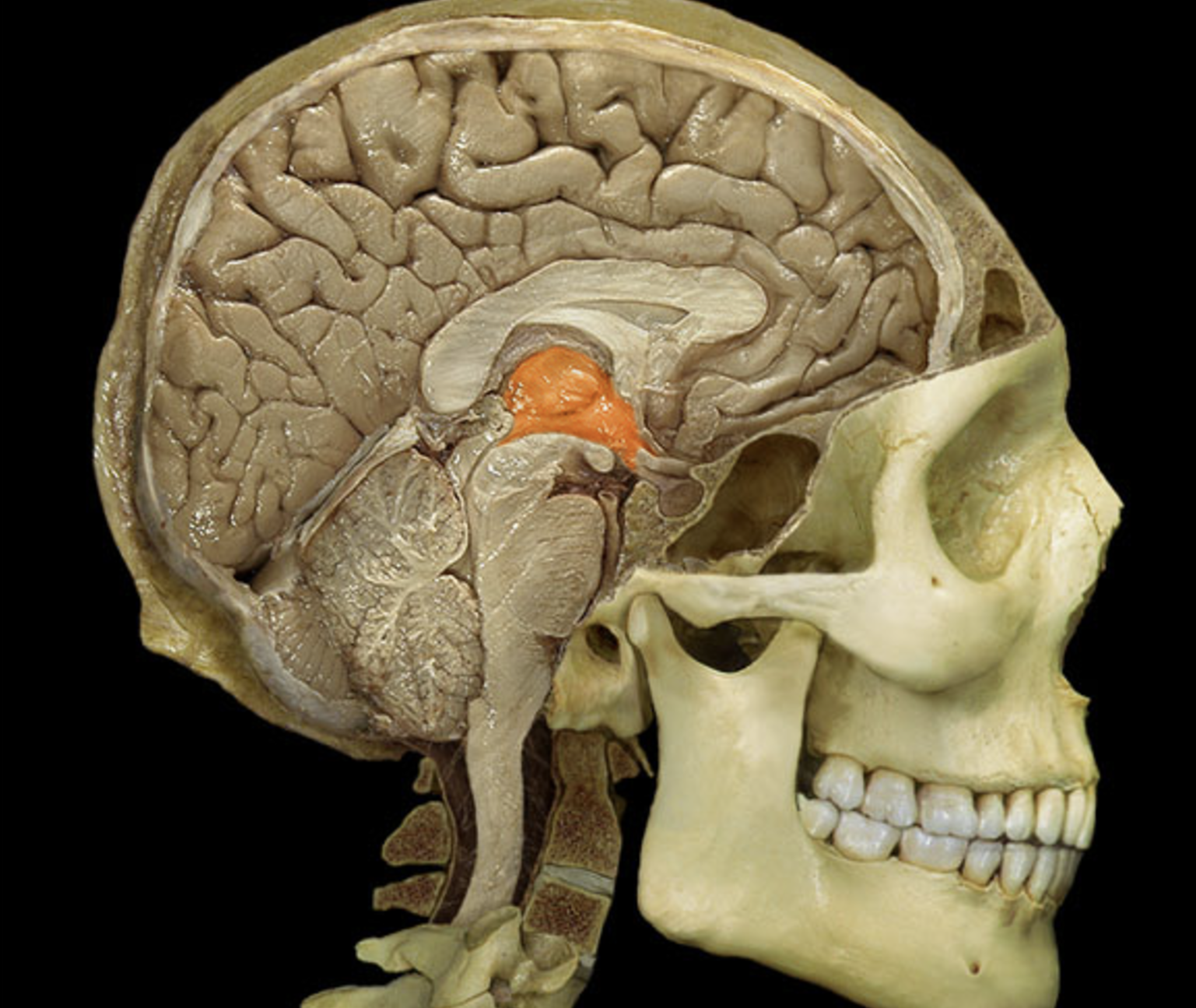
thalamus
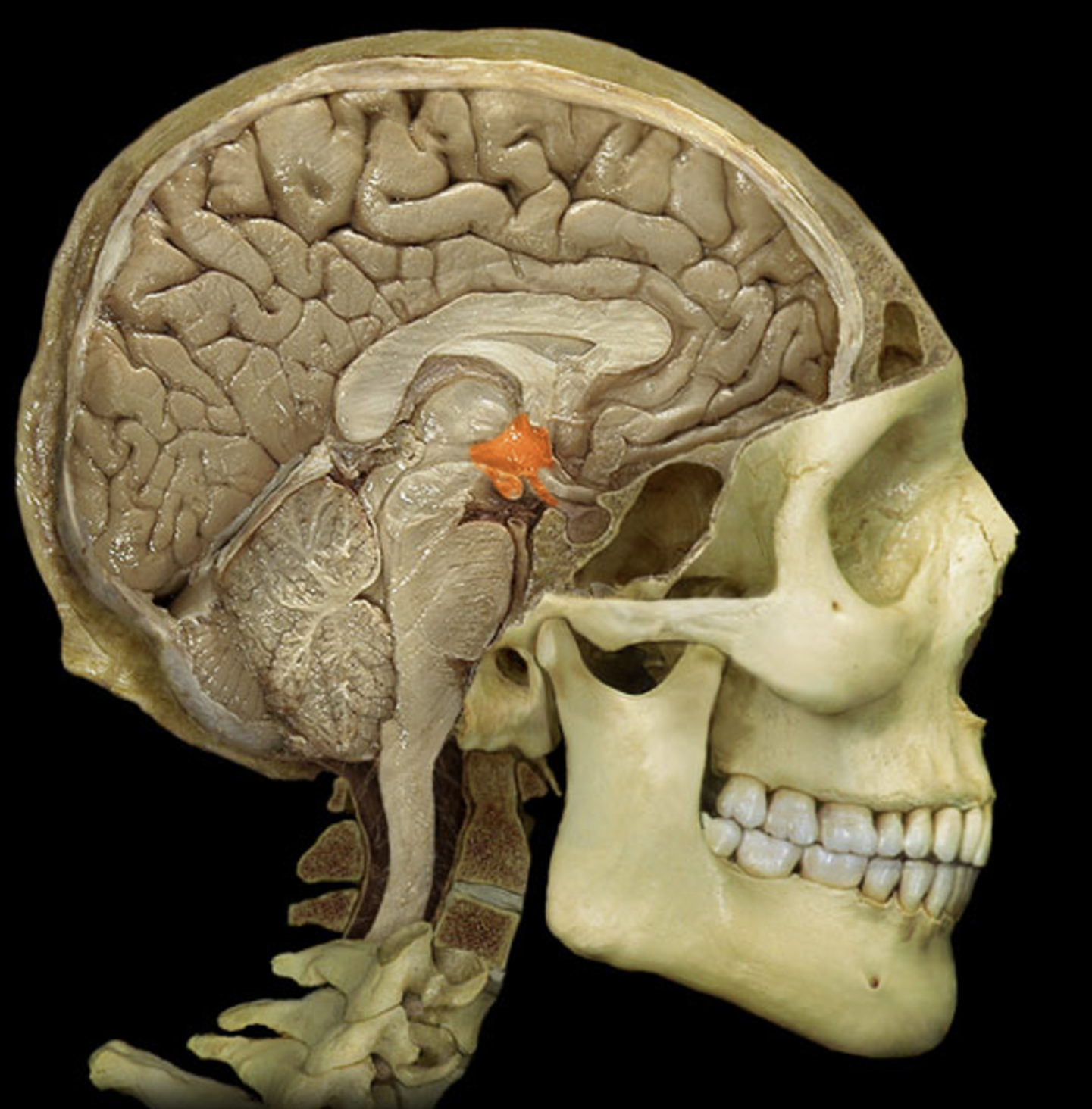
hypothalamus
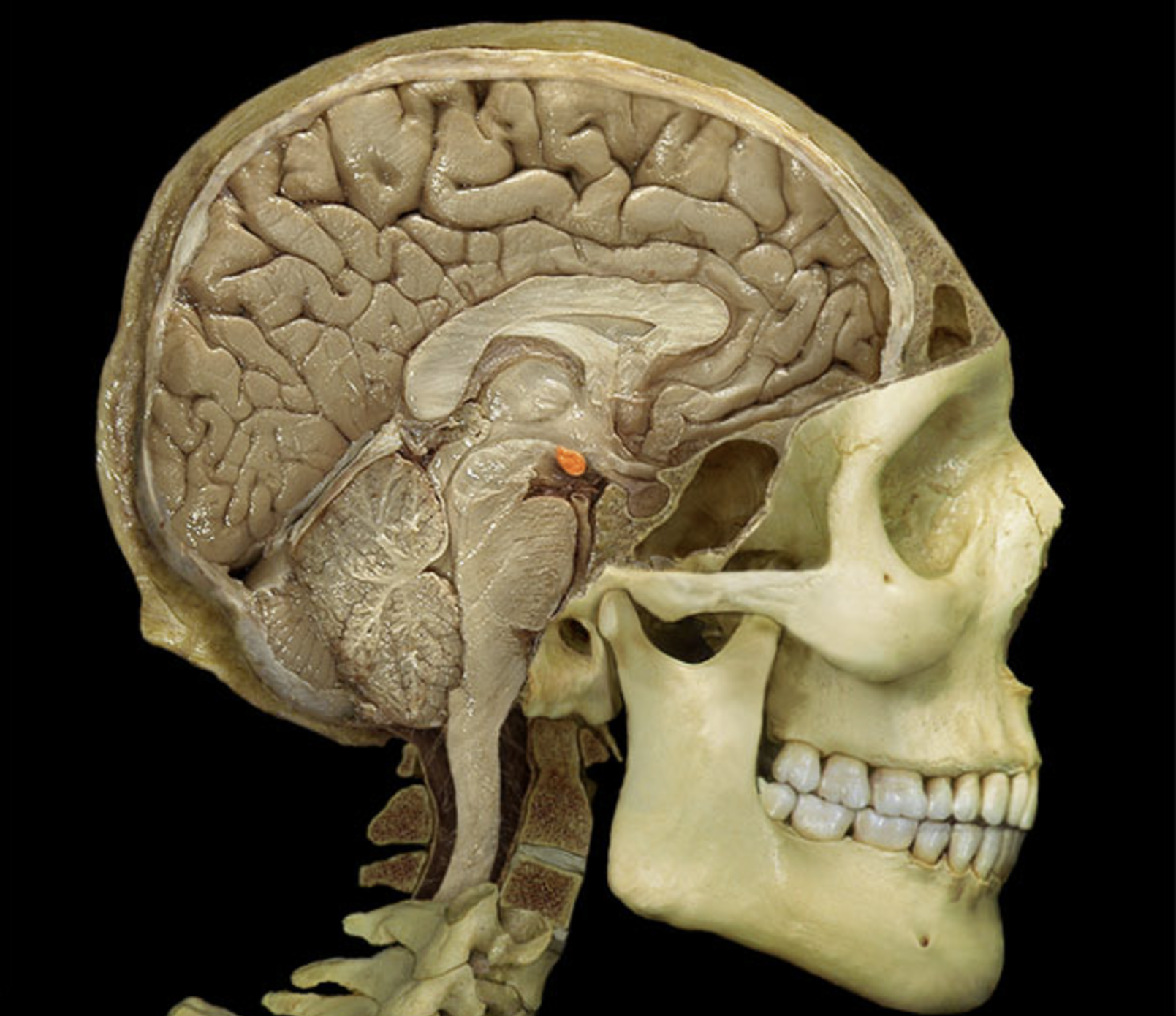
mammillary body
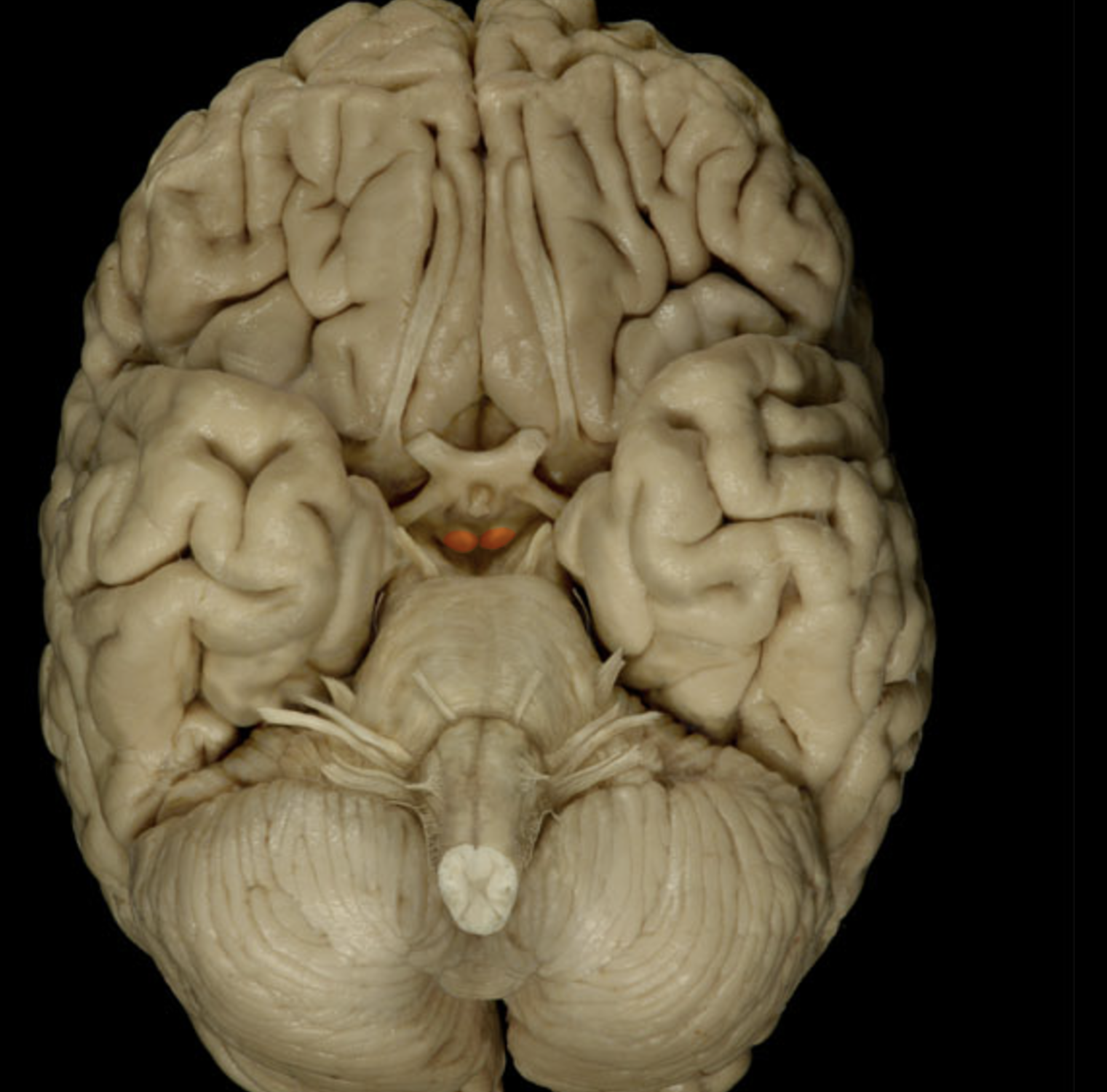
mamillary bodies
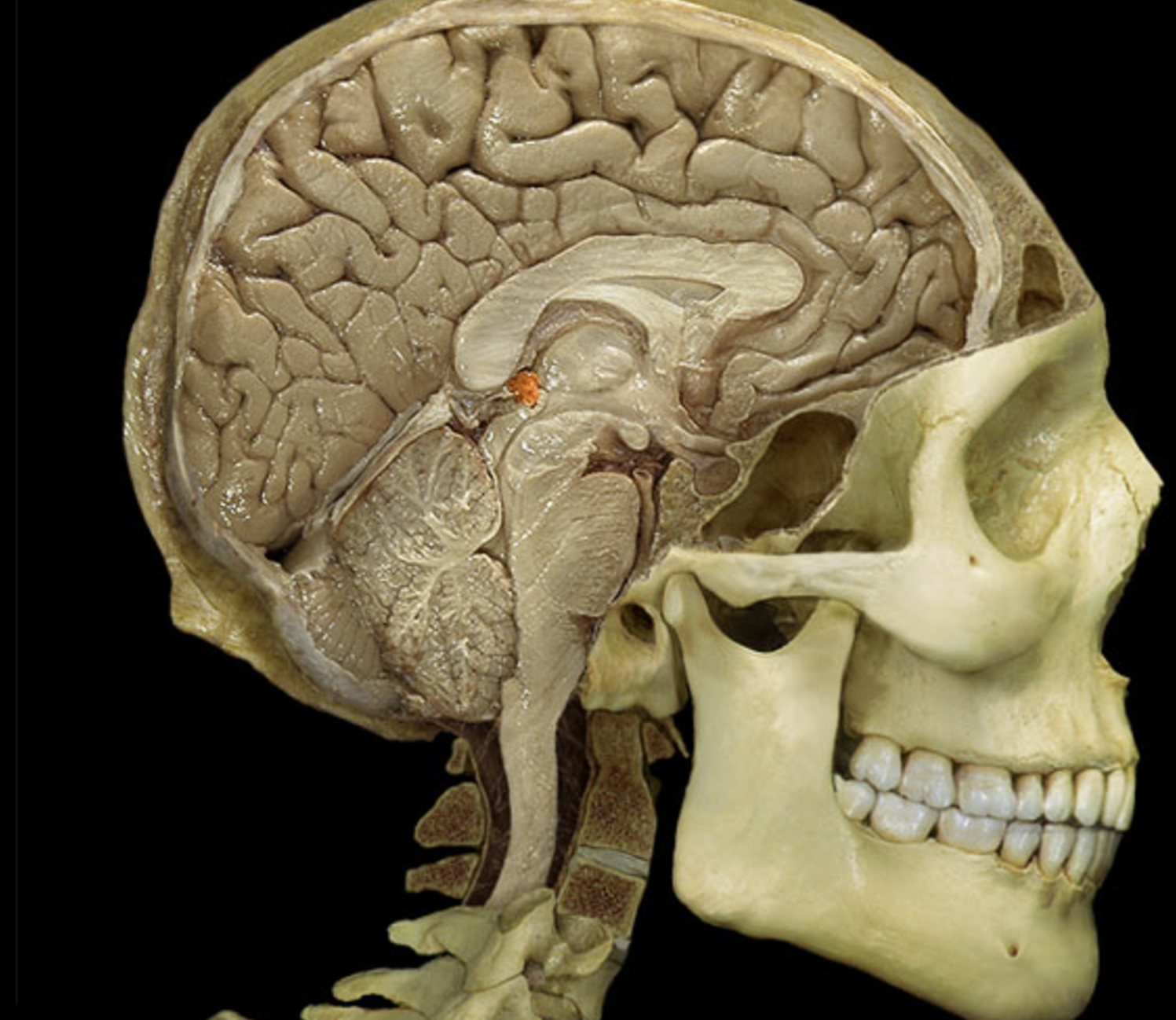
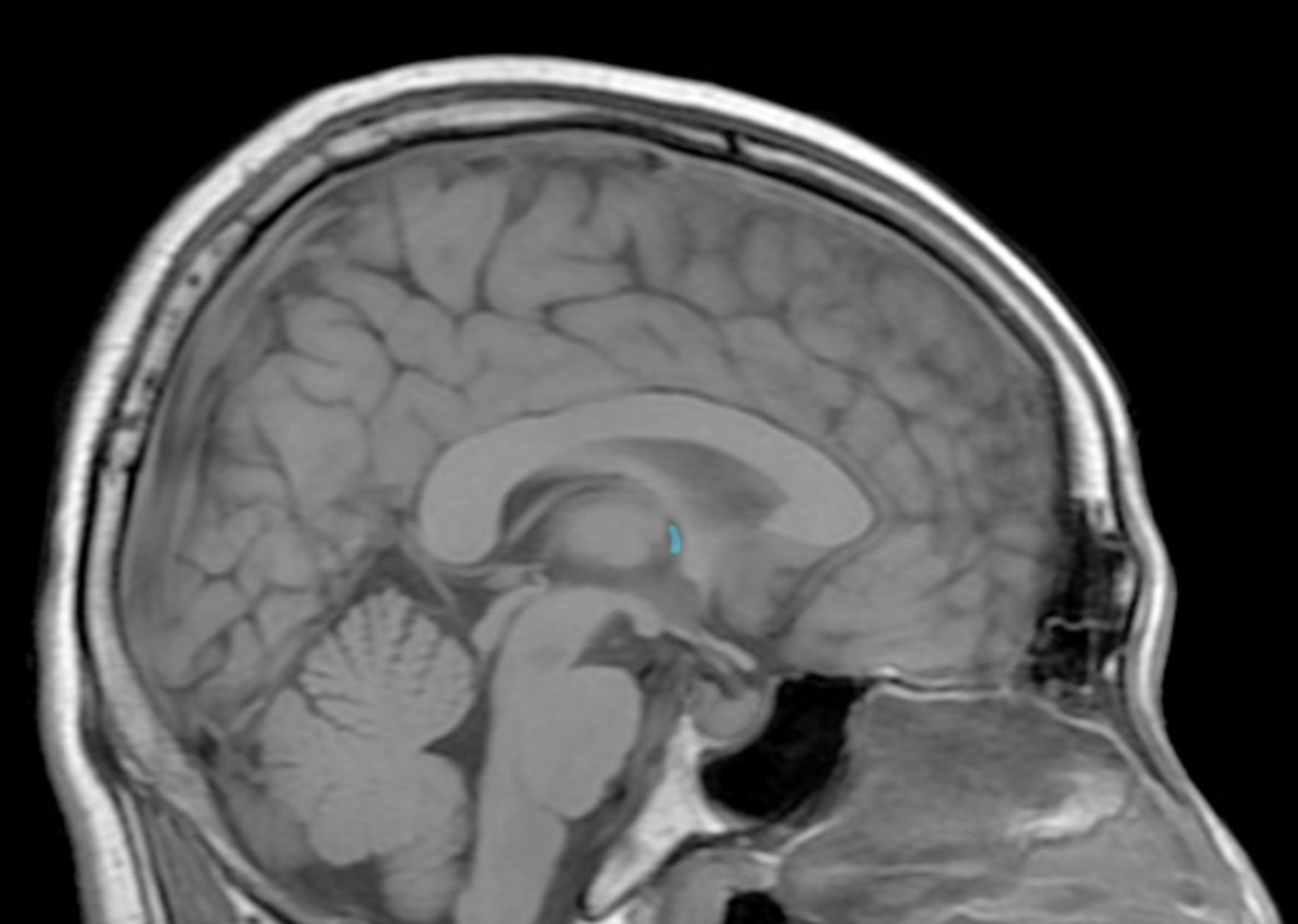
pineal gland
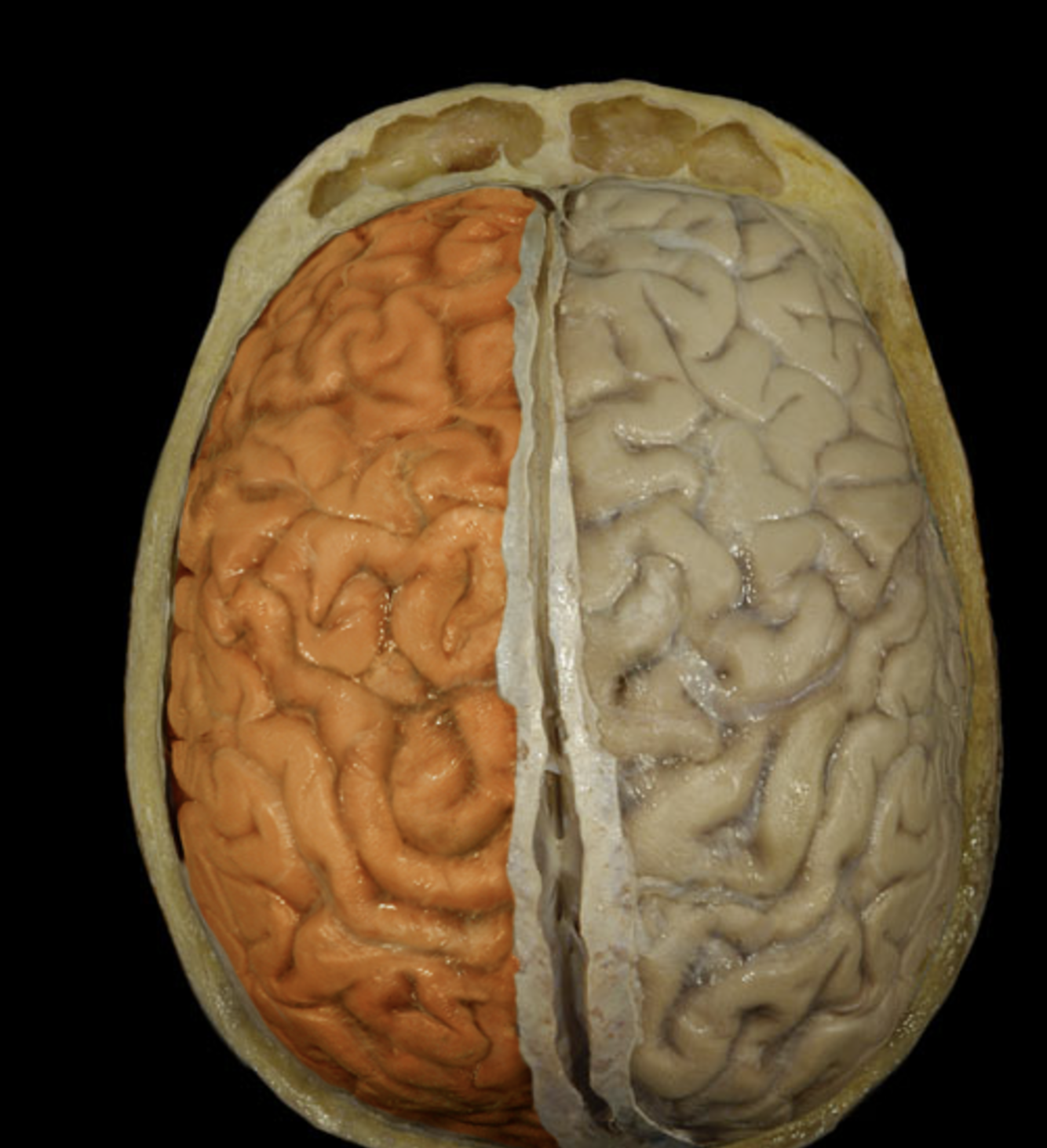
left cerebral hemisphere
What is a gyrus (gyri)?
