Unit 1: Introduction, Microscopy and Histology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Magnification of Microscope
objective lens x ocular lens = total magnification
ex: 4.0X × 10X = 40X (survey mode)
ex: 10X x 10X = 100x (low power)
ex: 40X x 10X = 400X (high power)
Parfocal
objects stay in focus with change in objective
Name the Parts of the Microscope
ocular lens
objective lenses
mechanical stage
condenser centering screw
condenser lens
condenser iris diaphragm lever
adjustable field diaphragm
light source
stage adjustment knobs
illuminating knob
fine focus knob
course focus knob
objective nosepiece
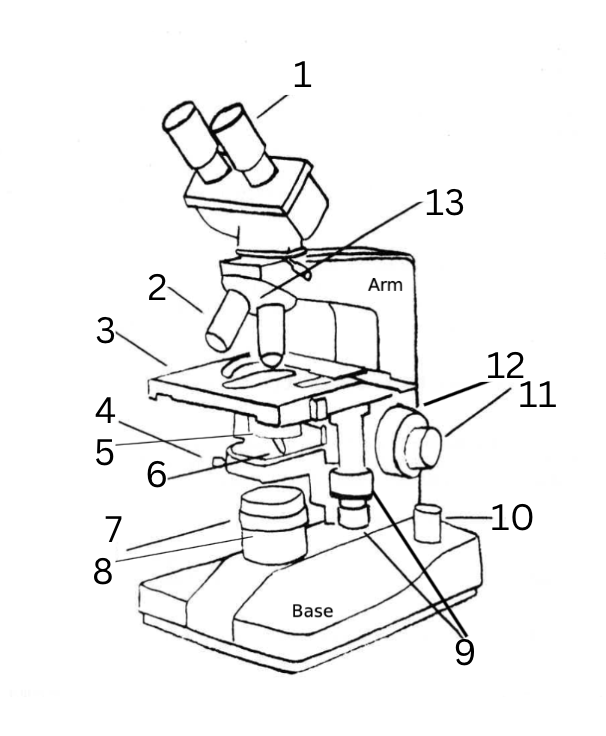
Microscope Functions
mechanical stage: rests slide, adjusts the position of the slide for viewing
ocular lenses: magnifies to see an image produced by the objective lens
objective lenses: capture incoming light and focus it at the image plane
condenser lens: gathers light and concentrates it into a beam to illuminate an object
iris diaphragm: adjust the amount of light that passes through the condenser
coarse focus knob: brings the specimen into approximate or near focus
fine focus knob: sharpen the focus of the image
light source: creates illumination for the slide
stage adjustment knob: controls the movement of the stage
arm: joins the base to the head and the ocular lens to the base
base: supports the entire microscope sructure
Plasma (Cell) Membrane Definition, Function and Picture
controls movement into/out of the cell
Cytoplasm Definition, Function and Picture
a gelatin-like substance, plus structural fibers and organelles that surrounds the nucleus
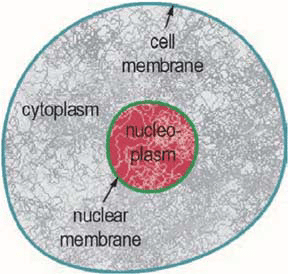
Nucleus Definition, Function and Picture
contains the genetic blueprint of the cell
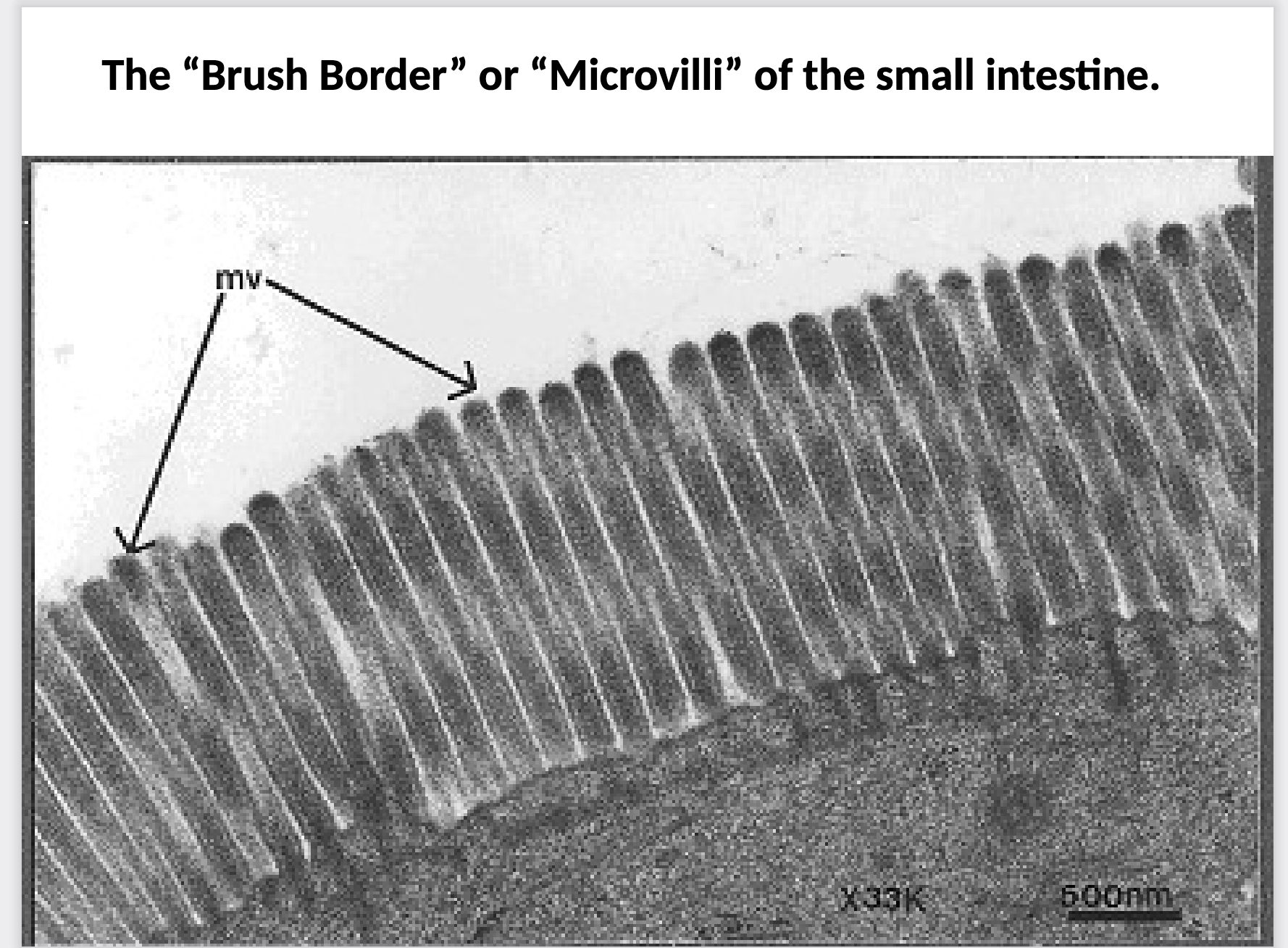
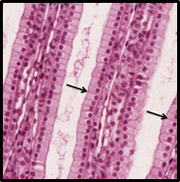
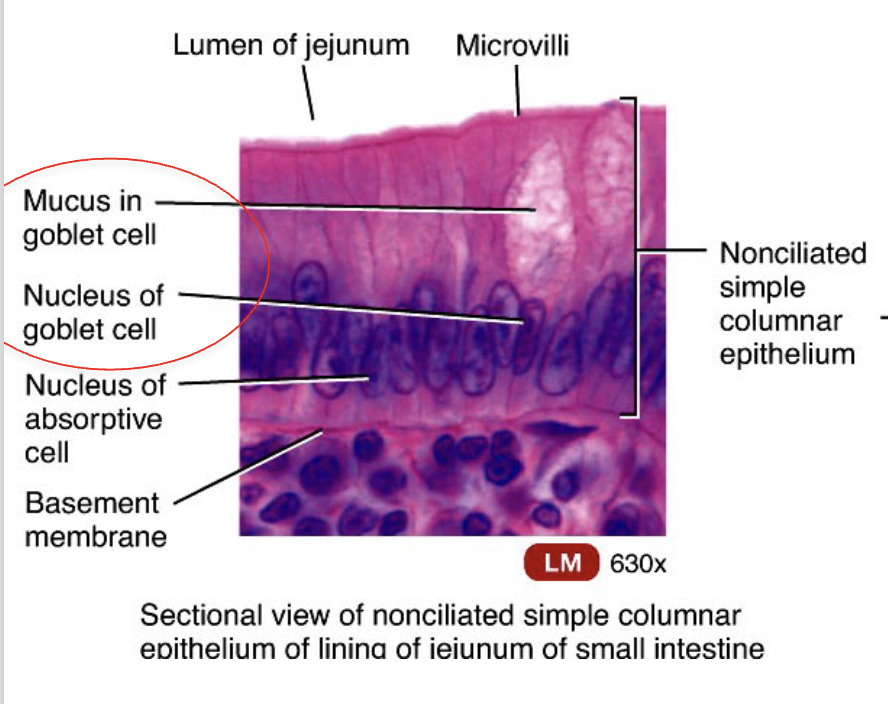
What cells do Microvili live on and what are their functions?
they live in the G.I. tract
they live on nonciliated simple columnar epithelium
increase surface area and is the site of absorption
looks like finger-like projections on apical surface (doesn’t move)
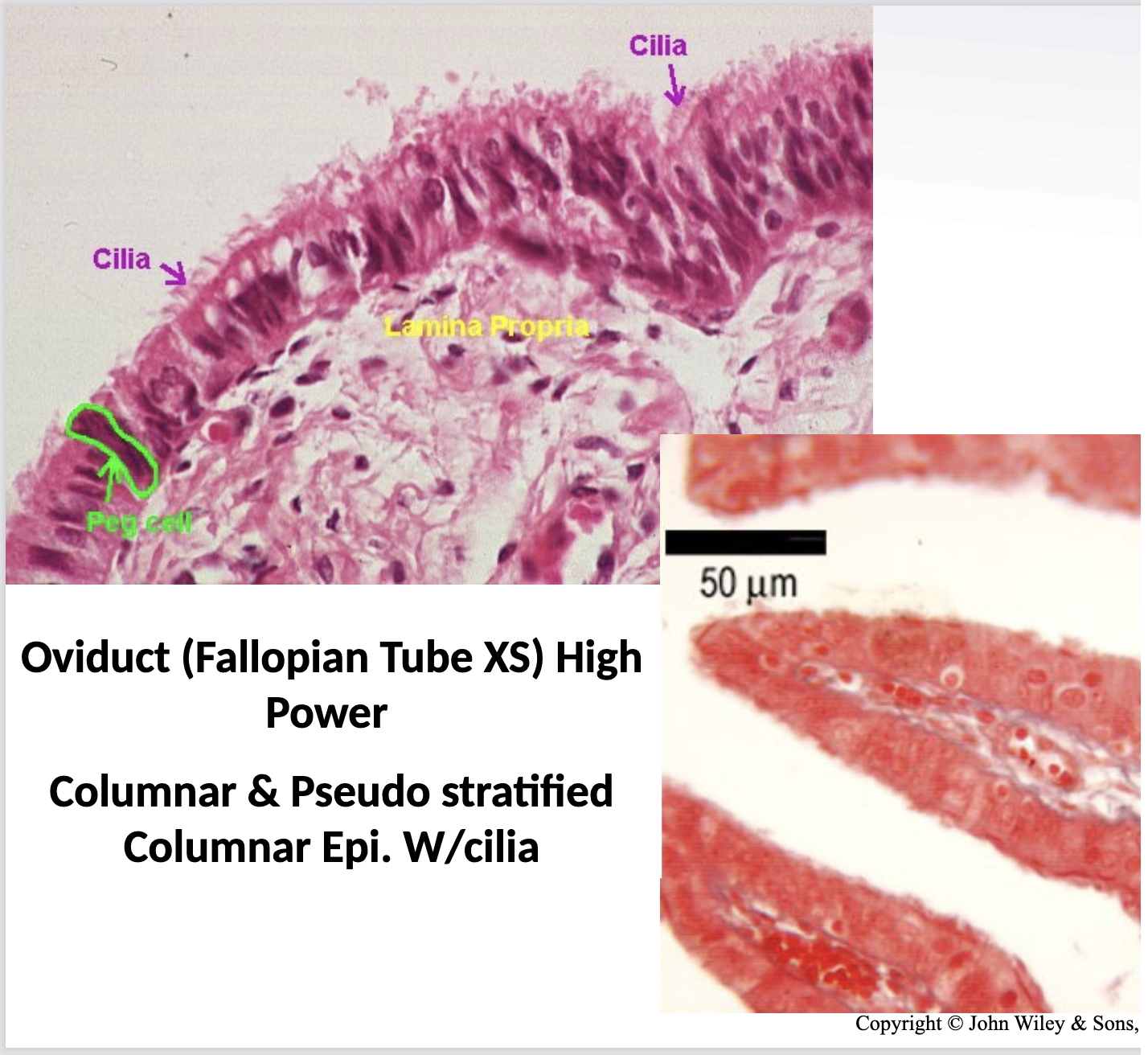
What cells do Cilia live on and what are their functions?
ciliated columnar epithelium
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
function is to move products
found in uterine tube and fallopian tube
looks like hair-like projections on apical surface (moves)
What cells do Flagellum live on and what are their functions?
sperm, male reproductive tract
Avascular Def
without vessels
all epithelial tissue is avascular
cartilage and tendons avascular
Vascular Def
with vessels
mostly all connective tissue is vascular
Epithelium Def and Functions
all epithelial tissue has an apical surface and an attached basal surface
avascular tissue composed of linked cells
function: lines surfaces and forms protective barrier. also good at secreting things like mucous, hormones and other substances
Basal Surface Def
attached to underlying CT
Apical Surface Def
free surface facing the inside of the organ - lumen, or surface of skin
Lumen Def
space
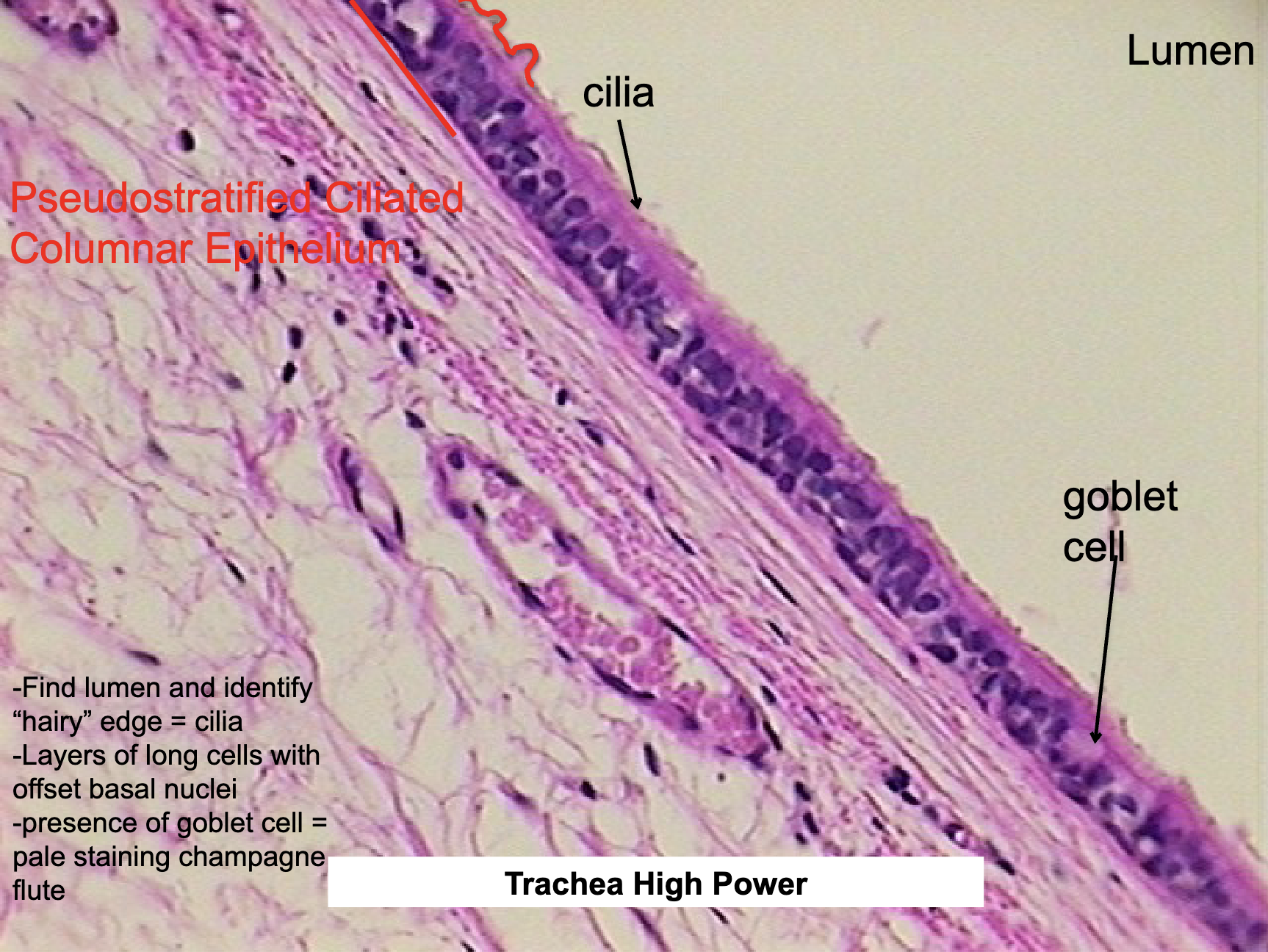
Goblet Cell Def
secretes mucus
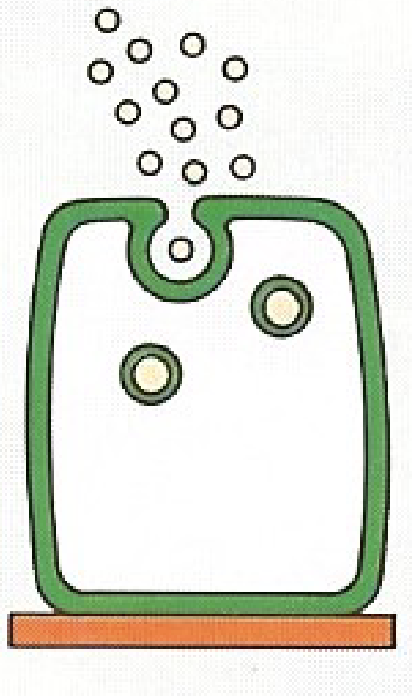
Merocrine Def
simplest form of exocytosis; vesicle dumps contents into lumen
sweat glands, salivary glands, pancreas
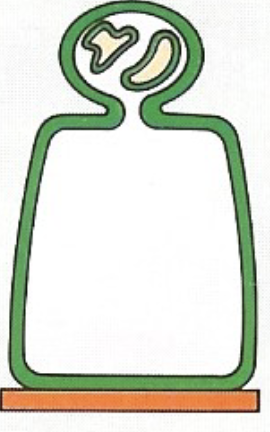
Apocrine Def
apical portion is shed (part of cell gets pinched off)
mammary glands, sweat glands in armpits and groin
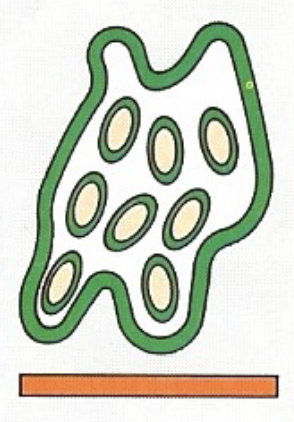
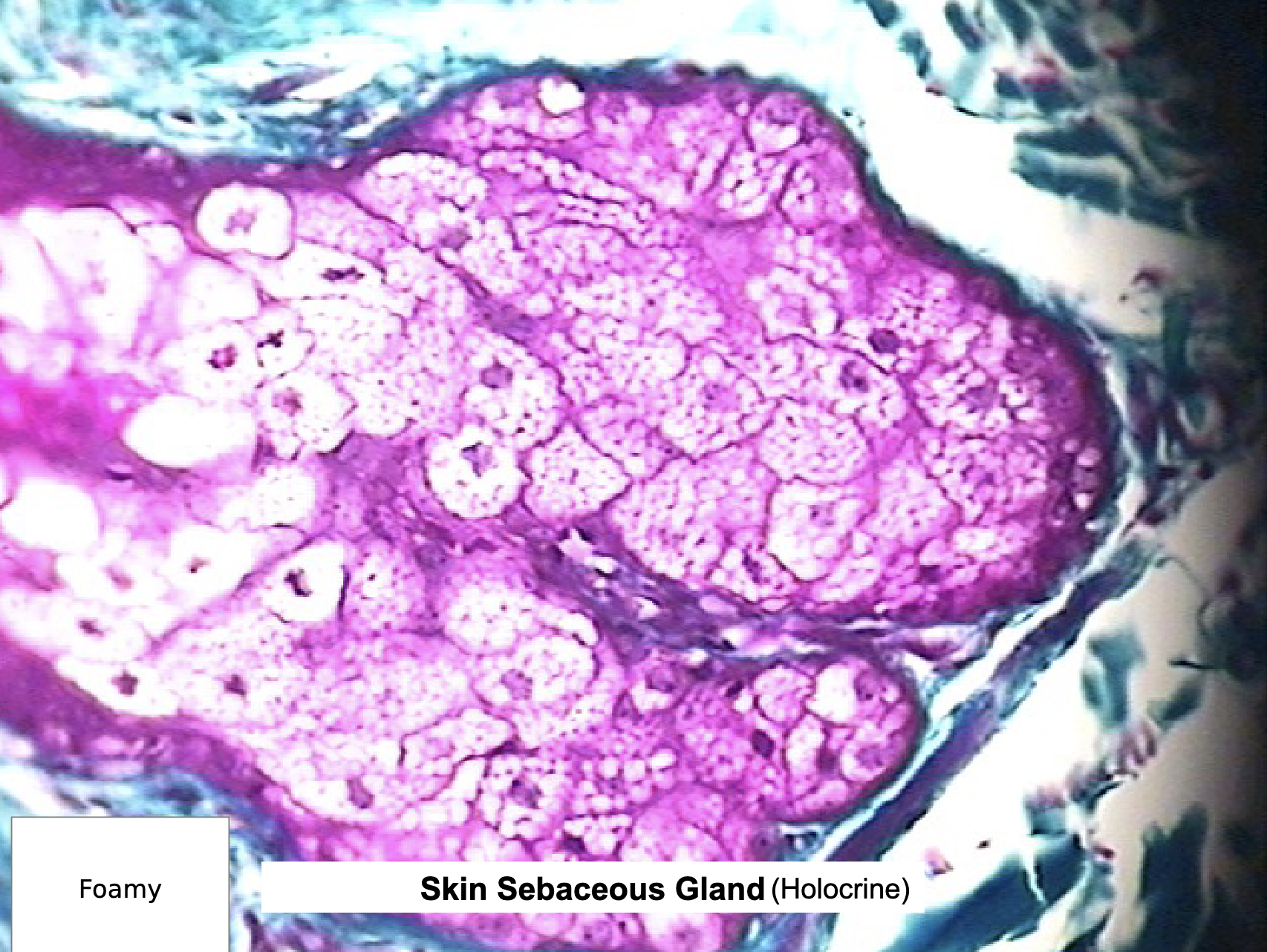
Holocrine Def
whole cell is lost
sebaceous glands
Endocrine Def
exocytosis via basement membrane
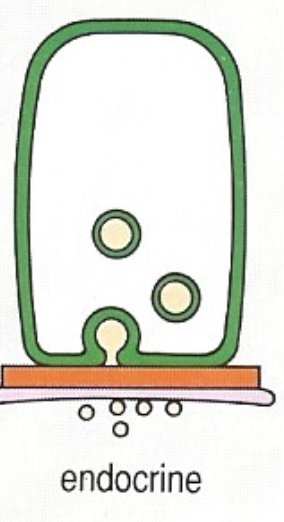
Where would you find Simple Squamous Epi. and what does it do?
