geog 370 - hydrology lab exam
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is a divide in a watershed?
high points that delineate watersheds
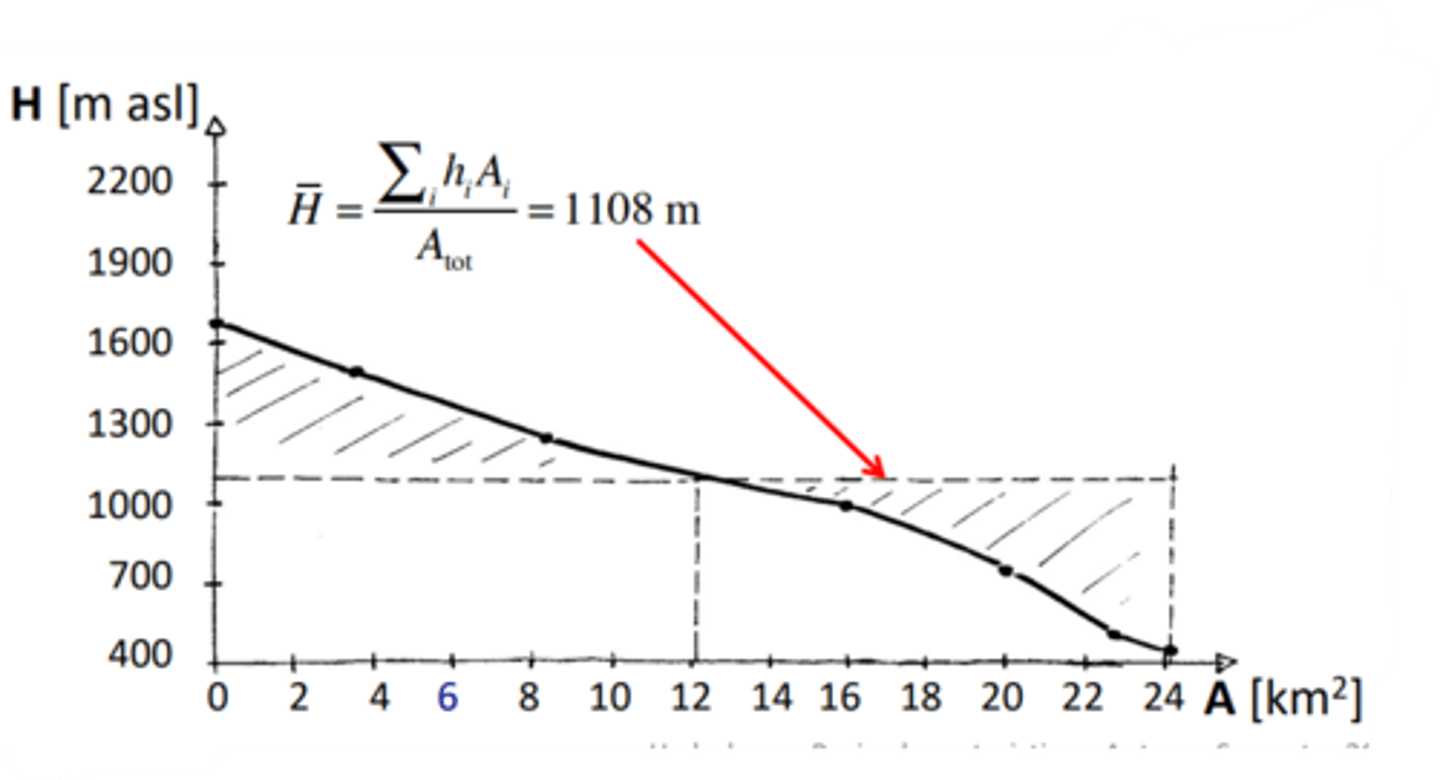
what is a hypsometric profile?
gives elevation within a watershed
a hypsometric chart can show you how water in a watershed may behave
ex. high elevation and steep curve = water moves quickly from divide to watershed. May also indicate presence of snowpack depending on elevation
what is PET
potential evapotranspiration
the amount of water that could be evaporated provided sufficient water and energy are available
what occurs if water in put (W) > PET?
ET will occur at the same rate as PET
W will work to recharge soil moisture, or add to the surplus
indicates that the system is energy (thermal) limited, not water limited
what occurs if W input < PET
then ET is equal to the sum of W + moisture removed from soil storage or:
ET = W + deltaSoil
when does a soil moisture deficit occur? Why?
when PET > ET, as this means the system is limited and water must be withdrawn from SOIL to satisfy demand
if W < PET, the "negative" amount required for ET will be extracted from soil (soil moisture utilization)
when does soil moisture recharge occur?
when W > PET, moisture is used to recharge soil moisture. When soil moisture = max, then additional W is considered a surplus
What is relative humidity?
equals the ratio of the actual air's vapour content to the potential vapour capacity at saturation
What is the dew point temperature?
the temperature at which saturation of an air parcel occurs
what is vapour pressure?
partial pressure exerted by water molecules (vapour) in the atmosphere
Only dependent on air temperature, therefore, you can find vapour pressure via temp
what is specific humidity?
is the mass fraction of water vapour in the air
what is mixing ratio used for?
what is absolute humidity?
the concentration of water vapour in air (units = grams of water vapour per cubic metre, g m^3)
what does the penman-montieth equation give you?
it is a model for estimating evapotranspiration, answer given in m/s
what are the steps for delineating a watershed in GIS?
Fill holes in DEM
Flow direction raster
Flow accumulations raster
Stream network (use classification threshold to determine what will be included and analyzed )
Stream links (each segment gets an ID and flow direction)
Delineate watershed
Additional step not mentioned: identify/create pour point
what are the steps for delineating a watershed without GIS?
Find highest points, then use topographic maps to delineate where the divide is.
Use GPS or other surveying techniques to mark boundaries
what are the different basin shapes and how will they affect water flow?
Linear: skinny and long, like a line. Water flows through quicker as streams are shorter. Generally associated with deep valleys w/ high elevation
Round: round basin. longer streams and slower flow times.
what is hypsometric profile? what is shown on each axis?
shows elevation on the y-axis versus % area of the water basin at each elevation
what is the Hamon equation? what units are used?
An empirical method that can be used to model evaporation given temperature.
T = degrees celsius
saturation vapour pressure (e*a) = kPa
output = mm/day
what are piezometric contours
lines displaying equal hydraulic head in a water table. Read these contours to find hydraulic head in a groundwater flow net diagram
what is Darcy's flow equation
how to go from mbar to kPa?
divide by 10
multiply by 10 to go from kPa to mbar
∆ = P − ρ g∆z
Hydrostatic Equation to find how pressure changes with height, we combine the equation relating pressure and weight with the equation of density to get the hydrostatic equation,
P = mg / A
pressure and weight of a parcel of air
rho = m/v = m/A(deltaZ)
Density (rho) is Mass (m) divided by volume, V and is usually expressed with the units of kg m-3
Measures of Vapour
the vapour content of the air can be expressed as relative humidity (RH), vapour pressure (ev), vapour density (absolute humidity, rv), specific humidity (q), mixing ratio (w), dew point temperature (Td), or wet bulb temperature (Tw).