folds in the brain matter
What is a sulcus (sulci)?
shallow grooves that separate the gyri
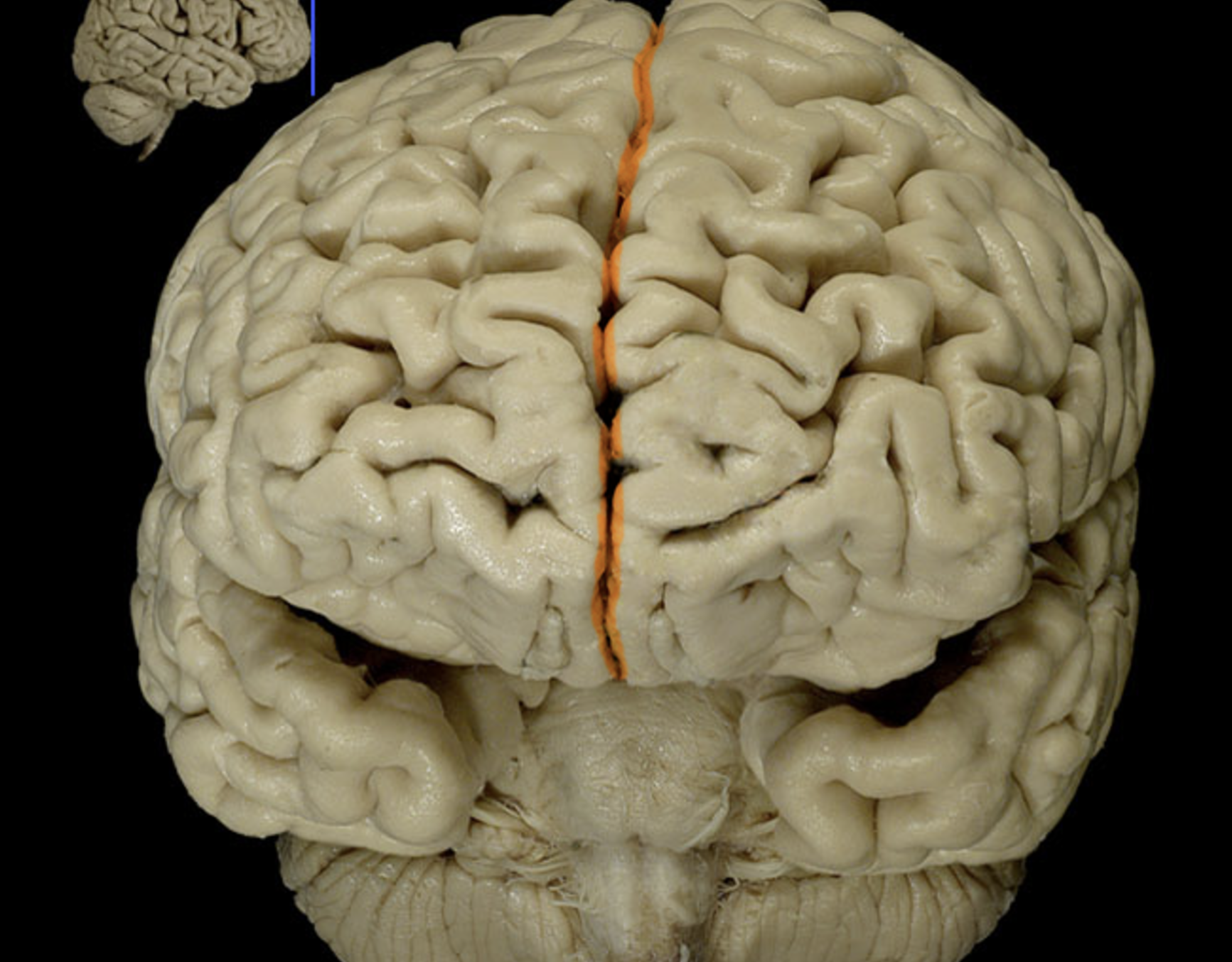
longitudinal fissure
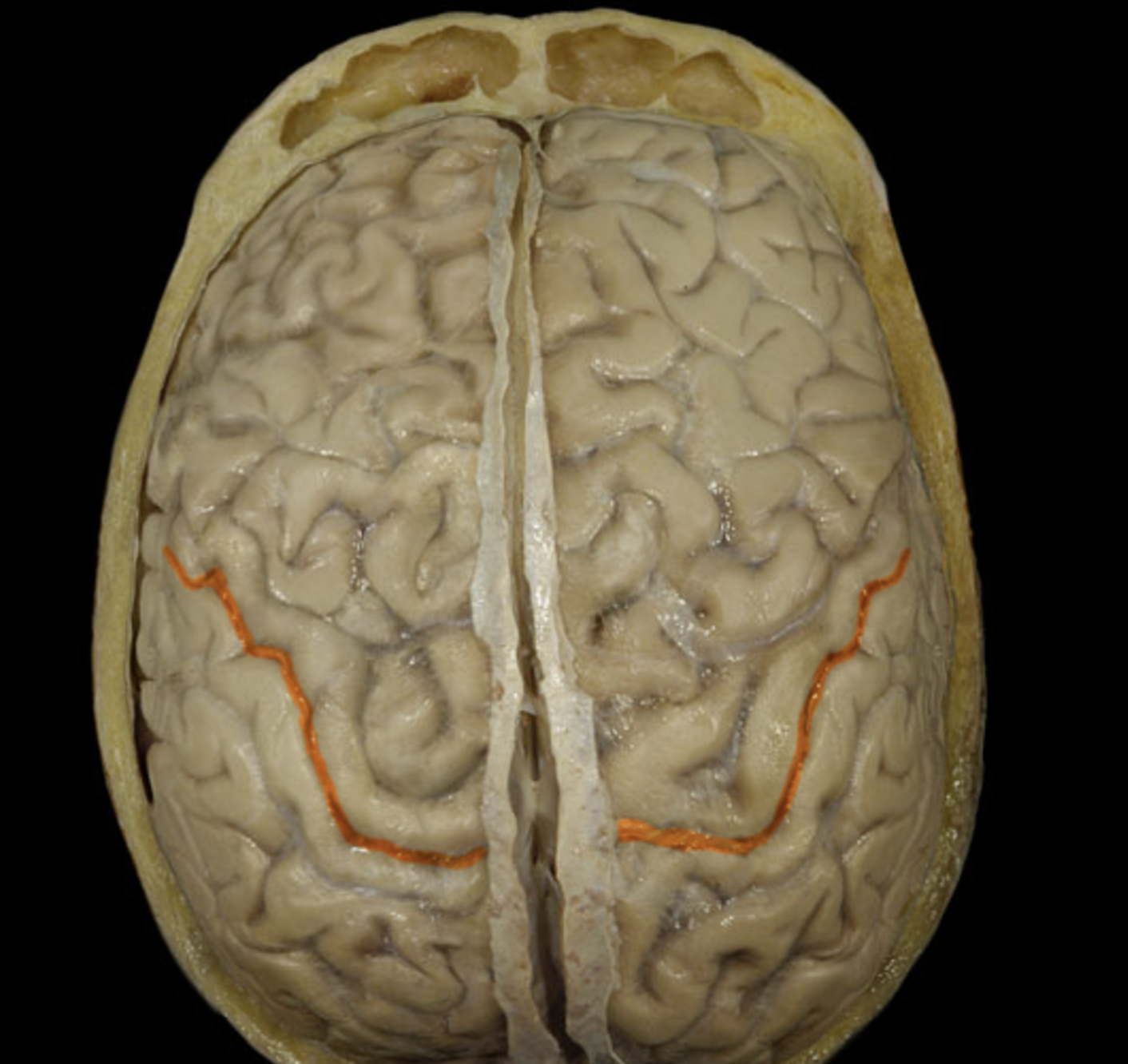
central sulcus
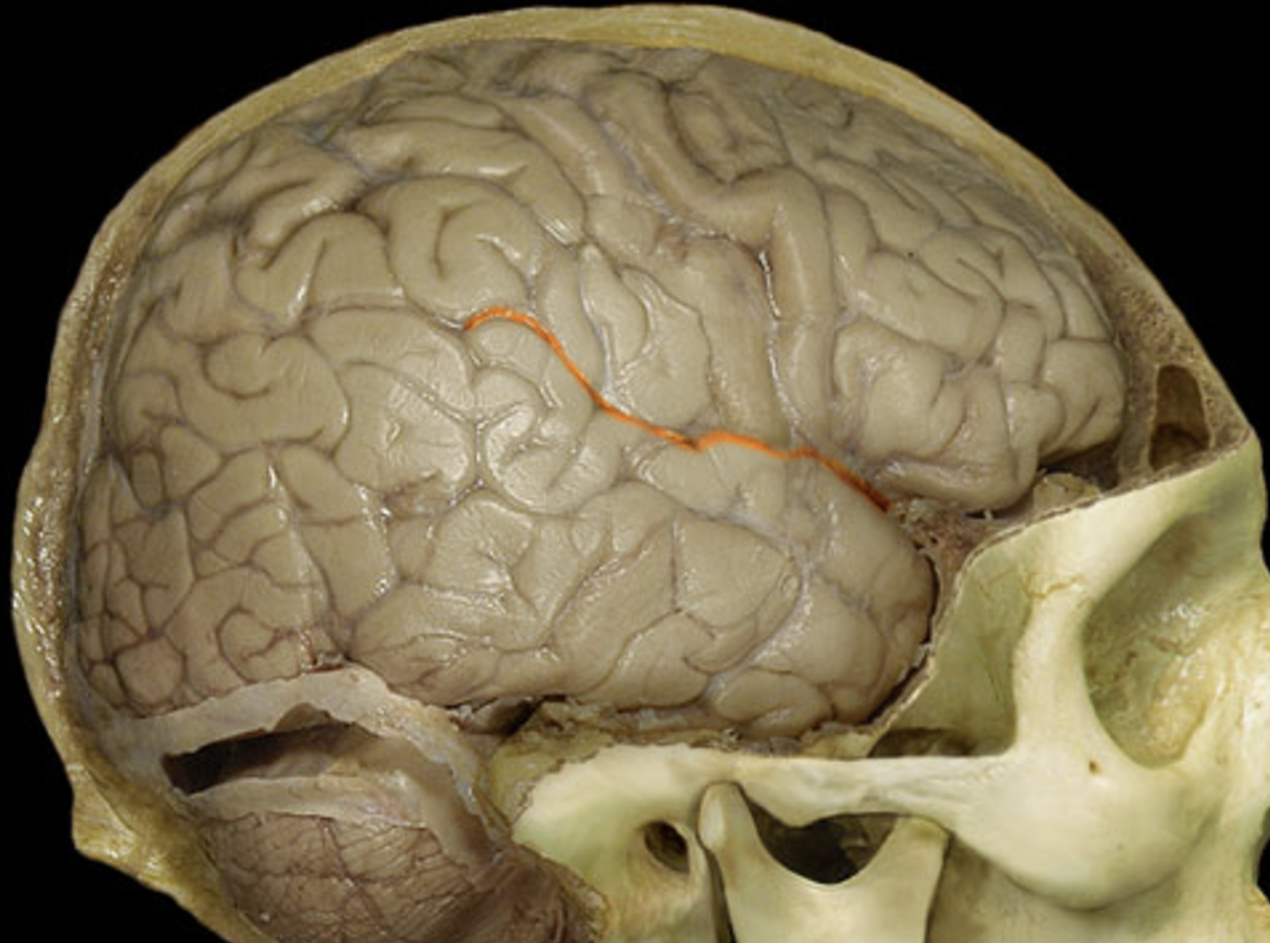
lateral sulcus
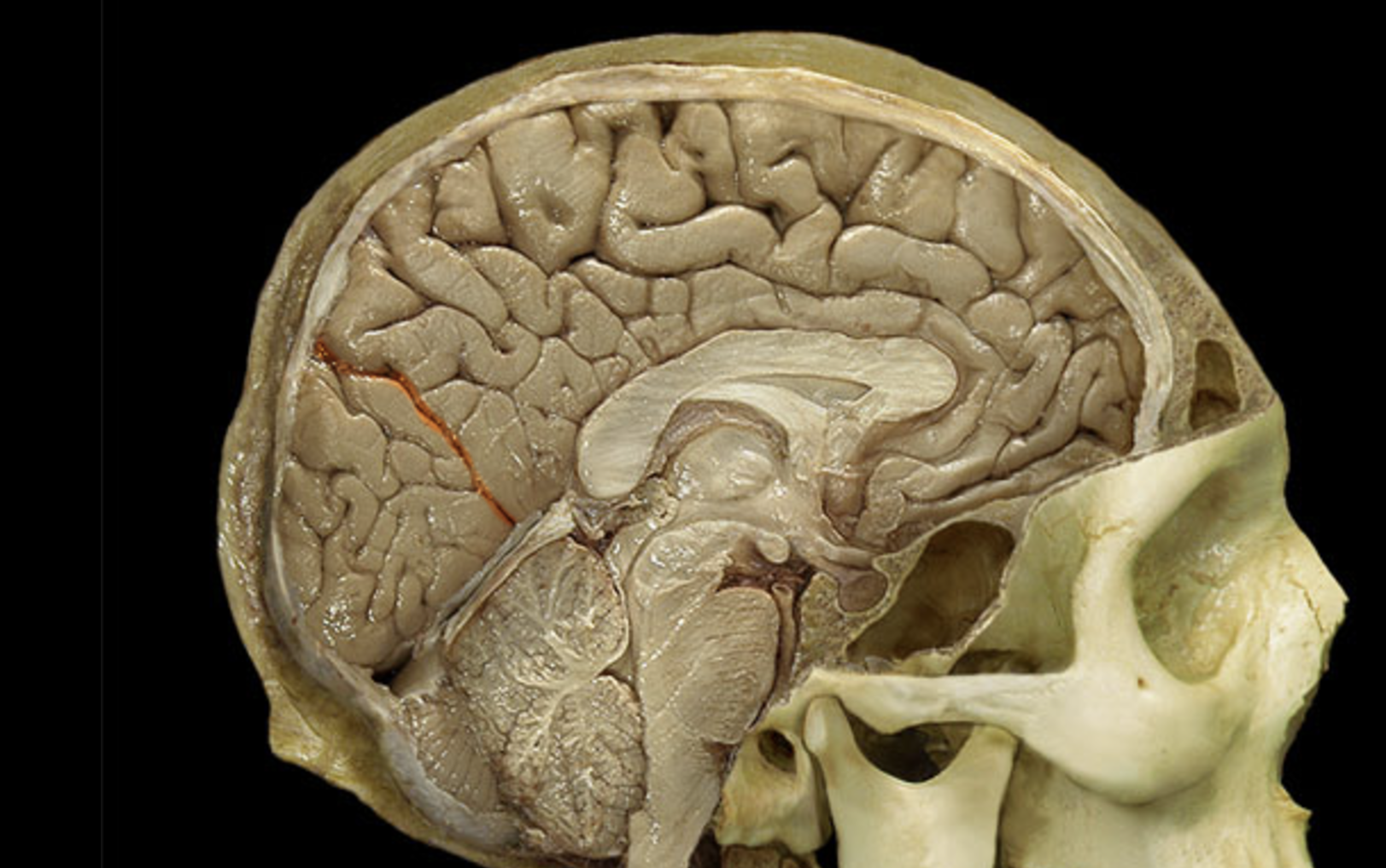
parieto-occipital sulcus
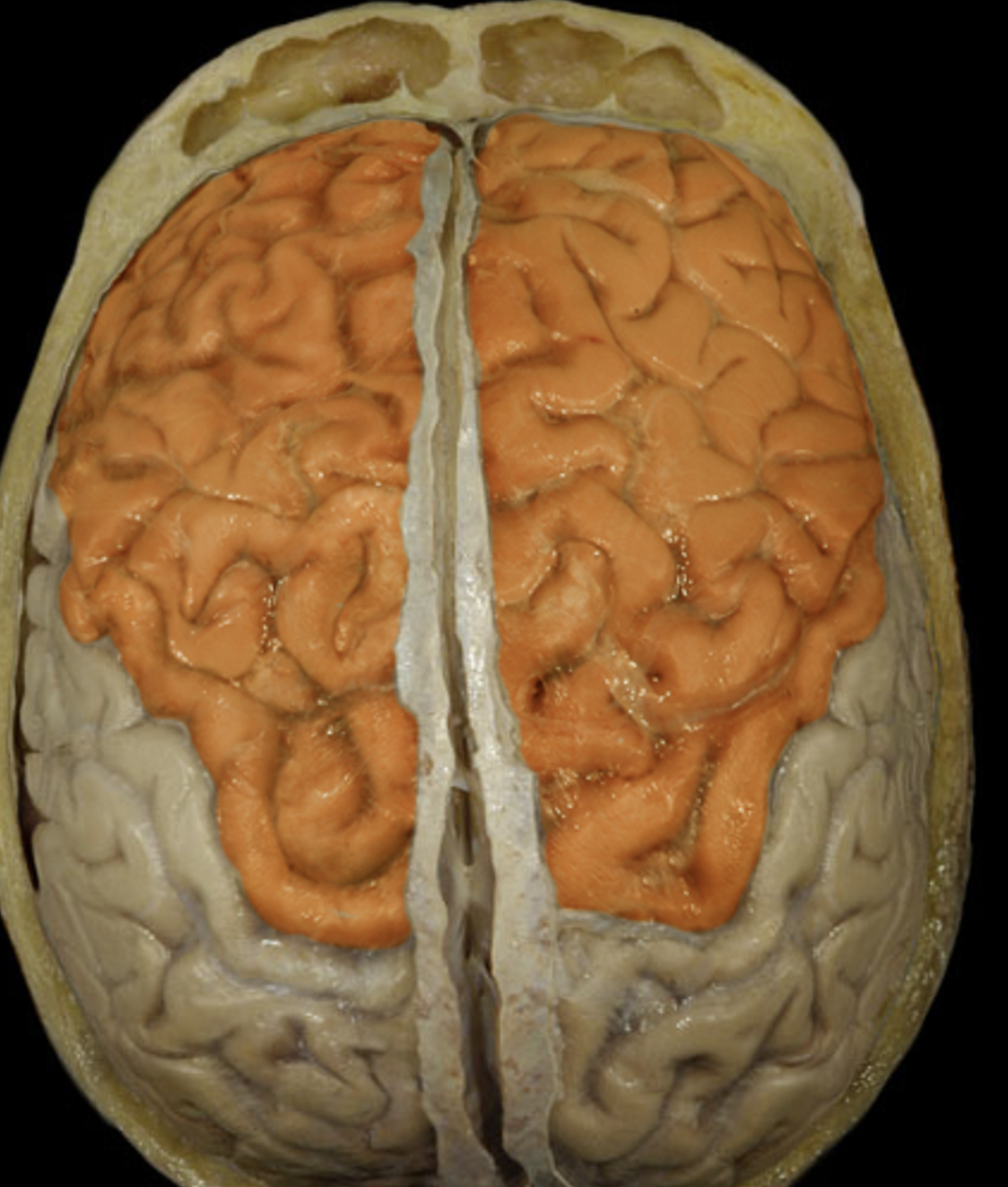
frontal lobe
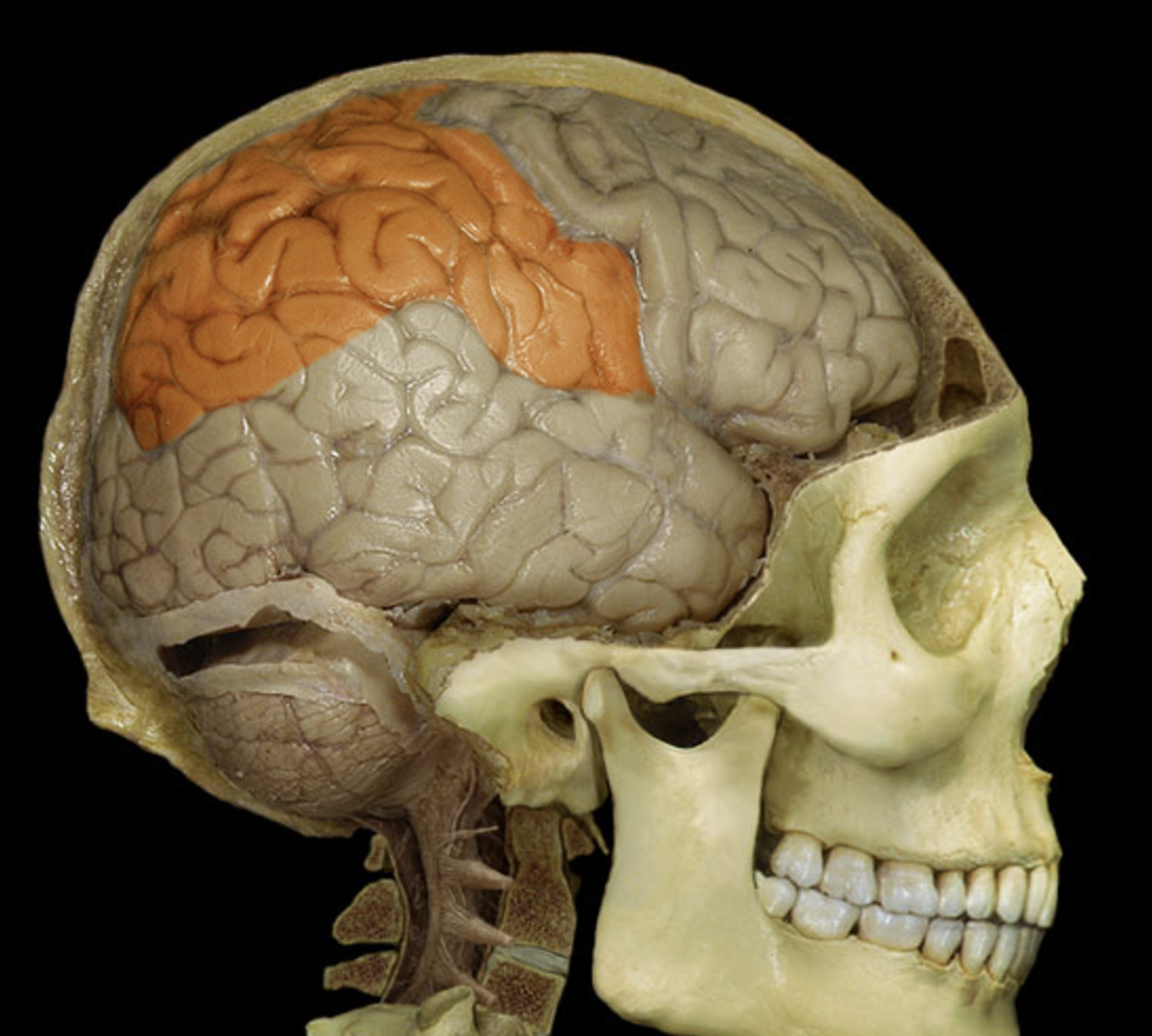
parietal lobe
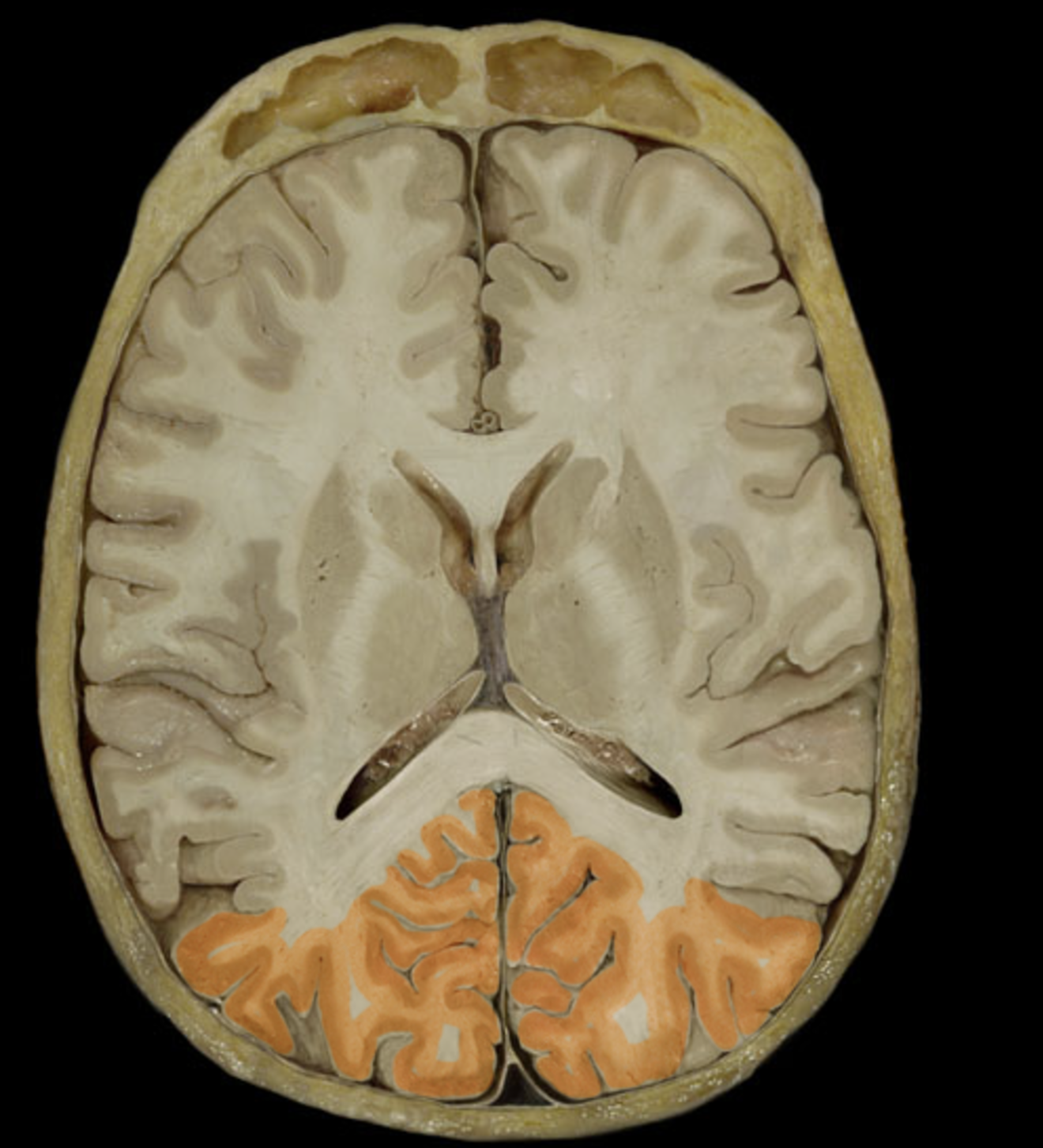
occipital lobe
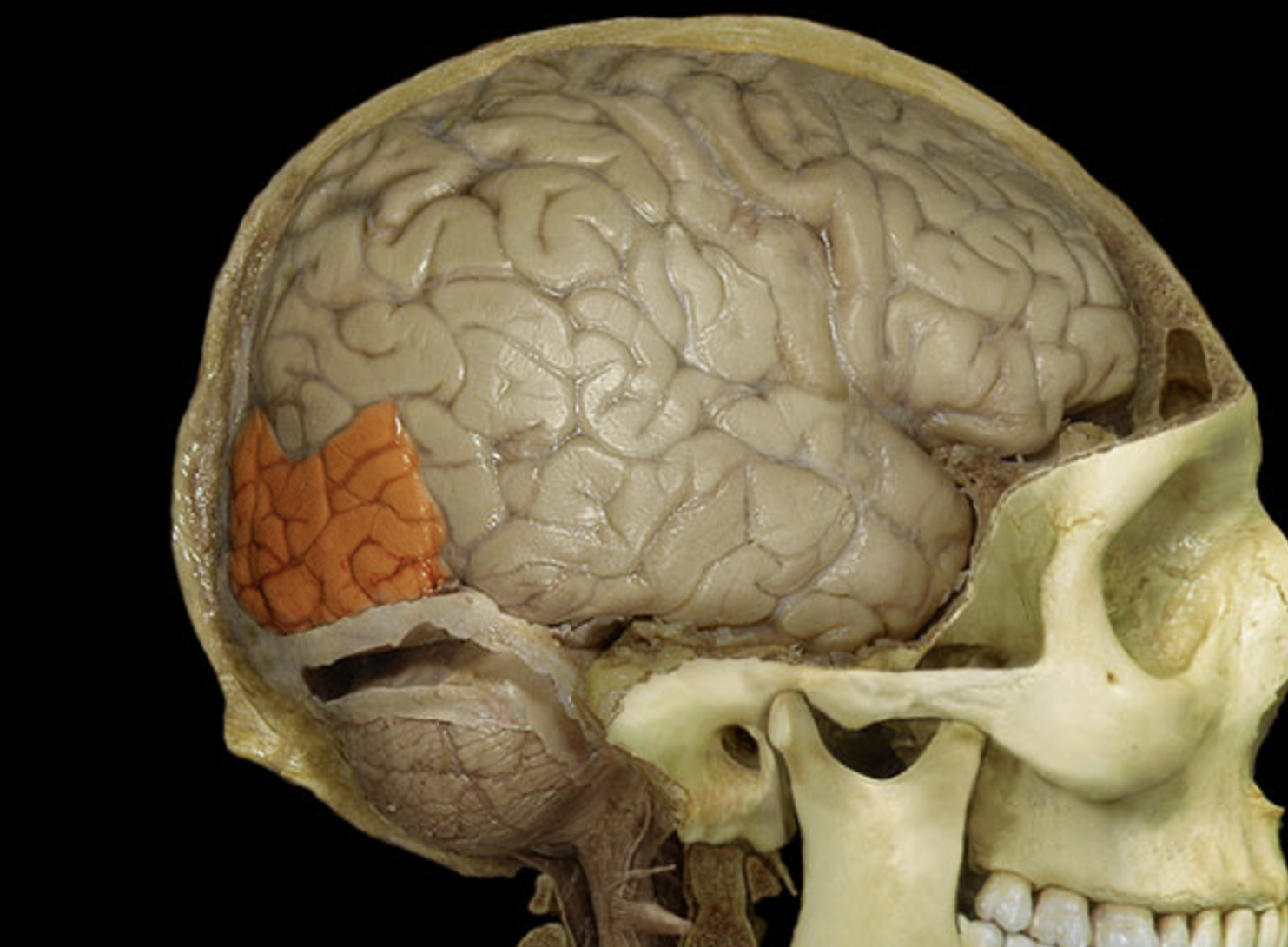
occipital lobe
