ARBUS 2, 4, 6
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Canada's Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL)
the federal law dealing with spam and other electronic threats
Companies have to:
Obtain your consent
Provide identification
Provide an unsubscribe mechanism
Is difficult to enforce for spammers outside of Canada
National policy
Implemented high tariffs to encourage east to west trade
Was used to encourage Canadian to Canadian businesses
Historical Infrastructure in the Economy
Government built railway to connect the country
Canada's Mixed economy
Economic system in which some allocation of resources is made by the market and some by the government
A mixture of capitalism and socialism
How government affects business
Crown corporations
Laws and regulations
Tax and financial policies
Government expenditures
Purchasing policies
Government services
Crown corporations
Companies owned by the federal or provincial government
Provide services not offered by businesses
Bail out a major industry in trouble
Provide special services not otherwise being provided by private sector
Canada Post, OLG, LCBO
Privatization
selling publicly owned corporations
Laws and regulations
Created by politicians/Political parties in power who should be considered when laws and regulations are created, modified, approved and implemented
Business law refers to rules, statutes, codes, and regulations that are established to provide a framework within which businesses must be conducted AND that are enforceable by court action
Federal, provincial, and municipal levels

Deregulation
government withdrawal of laws and regulations that hinder competition
Competition Bureau
Responsible for the administration and enforcement of a number of acts designed to protect consumers and promote fair competition
Competition act
Administered by federal government
Ensures mergers of large corporations will not restrict competition and that there is fair competition exists among businesses
Provides consumers with competitive prices and products choice
Health Canada
Responsible for:
Establishing standards for the safety and nutritional quality of all foods sold in Canada
Regulations related to food packaging, labeling and advertising
Food and drugs act
Enforcement is done by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency
Monitors both exports (to maintain Canada's reputation internationally) and imports
Agency is also responsible for regulations related to food packaging, labelling, and advertising
Tax and financial policies
John Maynard Keynes model vs. Friedrich Hayek model
World chose Keynes's model
Present is now accustomed to spending as a result
Model did bring end to recession and fixed problems during that time
Canada is one of countries with highest debts
Keynes Model - top down approach
Need for government oversight
Future is uncertain
Act immediately, cant wait for market
Need for a quick spark
To spark the economy
Inject money into economy will cause consumerism to spend
Hayek's model - bottom up approach
Let economy do the job
Don’t bail out losers
Felt we cant afford Keynes approach
Business cycles - busts were necessary to correct booms, if no booms (created by government intervention) then no busts
No real end to the spending of the alternative model
Fiscal policy
Government efforts to keep the economy stable through increases in
Taxes
Government spending
Raise taxes or cut spending
National debt increases
Federal budget
Comprehensive report that reveals government financial policies and priorities for the coming year
When governments increases spending, it increases economy which can increase job opportunities
Opposite occurs when spending decreases
Incentives removed
Quality of healthcare decrease
Etc.
Notional debt
Accumulation of government surpluses and deficits over time
Deficit: government spending > taxes collected
Surplus: government spending < taxes collected
Annual deficits contribute to the national debt, as governments have to borrow to fund deficits
Monetary policy
The management of money supply and interest rates
Controlled by the government of Canada
Overnight rate is used by Canadian banks to set the rate their loans and mortgages are based
What will be the impact of rising interest rates in the future?
Rising interest rates will slow business activity and consumer spending
When the cost of borrowing goes up, businesses and consumers will borrow and spend less
The cost of servicing debt (i.e interest) increases leaving less money for businesses and consumers to spend u
The subprime mortgage crisis
Subprime mortgages: loans targeted at people who do not qualify for regular mortgages
Their credit records not good enough or no credit history
Interest rates increased - couldn’t afford payments
Housing prices started to fall and couldn't afford to sell homes either - foreclosures
Value of mortgage backed securities plummeted
Lesson: not all regulation is bad
Government expenditures
Government spends huge sums of money on. . .
Education
Healthy
Transportation systems
Payments to individuals
Financial aid
Grants, loans consulting advice
Help industries and companies
Purchasing policies
Large purchasers and consumers of goods and services
Can favour Canadian businesses
Code of Conduct for Procurement
Government services
Innovation, science, and economic development Canada (formerly industry Canada)
Global affairs Canada (formerly foreign affairs, trade and development Canada)
four best practices can avoid common pitfalls as governments build needed infastructure
develep projects with tangible and quantifiable benefits
improve coordination of infastructure investments to account for network effects
engage and align community stakeholders to drive inclusive economic growth\
look to unlock long-term capita
Raging Bull Video
Red bull had trouble entering Canadian market until Canada created new legislation for natural products
whos responsibility is it to make sure that guidelines are being followed?
If the company advertisies in any way a use that goes against the label, that is considered an illegal practice and can cause cases like the product to stop being sold
Truth about CBD Video
CBD: cannabidiol
A lot of CBD products are illegal and sold illegally
Most stores are legal but many unsilenced stores have popped up because of demand
Government has banned talk of talking about extensive health benefits of CBD (such as claiming it solves everything)
Or having health claims on packaging
Even if CBD is safe, there is no regulations for black-markets
Legal regulation has lots of paperwork and processes to confirm
bank of Canada: Count on Us
Bank of Canada is also the banker for the federal government
Canadians have confidence in our money
Money is protected from high inflation, counterfeiting, and into ensuring that we have a reliable financial system by the bank of Canada
How do we know how much our money will buy in the future
As long as inflation is low and predictable, we can stay confident in our money
Low and stable inflation is our goal
The government and bank of Canada have a joint agreement to aim for an annual inflation rate of 2 per cent
This is called the inflation target
How is inflation kept in check
Economists monitor and survey the international economic environment
The bank of Canada sets the policy interest rate which influences commercial interest rates
All this economic activity tends to push inflation up
Interest rate up, cool things down
Interest down, heat things up
Bank of Canada's job is to oversee these large, complex systems that are used for making these financial transfers each and every day
By having hard to counterfeit notes (cash) / trustable notes, a good operating system, and keeping inflation in check, Canadians can have confidence in their money
Marketing
the process of creating, communicating, and delivering offerings that have value for customers
How you plan and present your product/services for a customer
Marketing mentality is currently learn your customers expectations and exceed them
Market
a group of people with unsatisfied needs and wants who have the resources and willingness to buy
"Find a need and fill it"
The evolution of marketing
Shift from helping the seller sell to helping the buyer buy
Consumer choice became more prevalent
Businesses needed to give a reason for customers to buy their product
Production era:
From late 1800's to early 1900's
Limited production capabilities
Demand > supply
Mentality was produce as much as you could
Consumer bought whatever they could
Sales era:
From 1920’s to 1960
Advancements in production processes led to mass production being born
Production capacity and supply often exceeded immediate market demand
Supply > demand
Focus shifted to selling and advertising
Businesses needed to start focusing on how to get customers to buy their excess supply
Demand increased because soldiers from war returned and demand became high
Marketing concept era:
From 1950's to 1990s
Mentality was trying to find the right product for the customers
A three-part business philosophy
Customer orientation
Idea of 'customer is always right' began
Find out what customers want and provide it
Service orientation
Aligns all sides of business to customer satisfaction
Profit orientation
Focus on profits rather than sales
"bottom line" = profit
"top line" = revenue
Market orientation era:
From 1990s to 2020
focused on the customer through
Collecting and sharing information throughout organization
Using information to create value, ensure customer satisfaction, and develop customer relationships
Main reason for era was technology
Companies made more personalized tactics to customers
Led to idea of loyalty from customers will lead to more sales
Its harder to find/replace new buyers
Loyalty programs
Customer relationship management (CRM)
The Social media influence
TikTok and platforms have added on to the market era
The ROI (return on investment) is five years for a business when using social media
How has social media impacted marketing and the role of marketers?
Opportunities
Connecting and responding directly to customers (personalized/customized)
Consumer generated marketing
Cheaper/reduced marketing costs
Additional data
Challenges
Needs to be maintained and managed (resources and time-dedicated staff)
Negative feedback in a very public forum (risk management)
Social media marketing era
2010s to 2020s
Consumers engage with organizations and other consumers to share information, opinion, knowledge, and interests
Heightened engagement level