lines blood vessels, alveoli of lungs, parts of kidney tubules
function: absorption, secretion, exchange
LINES ALL BLOOD VESSELS
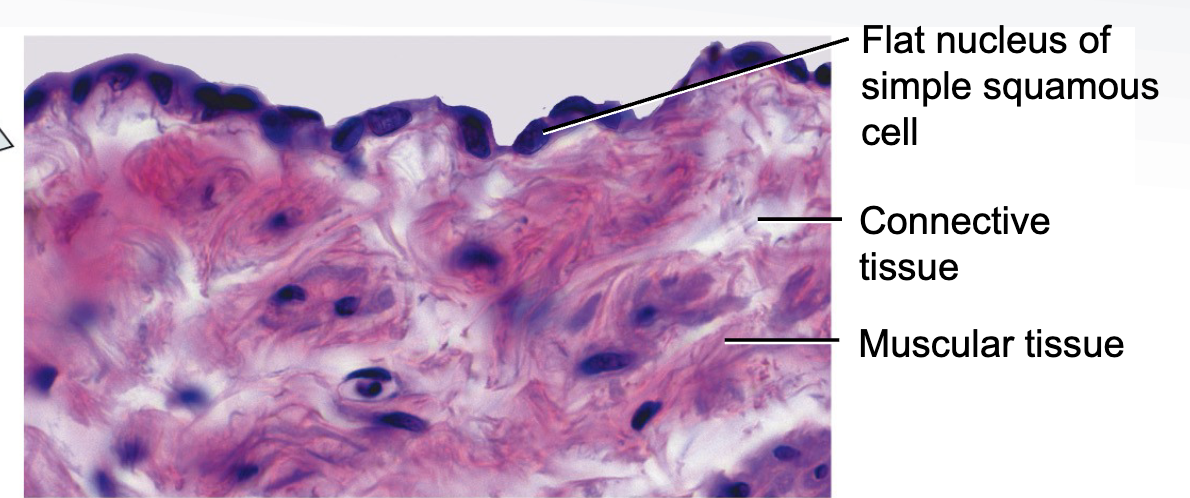
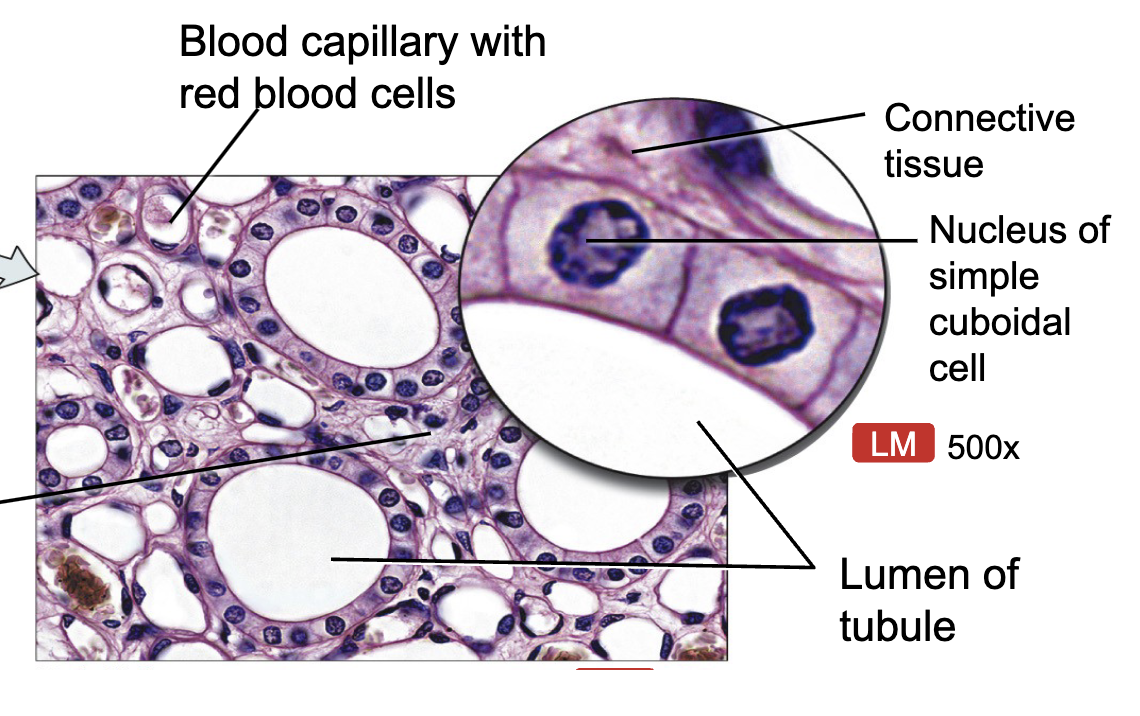
Where would you find Simple Cudoidal Epi. and what does it do?
parts of kidney tubules, ducts of glands, follicles of thyroid gland
function: absorption, secretion, exchange
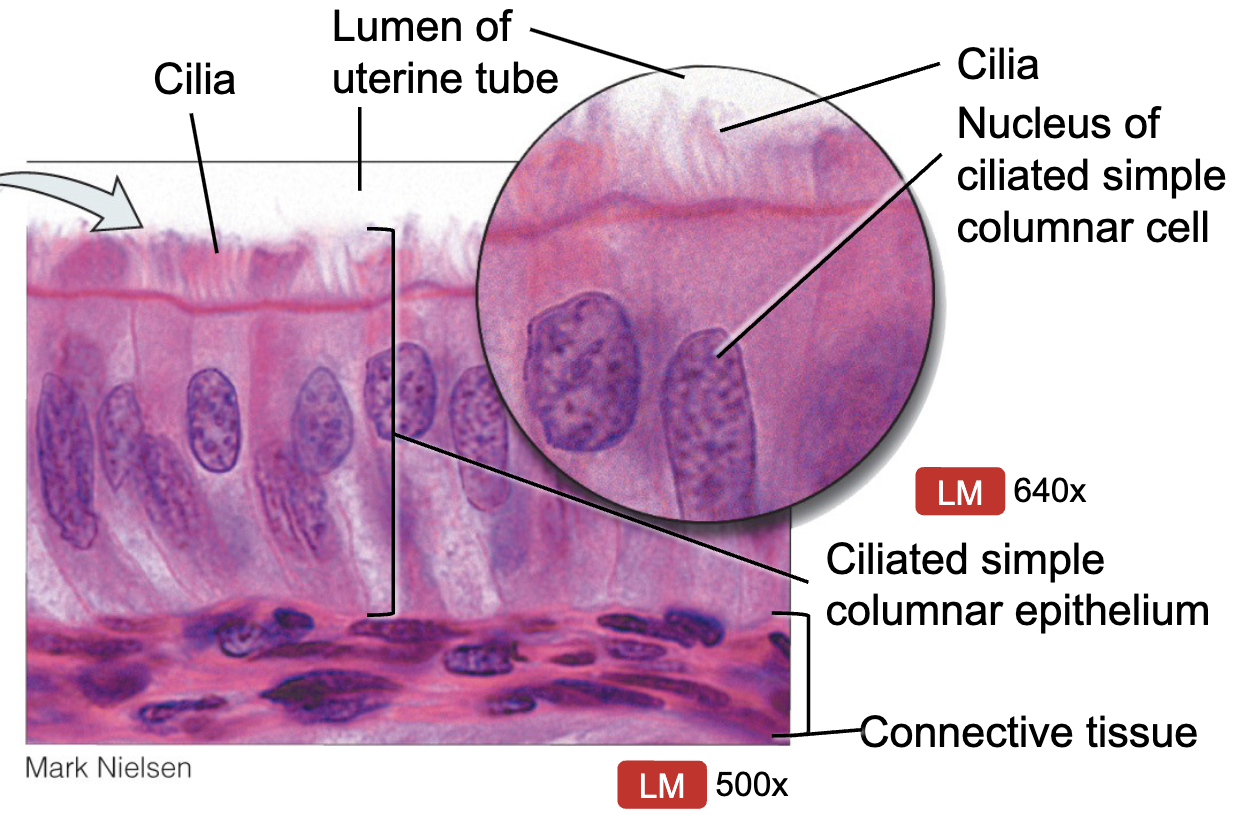
Where would you find Simple Ciliated Columnar Epi. and what does it do?
fallopian tubes (oviducts)
function: absorption, secretion, exchange
function of cilia: moves substances across apical surface
Where would you find Simple Columnar Epi. With Microvili and what does it do?
duodenum (small intestine)
function: absorption, secretion, exchange
function of microvili: increases surface area and aids absorption
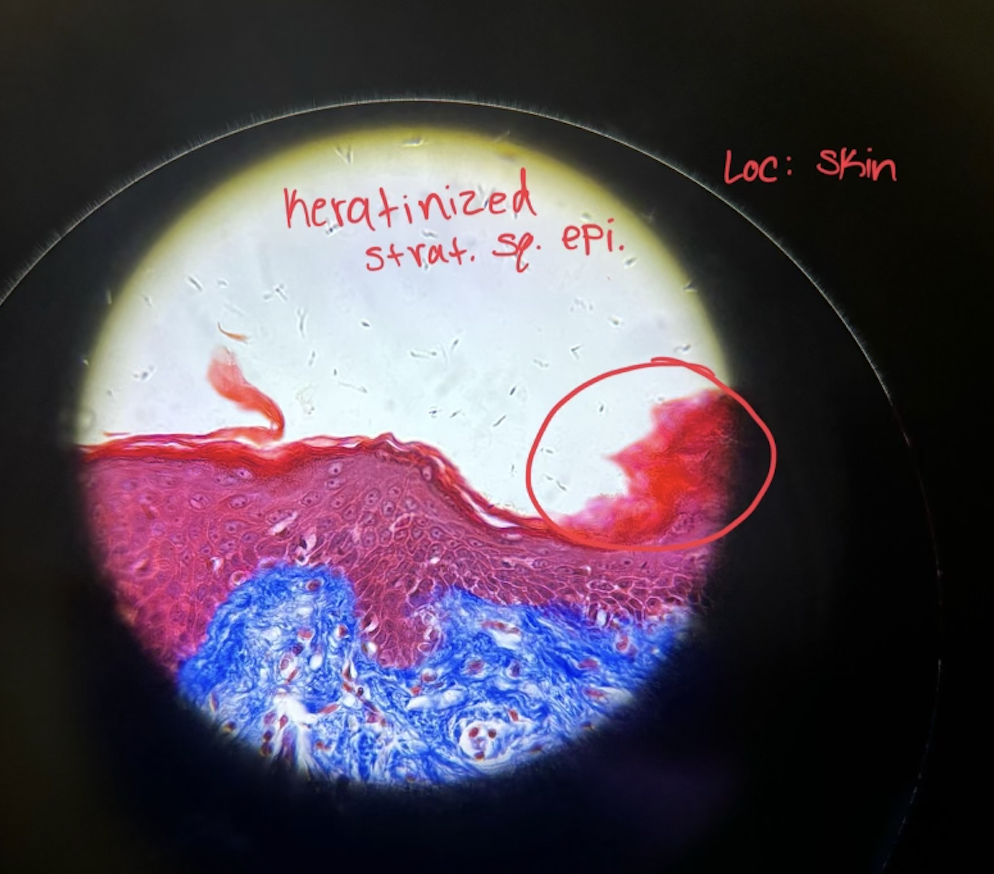
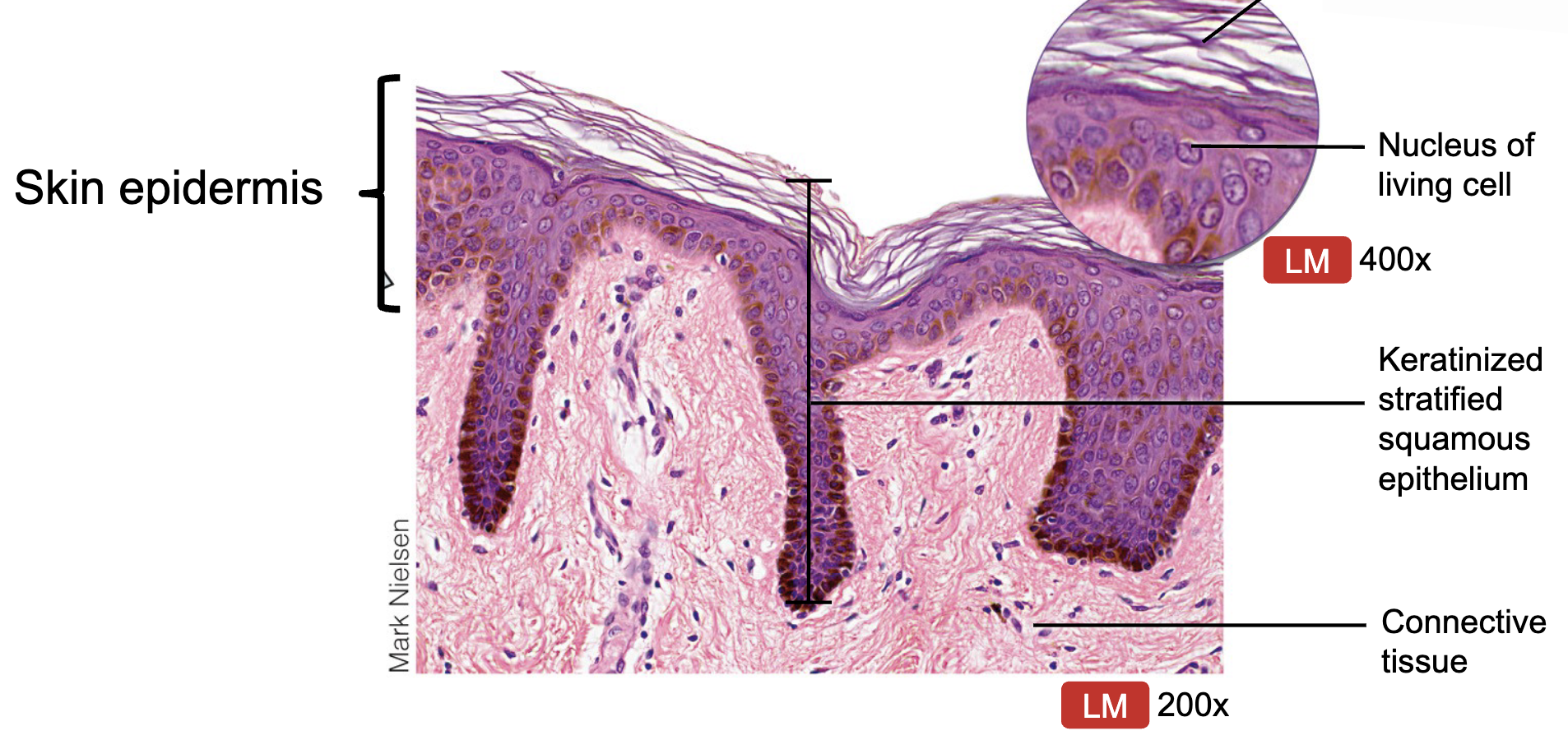
Where would you find Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epi. and what does it do?