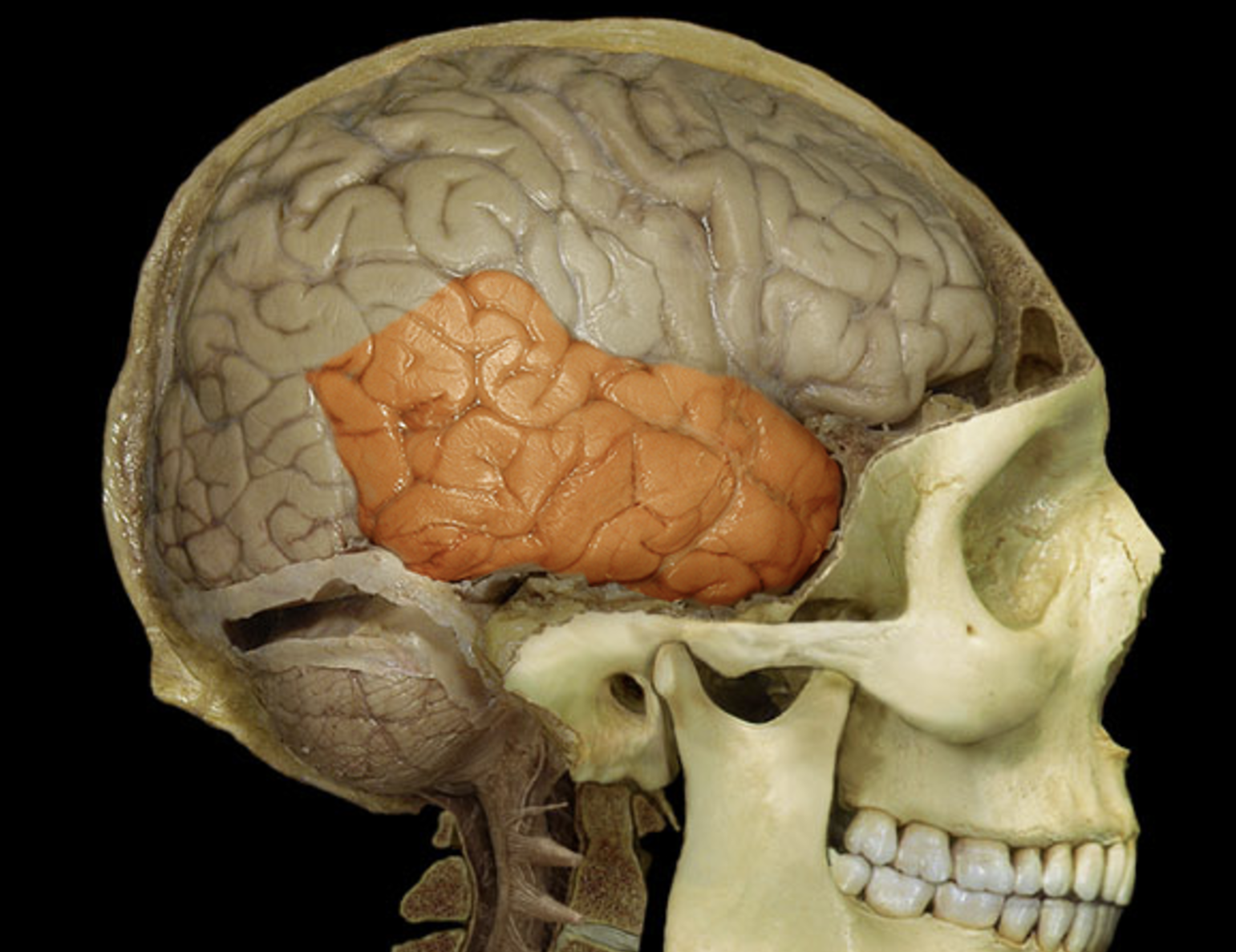
temporal lobe
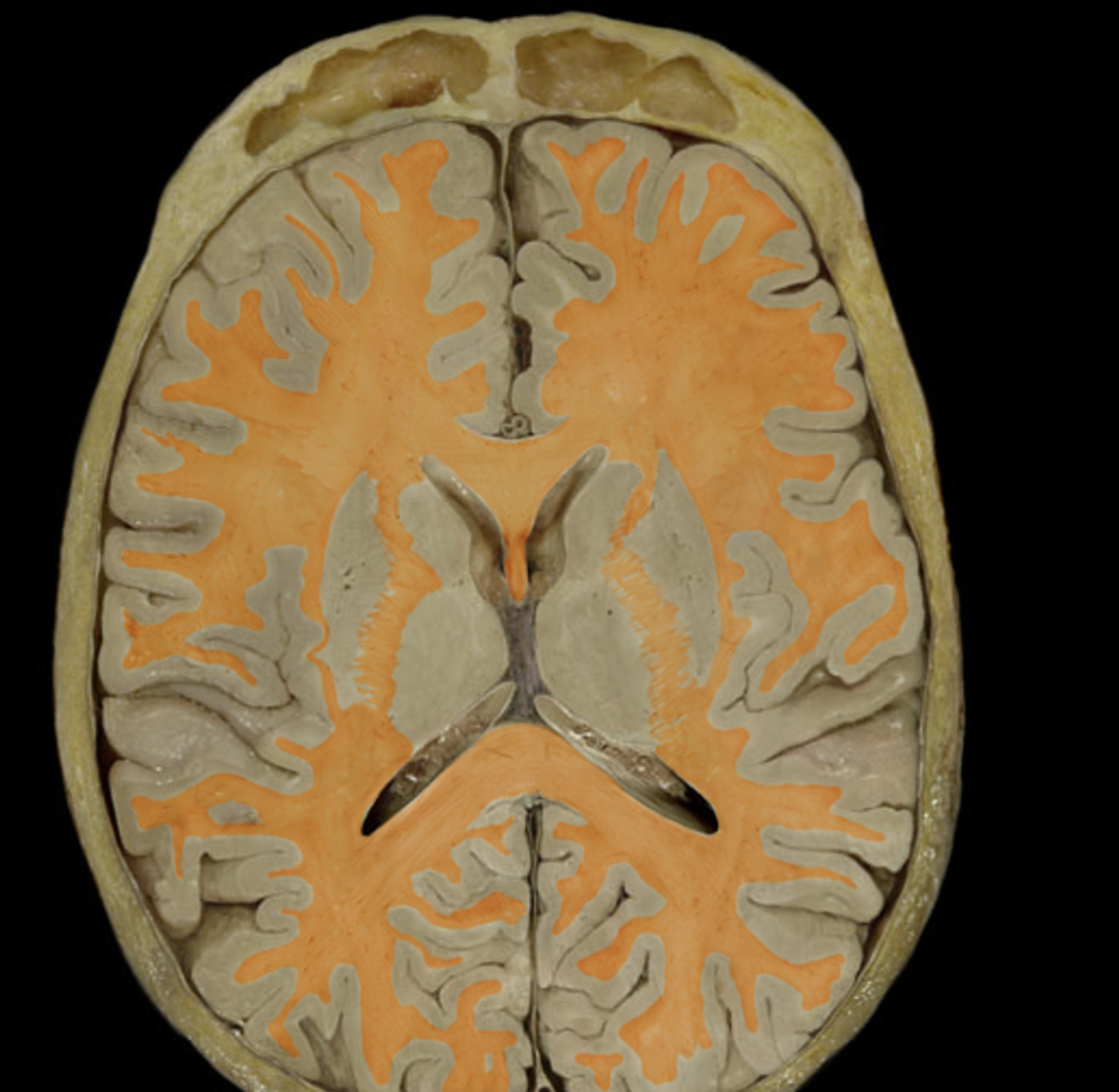
white matter
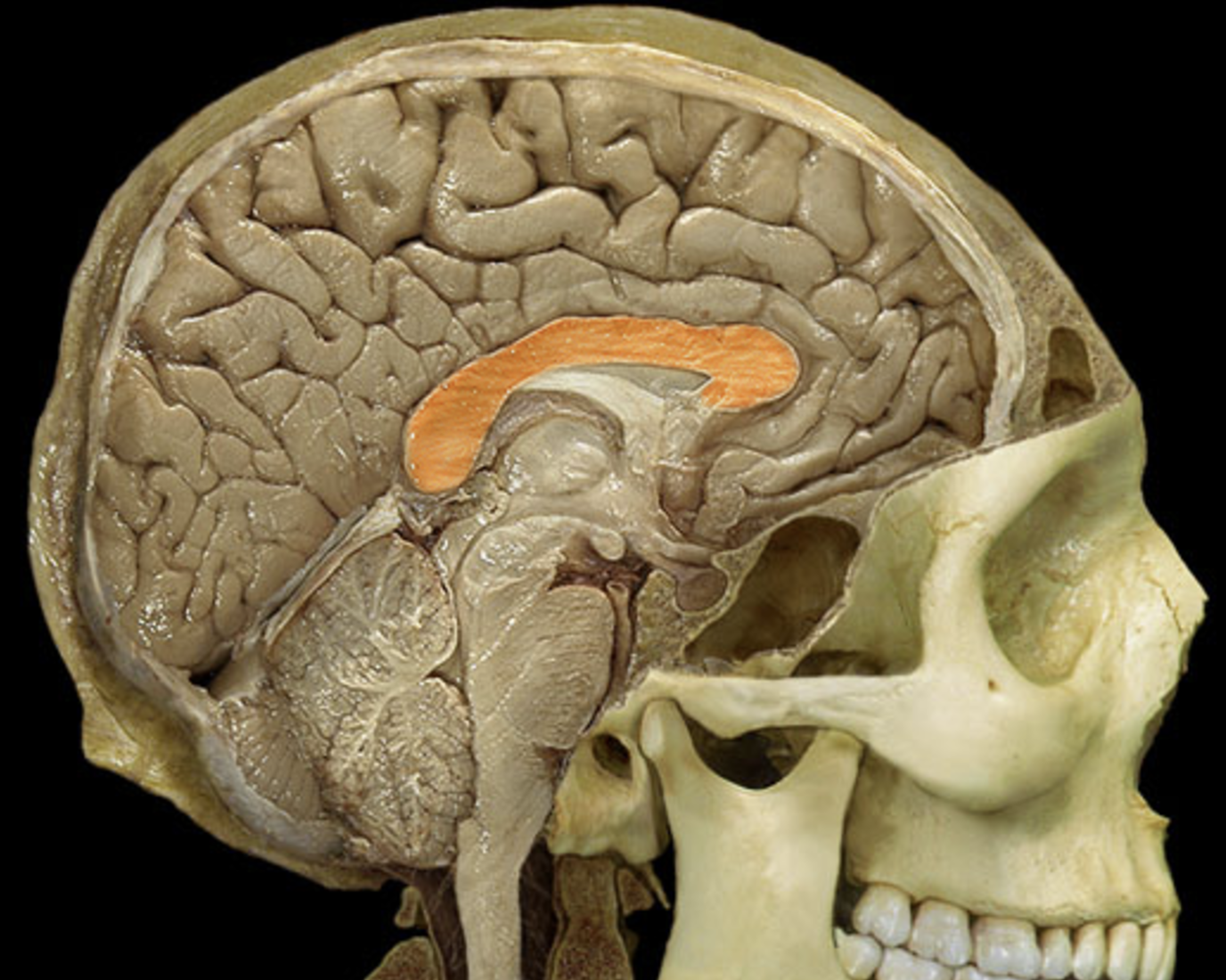
corpus callosum
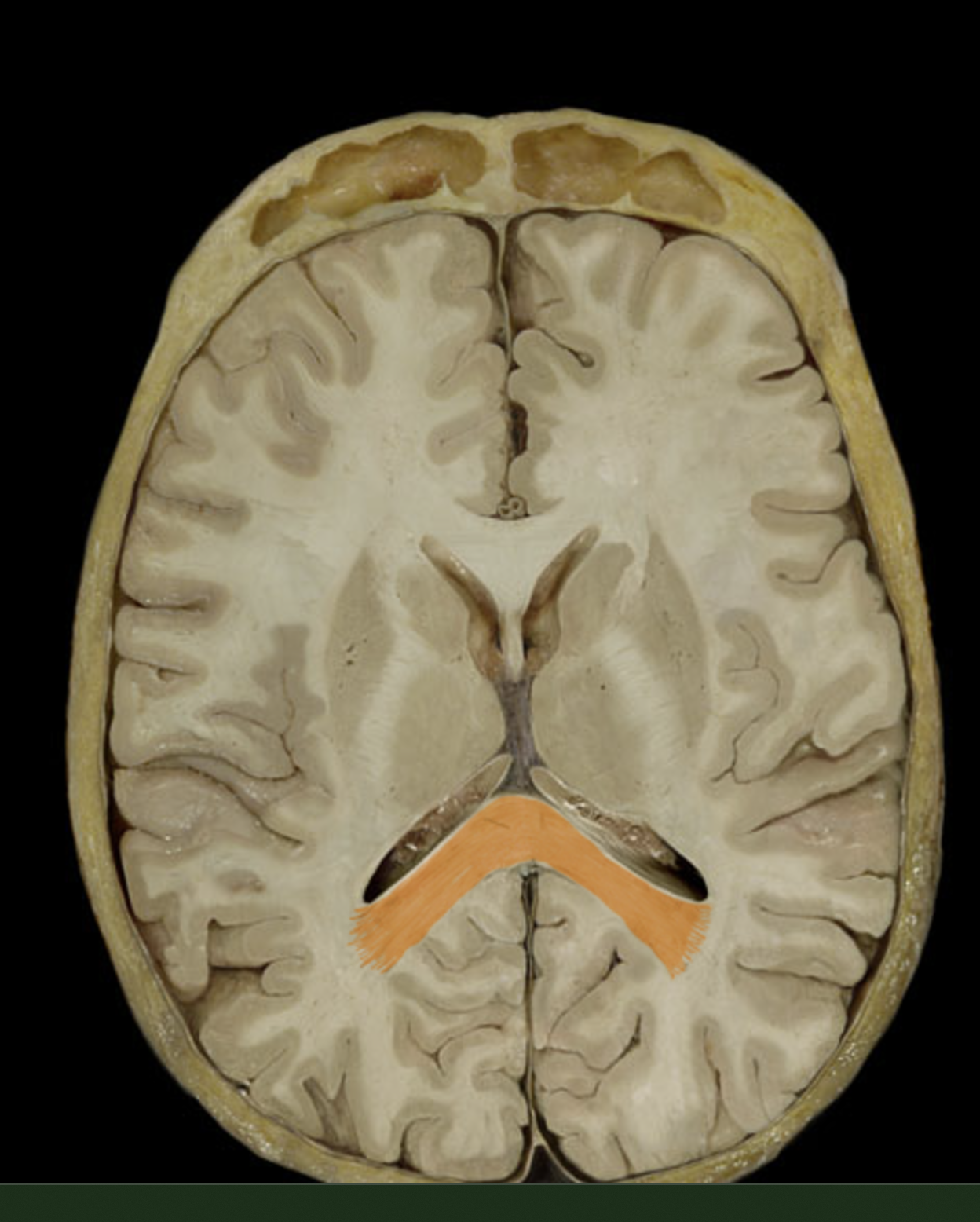
corpus callosum
gray matter
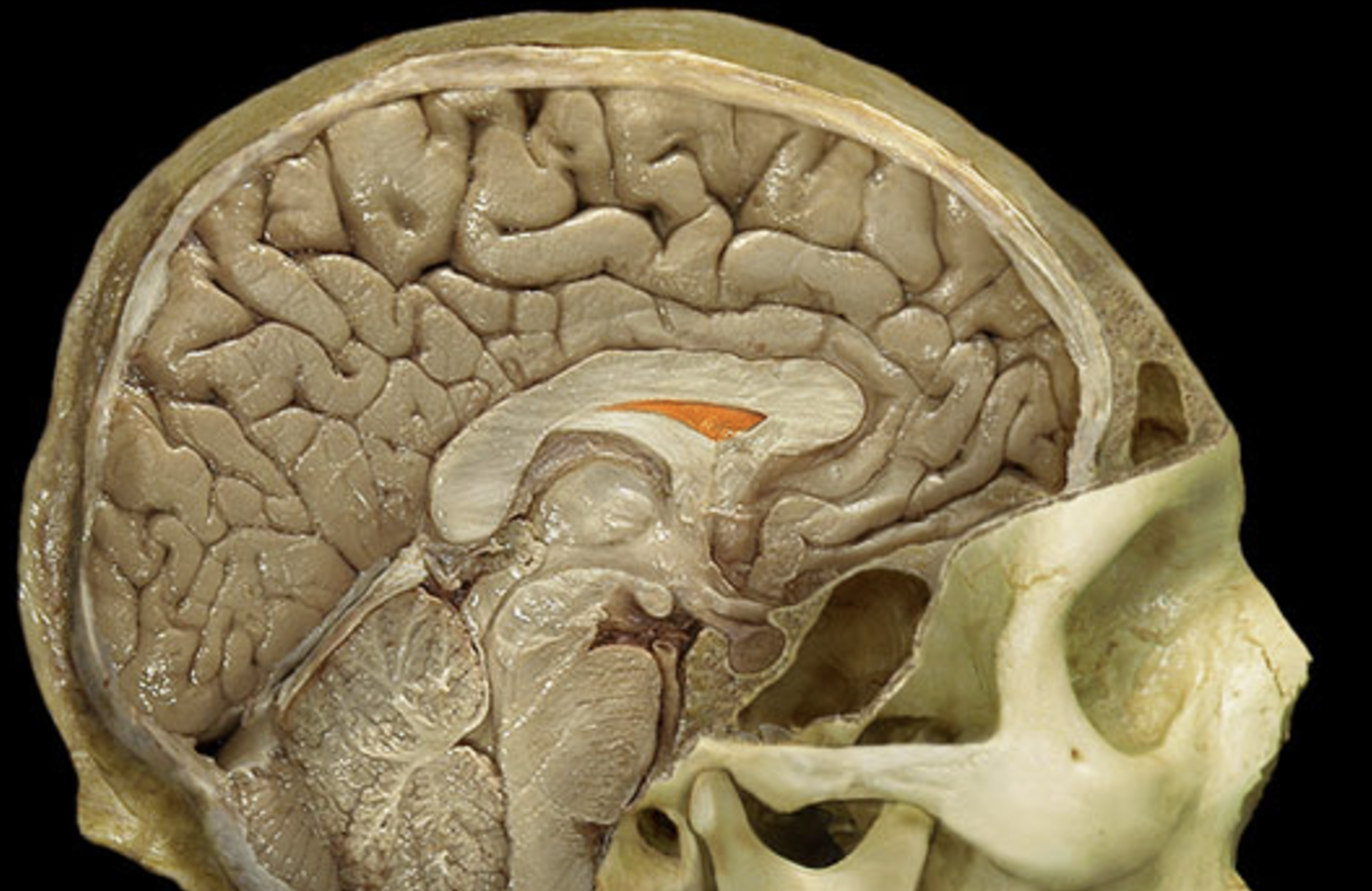
septum pellucidum
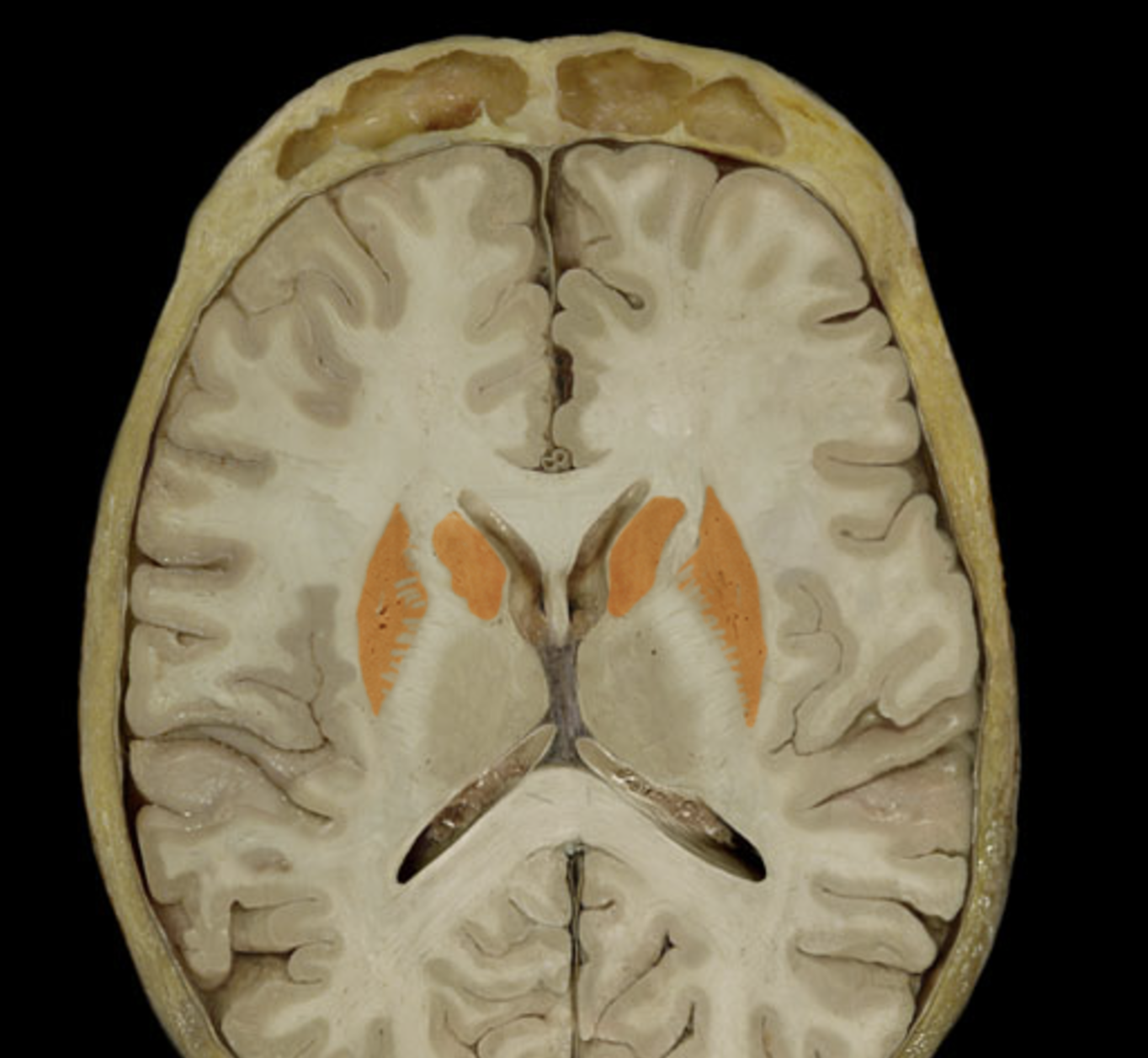
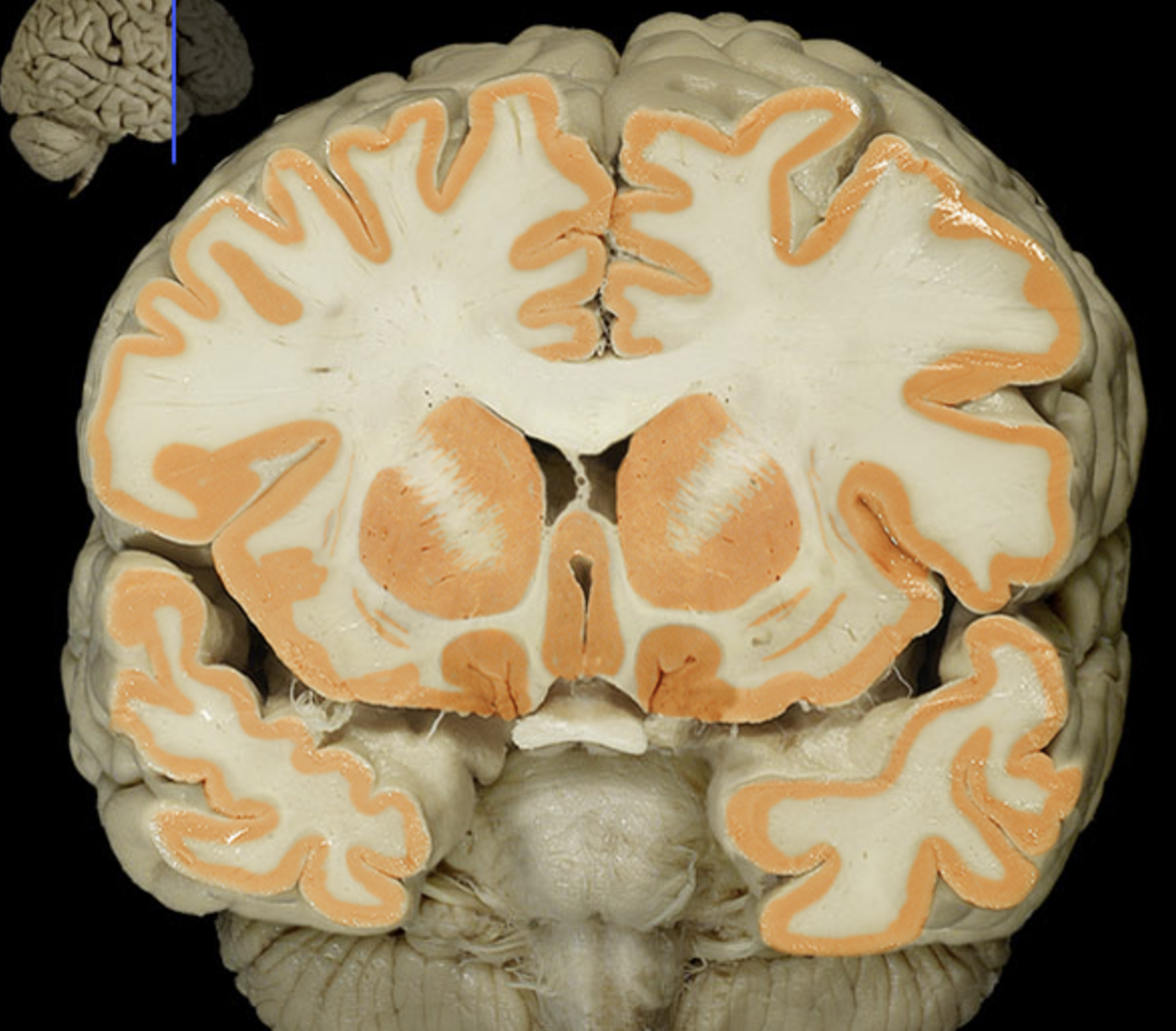
basal nuclei
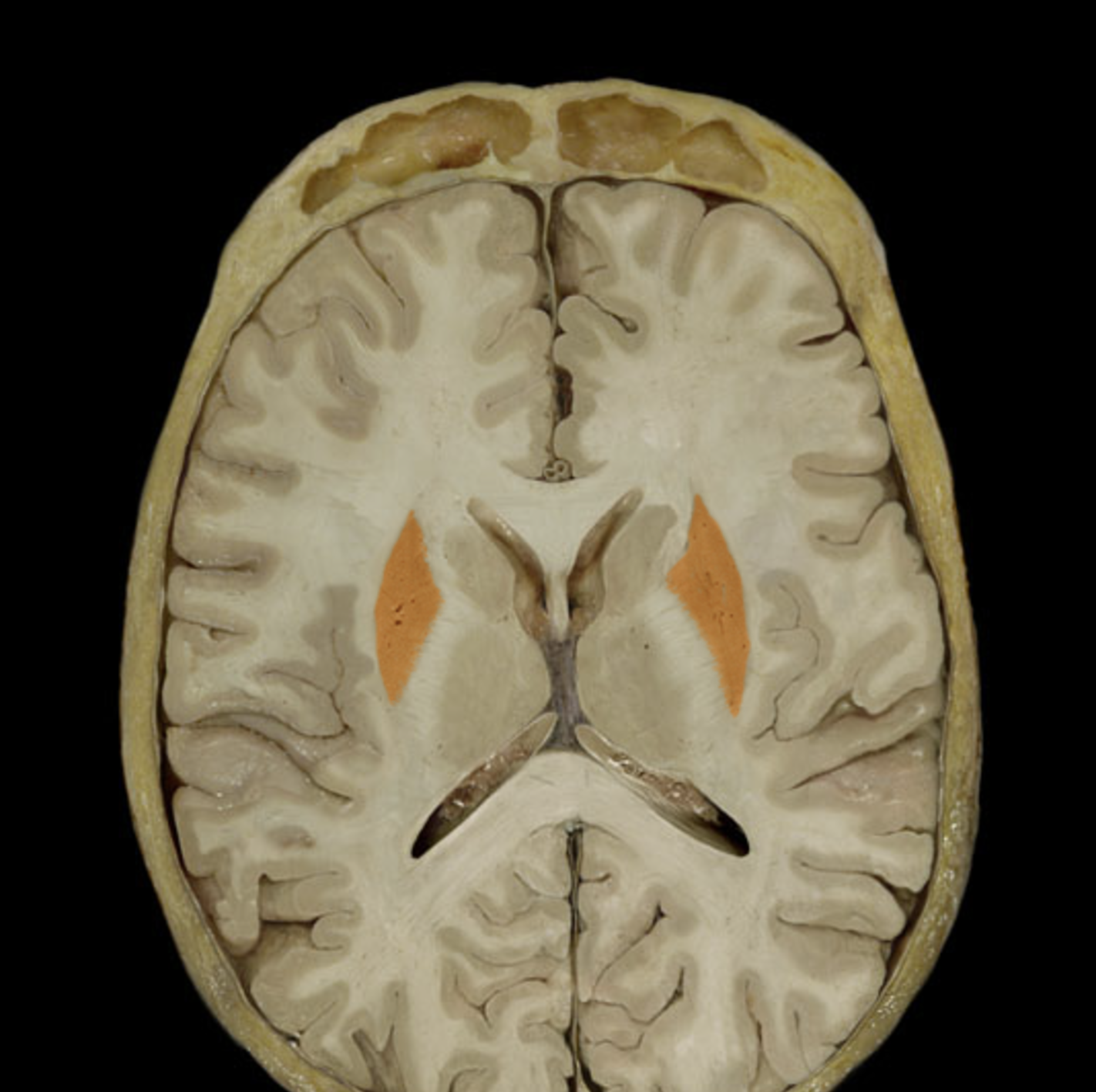
lenticular nucleus
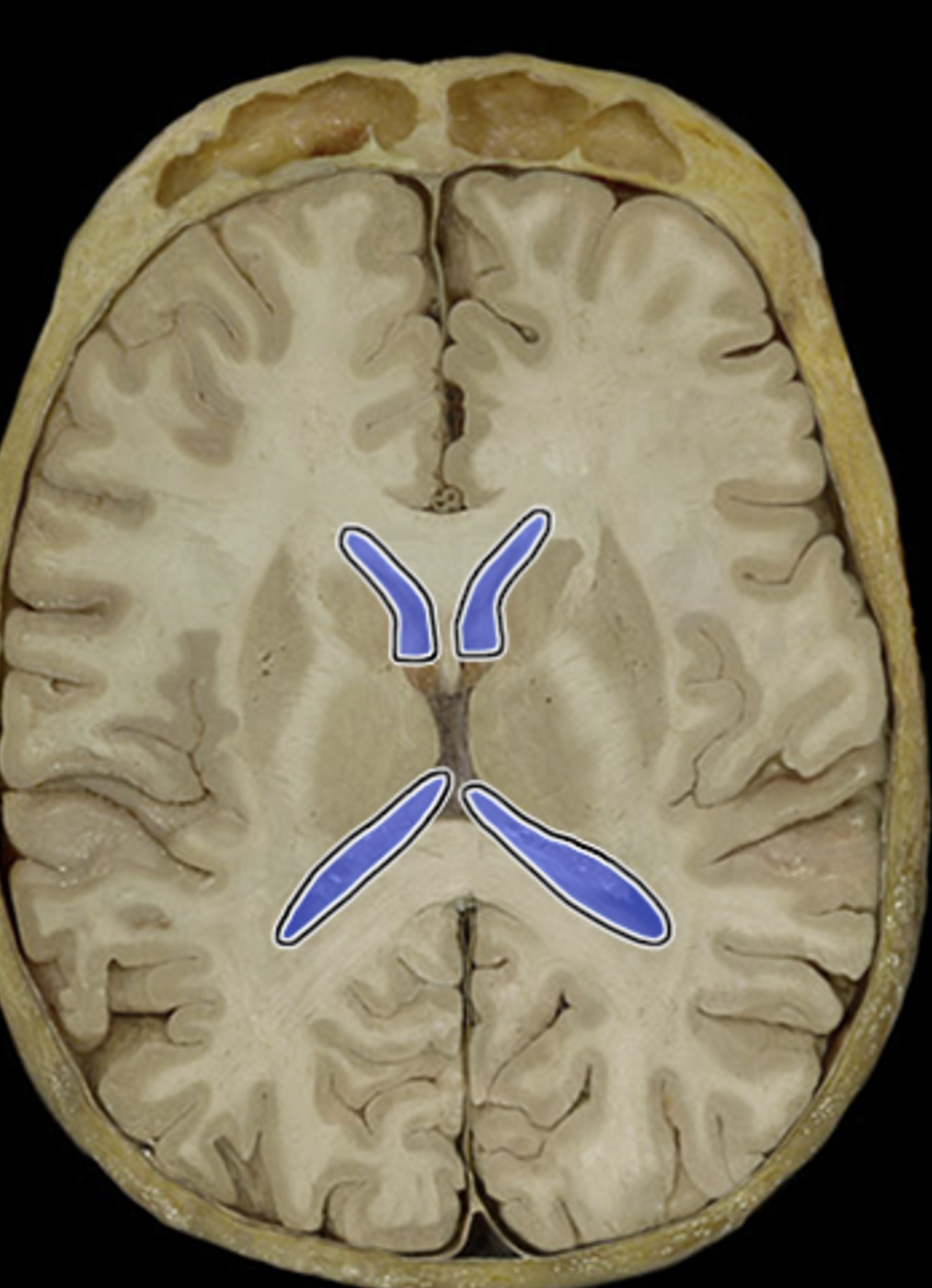
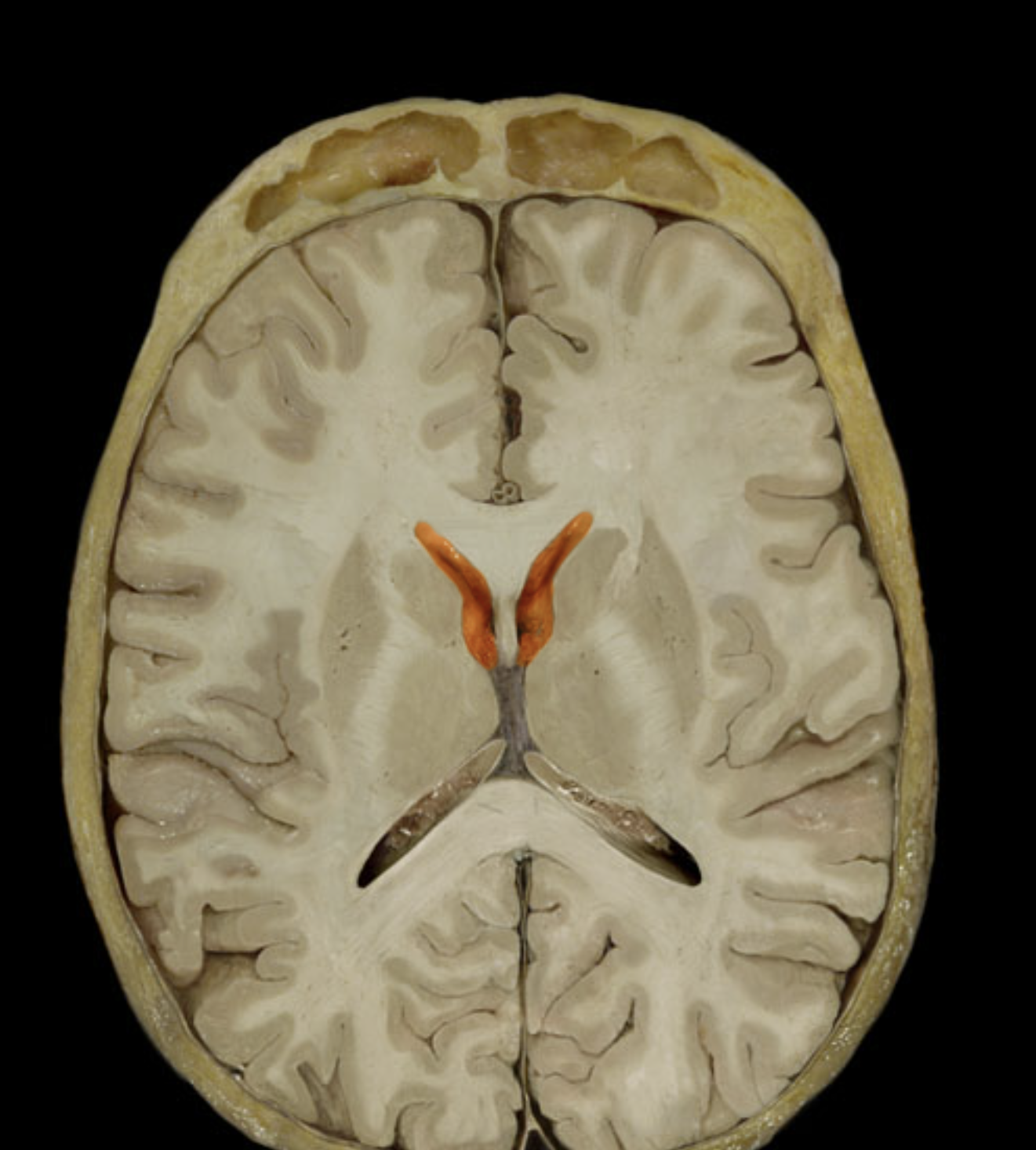
lateral ventricle
