Week 4 lab, Observing Prokaryotic Microorganisms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms

What flagella arrangement is this?
Monotrichous

What flagella arrangement is this?
Lophotrichous
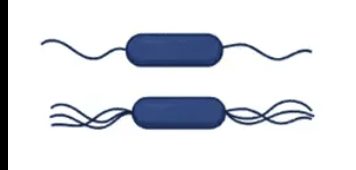
What flagella arrangement is this?
Amphitrichous

What flagella arrangement is this
Peritrichous
What are Cyanobacteria
Prokaryotes that can photosynthesize
What does oil immersion do?
Reduce the refraction of light
absorbs the light
What is cocci shape?
small spheres
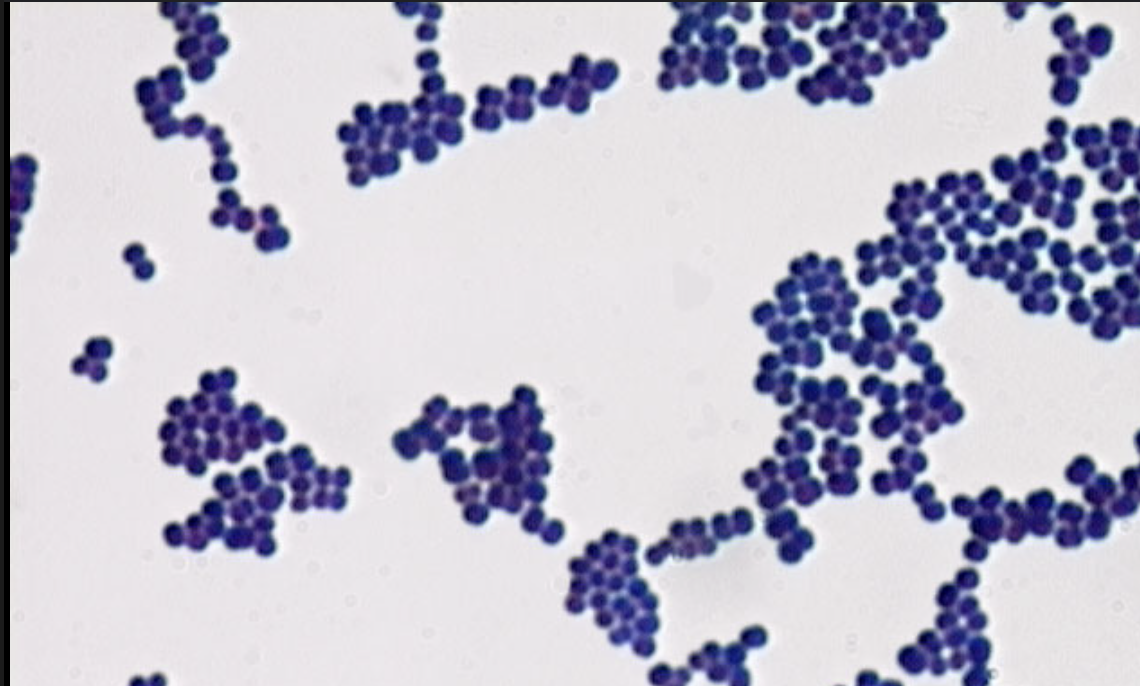
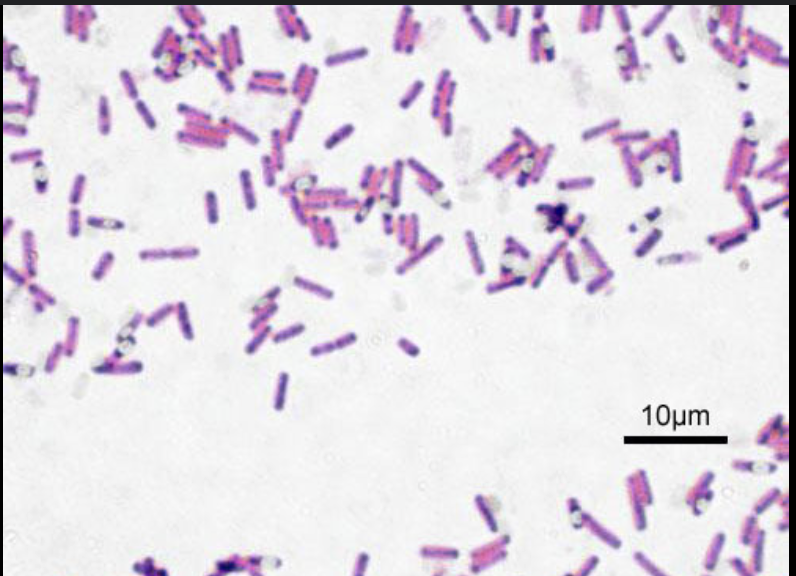
What is bacilli shape?