epidermis of skin
function: protection, water resistance, resists abrasion
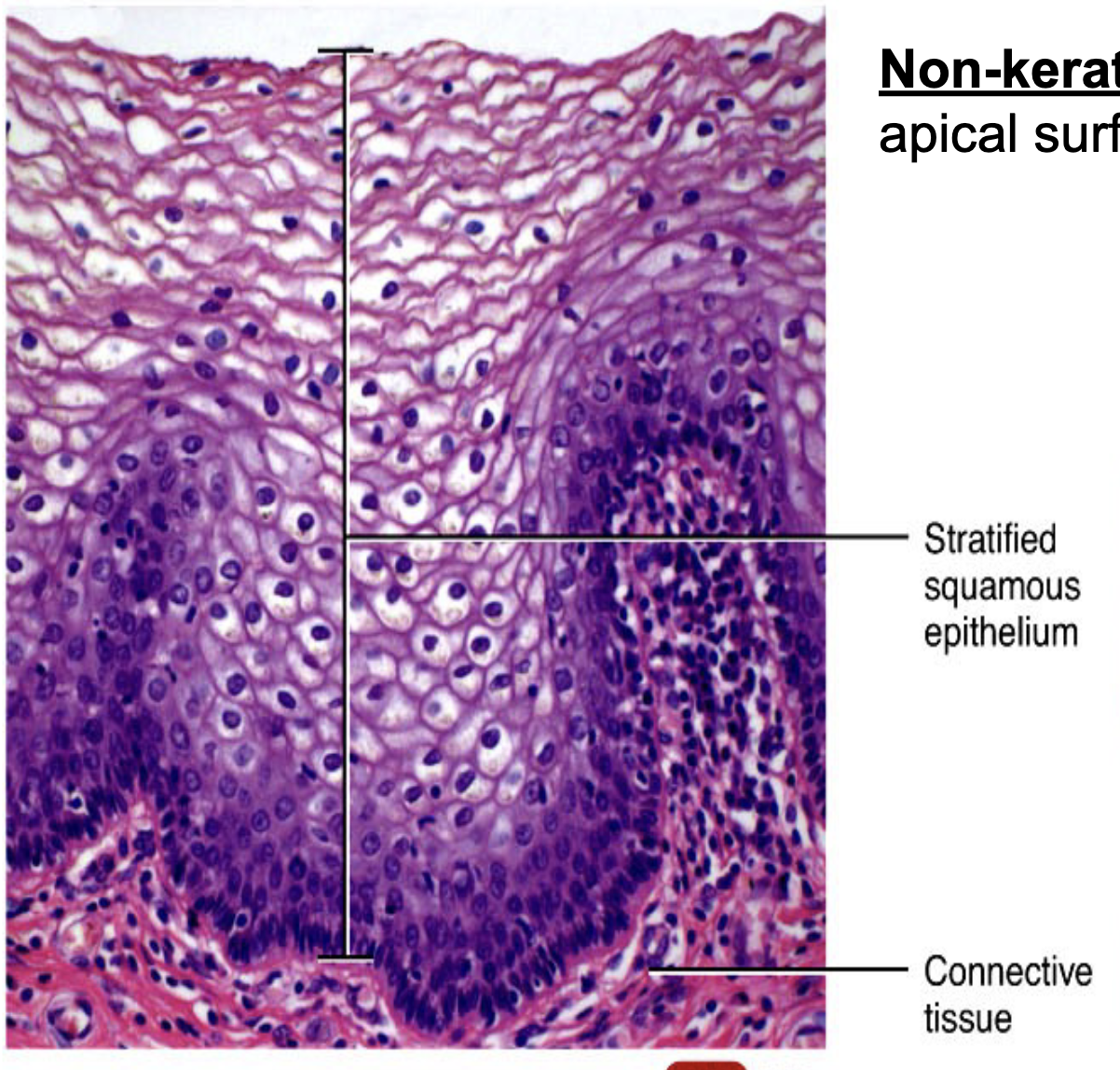
Where would you find Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epi. and what does it do?
inside of mouth, esophagous, vagina, anus, pharynx
function: protect from abrasion
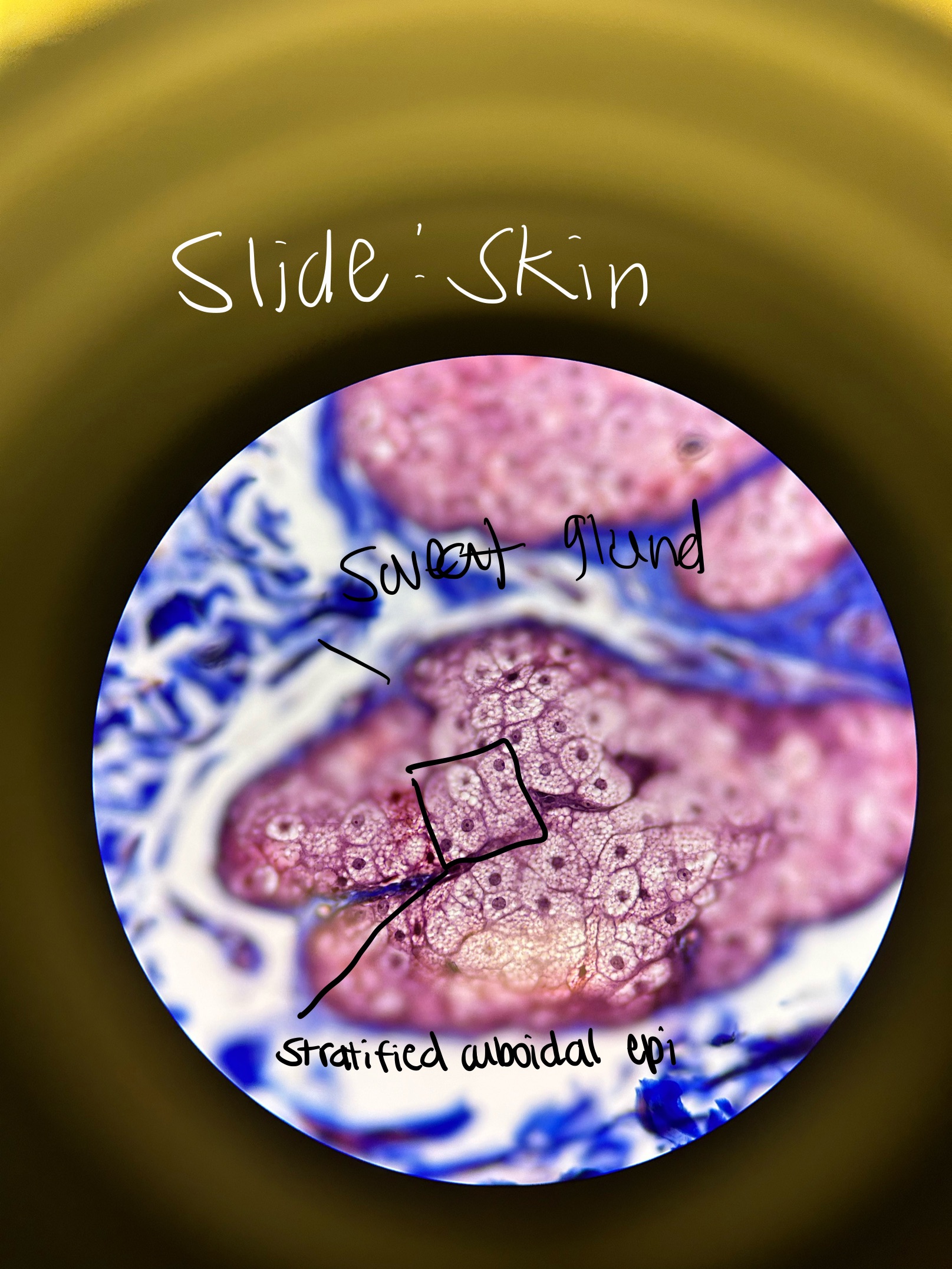
Where would you find Stratified Cuboidal Epi. and what does it do?
sweat glands, mammary glands, salivary glands
absorption, secretion, exchange
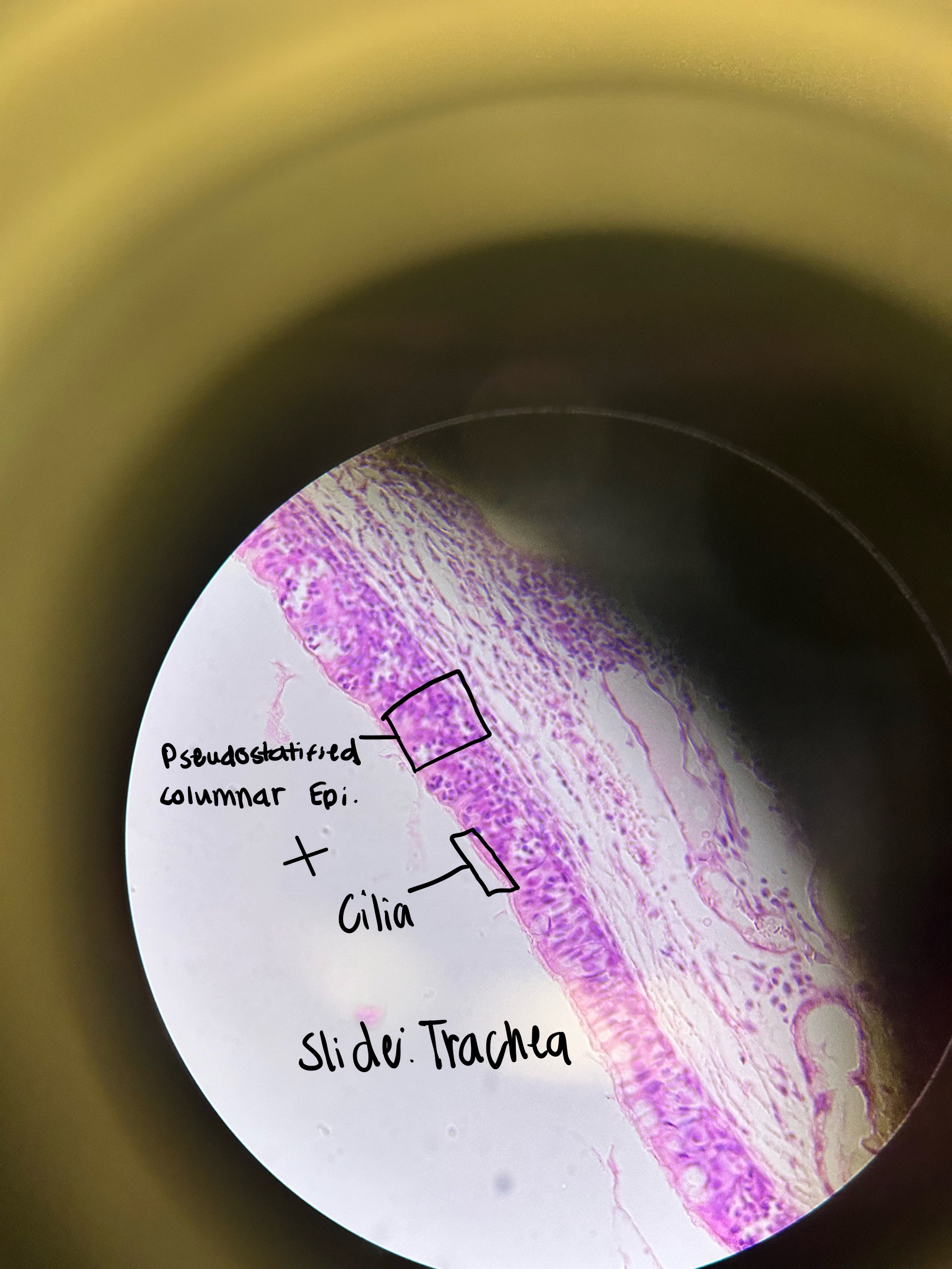
Where would you find Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epi. and what does it do?
trachea, nasal cavity, bronchi
absorption, secretion, exchange
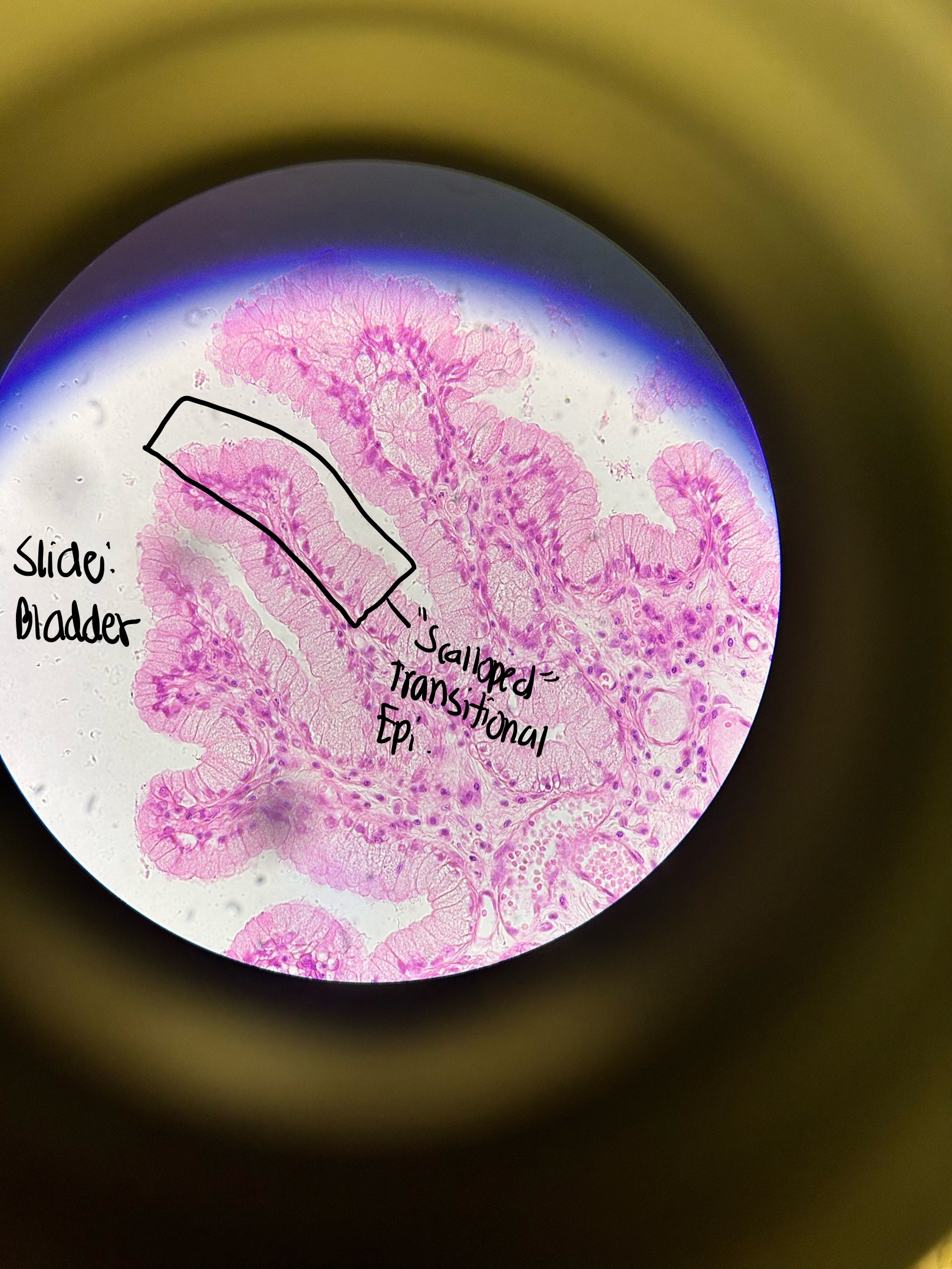
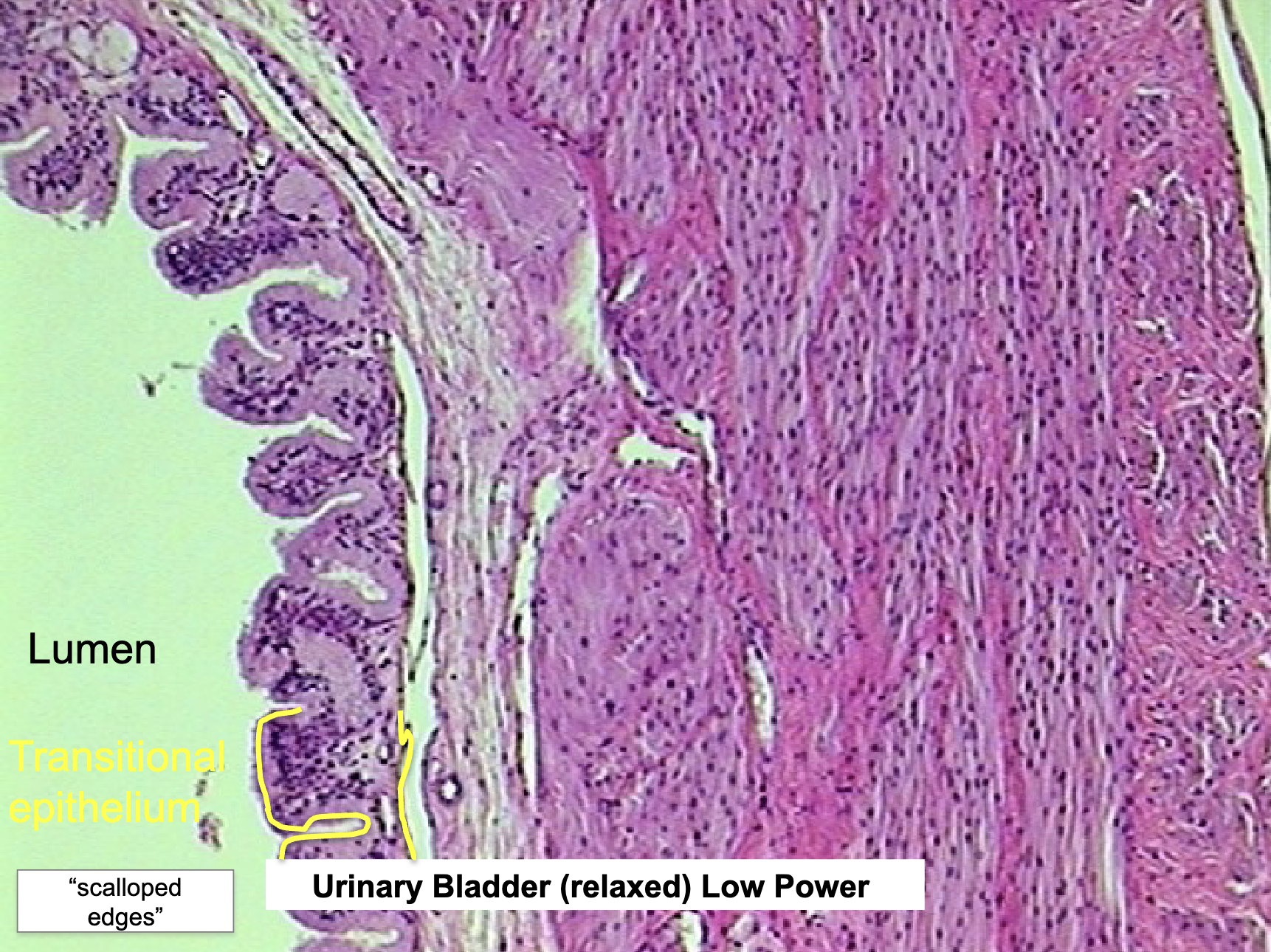
Where would you find Transitional Epi. and what does it do?
bladder, urethra, ureters, renal pelvis
allows for distension (holds and empties urine)
Mucous, Serous, Cutaneous Def
mucous: openings to outside
serous: no openings to outside
cutaneous: skin
Major Characteristics of Connective Tissue (CT)
functions: provides support, binds tissues together,
made up of three parts: cells, fibers, ground substance
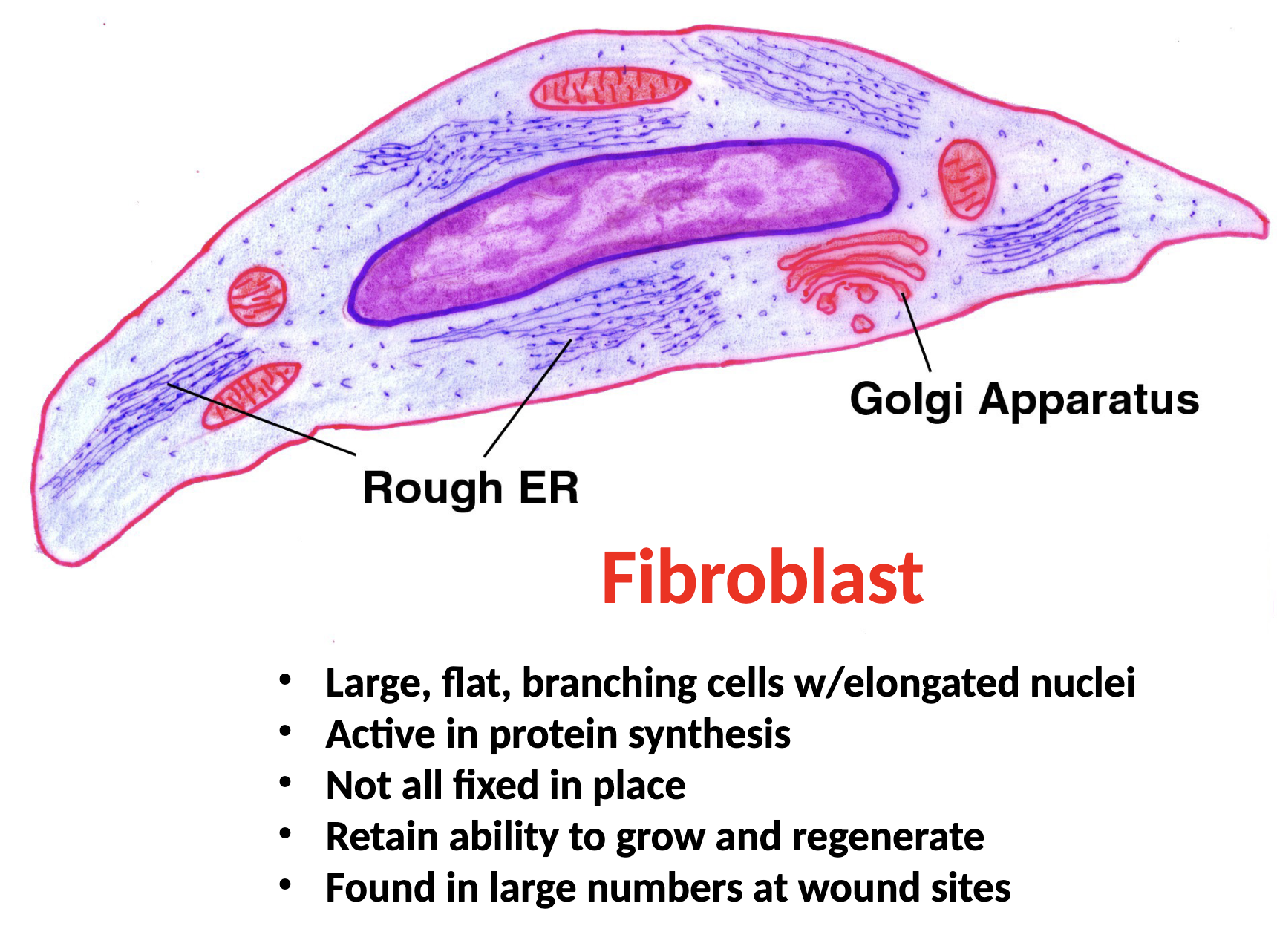
Fibroblasts Function
secrete protein fibers and ground substance
Adipocytes Function
stores triglycerides
Chondrocytes Function
make the various cartilagenous C.T.