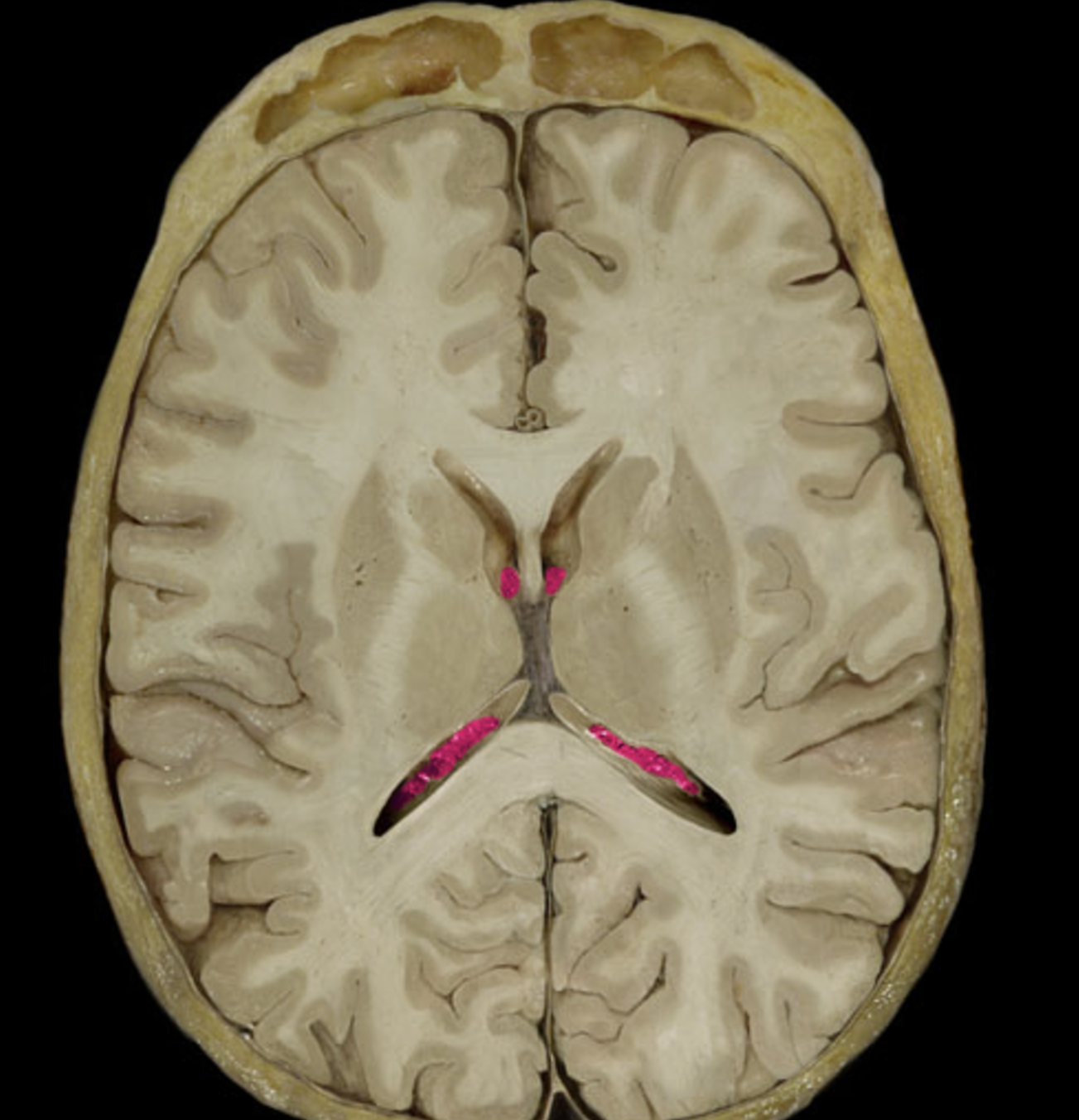
choroid plexuses
interventricular foramen
third ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
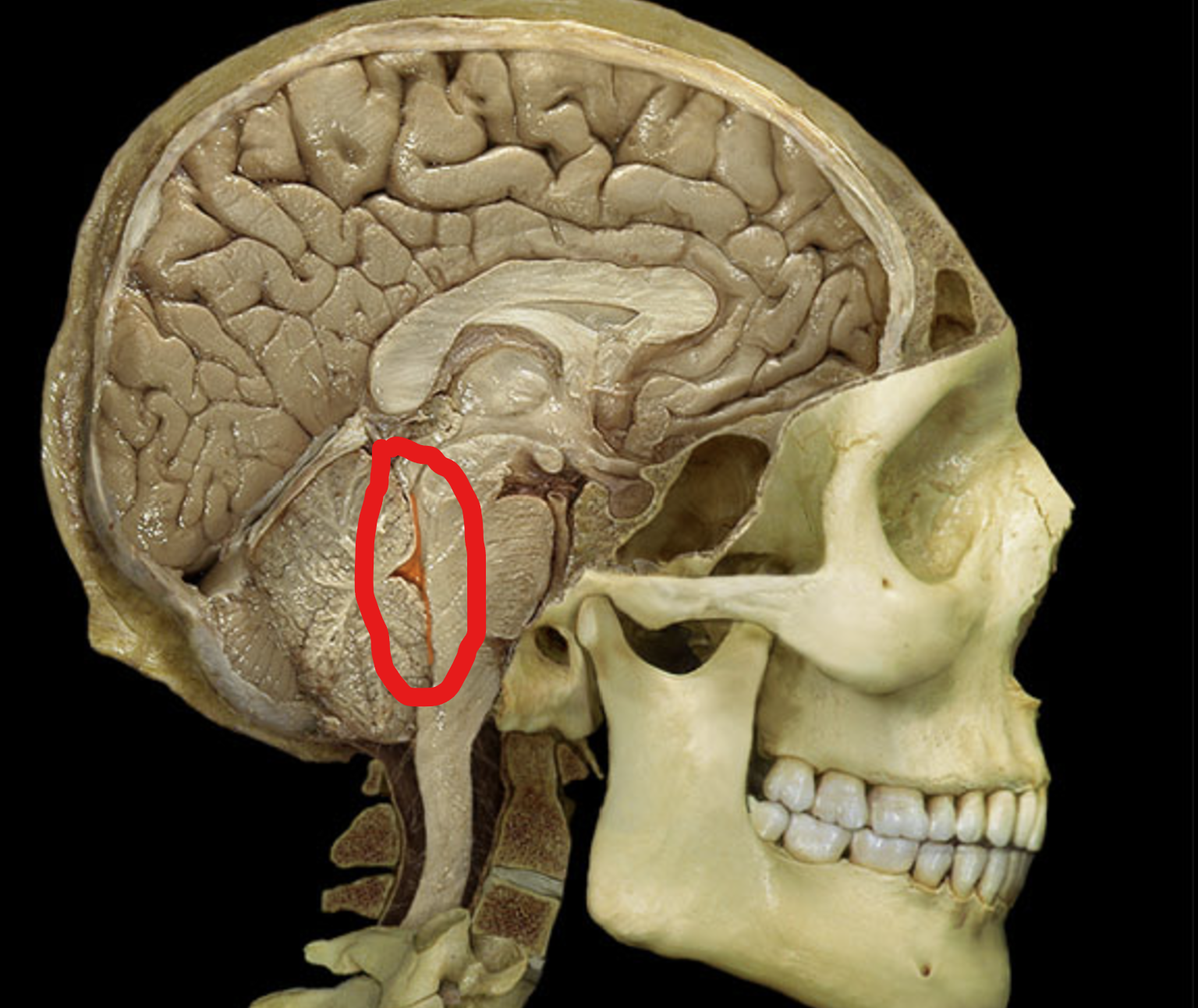
fourth ventricle
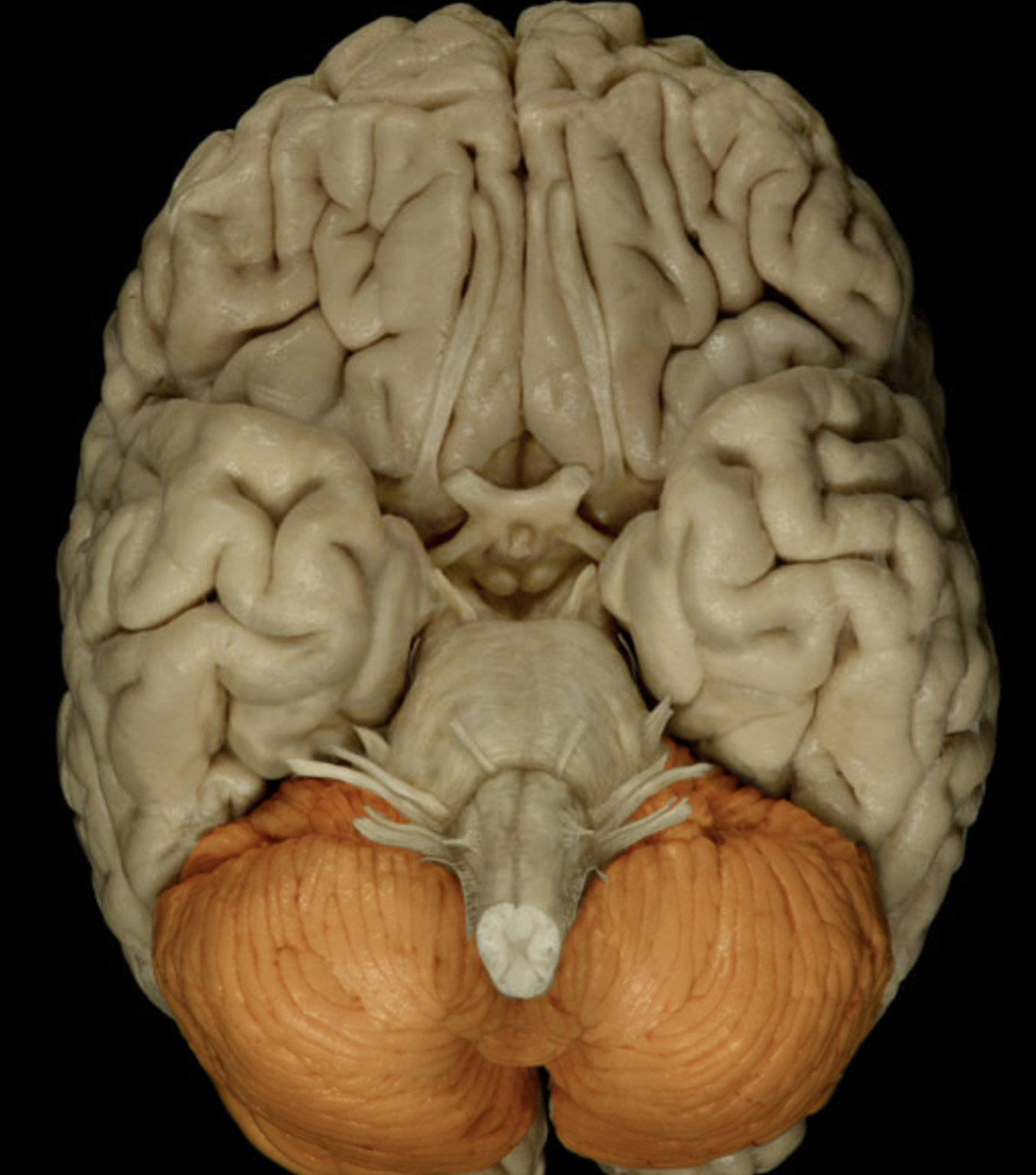
cerebellum
What is the vermis?
connects the hemispheres of the cerebellum
What are folia?
the folds on the cerebellum (the grooves are called sulci like the rest of the brain)
What is the epidural space?
the space in between the spine and the dural sheath, filled with blood vessles, adipose tissue, and loose connective tissue