Customer champions
Businesses want to identify and sell to these people with obsessive interest
These individuals often spread stuff word by word
These people are likely the ones willing to pay extra to try something new
Non profit organizations and marketing
Charities
Need financial support to continue
Churches
Experience an aging membership
Need newer members
Older membership can oppose new membership however
politicians
Profit and charity
Profit organizations can team up with charity programs
e.g., times raising money for camp day
Bells 'lets talk' program
Cause marketing
Occurs when the charitable contributions of a firm are tied directly to the revenues generated from its product(s)
Marketing managers and the marketing mix
marketing managers must choose how to implement the four Ps of the marketing mix: product, price, place, and promotion. The goals are to please customers and make a profit
Product
Any physical good, service, or idea that satisfies a want/need
Includes product enhancements
Concept testing vs. test marketing
Concept: Involves describing the product and surveying to see if they like it
Test: Bringing samples to see if consumers will like it
Using crowdsourcing for development
Price
Money or other consideration exchanged for ownership or use of a good/service
The money a customer is willing to pay for the product
Sellers want to make sure they are making a profit
Veblen goods
Psychology
Setting a price that appears cheaper than it really is
e.g. 98 cents
Veblen goods
A Veblen good is a good for which demand increases as the price increases, because of its exclusive nature and appeal as a status symbol.
A Veblen good has an upward-sloping demand curve, which runs counter to the typical downward-sloping curve
Is an outlier to the idea that expensive sells less
Place
How to get your product to your customer
Intermediaries make it easier for the consumer to buy
Helping buyers buy
Amazon go - a new way to grocery shop
Promotion
All of the techniques used to motivate customers to buy
Are super bowl ads worth it?