Osteocytes Function
make bone
Erythrocytes (RBC)
transport gases
Leukocytes (WBC)
immunity
Loose Connective Tissue: Areolar CT Location and Function
beneath epithelial tissues all over body (deep to epithelium)
support
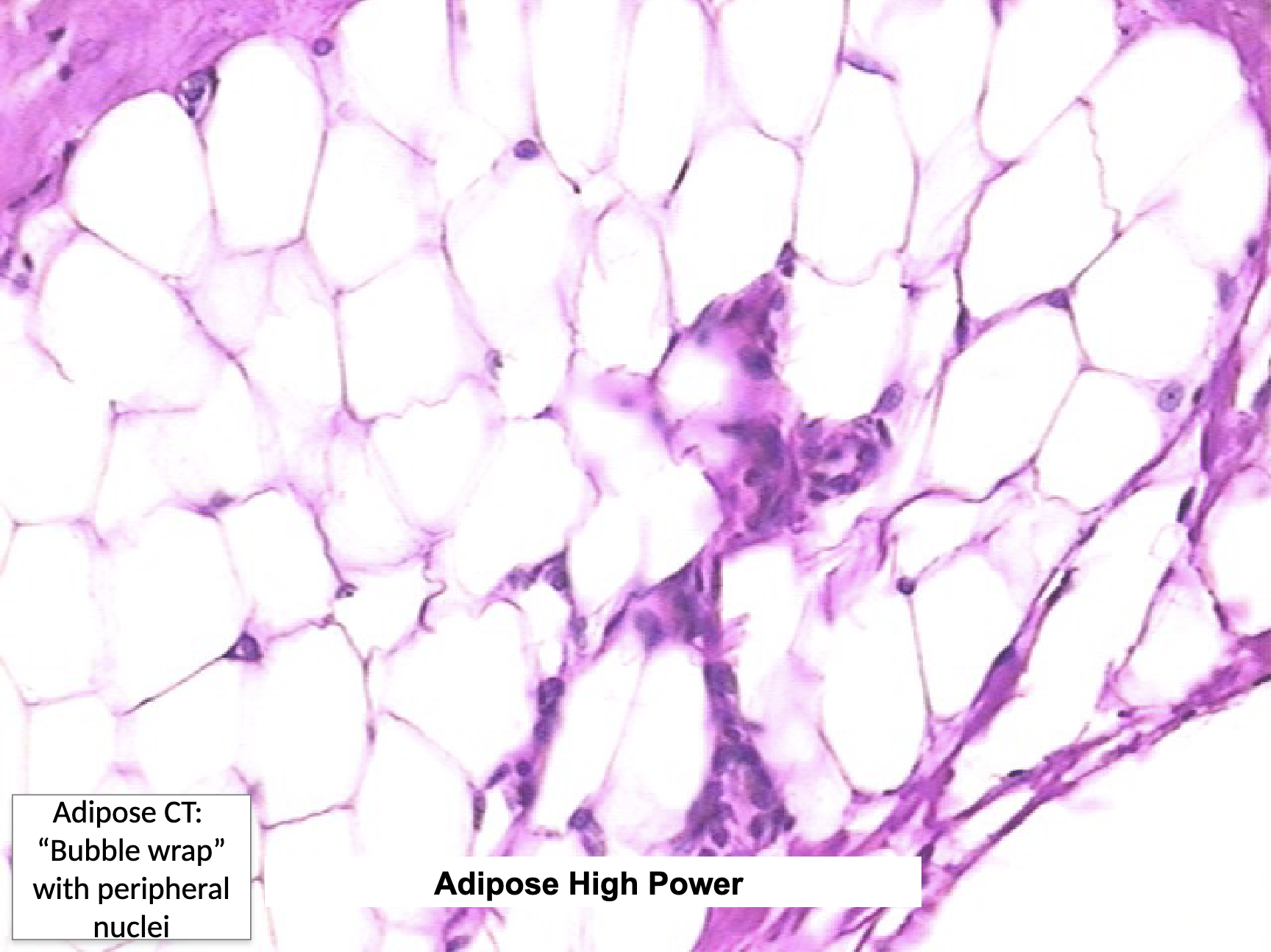
Loose Connective Tissue: Adipose CT Location and Function
subcutaneous layer deep to the skin, around organs and joints
protection (padding), energy storage, insulation
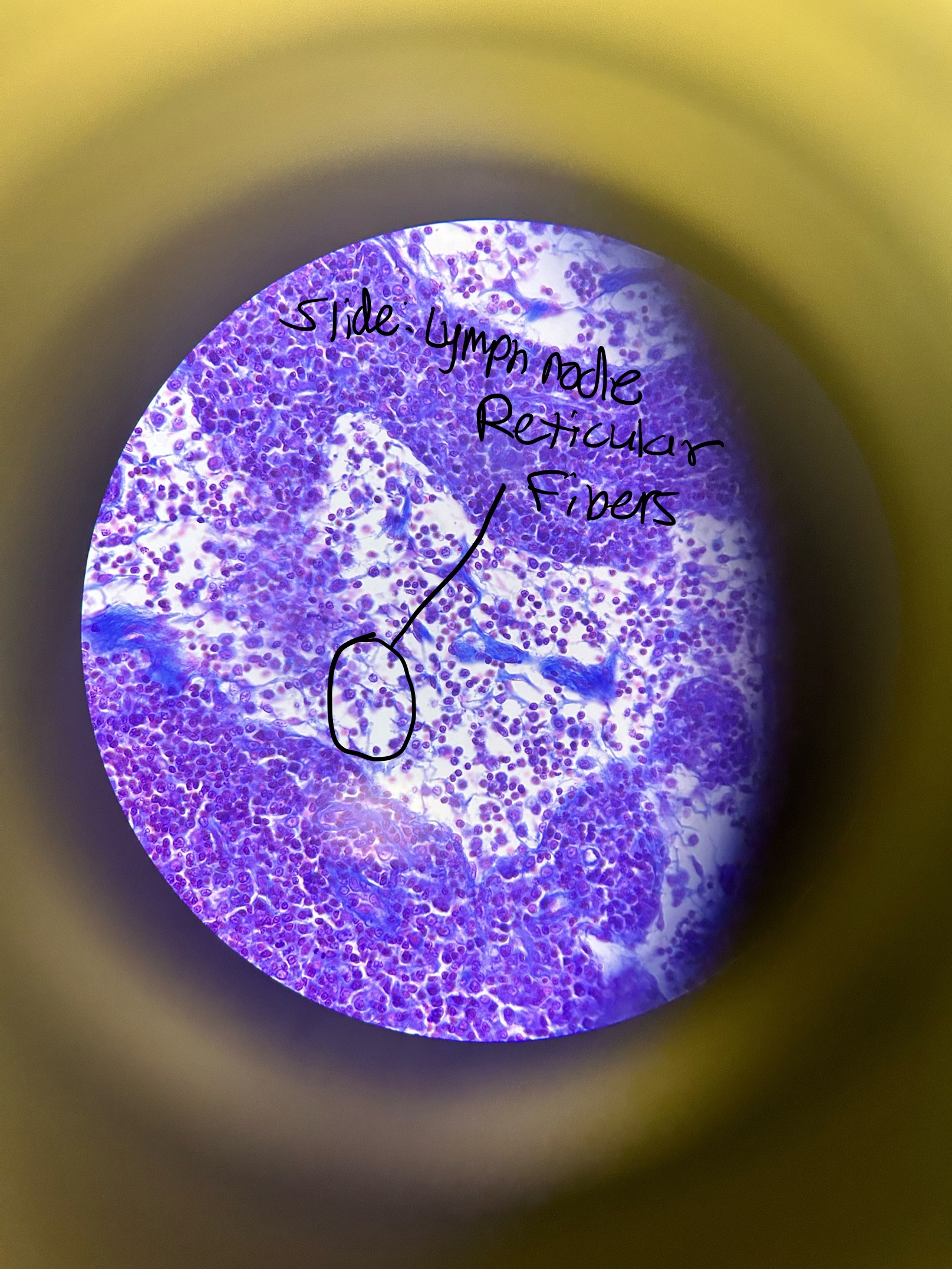
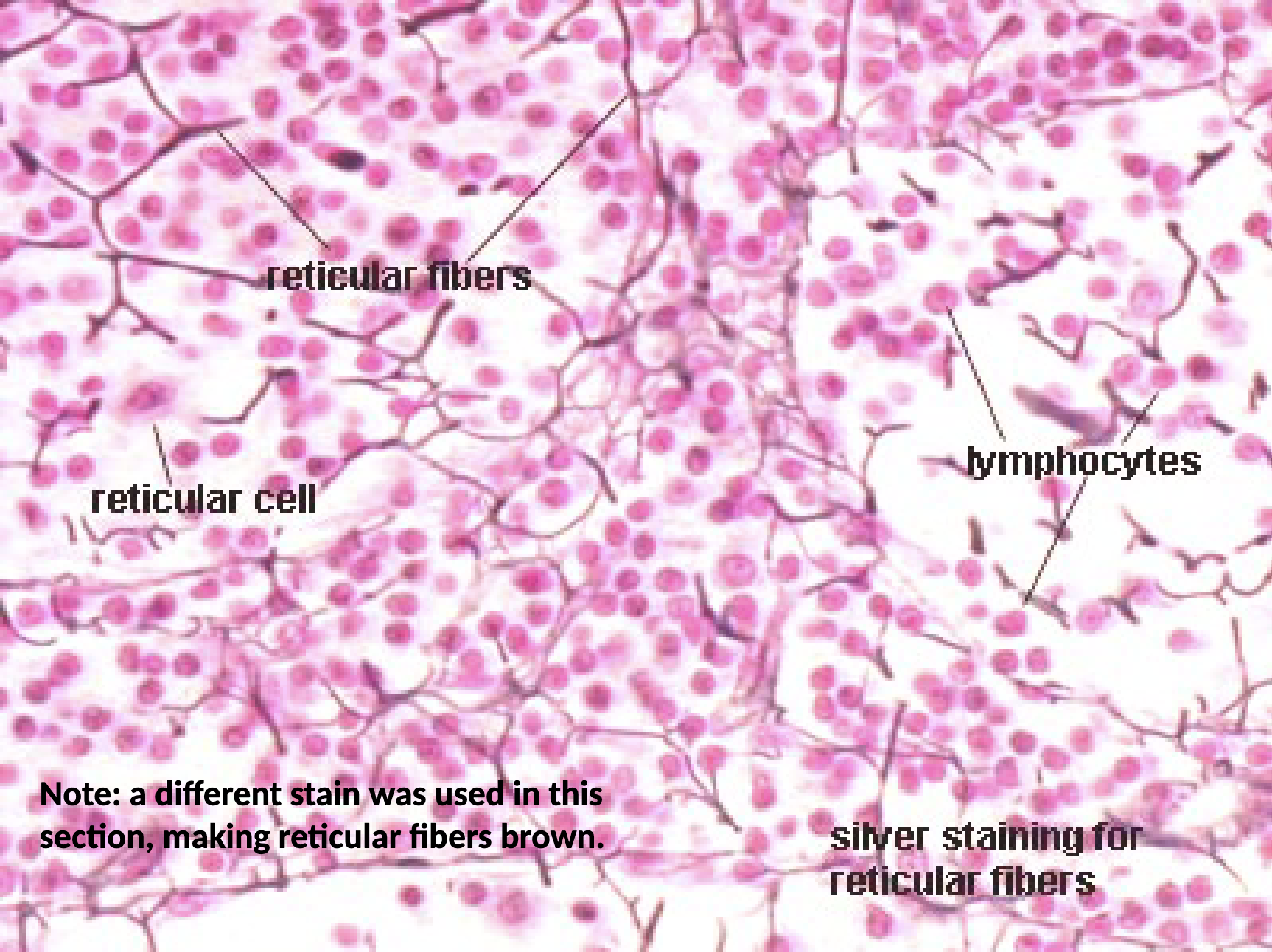
Loose Connective Tissue: Reticular CT Location and Function
lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, liver kidney
support
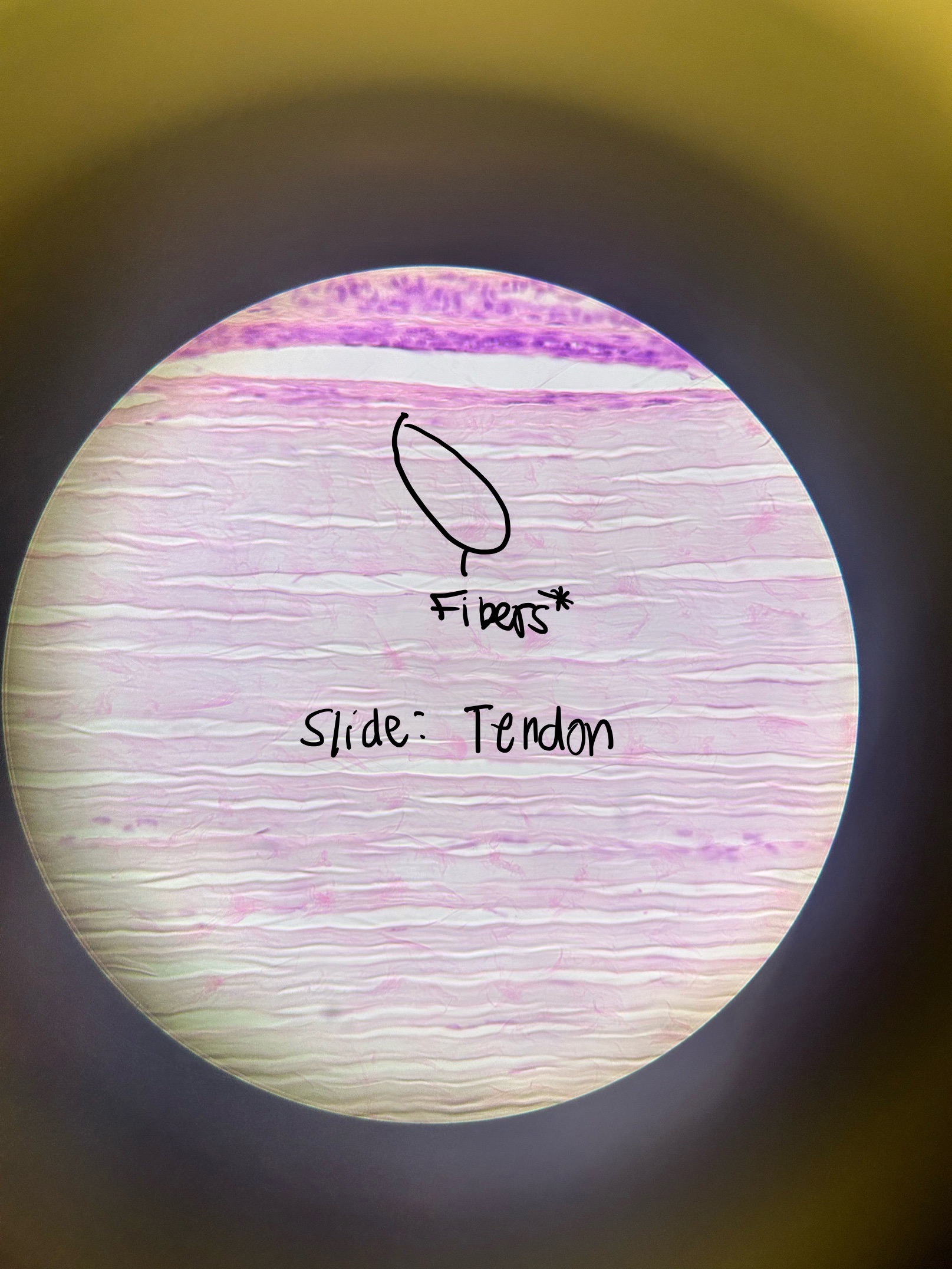
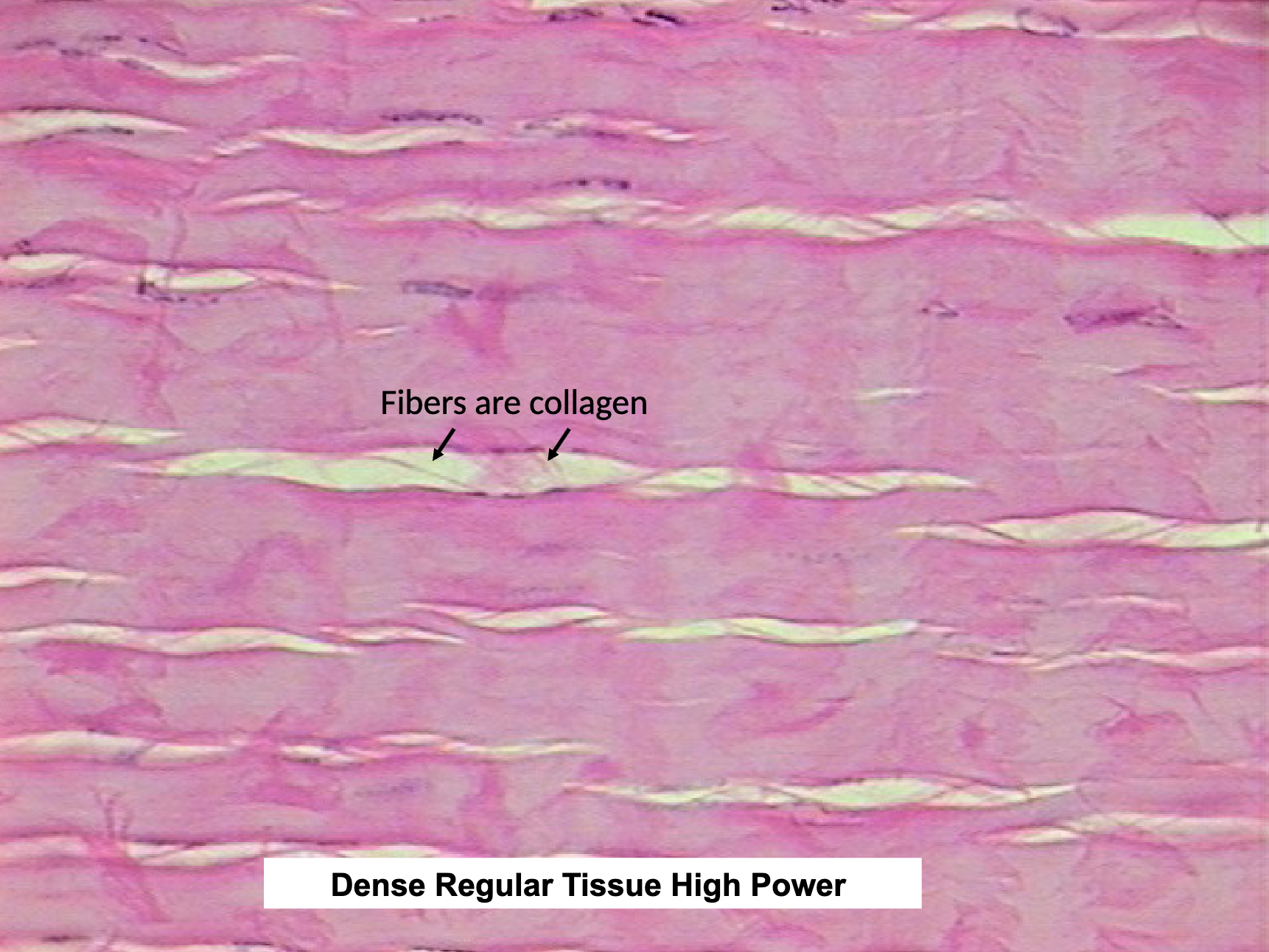
Dense Connective Tissue: Dense Regular CT Location and Function
tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses
strength in one direction
*LOOK FOR FIBERS
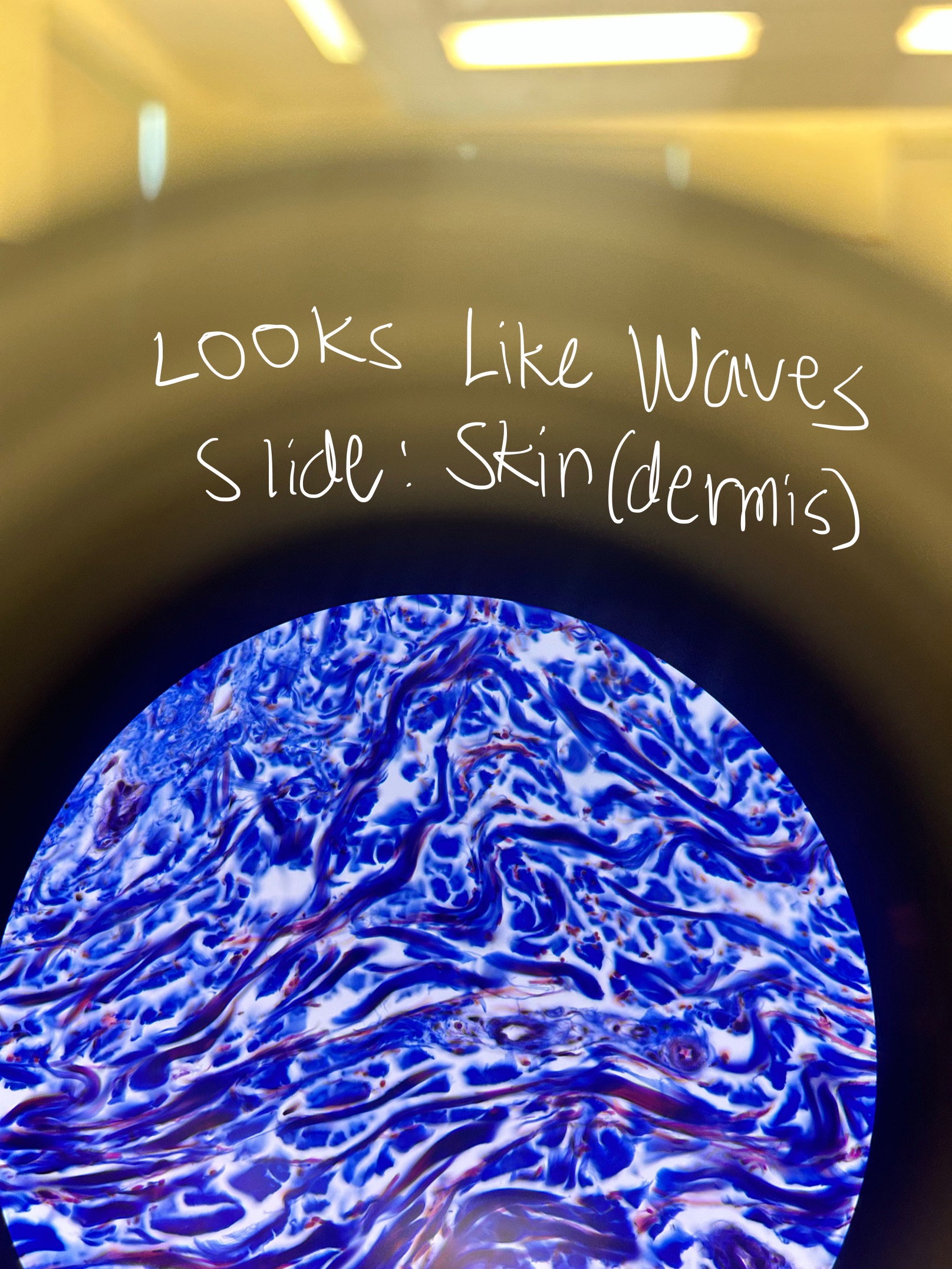
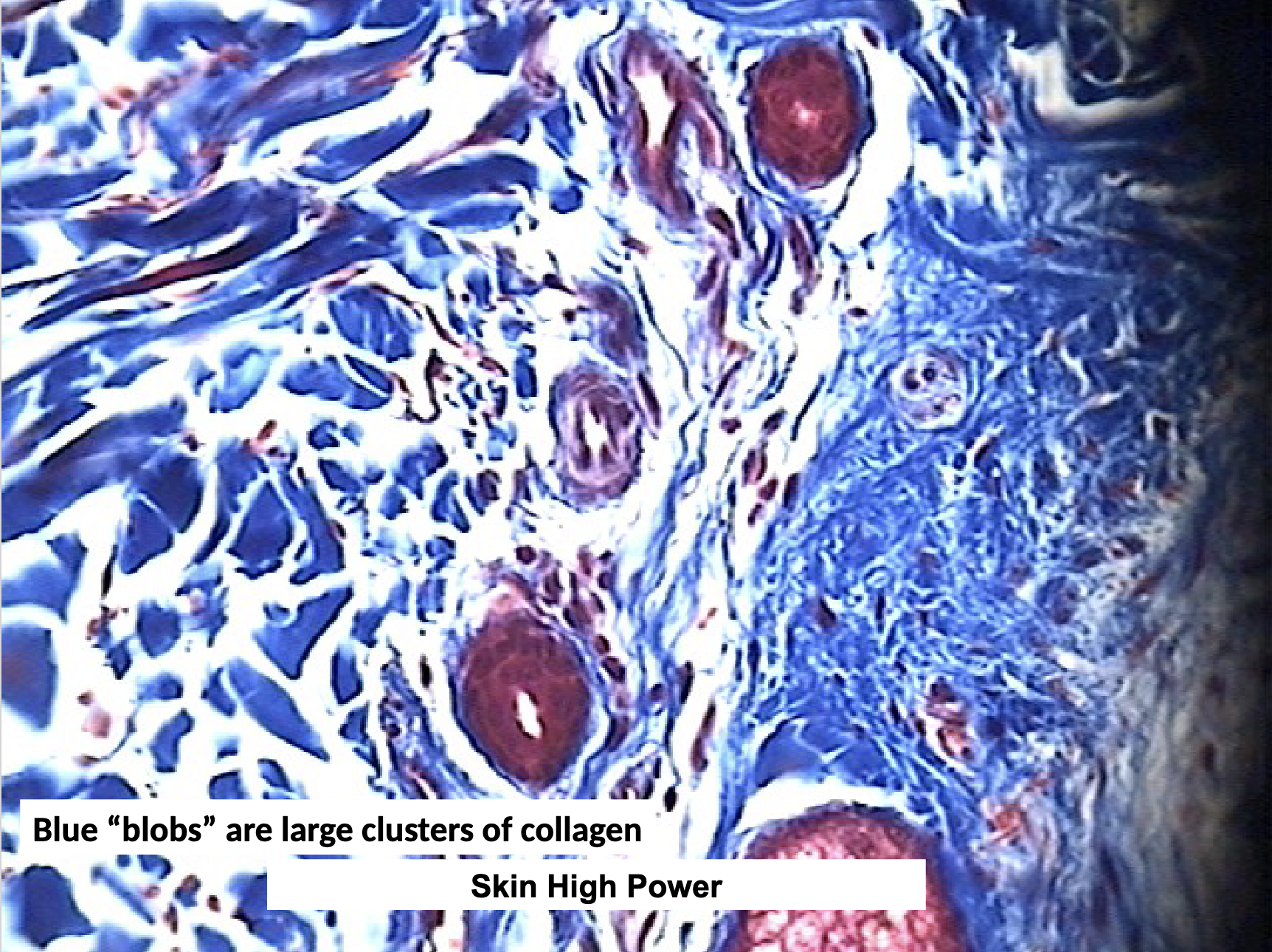
Dense Connective Tissue: Dense Irregular CT Location and Function
dermis of skin, periosteum, capsules of viseral organs, epi- and peri- mysium surrounding cells
strength in multiple directions
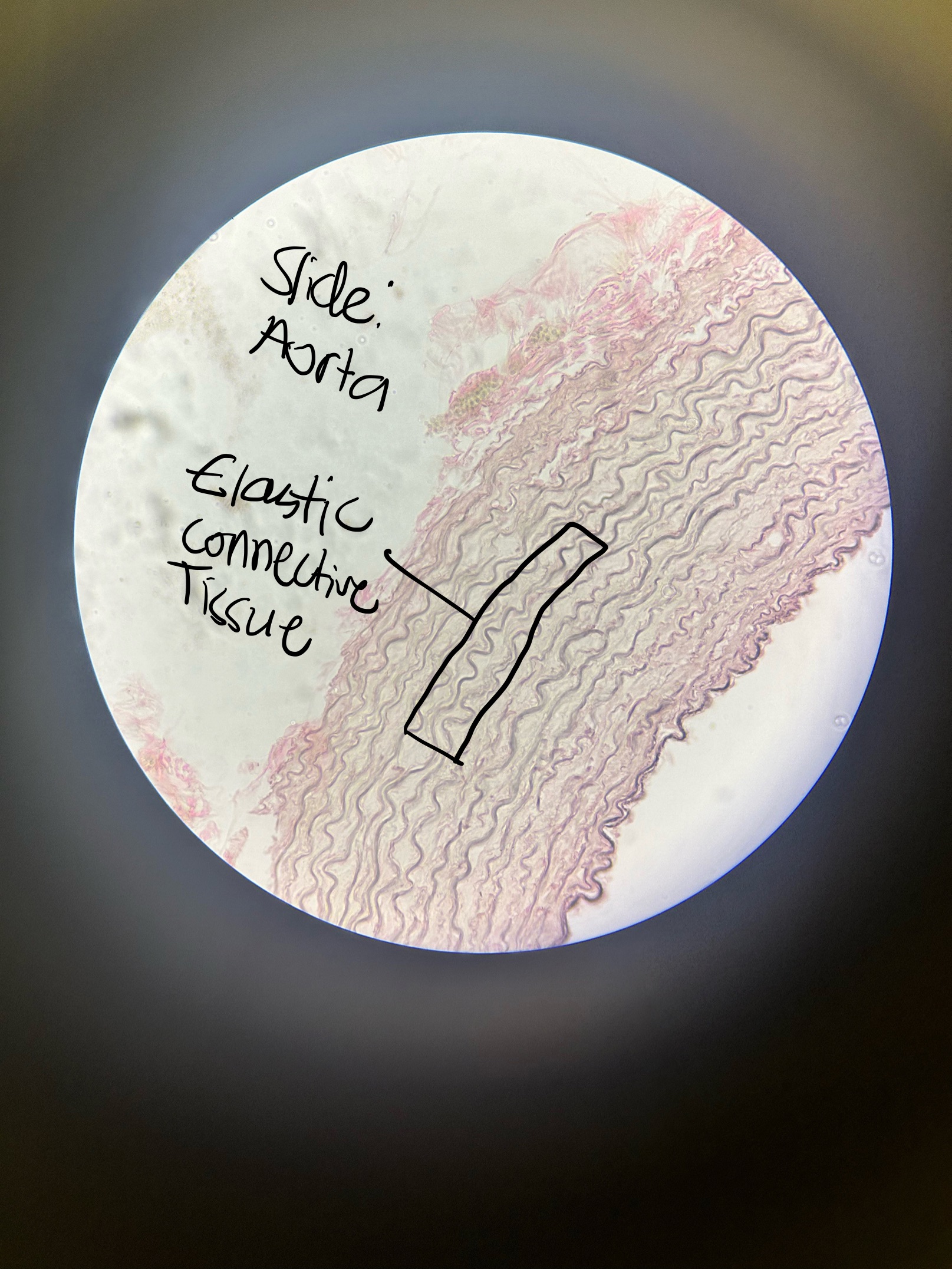
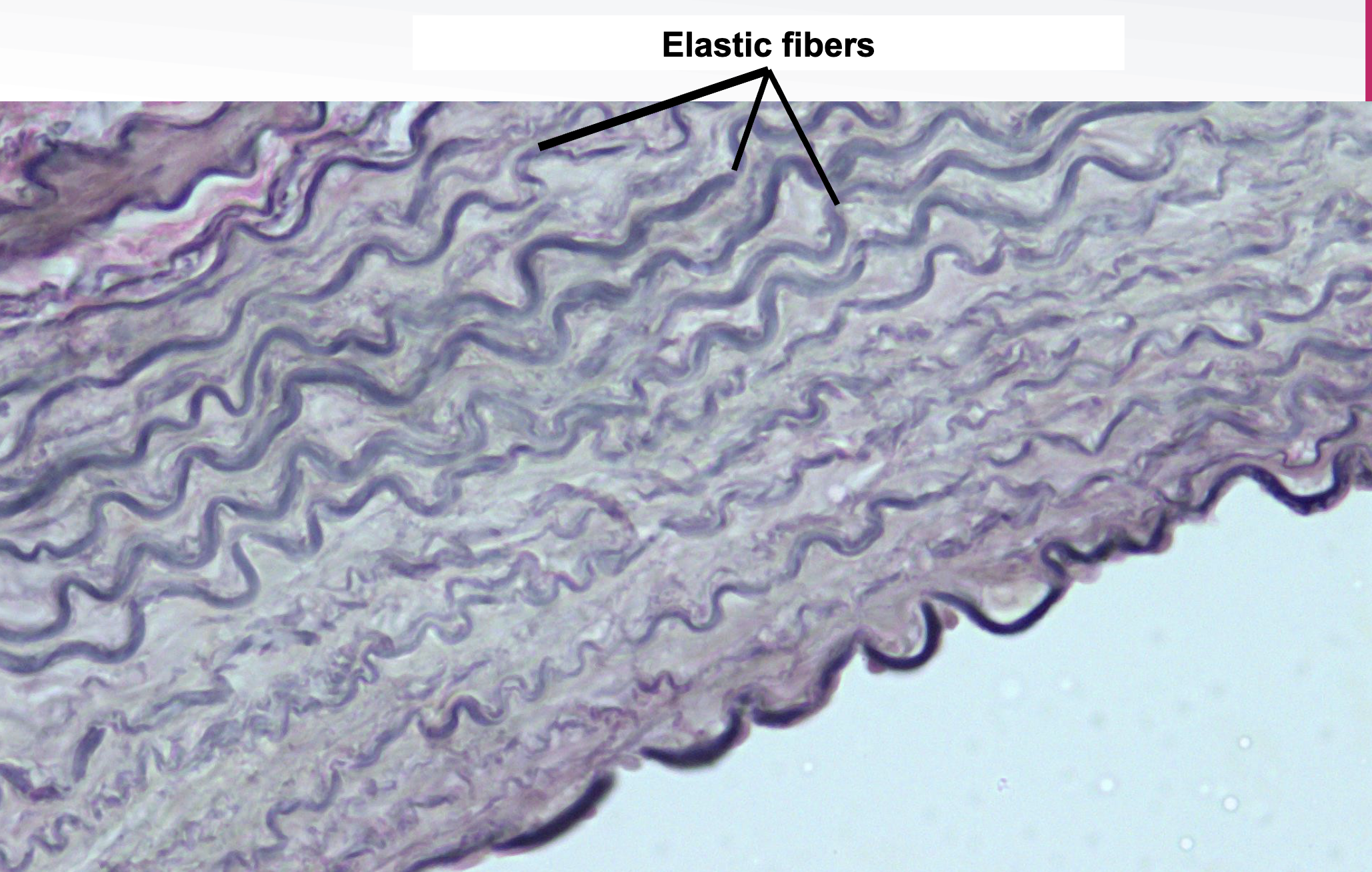
Dense Connective Tissue: Elastic CT Location and Function
arteries, lungs, skin, periodontal ligament, fetal tissues, connective tissues proper
stretch and recoil
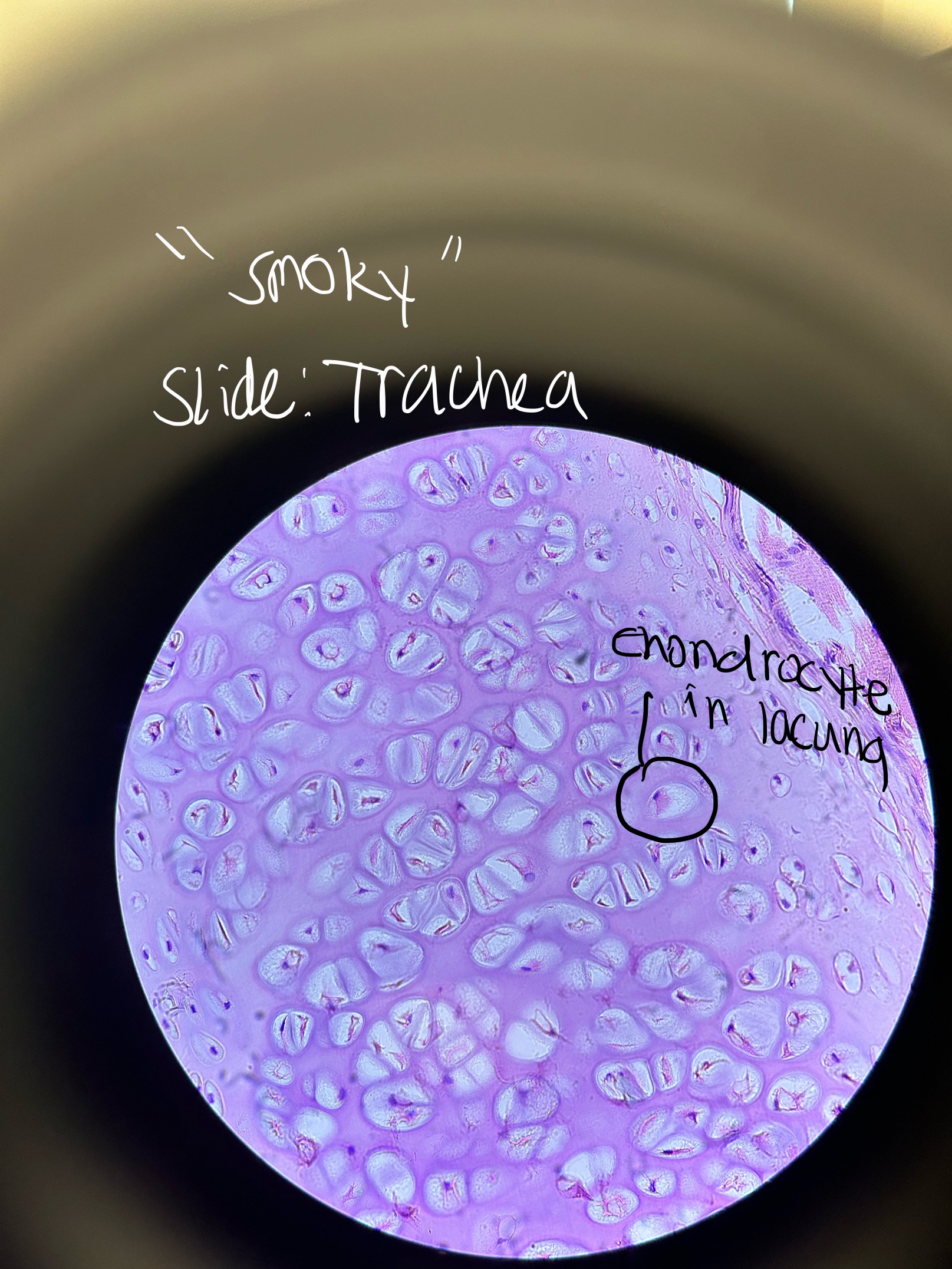
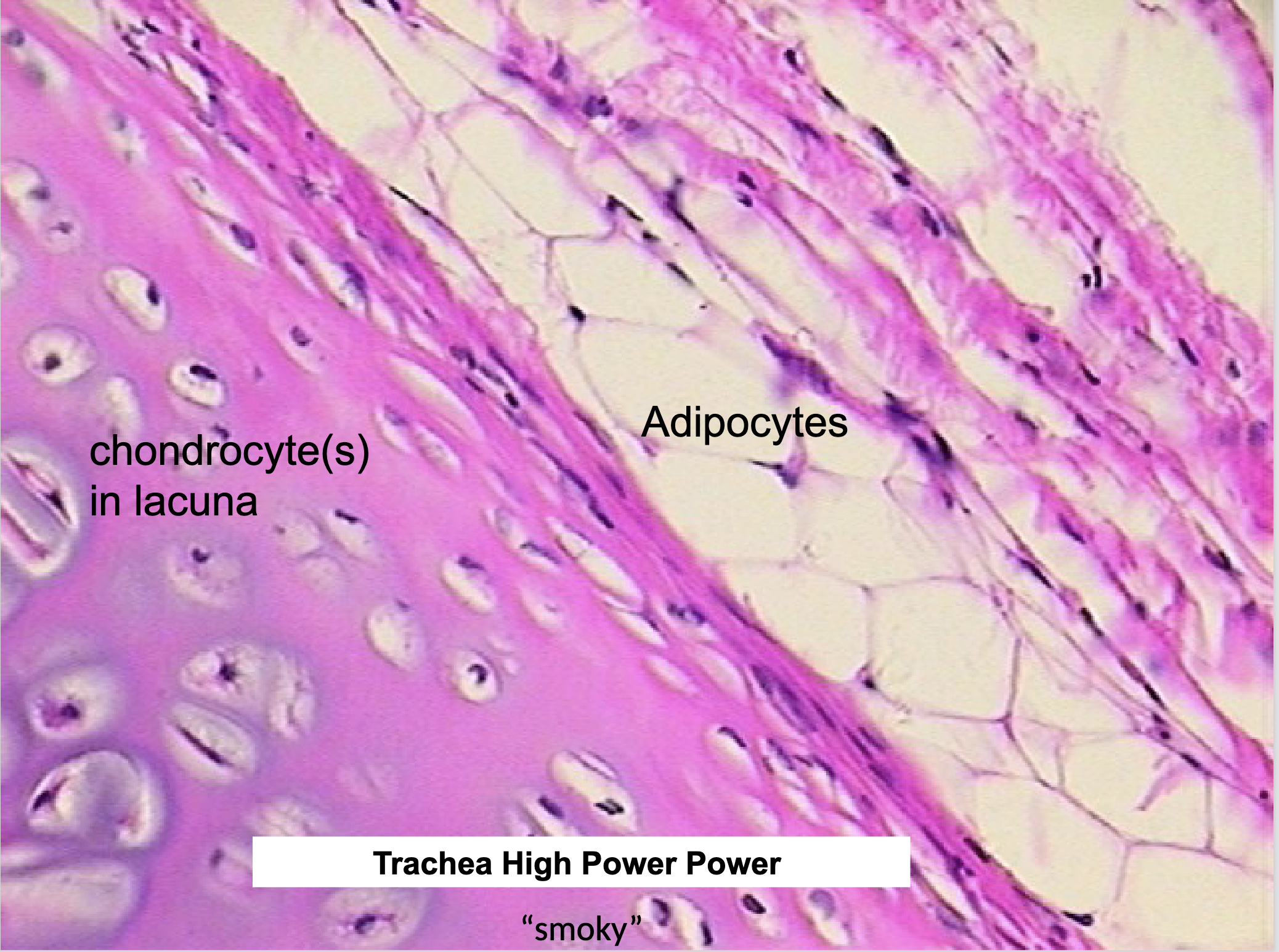
Where would you find Hyaline Cartilage and what does it do?