What is the dural sheath?
loose fitting sleeve of dura matter around the spinal cord, iimm
What is the arachnoid membrane?
made of arachnoid matter,
What is the subarachnoid space?
the gap between the arachnoid membrane and the pia matter
What is pia matter?
the deepest layer of the spinal chord
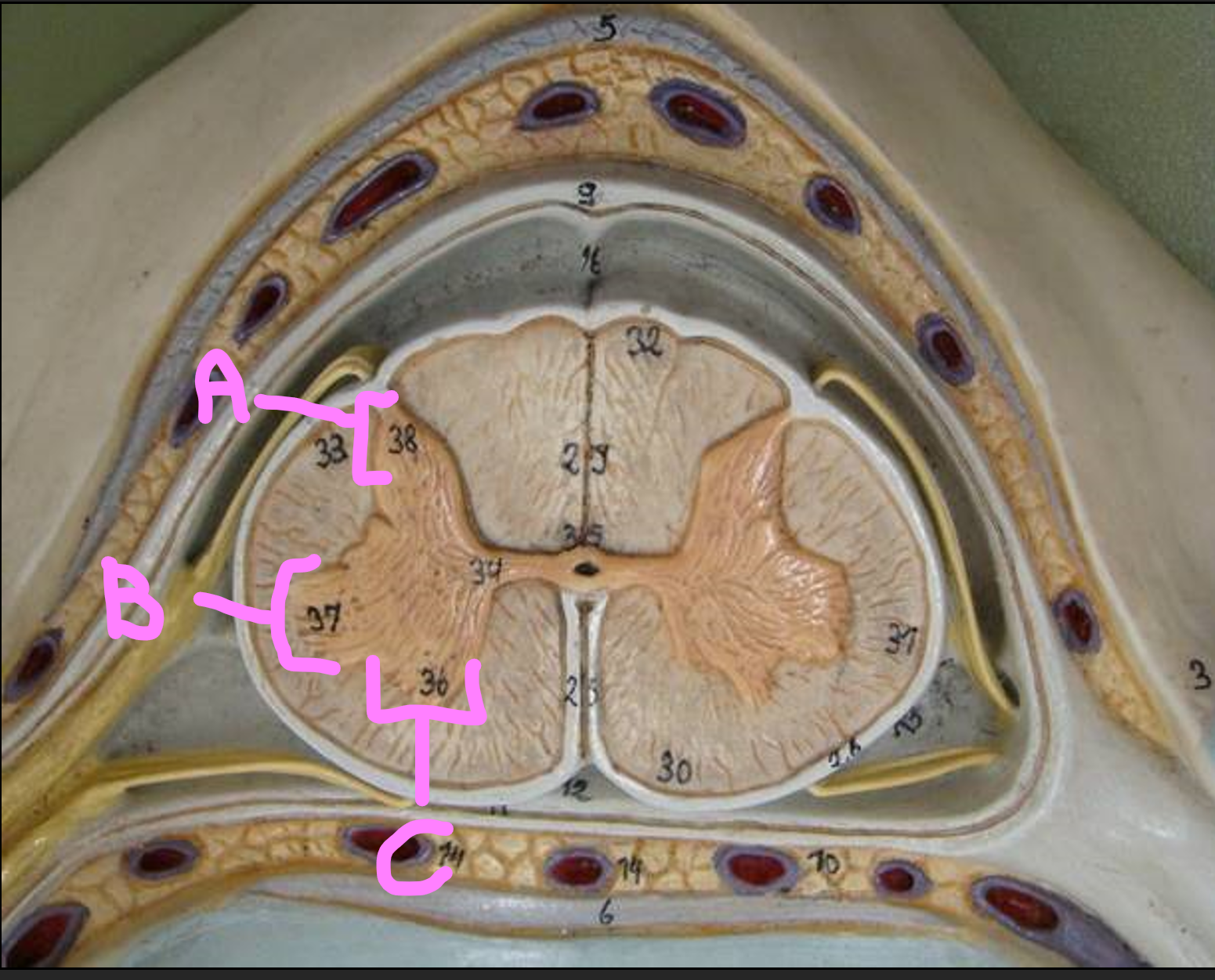
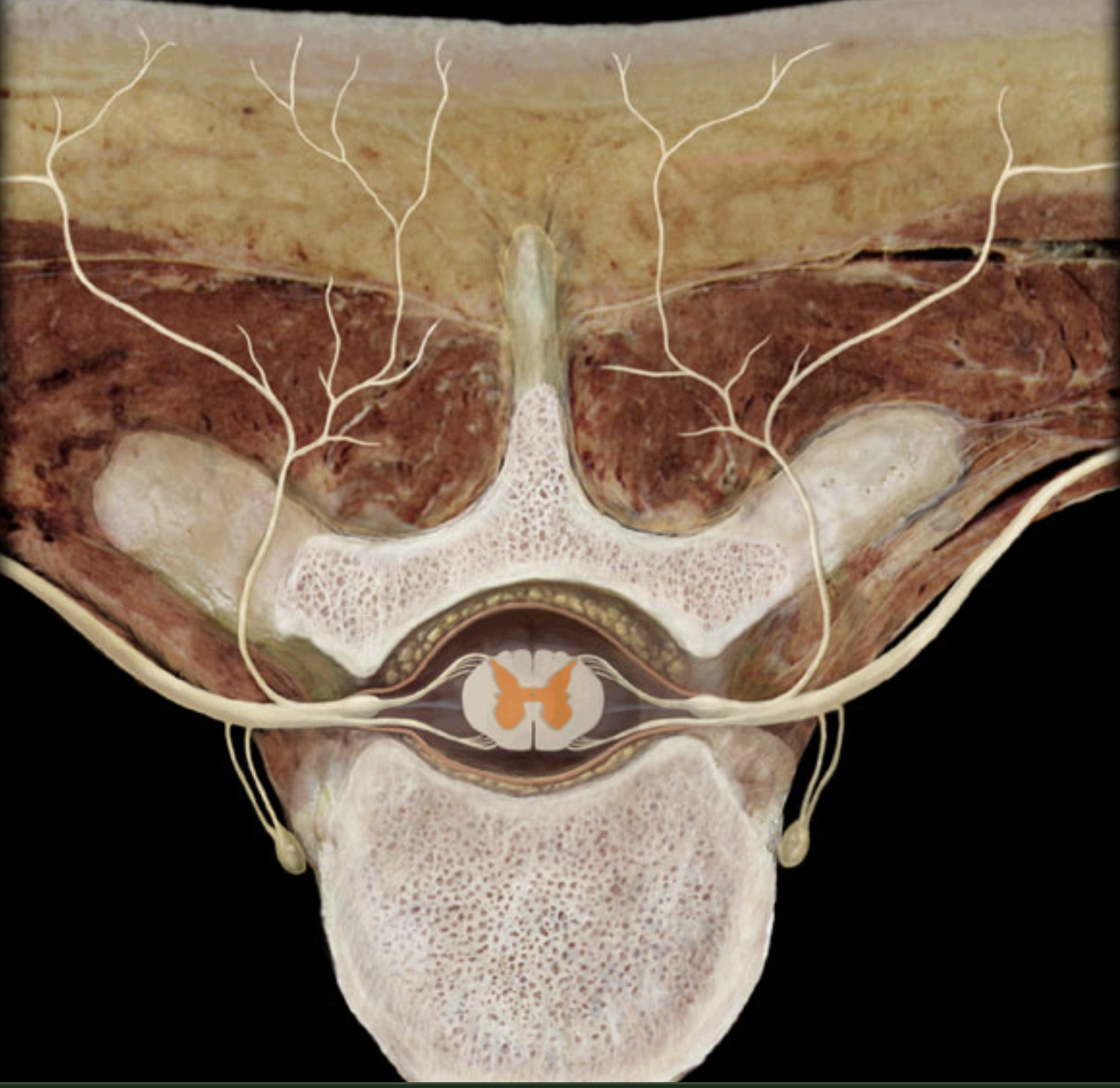
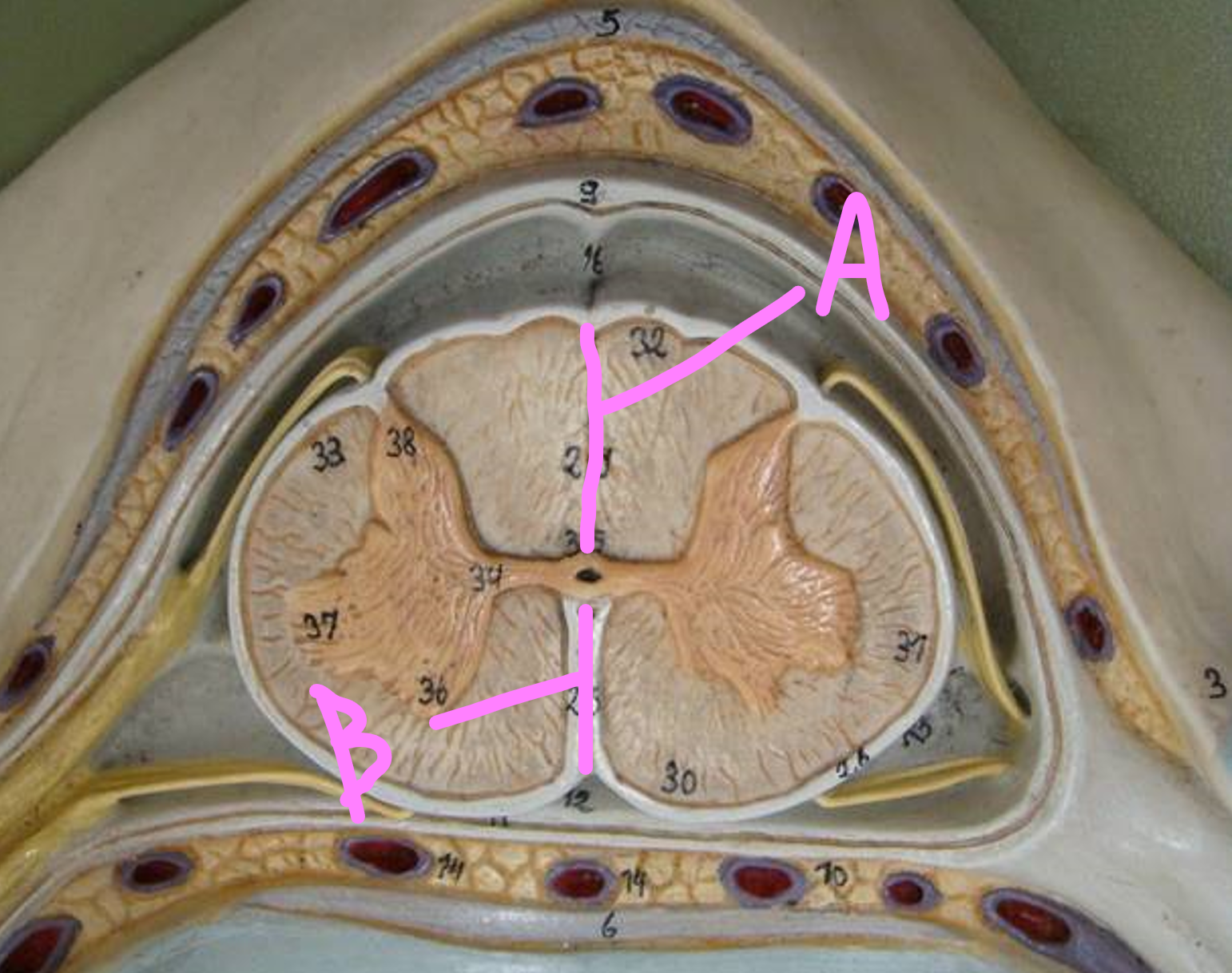
What is A?
posterior horn of gray matter
What is B?
lateral horn of gray matter
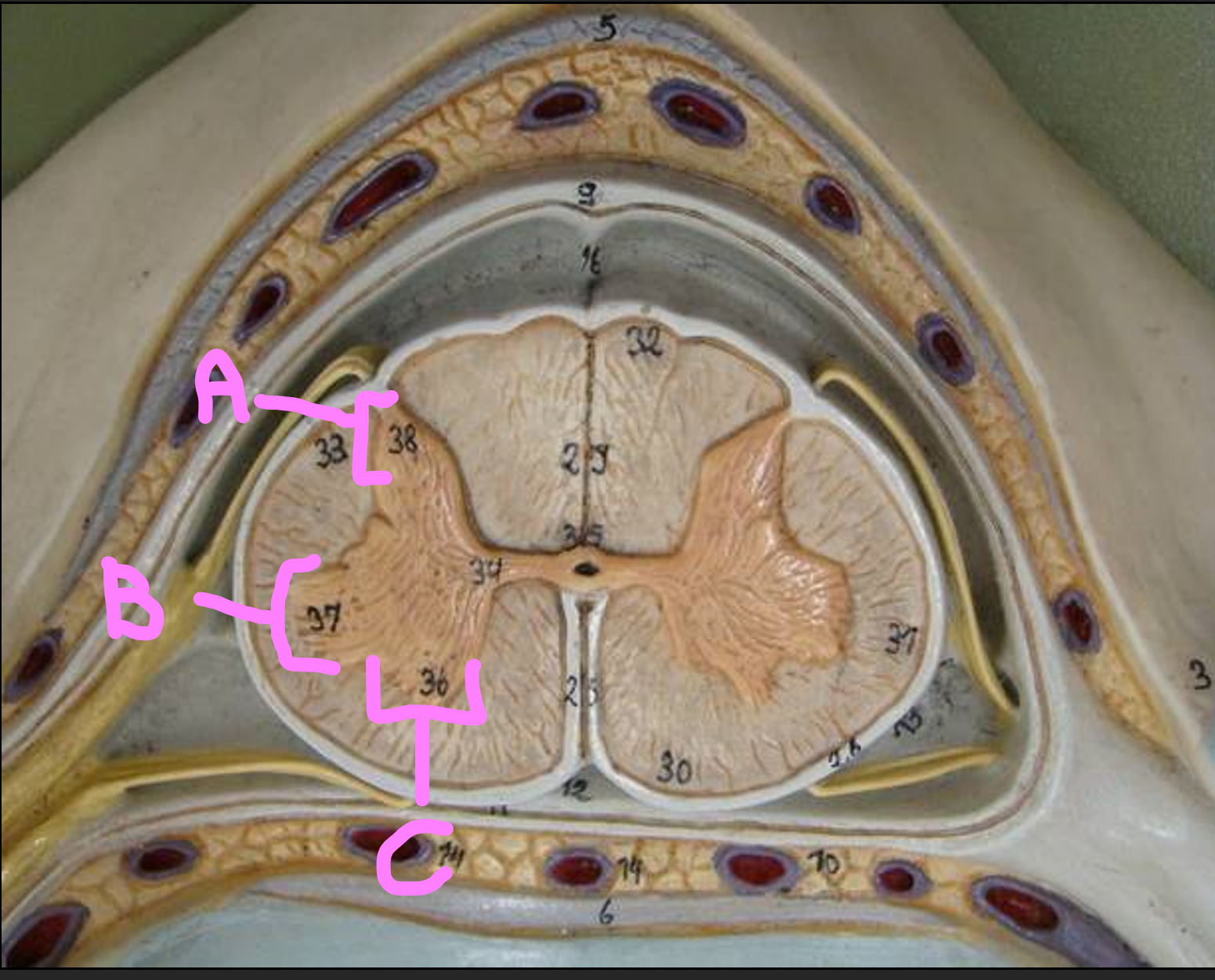
What is C?