Rod shape
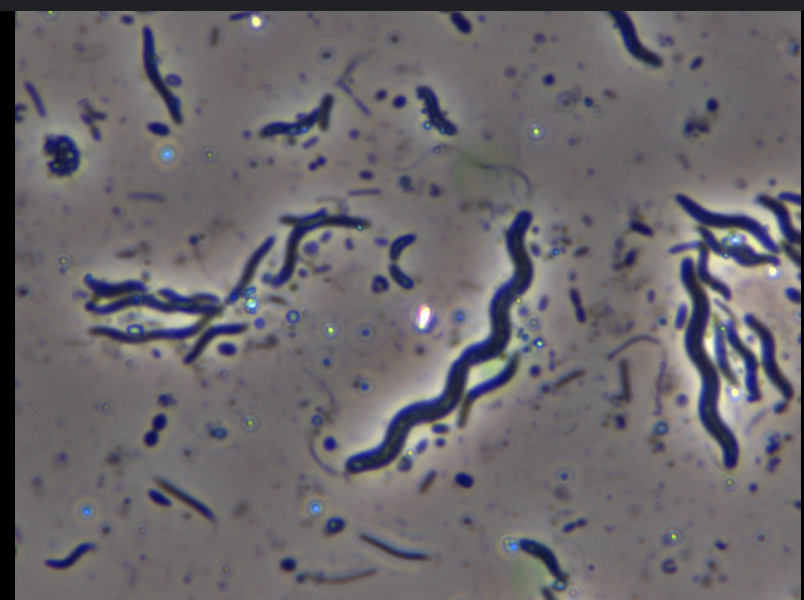
What is Spirilla shape?
Spiral wiggly rod shape
What is a capsule
A thick, polysaccharide or polypeptide layer outside the cell wall that increases virulence and protects the cell. Seen as white halos around cells
Why is it difficult to visualize spirochetes?
Because they are extremely thin, poorly stained, and require exact fine focus to see.
What is the point of a negative stain?
Negative Space (Background)
Stained with acidic dye
What are the advantages of negative stain over a positive stain?
You don’t need to heat fix, so organisms keep their size
useful in determing organism size
What is a positive stain?
Positive space (cell) stained with base dye
What is a simple stain?
One dye is used
Need to smear and heat fix
What is a capsule stain?
Similar to negative Stain,
What is a Chromophore
Colored part of a dye molecule
What is a basic chromophore dye?
Positive Chromophore, Gives off Hydrodrixide
Stains the cell, attracted to the negative bacterial components
What is a acidic chromophore dye?
Negative Chromophore, Gives off Hydrogen acid shi
Stains the positive area surrounding cell, repelled by the negative cell
What is a smear?
Bacteria spread onto slide usally mixed with water
Heat fixed onto stick
What is heat fixing?
Gentle heating to make sure bacteria sticks onto slide
What is a capsule?
Thick glycocalyx, it does not absob dye, allows for a white halo effect that surround cell
What is a biofilm
A type of glycocalex that is sticky
What are the steps of a smear
1) Add a drop a water to a slide
2) Aseptically transfer bacteria from isolated colony onto the slide
3) Air dry
4) run it a couple times in front of insintator to heat fix
5
What are the steps of a simple stain?
1) Make smear
2) Apply Positive chromophore basic,
3) Wait,
4) Blot using bibilus paper
5) now you can see that shit
What is the common dye used in simple stain?
Methylene Blue
In a simple stain how does it differentiate different bacteria?
It’s non differential, all bacteria is the same color
What is the main point of doing a simple stain?
To just see the bacteria in the first place
What are the dyes used a negative stain?
Negative acidic dye
Nigrosin
India Ink
Which stains do you heat fix?
Simple stain, negative and capsule don’t require heat fixing
What are the steps for a negative stain?
1) Place a drop of your acidic dye onto the slide
2) Aseptic tranfer colony onto the drop of dye
3) You take another slide and then use it to drag the dye mixture across the slide using capillary action
4) Let the long streak dry completly
5) View under oil immersion lens
What are the main reason why you need to do a negative stain?
Some bacteria are hard to stain
What are the steps of a capsule stain?
1) Place a drop of acidic dye onto slide
2) Aseptic transfer culture onto dye
3)Use another slide to spread dye across slide
4) Allow for it to dry
5) Flood smear with safranin stain (basic positive)
6) Blot dry
7) Visualize under oil lens
How does the capsule stain work, and what is the reason for using it
It combines negative and simple stain
Uses both acidic and basic dyes
Stains background, stains bacteria
Capsule can’t be stained so it will appear as a clear halo
What is the point of a capsule for a bacteria?