TRACHEA, ends of long bones, between ribs and sternum, nose, larynx, bronchi, embryonic skeleton
support
“smoky”
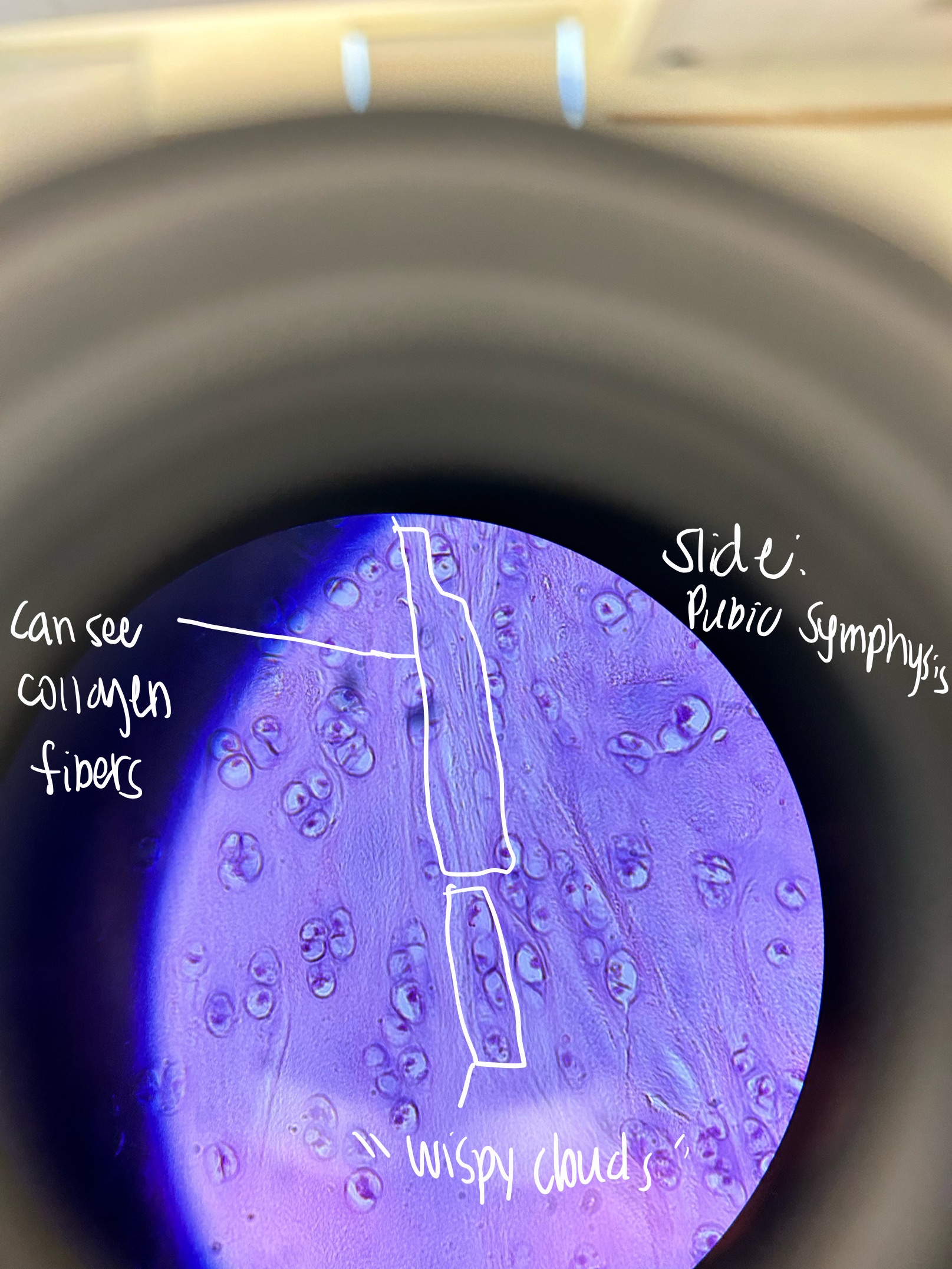
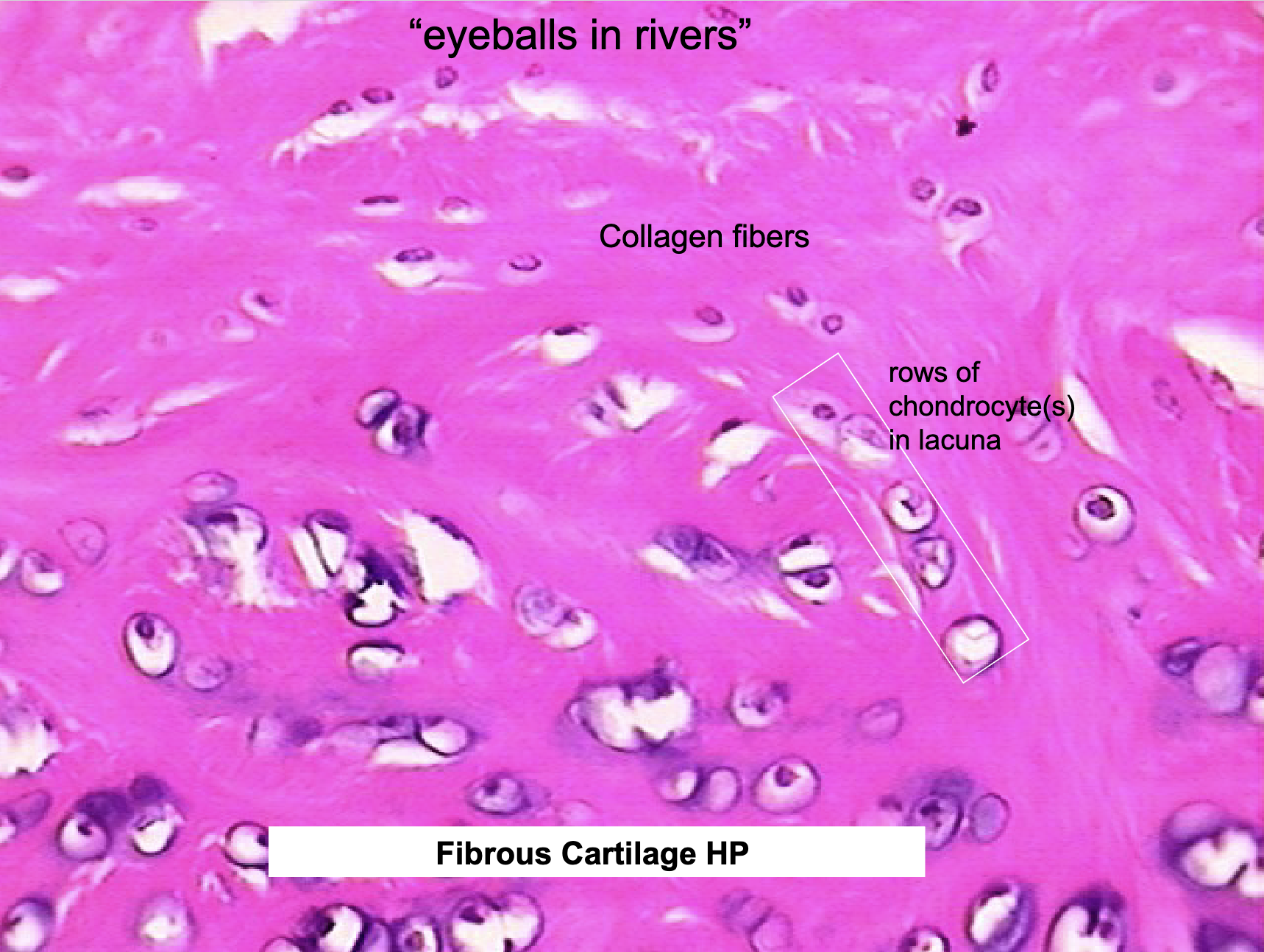
Where would you find Fibrocartilage Cartilage and what does it do?
pubic symphysis, intervertebral disks, knee joint
resists compression
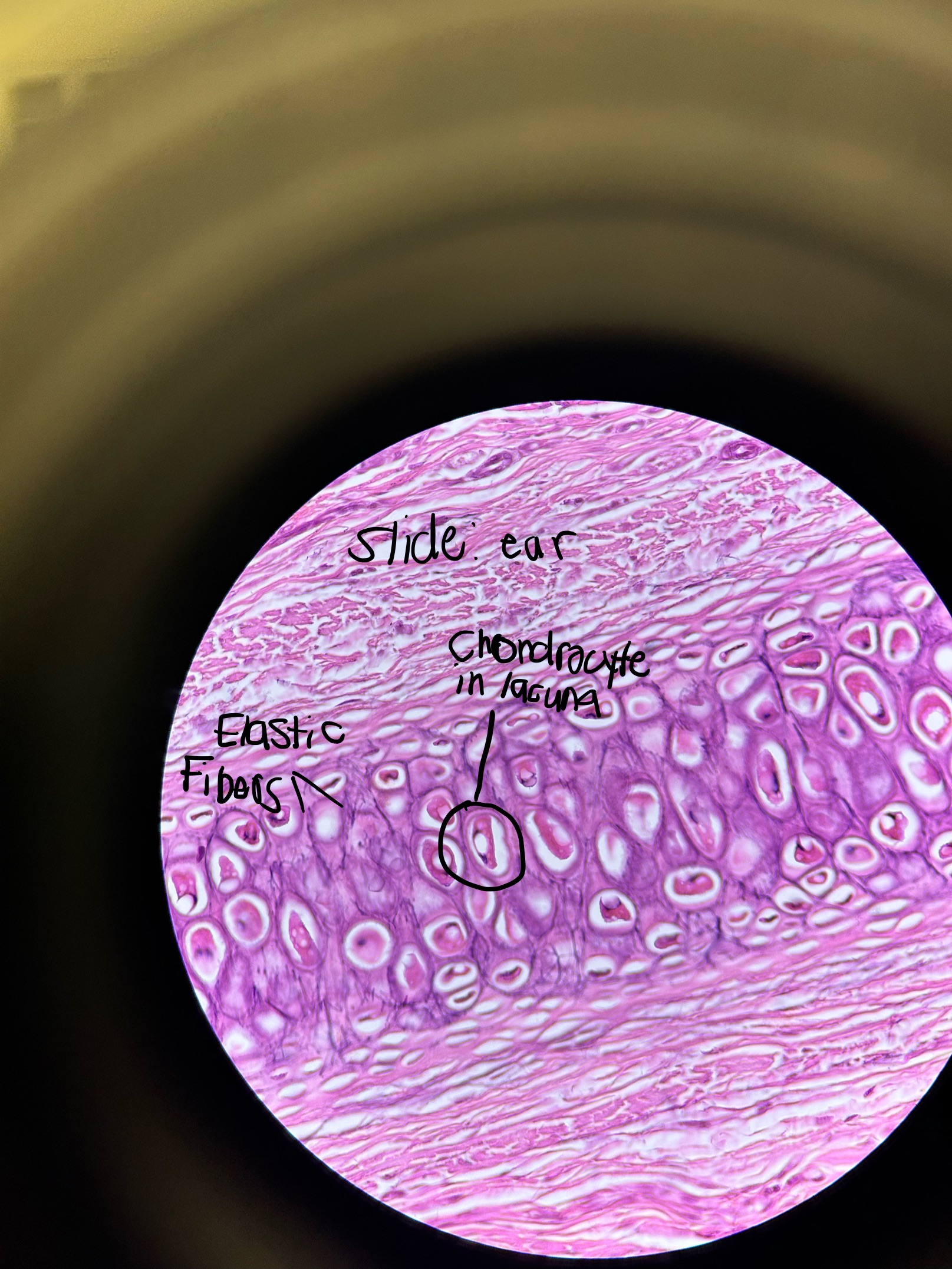
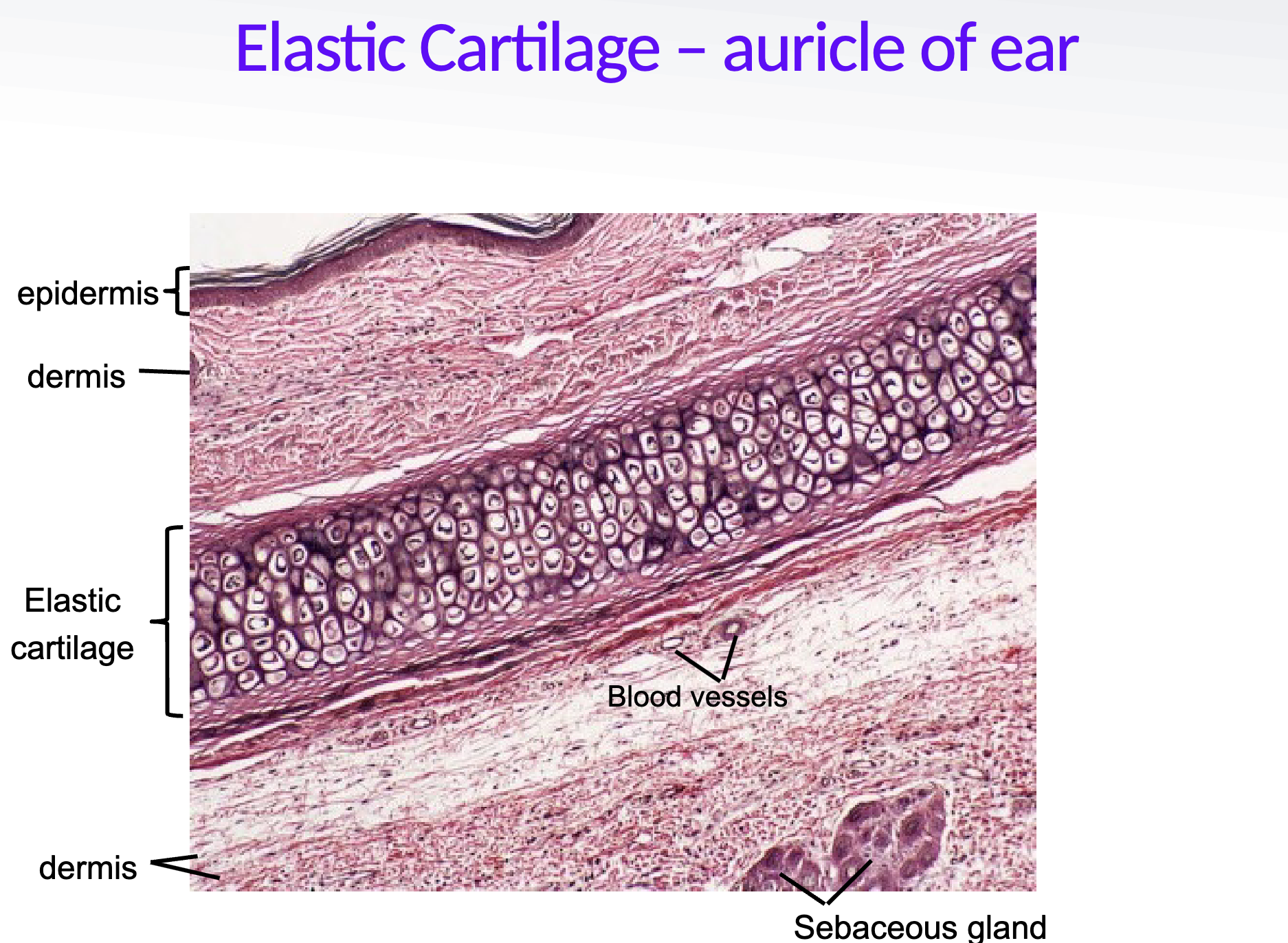
Where would you find Elastic Cartilage and what does it do?