anterior horn of gray matter
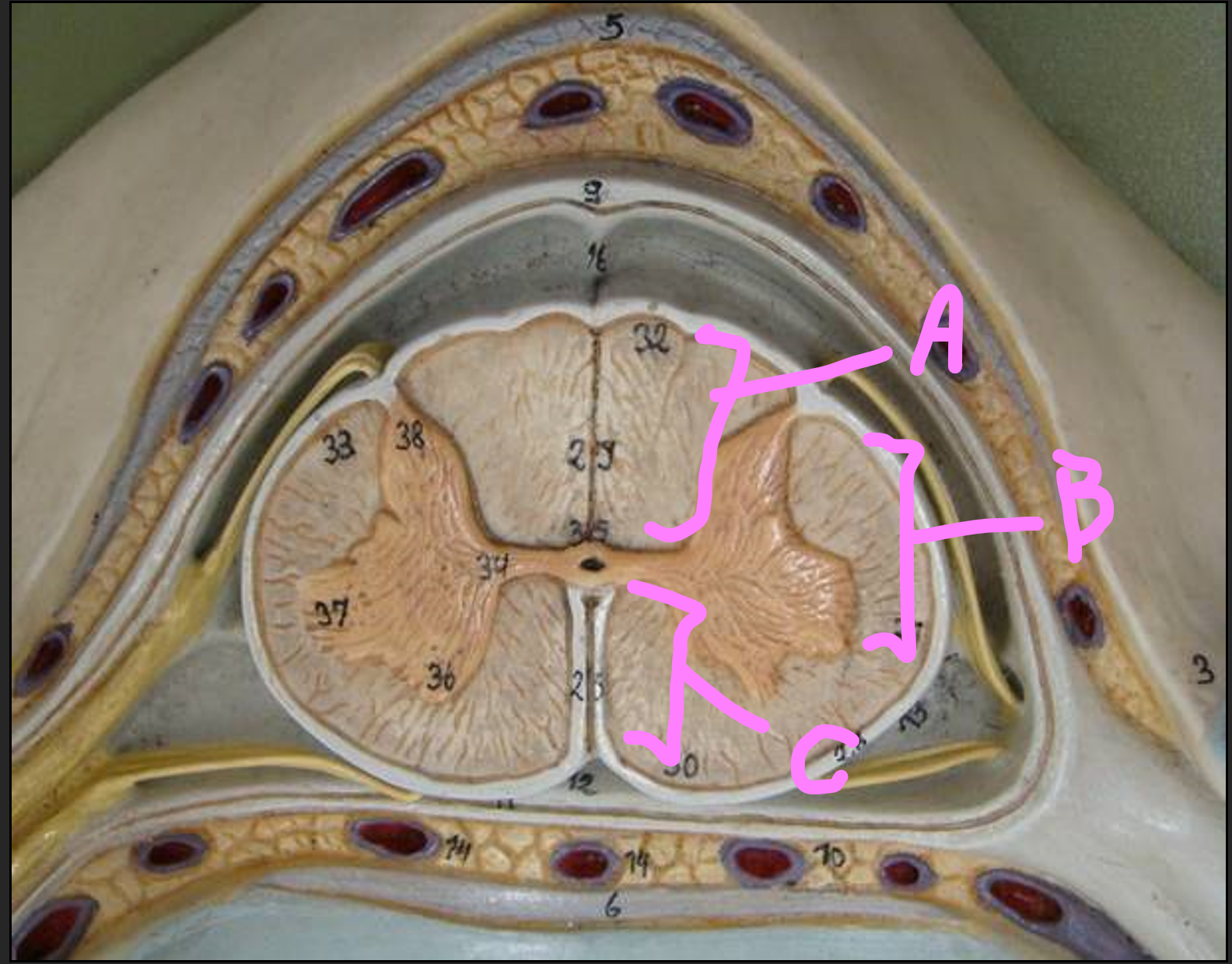
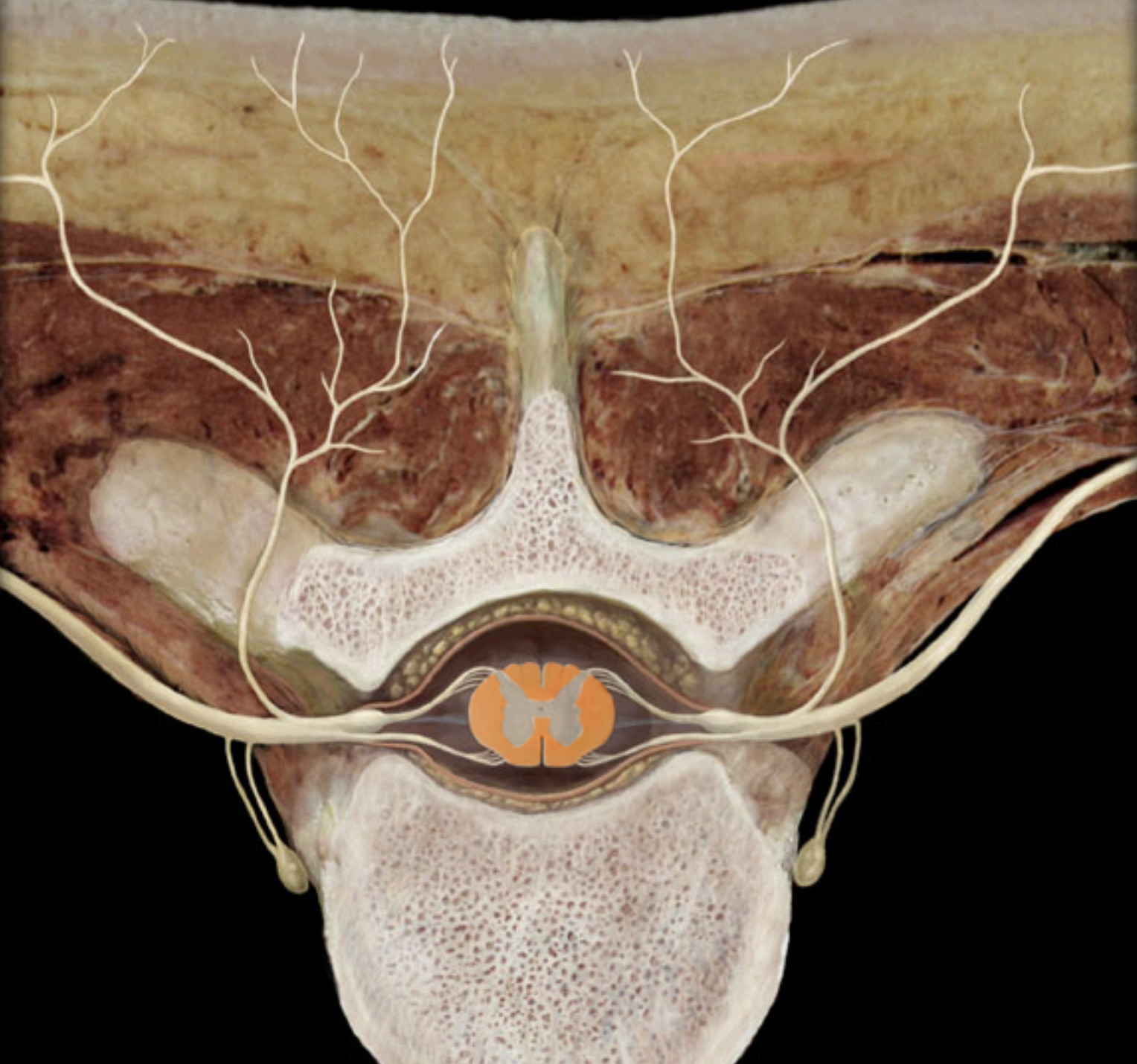
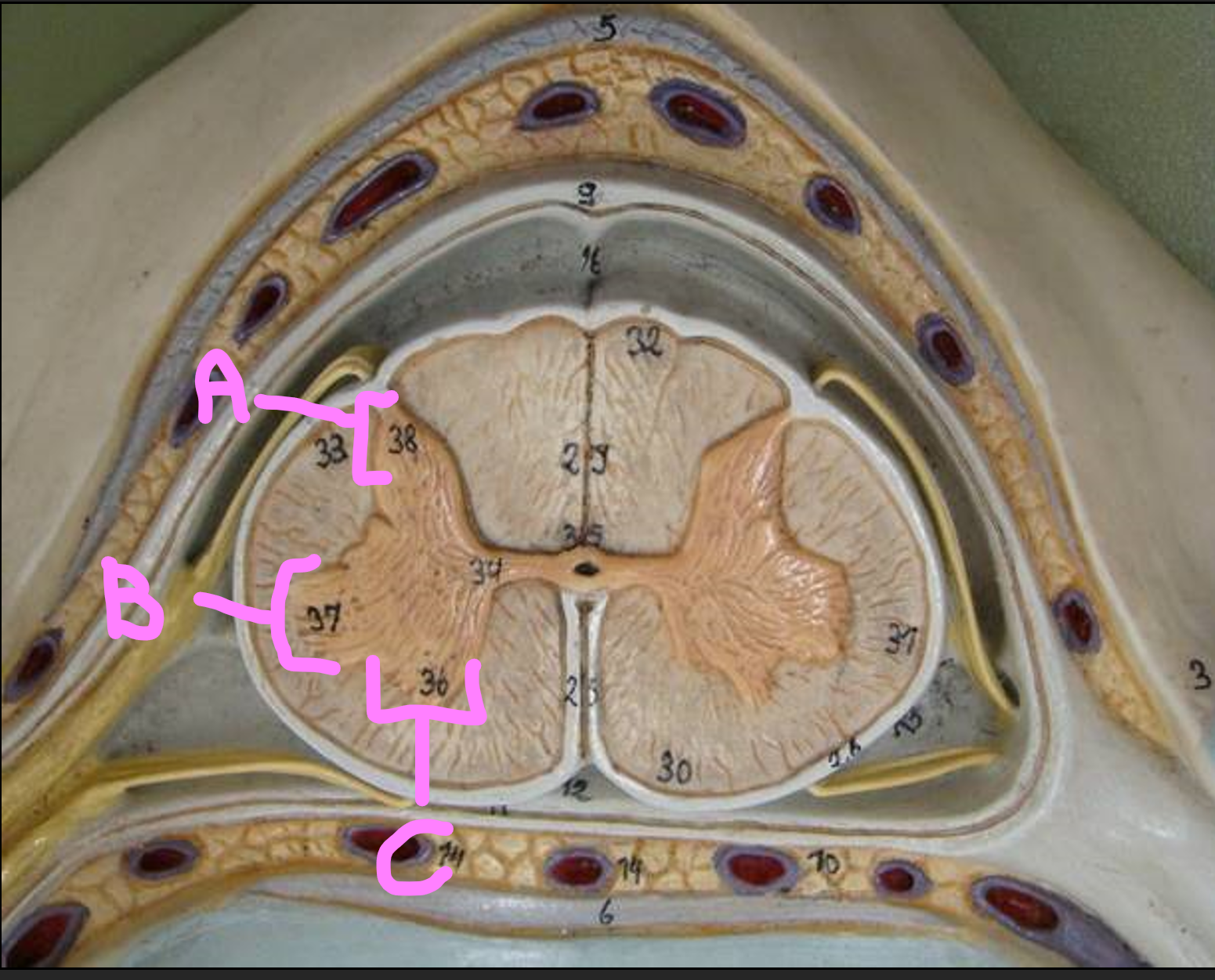
What is A?
posterior column of white matter
What is B?
lateral column of white matter
What is C?
anterior column of white matter
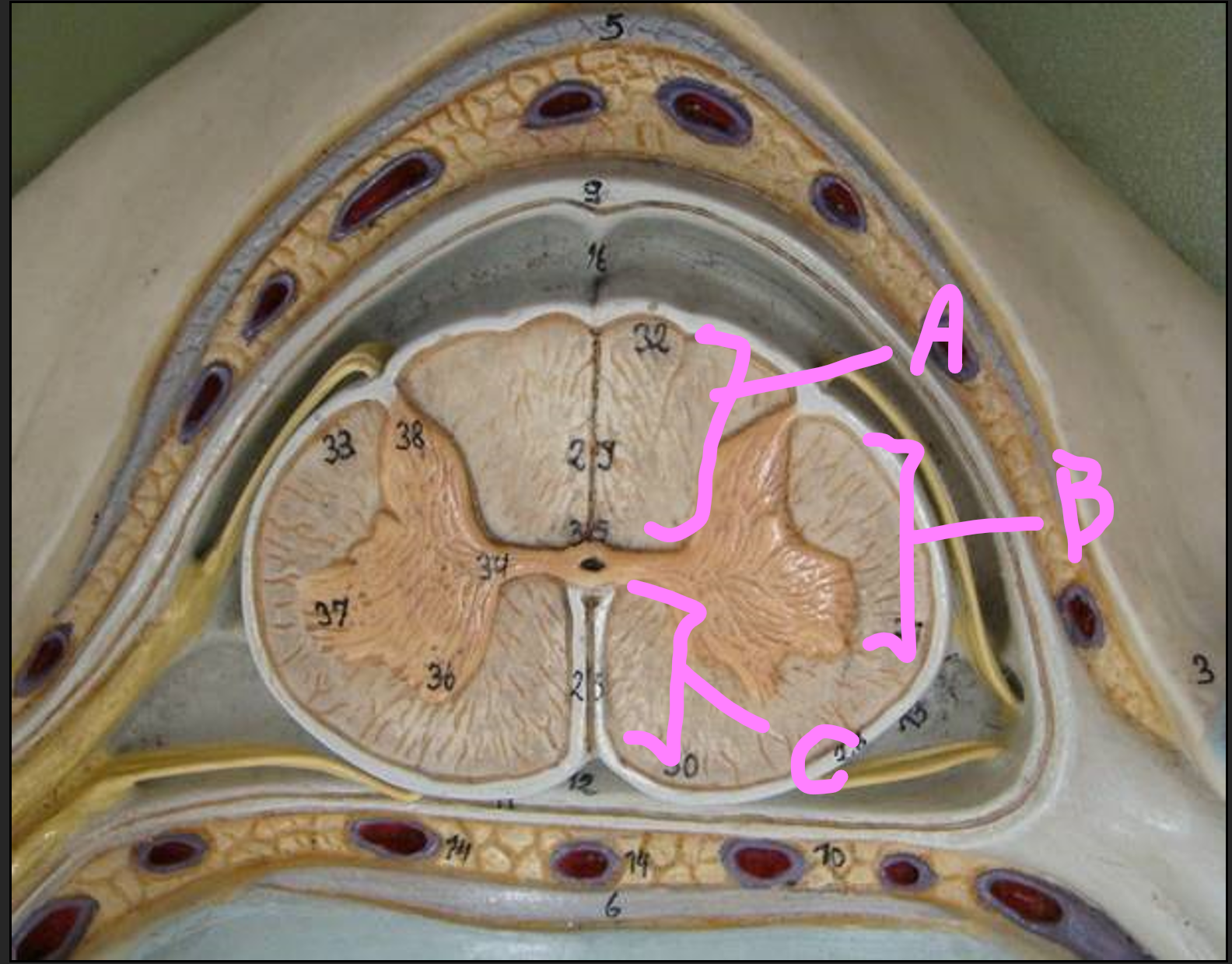
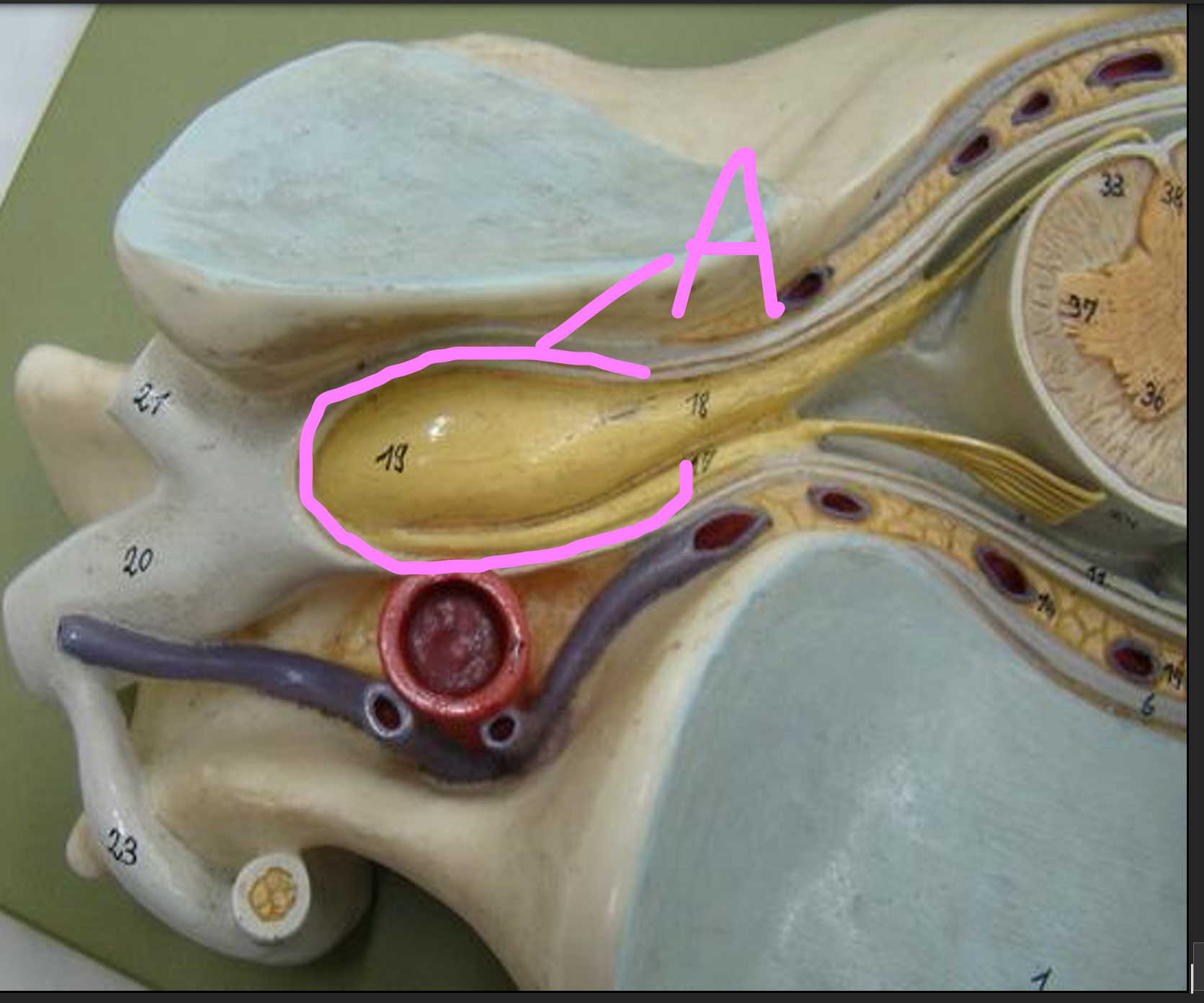
What is A?