Allows for protection
Organized structure
Firmly attached
Strong
Slime layer characteristics
Unorganized
Loosely attached
Allows for adhesion
Forms biofilms
Biofilm characteristics
Community of bacteria
Resiliitant
Resistant to antibiotics
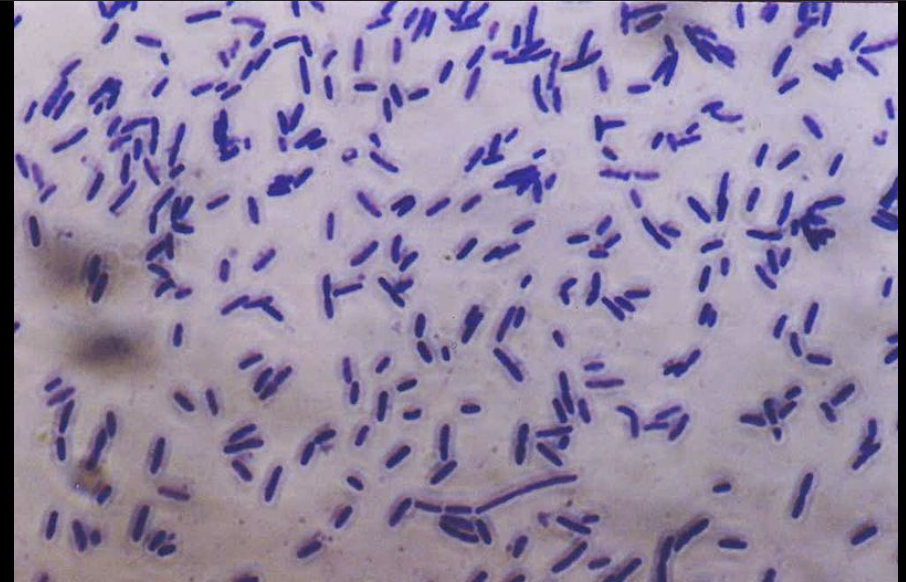
How do you know if you are looking at a simple stain?
Background is clear
Bacteria is all one color
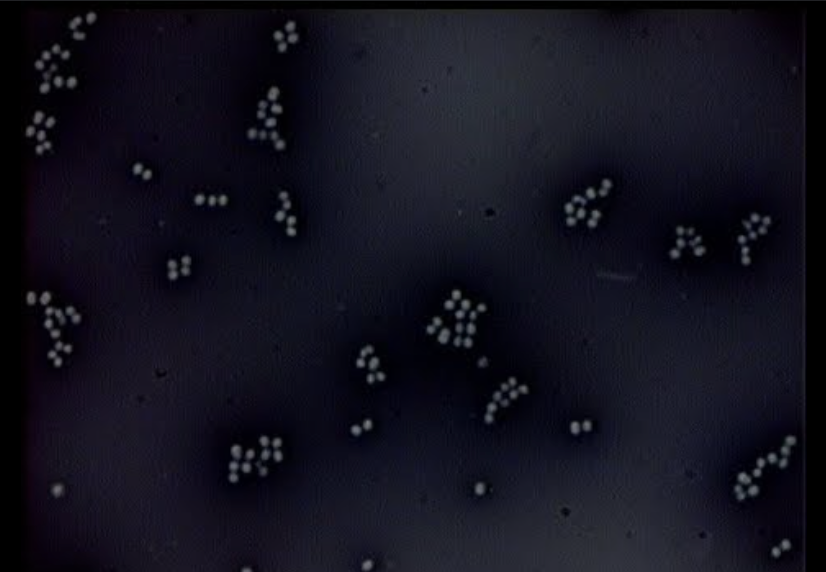
How do you know if you are looking at a negative stain?
Background is stained
Cells remain clear/white
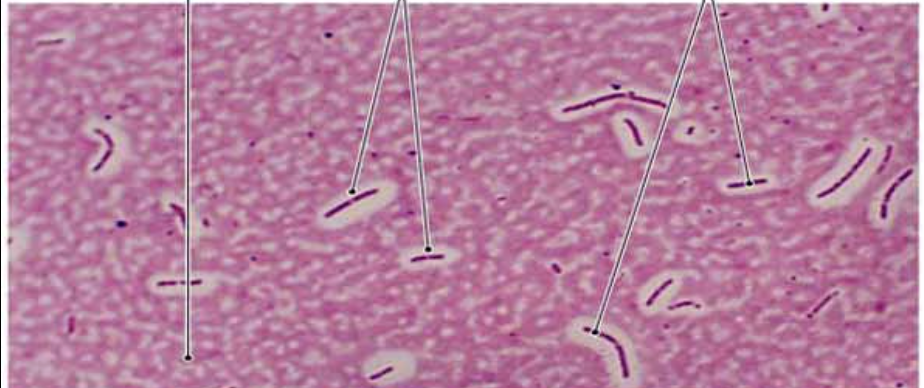
How do you know you are looking at a capsule stain?
Background is stained
Bacteria is pink
There are visible halos around the bacteria, those are the capsules