external ear, epiglottis, external auditory meatus
flexible support
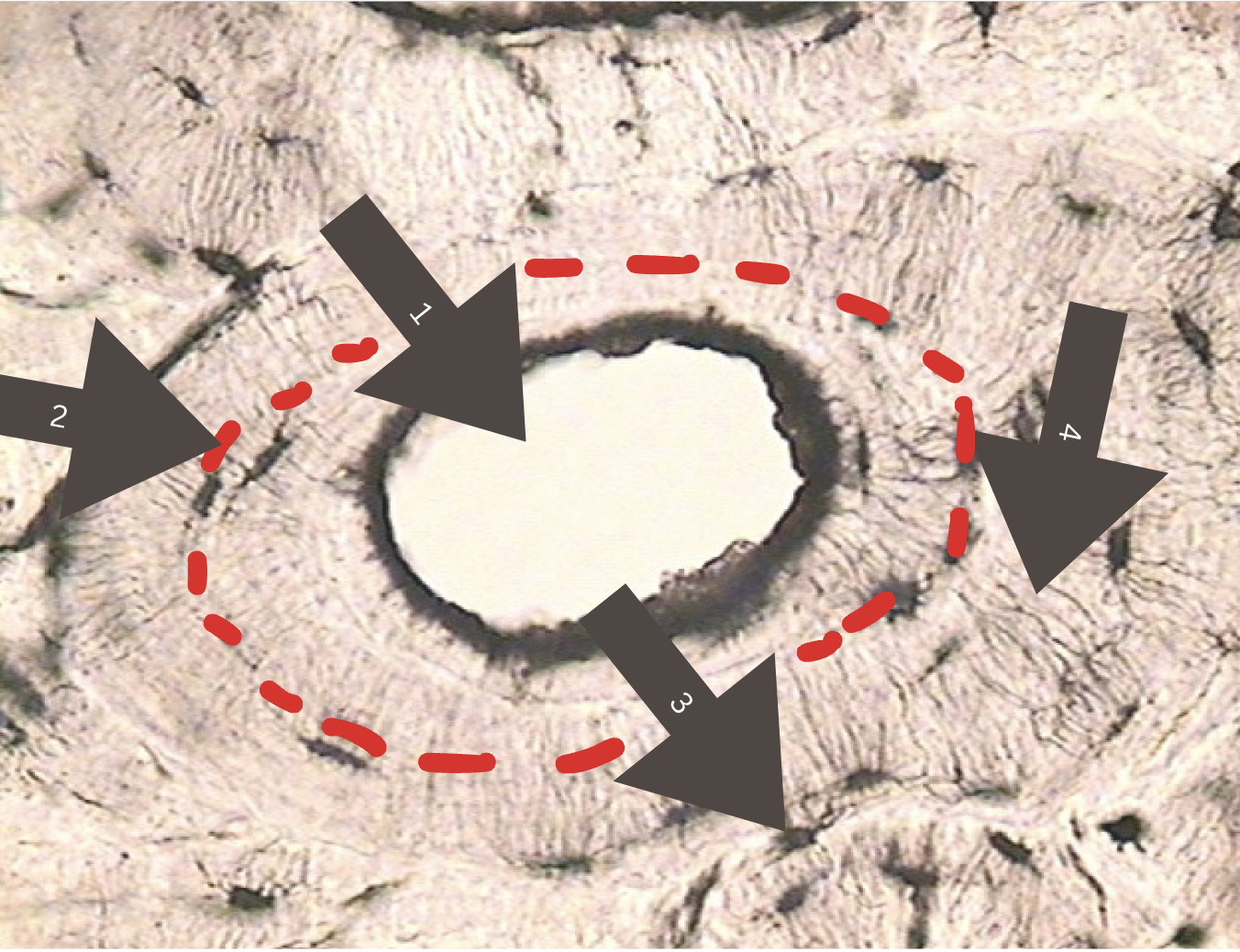
Name the Parts of the Bone
central canal
lamella (lamellae plural)
osteocyte in lacuna (plural lacunae)
canaliculi
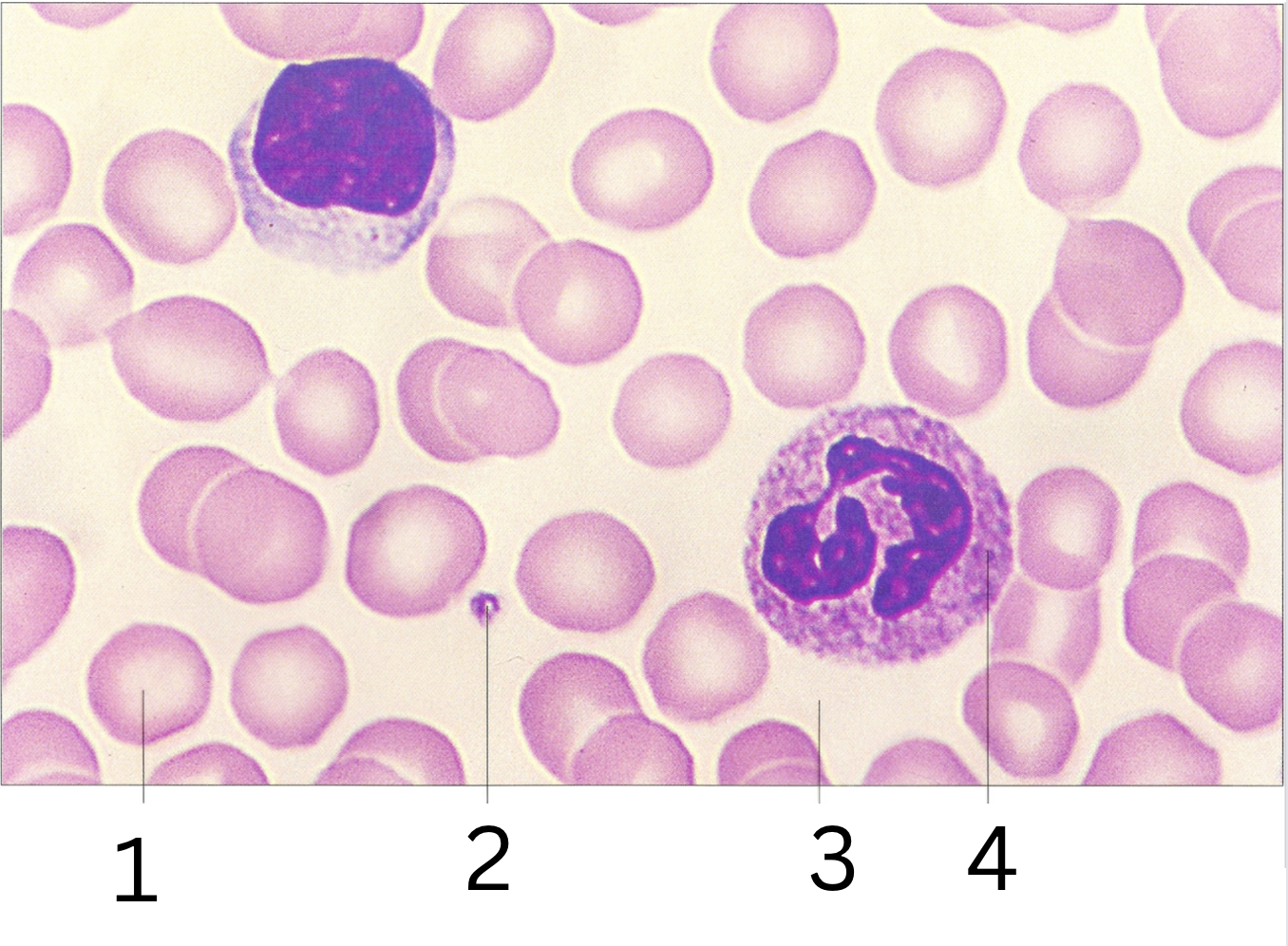
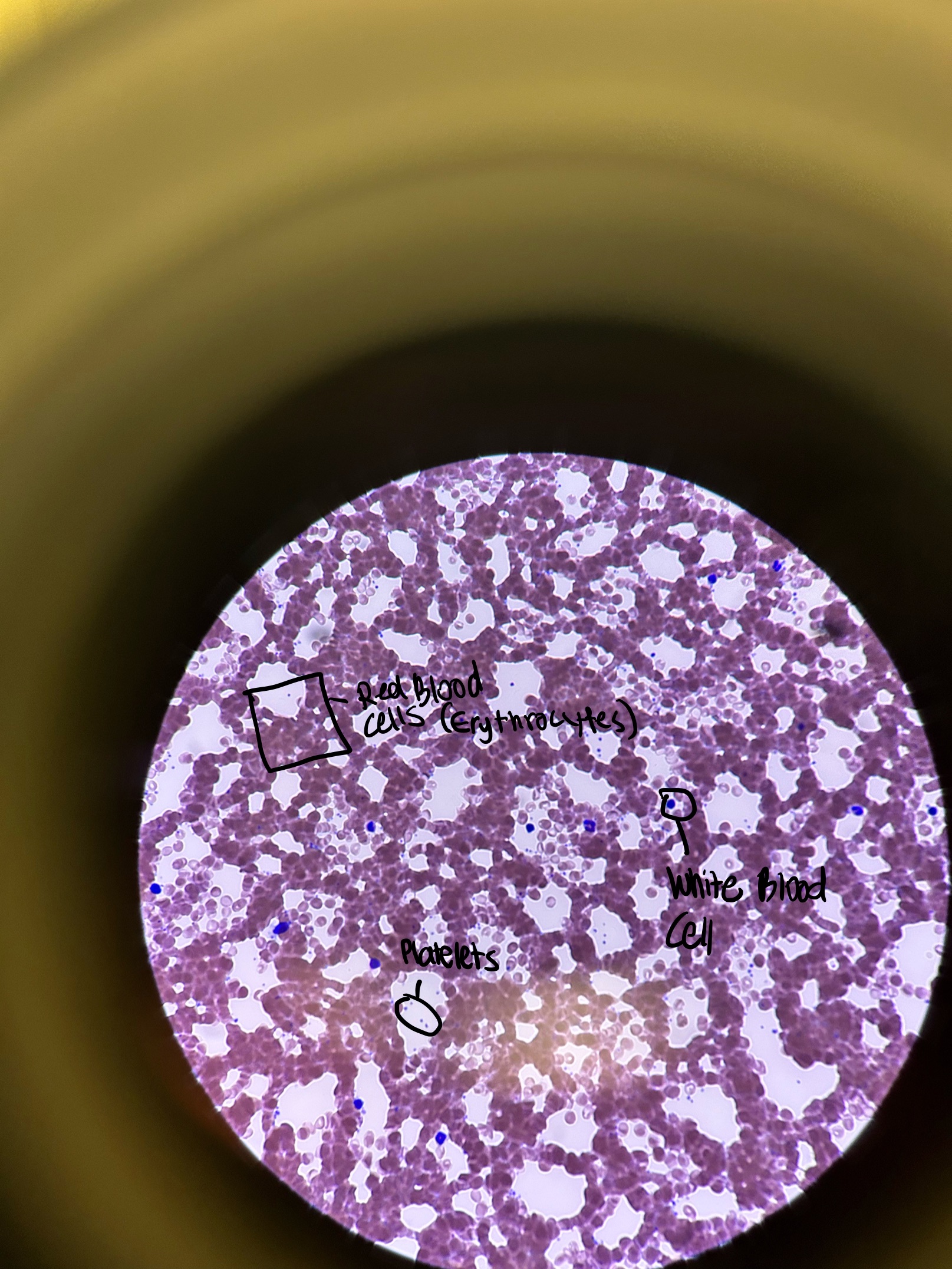
Name the Components of Blood and Give Their Function
erythrocyte
transport gases
platelet
blood clotting
plasma
remove waste and prevent infection
leukocyte
immunity
Actin Filaments (Thin Filaments) Function and Location
function: forming microfilaments
location: cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, beneath the plasma membrane
Myosin Filaments (Thick Filaments) Function and Location
function: muscle contraction
location: myofibrils
Muscle Tissue Functions and Specific Properties
produces body movements, maintains posture, generates heat, protects internal organ
electrically excitable, contracility, extensibility (limited), elasticity
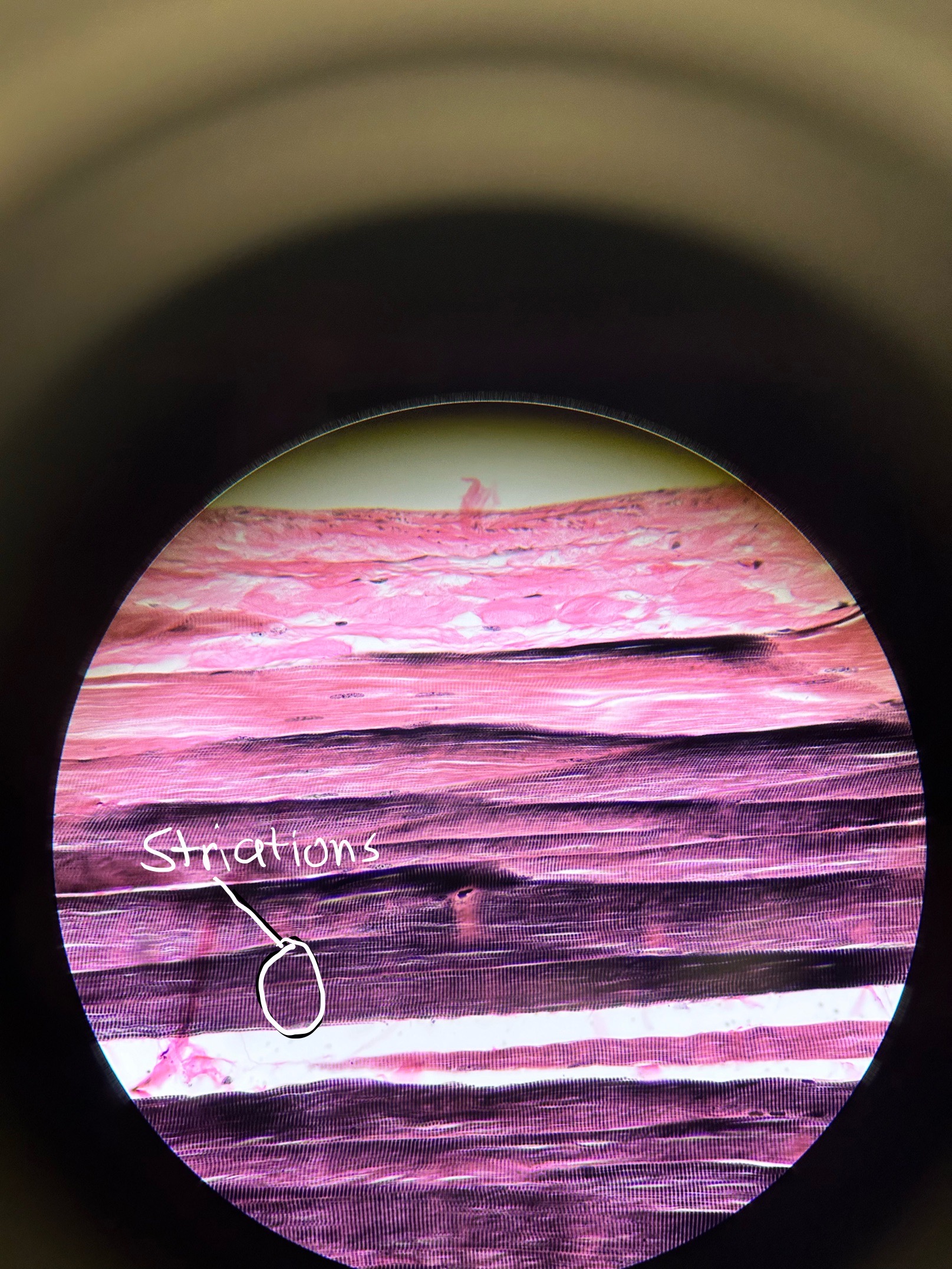
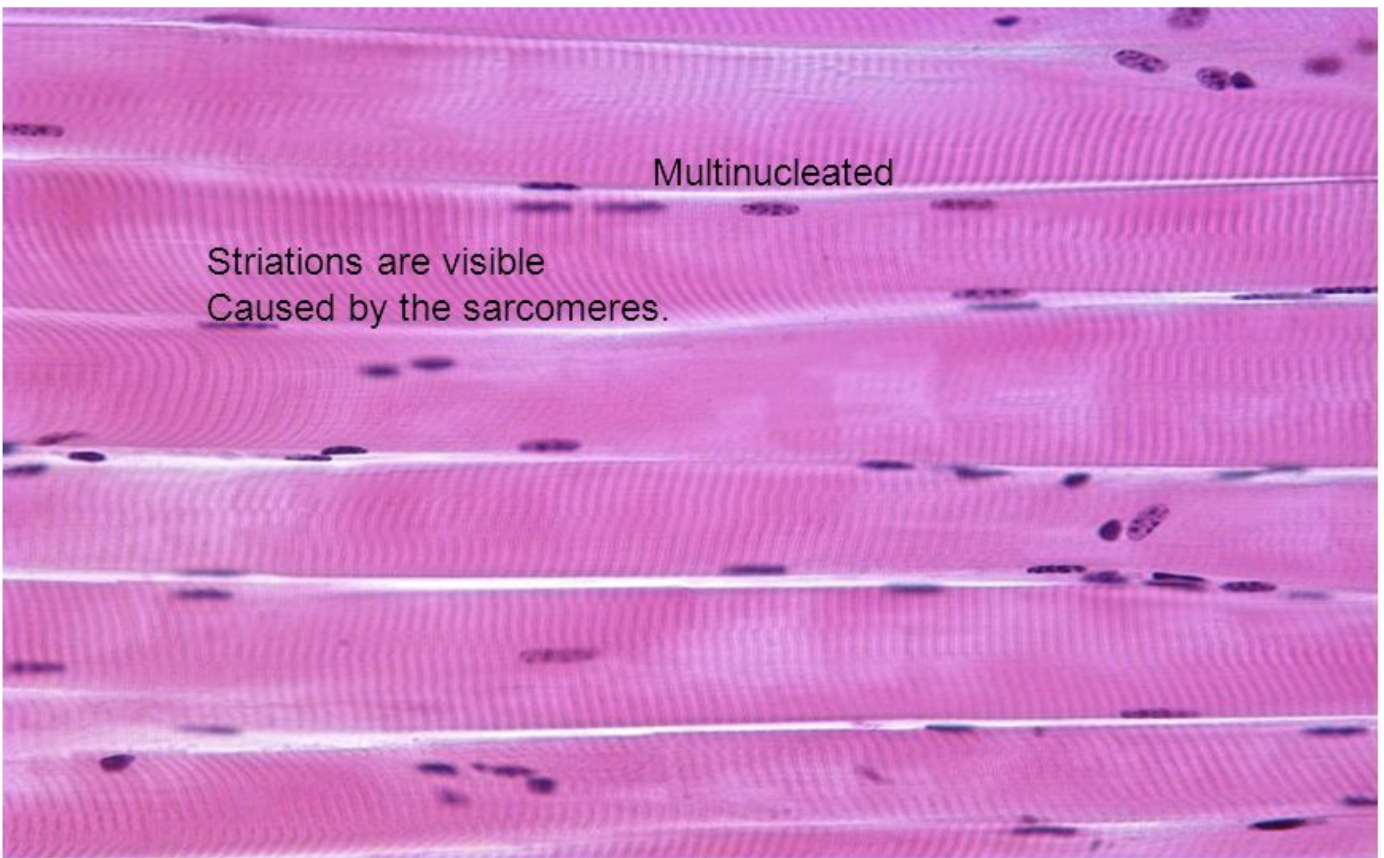
Where would you find Skeletal Muscle and what does it do?