Posterior median sulcus

What is B?
anterior median fissure
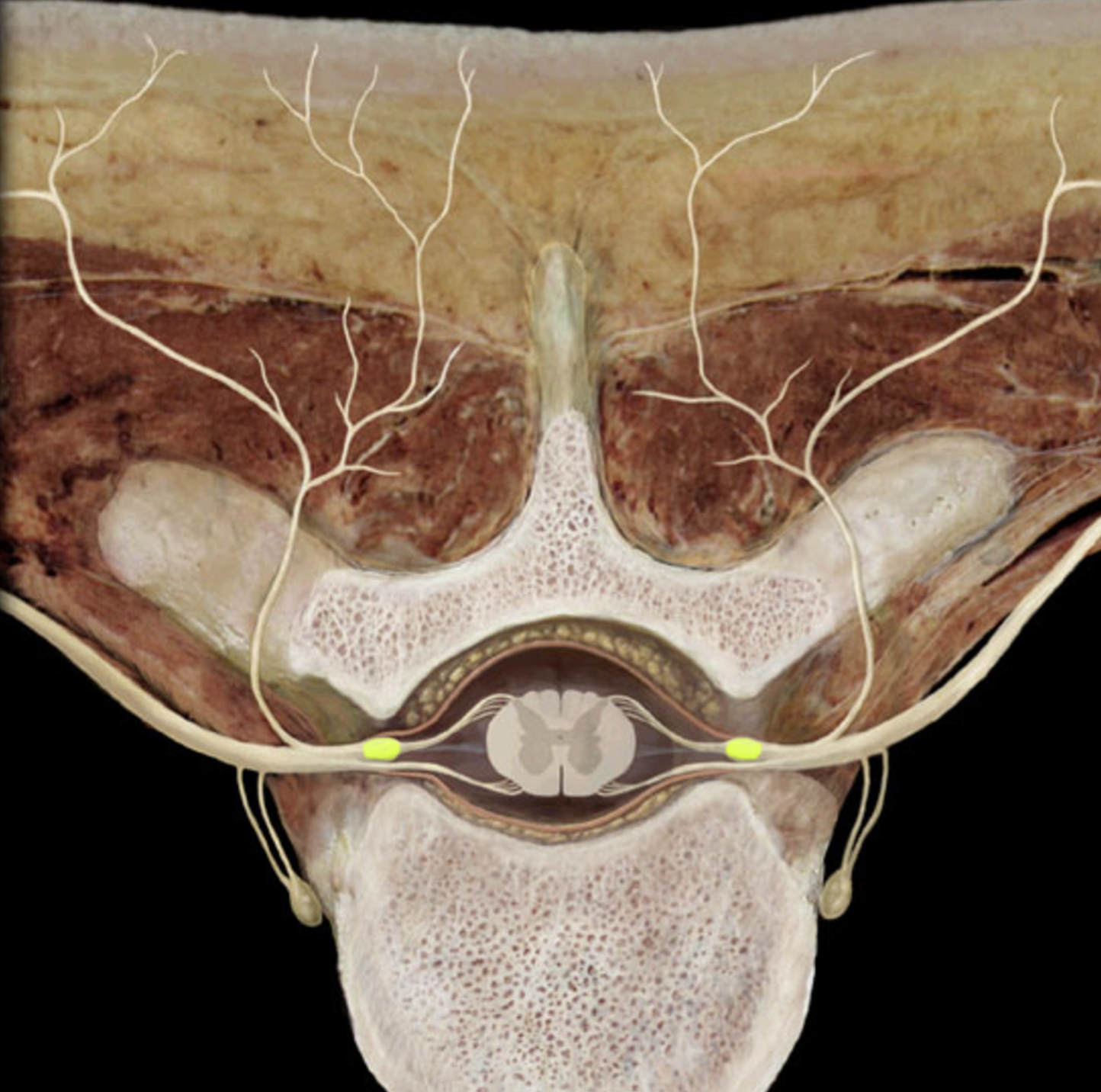
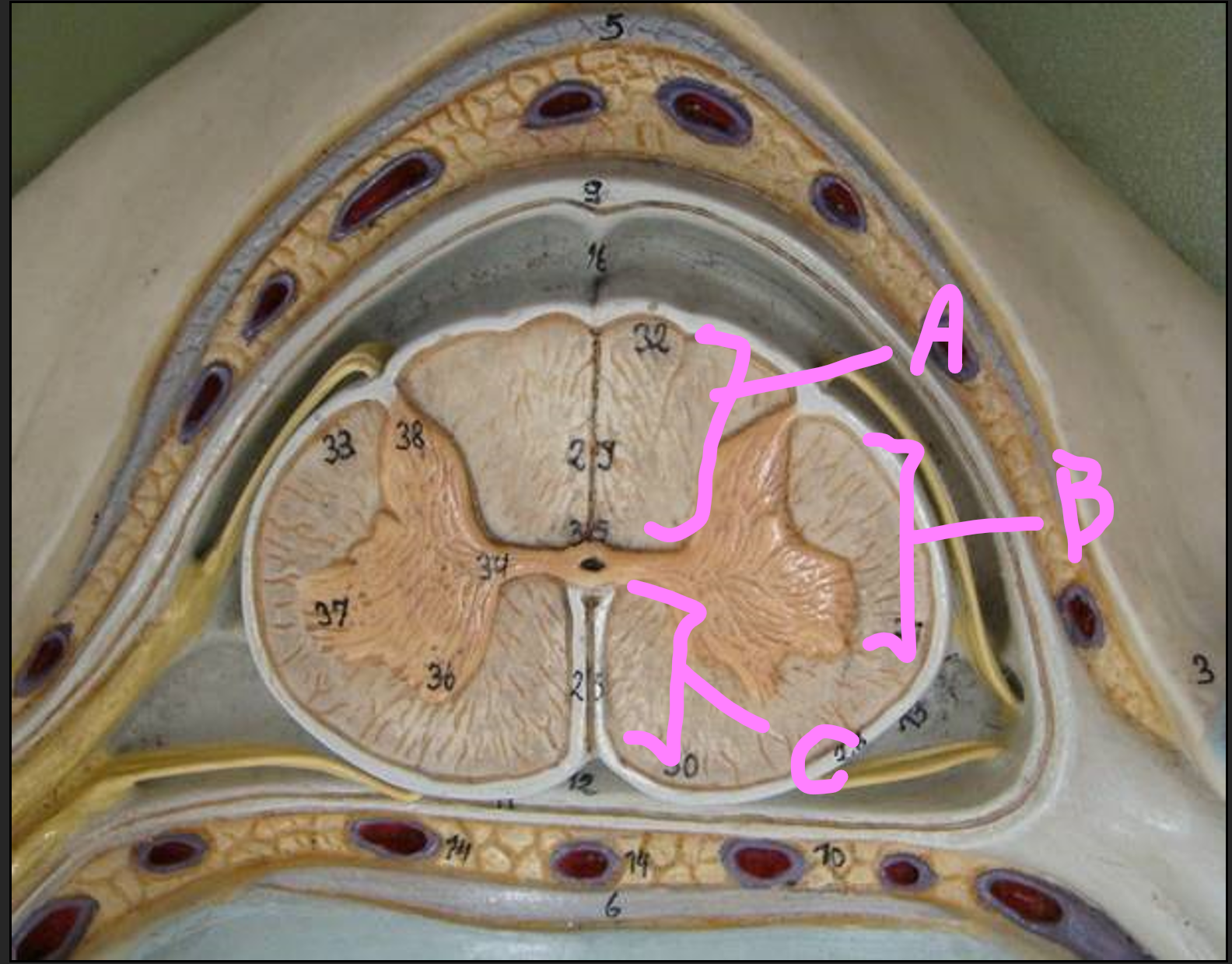
posterior root ganglion
posterior root ganglion
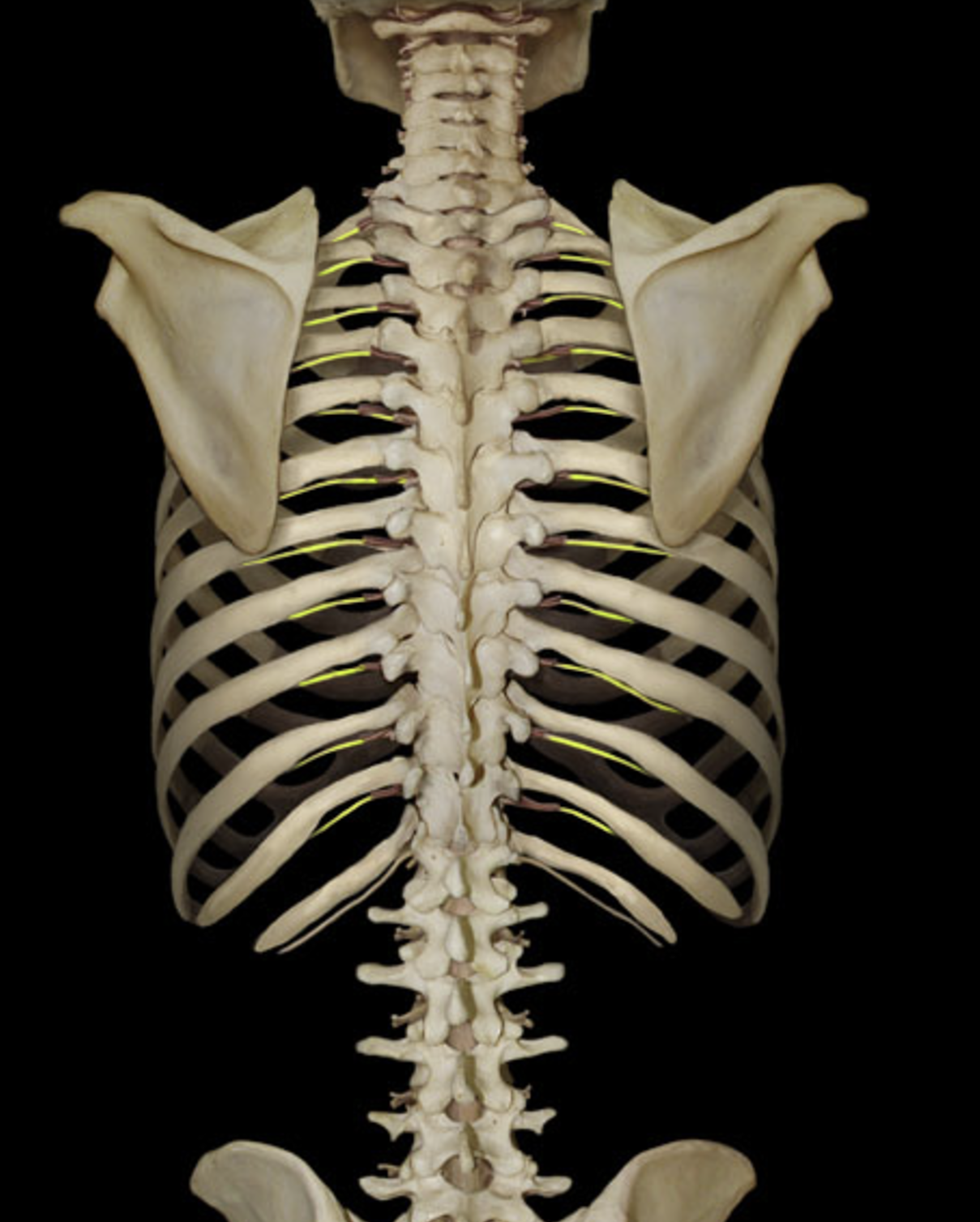
anterior ramus
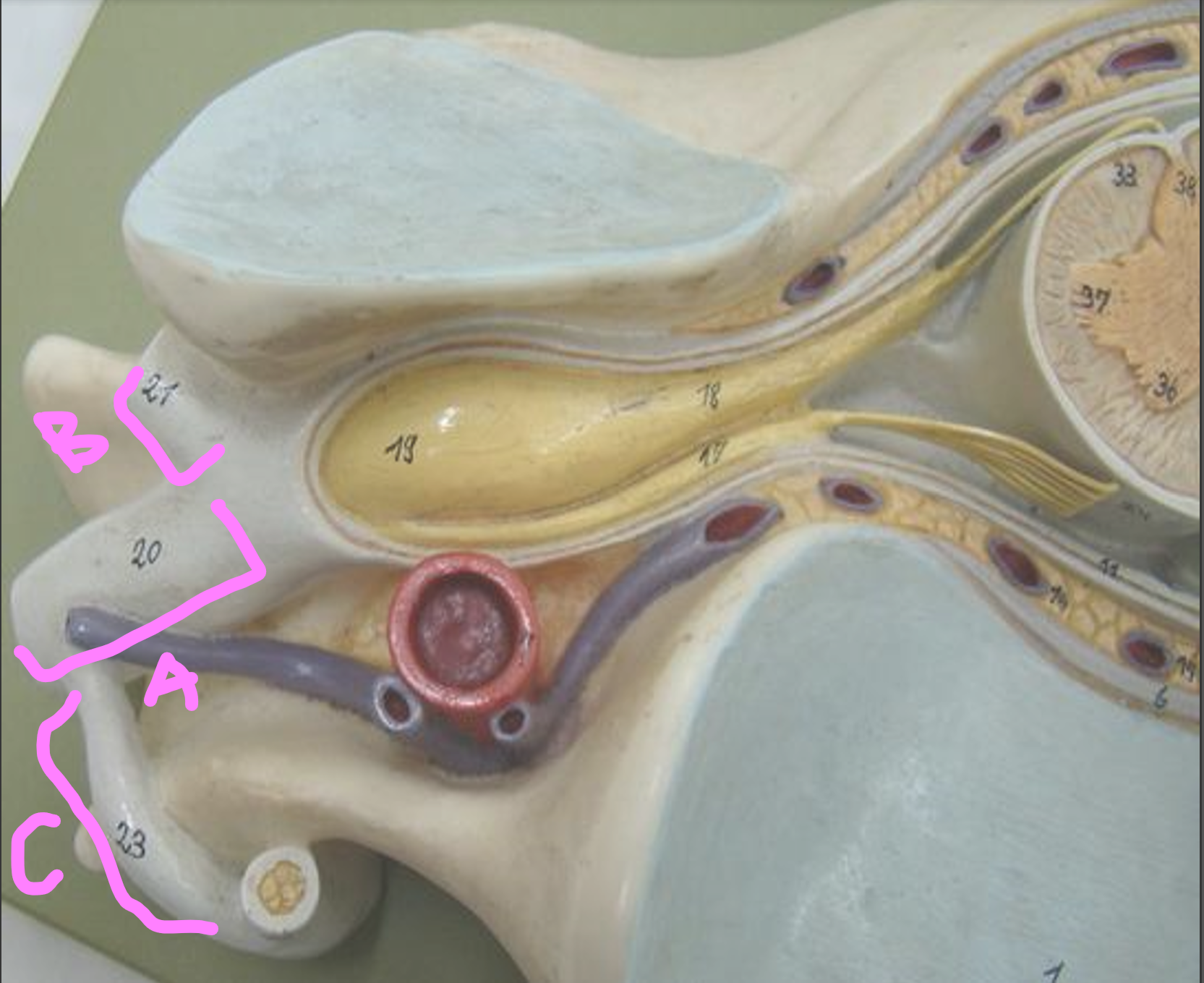
What is A?
anterior ramus
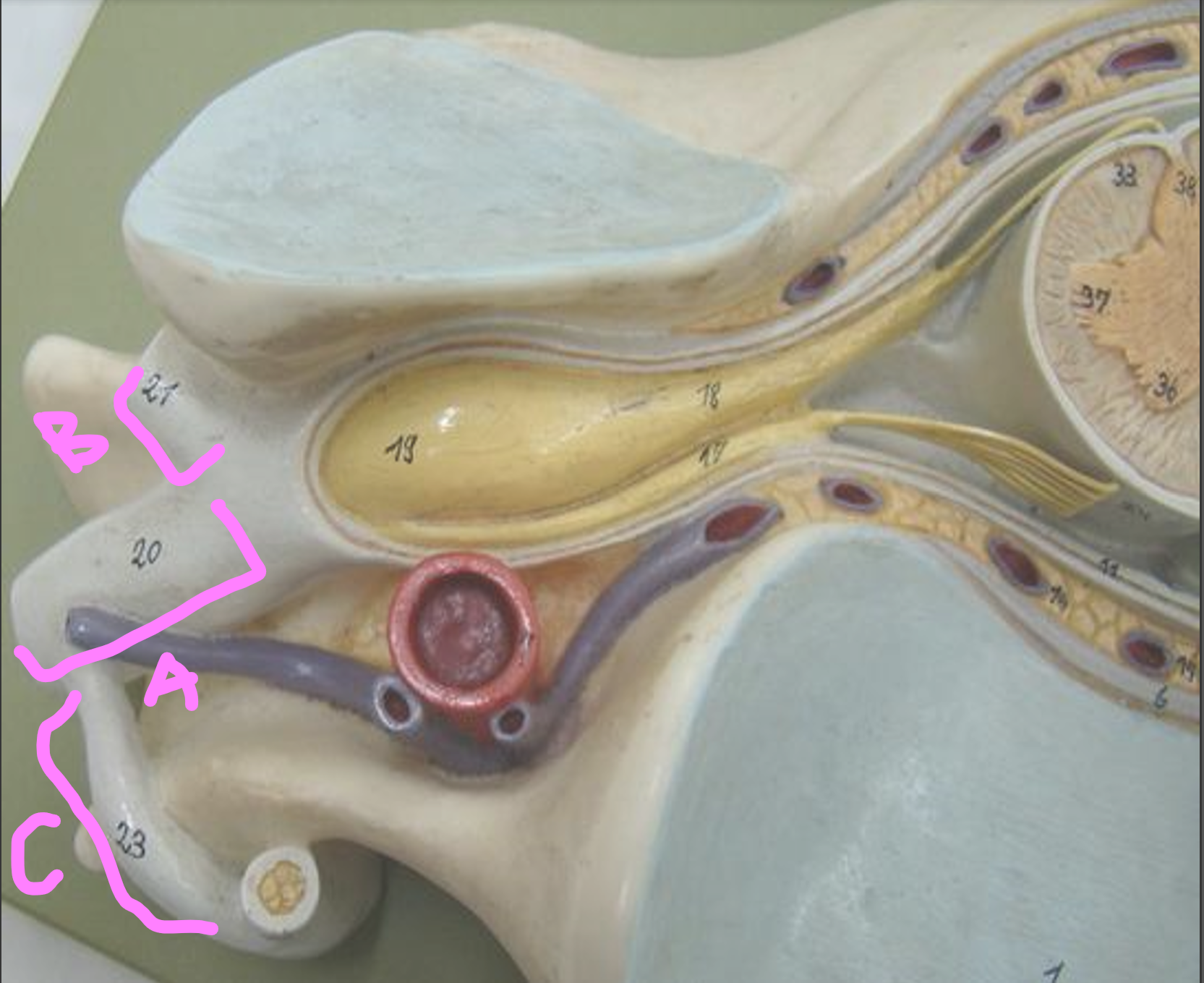
What is B?
posterior ramus
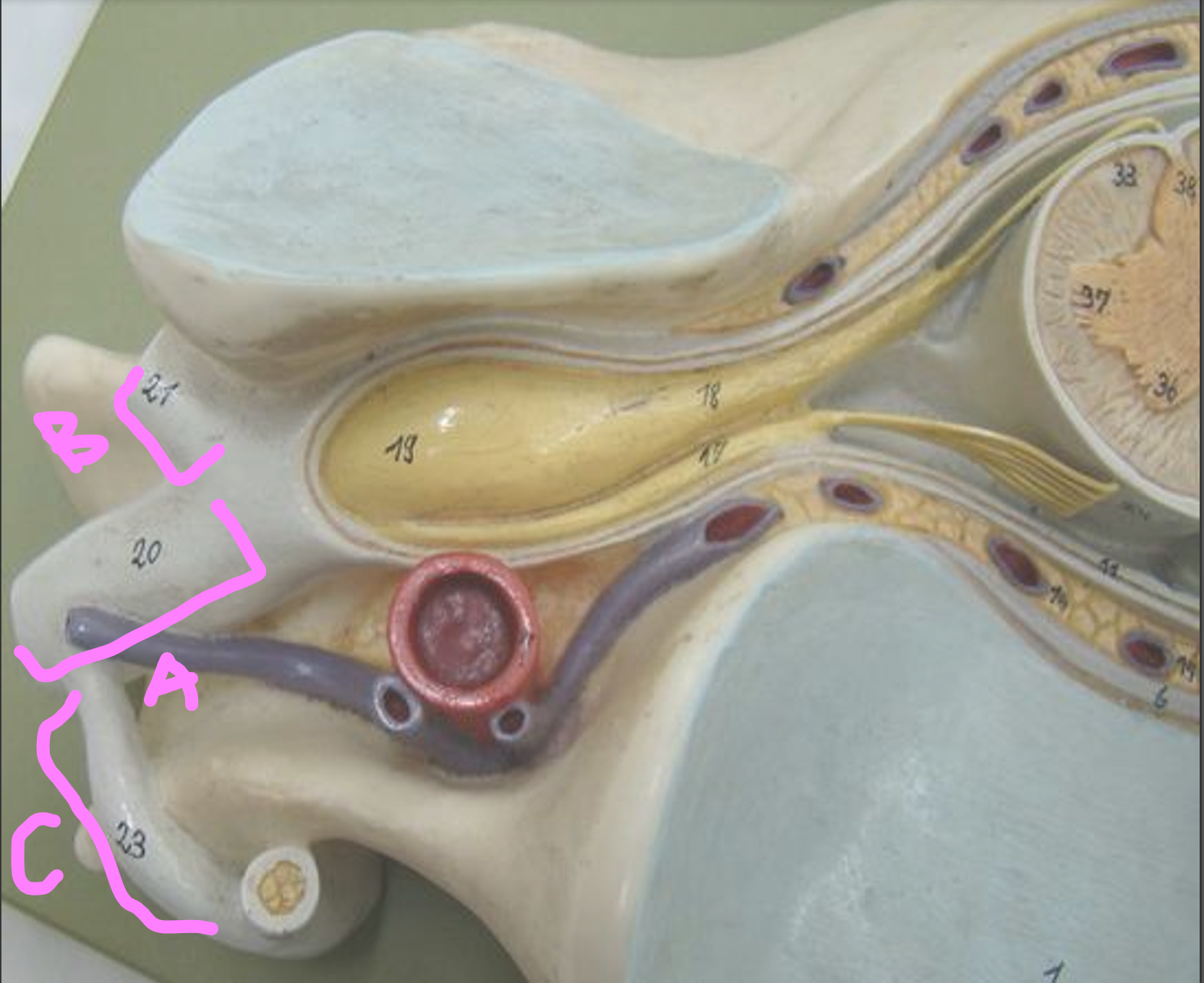
What is C?
communicating ramus
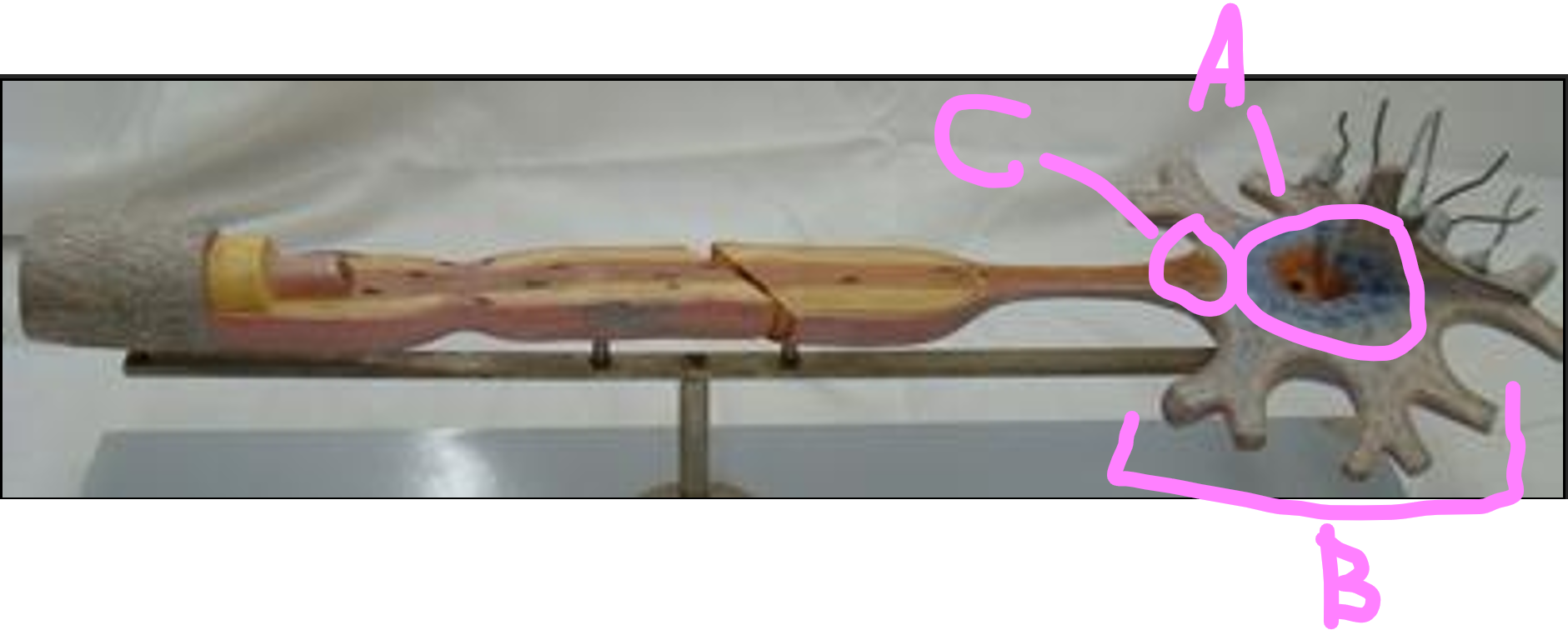

What is A?
soma
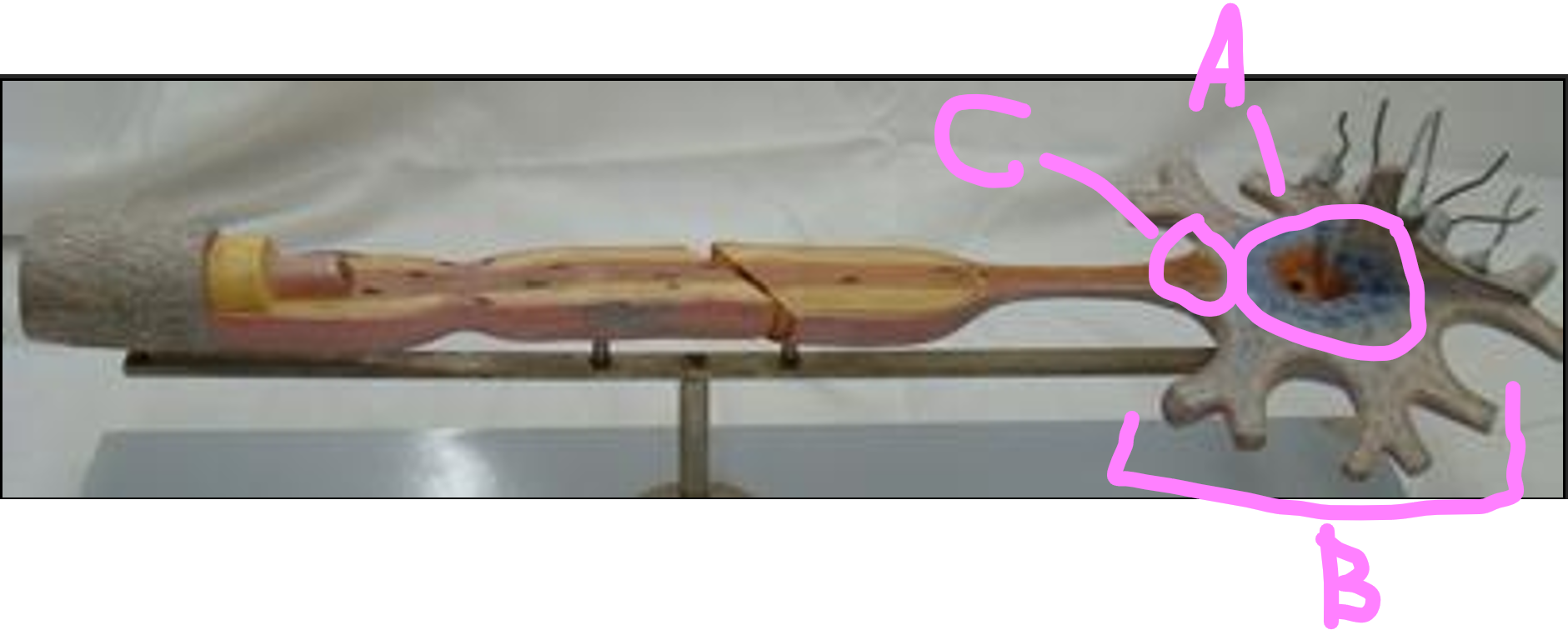

What is B?