Marketing research process
Keep building relationship with customers to build loyalty
Much easier to sustain than finding new customers
Collect data
Analyze the data into information that is actional-able
Choose which info to act on
Environmental scanning

Consumer market (B2C)
Individuals/households that want goods and services for personal consumption or use

Business to business (B2B)
Individuals/organizations that want goods and services to use in producing other goods and services or to sell, rent, or supply to others

Business-to-Business (B2B) market
Relatively fewer customers
Size of business customers is relatively large
Markets tend to be geographically concentrated
Business buyers are generally more rational than consumers
Sales tend to be direct
More emphasis on personal selling
Larger customers means bigger purchases/purchases more often
There are more consumers in numbers, but B2B can resell items
Can be geographically located to be closer (place), close proximity makes it easy to sell or to build customer relations
The Consumer Market
Consumer groups differ greatly in age, education level, income, and taste
Cannot fill needs of every group
Market segmentation
Process of dividing the total market into groups with similar characteristics
Target marketing
marketing directed at those groups an organization decides it can serve profitably
Segmenting the consumer market
Geographic segmentation
Dividing by city, geographic area
Demographic segmentation
Divided by religion, age, education, etc.
Psychographic segmentation
Dividing market to lifestyle, personality, or attitudes interests
Behavioural segmentation
Considers buying patterns and what benefits consumers
e.g, hair color, bus passes, usage rates
Niche marketing
finding small but profitable market segments and designing products for them
One to one marketing/customized marketing
developing a unique mix of products for each individual consumer
Individualized towards consumer
Identifying the target market
For each product below identify the target market:
Disposable diapers
***Remember: A market is a group of people with unsatisfied wants and needs who have the resources and willingness to buy
Relationship marketing
keeping individual customers over time by offering new products that exactly meet their requirements
CRM systems
Database that should capture contact information, past communication, purchases, preferences
Analysis of the data can help develop strategy to enhance customer satisfaction and encourage loyalty
Identify best customers or key segments
Customize communications
Monitor/assess effectiveness of marketing campaigns and promotions
Marketing mix influences
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Customer decision making
Sociocultural influences
Reference groups
Family
Social class
Culture
Subculture
Psychological influences
Based on
Perception
Attitudes
Learning
Motivation
E.g., Think of buying environmentally friendly products (eg. Compostable dog waste bags, eco-friendly packaging)
Consumer decision making
Situational influences
phycological influences
sociocultural influences
Social media revolution Video
Over 50% of the world population is under 30 years old
Facebook has the biggest population over countries like india and china
Social media = relationships
The ROI of social media in your business will still exist in 5 years
93% of buying decisions are influenced by social media
By 2018, video will account for over 2/3 of mobile usage
Shrinking attention spans
Every second two people join linkedin
That’s like the entire enrollment of the ivy league joining linedin
Veblen good video
Named after Thorstien Veblen who introduced the term conspicuous consumption
Veblen good is one whose demand increases as its price increase
Consumers see it as a exclusive status symbol
because demand goes down as price goes up, a Veblen good was an upward sloping demand curve
Veblen goods are high quality coveted items
Designer
Brand identity
Luxury
Not at the store
Goods are priced so high only the affluent can afford them
The higher the price, the less likely other consumers can afford them
And the more buyers perceive them to signal great wealth and sucesss
If a veblen goods price decreases the demand will decrease because status conscious consumers will see it as less exclusive
The moving assembly line
Henry ford
Over 100 years ago
Radical transformation of manufacturing
Radical transformation of society
Canada Today
Focus
Natural resources
Auto industry
Going through innovation
Challenges
Dependence on US
Increasing globalization
Strengthening emerging markets like India and China
Businesses need to recess and make changes
Global competitiveness Rankings
Two organizations prepare this:
World economic forum (WEF)
International institute for management development (IMD)
These organizations set themselves to regulate business competitiveness
Canada's challenges
Inadequate improvement in productivity
Inadequate education/retraining of work force
Foreign owned companies
Inadequate spending R&D
Canada's solutions to challenges
Making Canada more competitive
Innovation
Government role
Tax credits and incentives
Government grants
Trade policy and regulations that expand trade corridors
Strategic partnerships
Role of business
Strengthen relationships (customers and suppliers)
Focus on quality
Practice continuous improvement (culture)
Want a culture driven by continuous improvement
Research and development (R&D)
Work directed toward the innovation, introduction, and improvement of products/processes
Increases production capability
Improve product quality
Extend product range
Innovation leads to increased productivity and group