diaphragm, brachii
purposeful movement or voluntary movement
* PERIPHERIAL NUCLEI
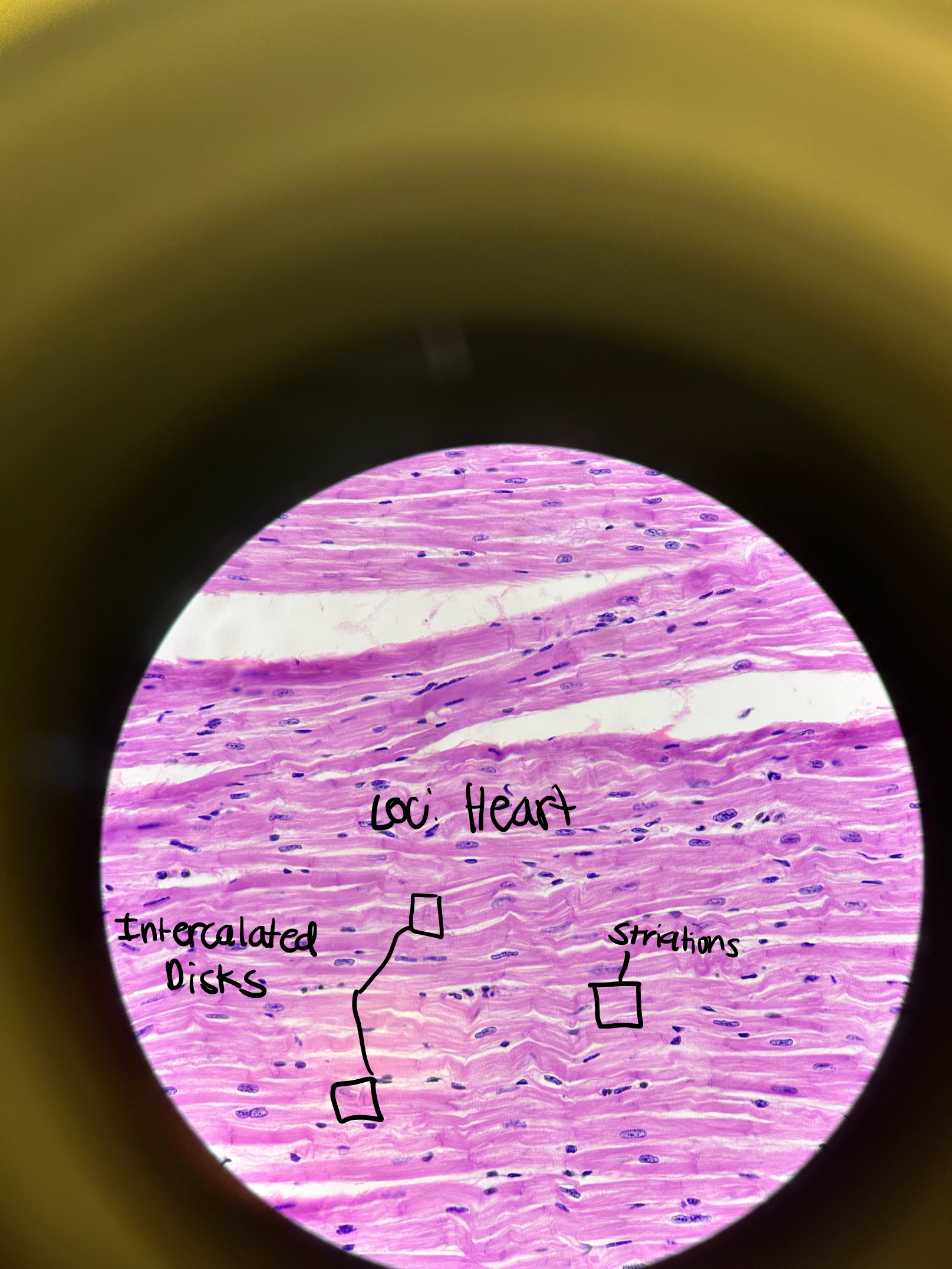
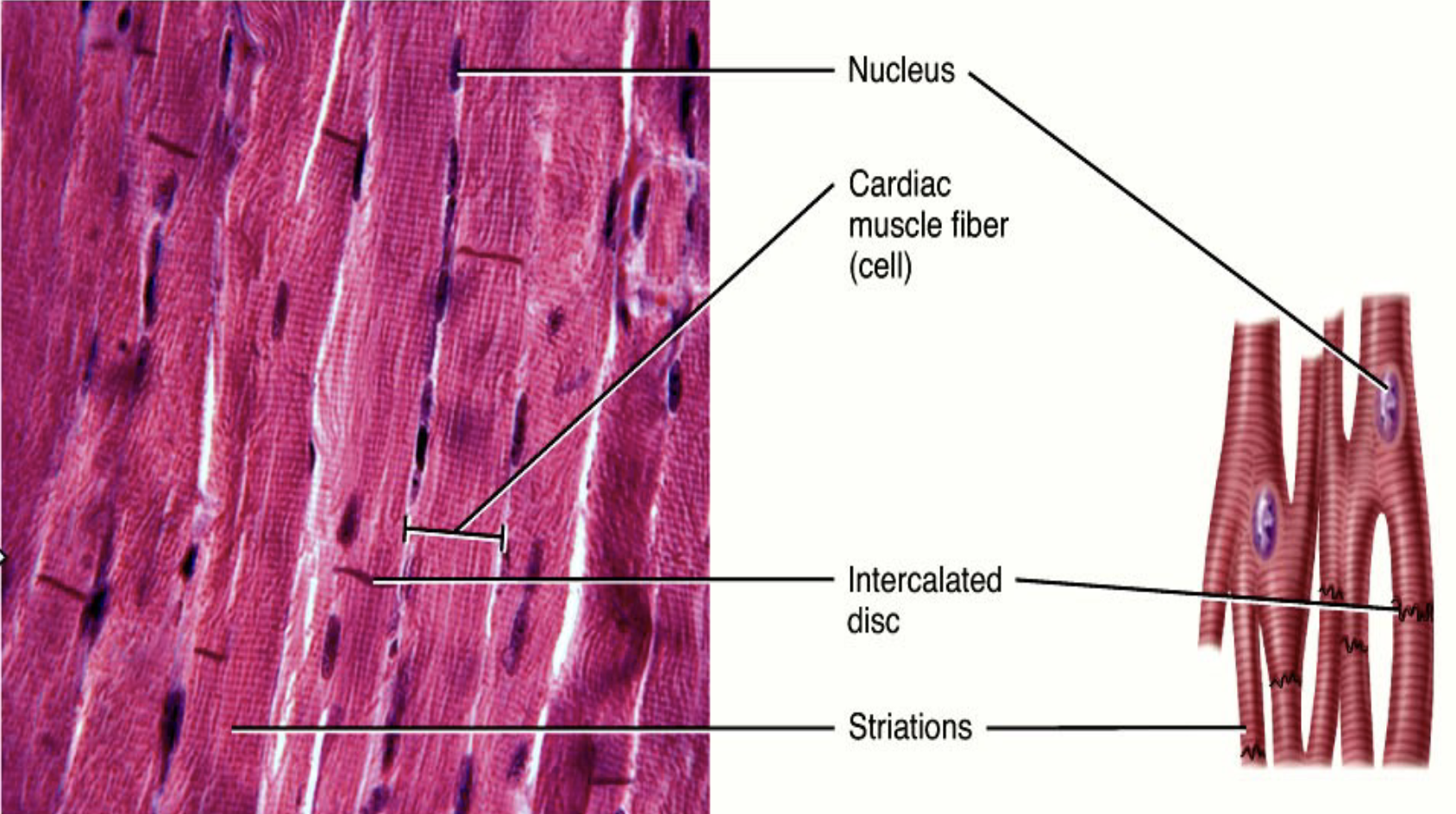
Where would you find Cardiac Muscle and what does it do?
heart
involuntary contraction of heart

Where would you find Smooth Muscle and what does it do?
G.I. Tract, walls of organs, ducts, tubes
involuntary contractions

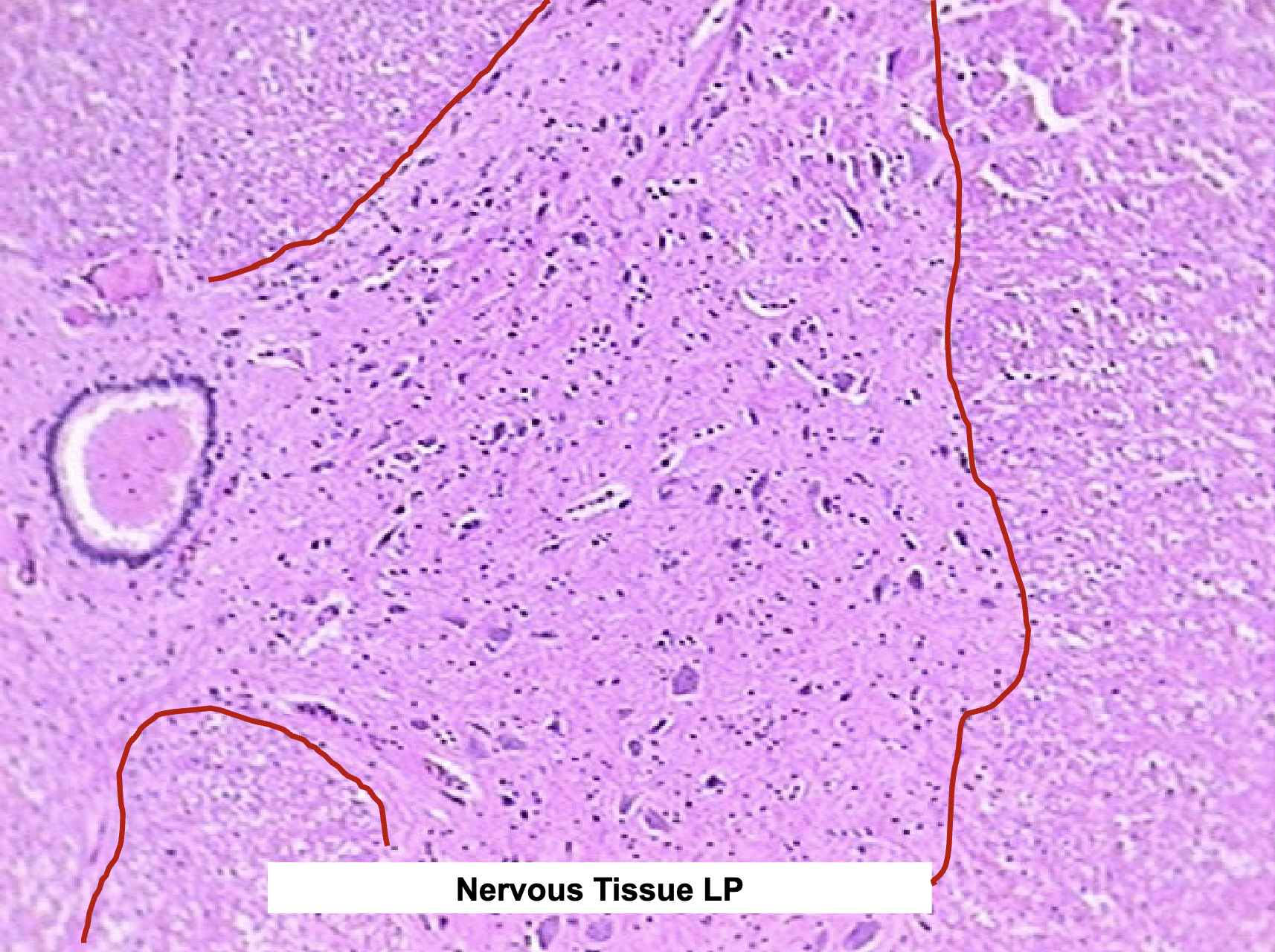
Nervous Tissue Functions and Characteristics
integration
coordination
derived from Embryonic Neuroepithelium
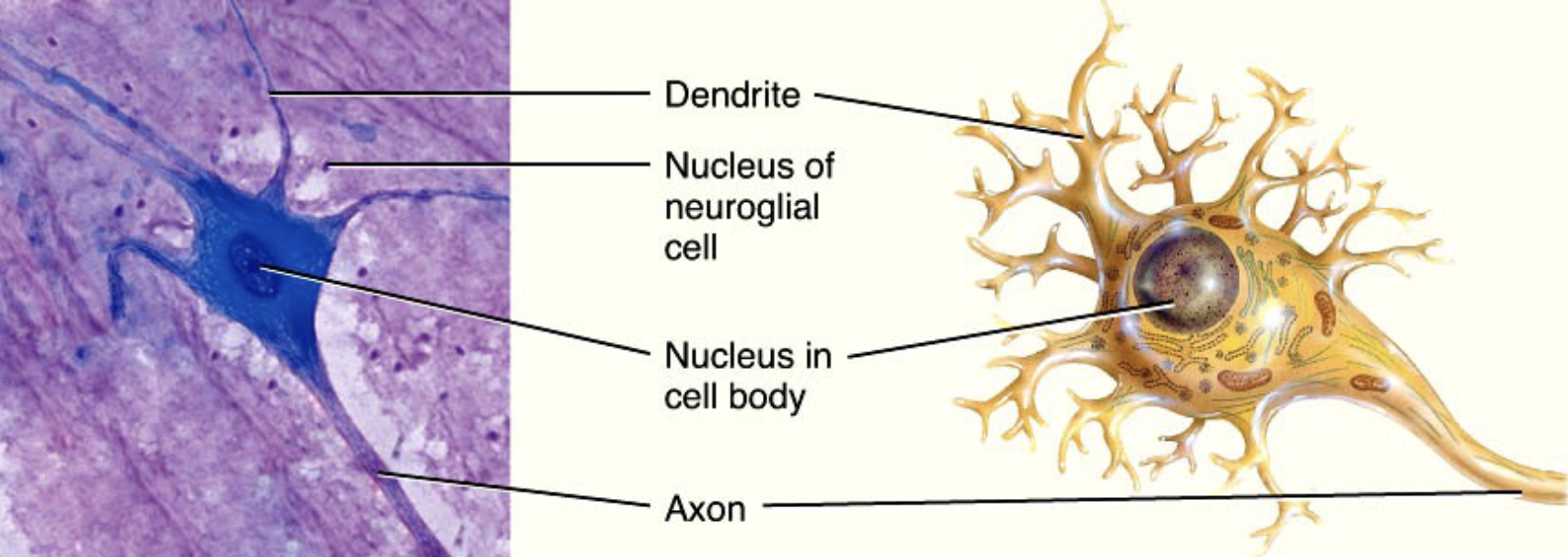
Where would you find Nervous Tissue, what is it composed of, and what are their functions?
brain and spinal cord
composed of:
cell body (soma) - houses organelles; signal integration
dendrites - input
axon - output
neuroglia - support neurons
What is the difference between grey vs. white matter and where would you find it?
grey: unmyelinated cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia (inside of spinal cord, outside of brain stem)
white: myelinated axons, neuroglia (outside of spinal cord, inside of brain stem)
spinal cord and brain stem
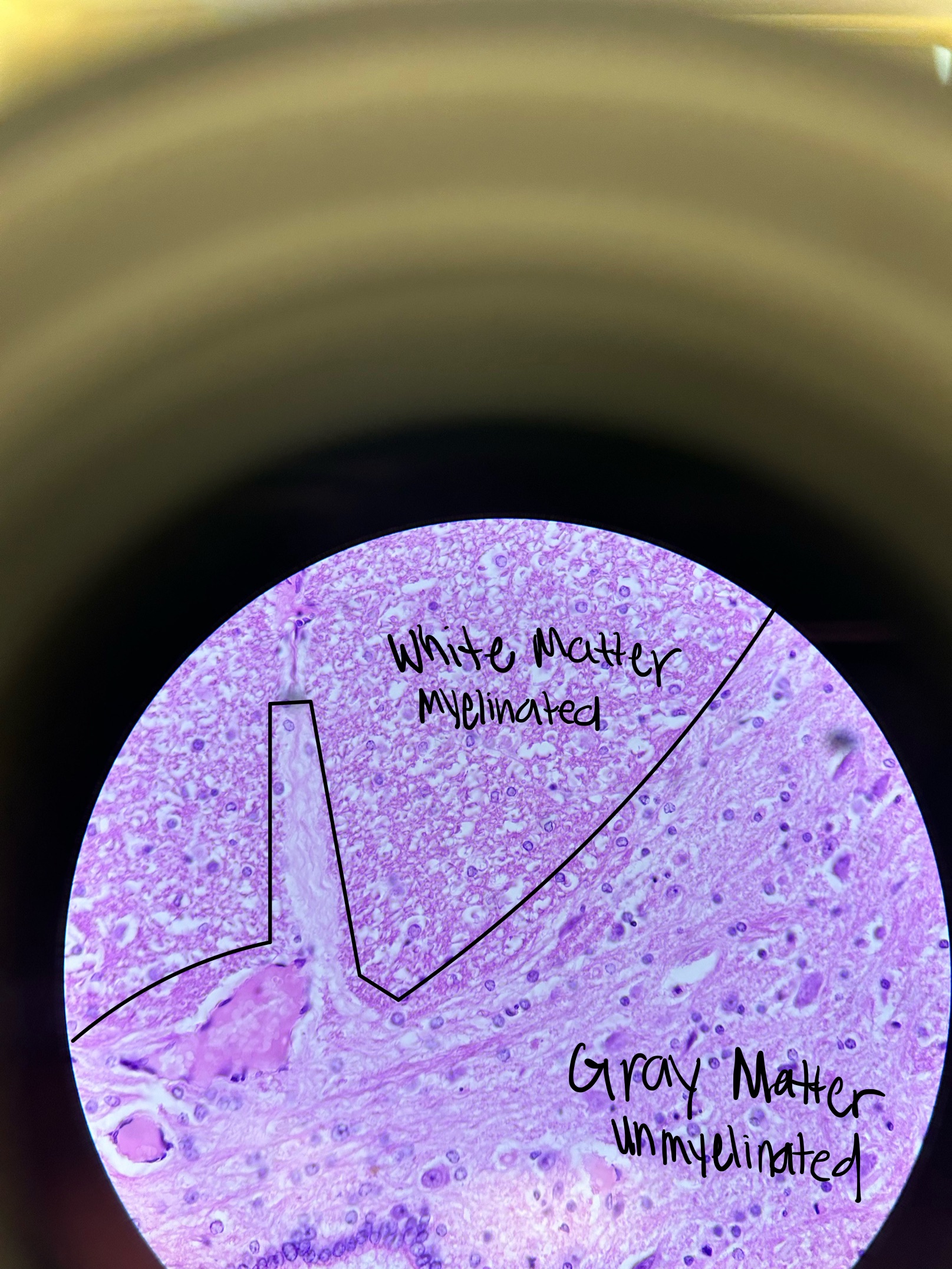
Grey and White Matter in Spinal Cord Picture