dendrites
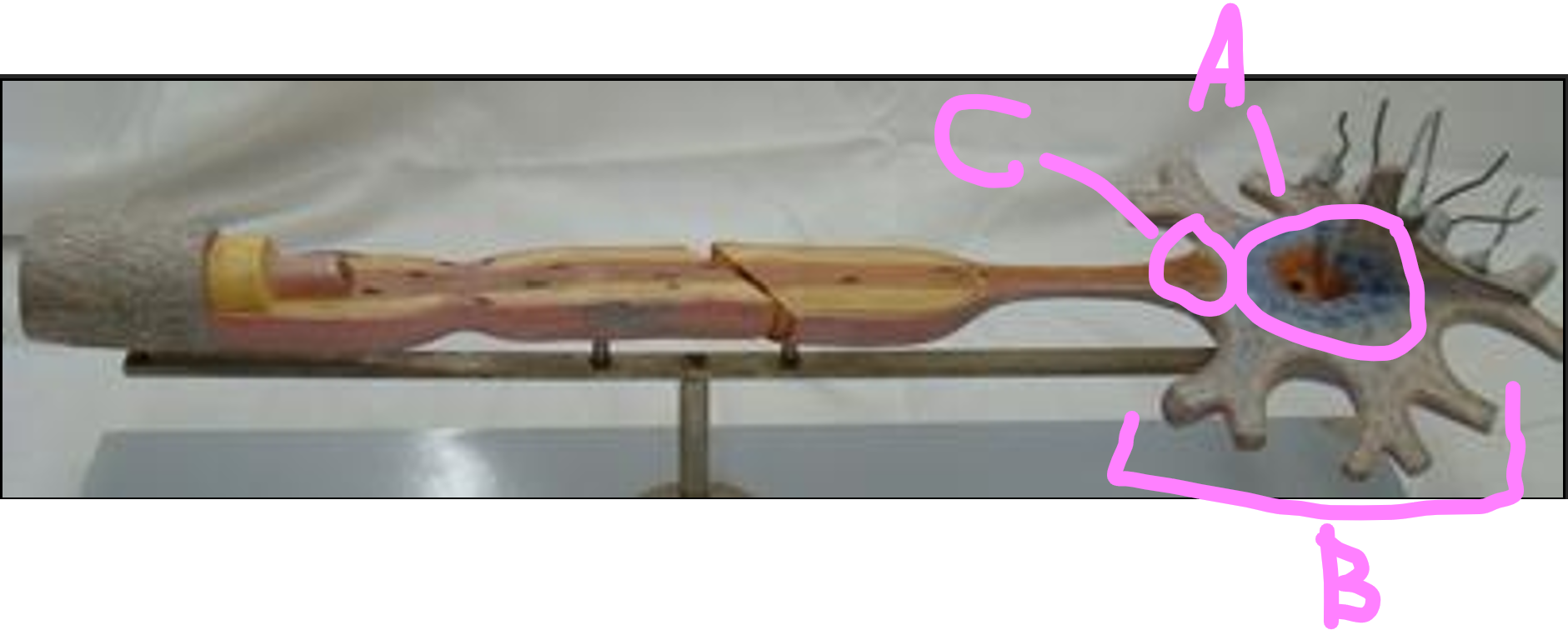

What is C?
axon hillock
What do the axon hillock and initial segment makeup?
trigger zone
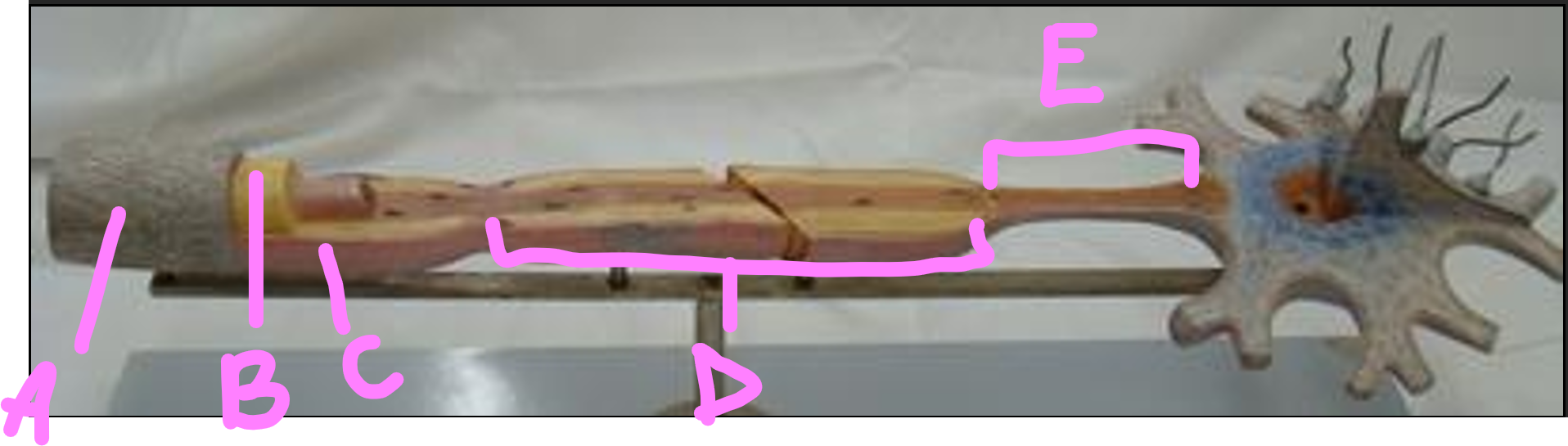
What is A?
endonerium
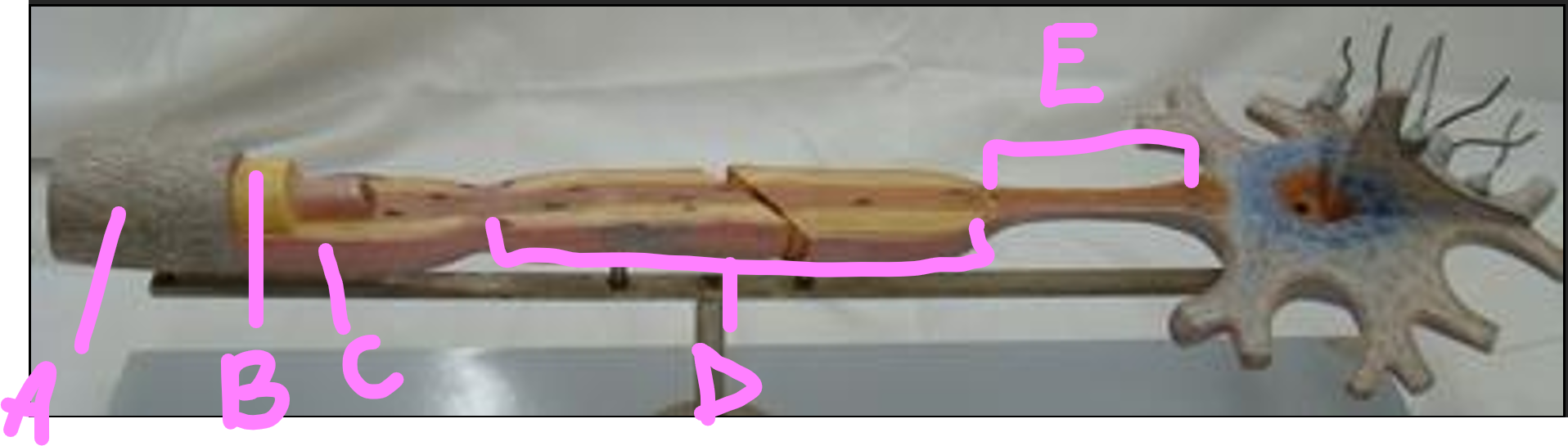
What is B?
schwann cell
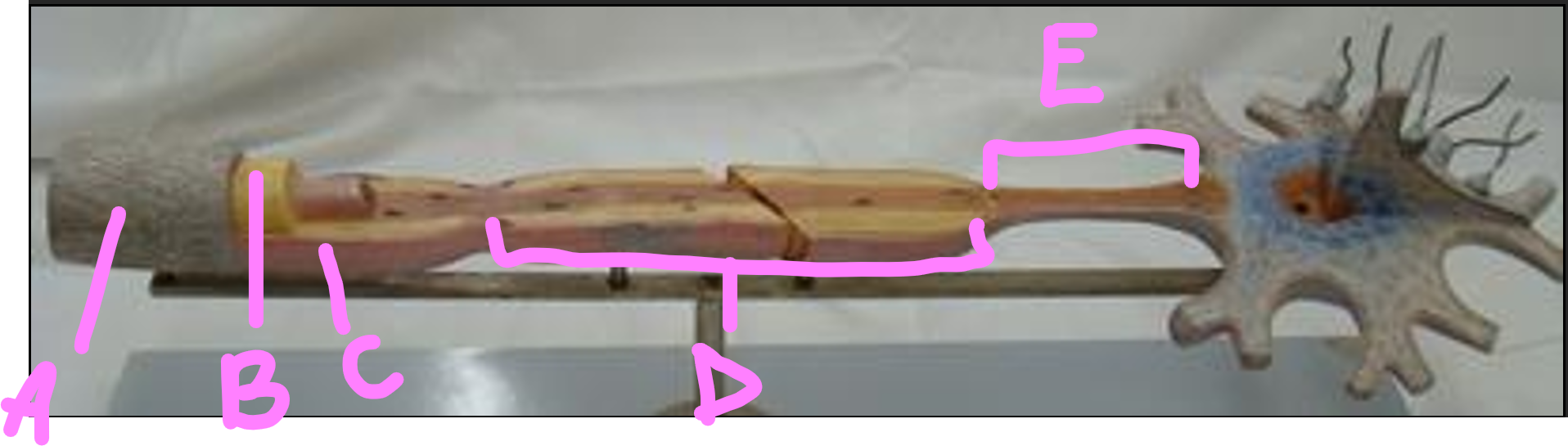
What is C?
myelin sheath
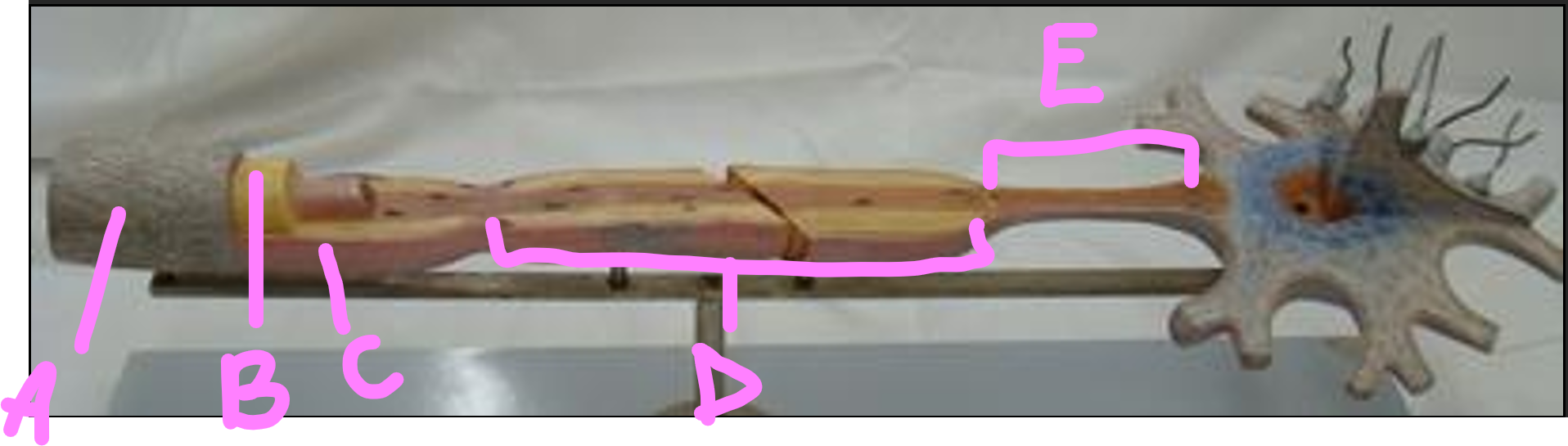
What is D?
internode
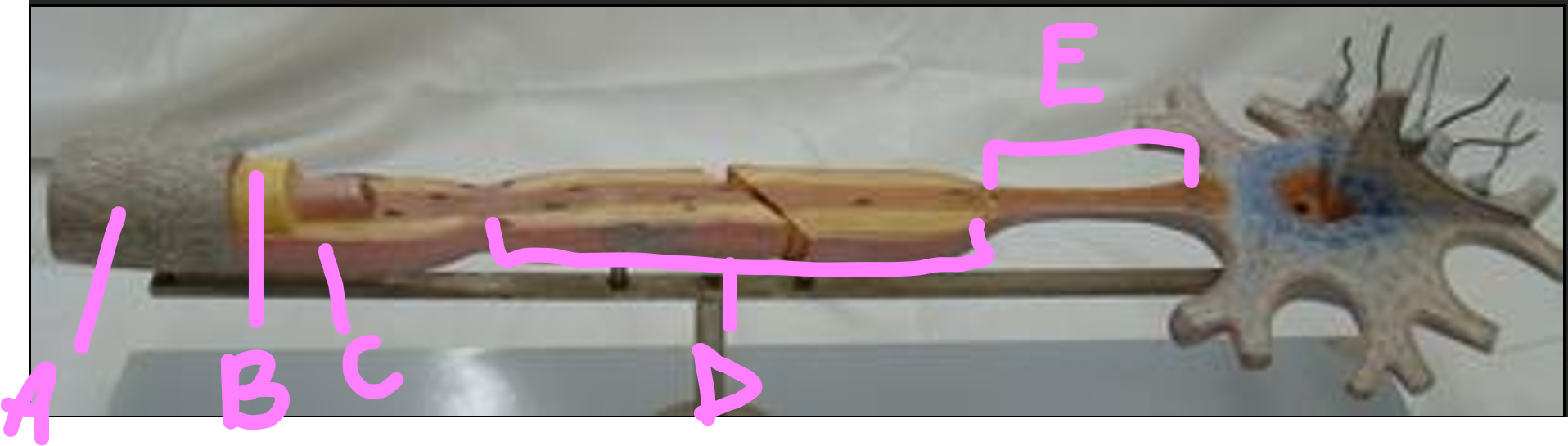
What is E?
initial segment
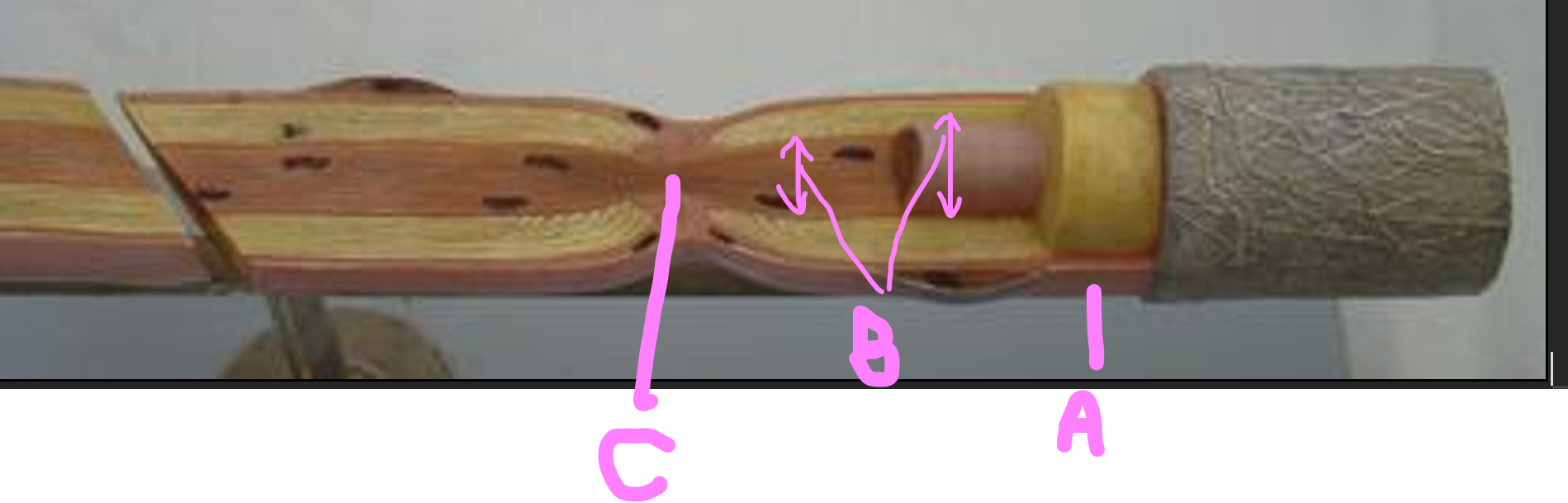
What is A?
neurilemma
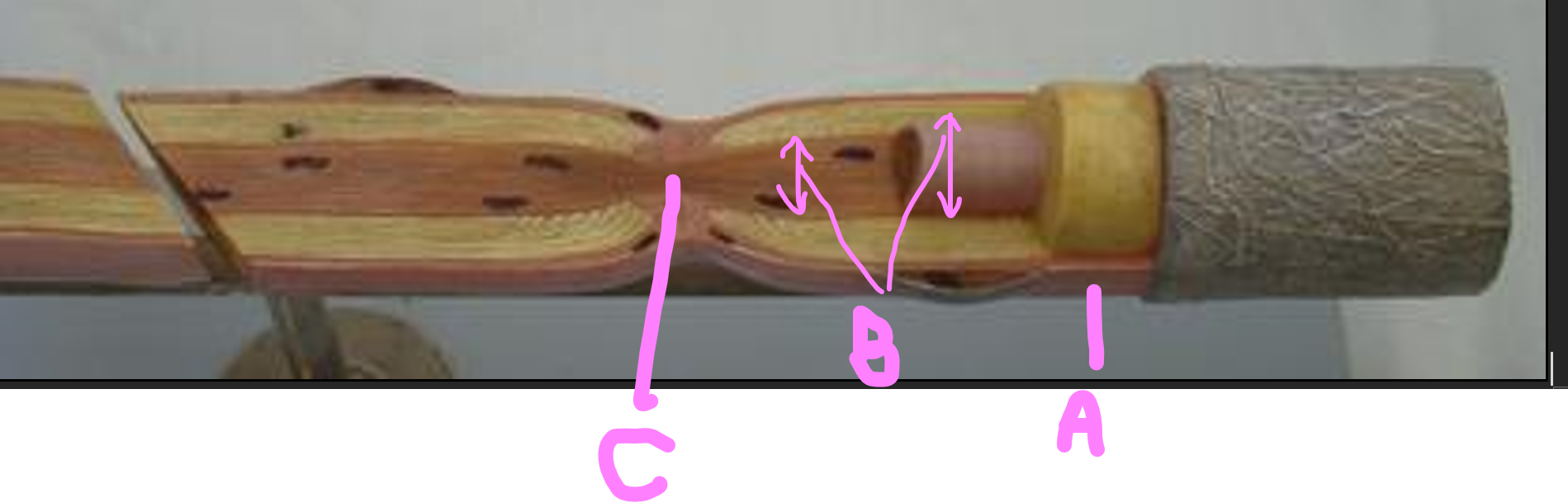
What is B?
axon (nerve fiber)
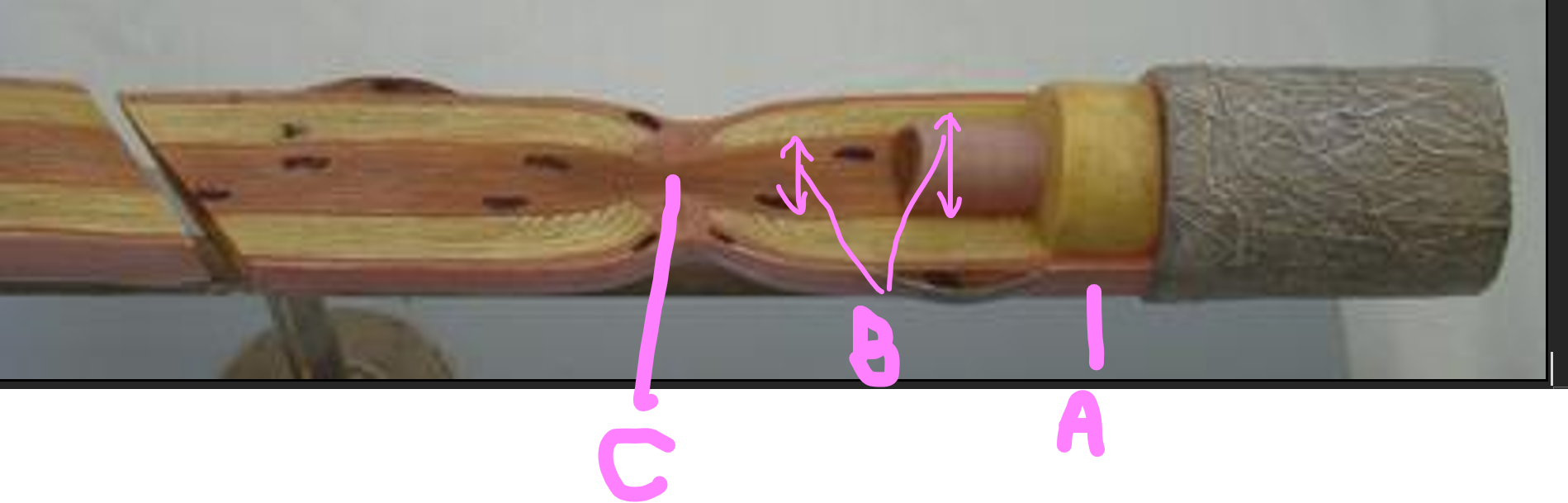
What is C?
node of ranvier
Name all 12 cranial nerves (in order) and their basic functions:
I. olfactory nerve: sense of smell
II. optic nerve: vision
III. oculomotor nerve: opening, moving eyes, adjusting pupil width
IX. trochlear nerve: looking down, move eyes towards/away from the nose
V. trigeminal nerve: sensation in eyes, face, inside of mouth, chewing food
VI. abducens nerve: moving eyes left to right
VII. facial nerve: controls muscles of facial expression, provides taste in part of tongue
VIII. vestibulocochlear nerve: hearing, balance
IX. glossopharyngeal nerve: taste sensations, swallowing muscles, it has parasynthetic nerve fibers that control blood pressure regulation and saliva production
X. vagus nerve: digestion, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, mood, saliva, etc, main nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system
XI. accessory nerve: shoulder and neck movements
XII. hypoglossal nerve: tongue movement (speaking, eating, swallowing)