How to improve productivity?
Reduce cost of inputs
Improve quality
Eliminate waste
Improve efficiency of production processes
Activity-based management
Reduce non-value-added processes
Lean manufacturing
Production of goods using less of everything compared to mass production
Less
Human effort
Manufacturing space
Investment in tools
Engineering time to develop a new product

Flexible manufacturing
Designing machines to do multiple tasks so that they can produce a variety of products
Reduces downtime
Respond to unique demands faster
Computer-aided design and manufacturing
The use of computers to help create 3D diagrams, etc.
Computer-aided design (CAD)
Computer aided manufacturing (CAM)
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM)
Mass customization
Tailoring products to meet the needs of a large number of individual customers
Production
Creation of goods/services using the factors of prodution
Land, labour, capital, entreprenurship and knowledge
Production management
Activities that managers do to help their firms create goods
Operations management
Transforming resources (including human resources) into goods AND services
Operations management in the goods sector
Focus on creating a good product
Operations management in the service sector
Focus on creating a good experience
Operations managers are responsible for
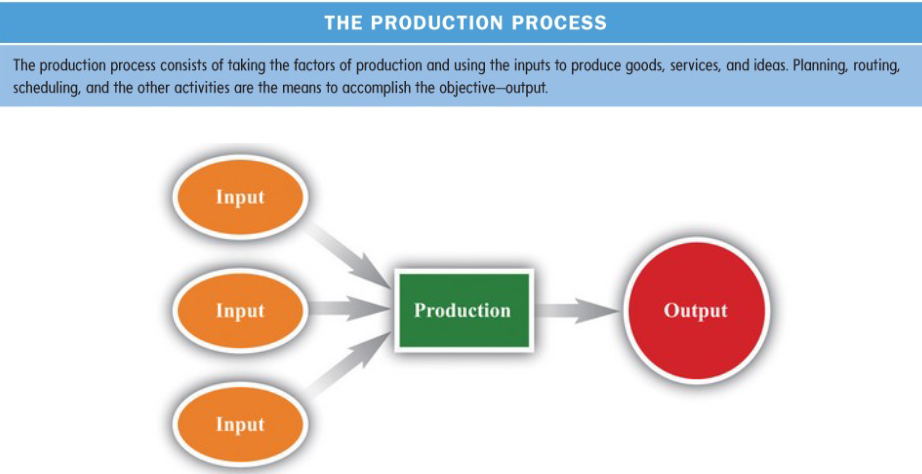
Operations planning - production process
Relationship between inputs and outputs
Inputs come together to form outputs
Find everything at the lowest cost
Process manufacturing
physically/chemically changing materials e.g., boiling an egg
Continuous process
long production runs turn out finished goods over time, uniform goods (soda)
Intermittent process
production run is short and the machines are changed frequently to make different products e.g., customized goods
Most processes now adays are intermittent
Outsourcing
Canadian companies benefit from other countries doing this
Doesn't always mean out of country, just means outside of business
Top reasons for doing it
Reduce/control costs
Gain access to resources
Free up internal resources
Improve business/customer focus
Will we see more or less outsourcing in the future
Wage rate differences are getting smaller
Different labor rules in other countries
Use of technology
Shipping costs rising
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
a system that allows information to be shared between various functions across a company to manage operations
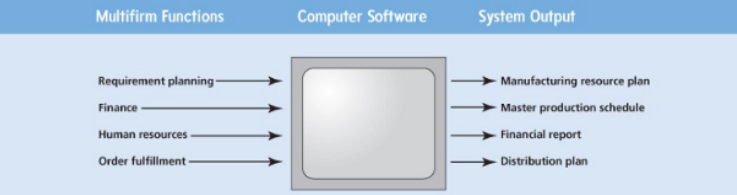
Materials requirement planning (MRP)
Uses sales forecasts to ensure needed parts are available at the right time/place
Site selection
Selecting a geographic location for a company's operations while considering:
Availability of resources and labor
Time to market (accessibility to transportation)
Proximity to suppliers
Proximity to customers
Government support
Facility layout
Physical arrangement of resources (including people) in the production process

Assembly line layout
used for repetitive tasks
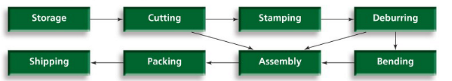
Process layout
frequently used in operations that serve different customers different needs
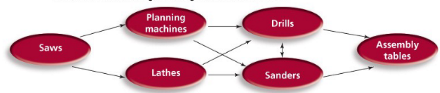
modular layout
can accommodate in design or customer demand
fixed position layout
a major feature of planning in scheduling work operations