Quantum Mechanical Wave Model
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Louis de Broglie
Showed that electrons can be thought as a wave of energy instead of a particle
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Basically stated that its impossible to know both exact momentum & location of an electron
Bc electrons are so small & charged, any beam of light used to find it would MOVE it!
De Broglie + Heisenberg
We cannot know where an electron is. So instead of attempting to find the exact location, we get to know the probability of finding an electron in a specific region of space called orbitals
Principle Quantum Number (LEVEL / N)
whole numbers (n= 1,2,3,4)
relates to distance the electron is from the nucleus
tells us energy level
What are the 4 quantum numbers that are assigned to electrons?
n, l, ml, ms
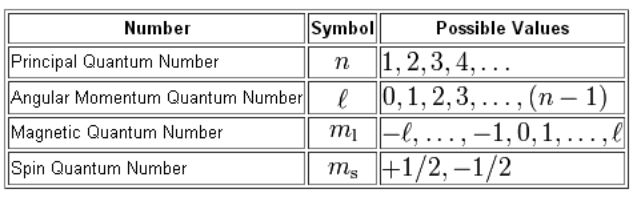
Secondary Quantum Number (SECTION/L)
Defines shape of the orbital
# of values is determined by the value ‘n’
for each value of ‘n’, l= 0,1,2…-1
each value of l is designed by a letter: s,p,d,f
L=0 means s orbital, sphere
L=1 means p orbital, dumbbell/hourglass
L=2 means d orbital, double dumbbell
L=3 means f orbital
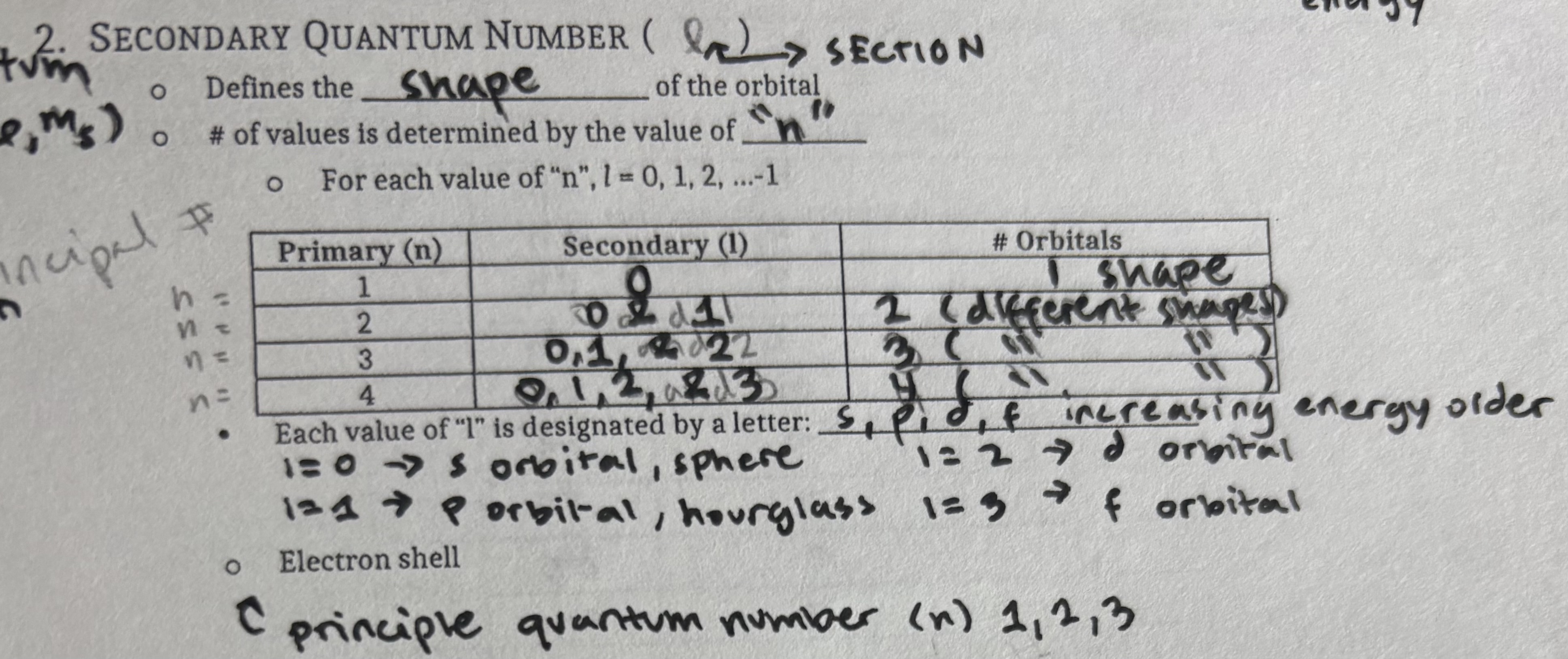
Magnetic Quantum Number (ROW/ml)
orientation in space of the orbital
splits subshells into individual orbits
an orbital fan hold 2 electrons total
It may hold 0,1, or 2 but never more than 2
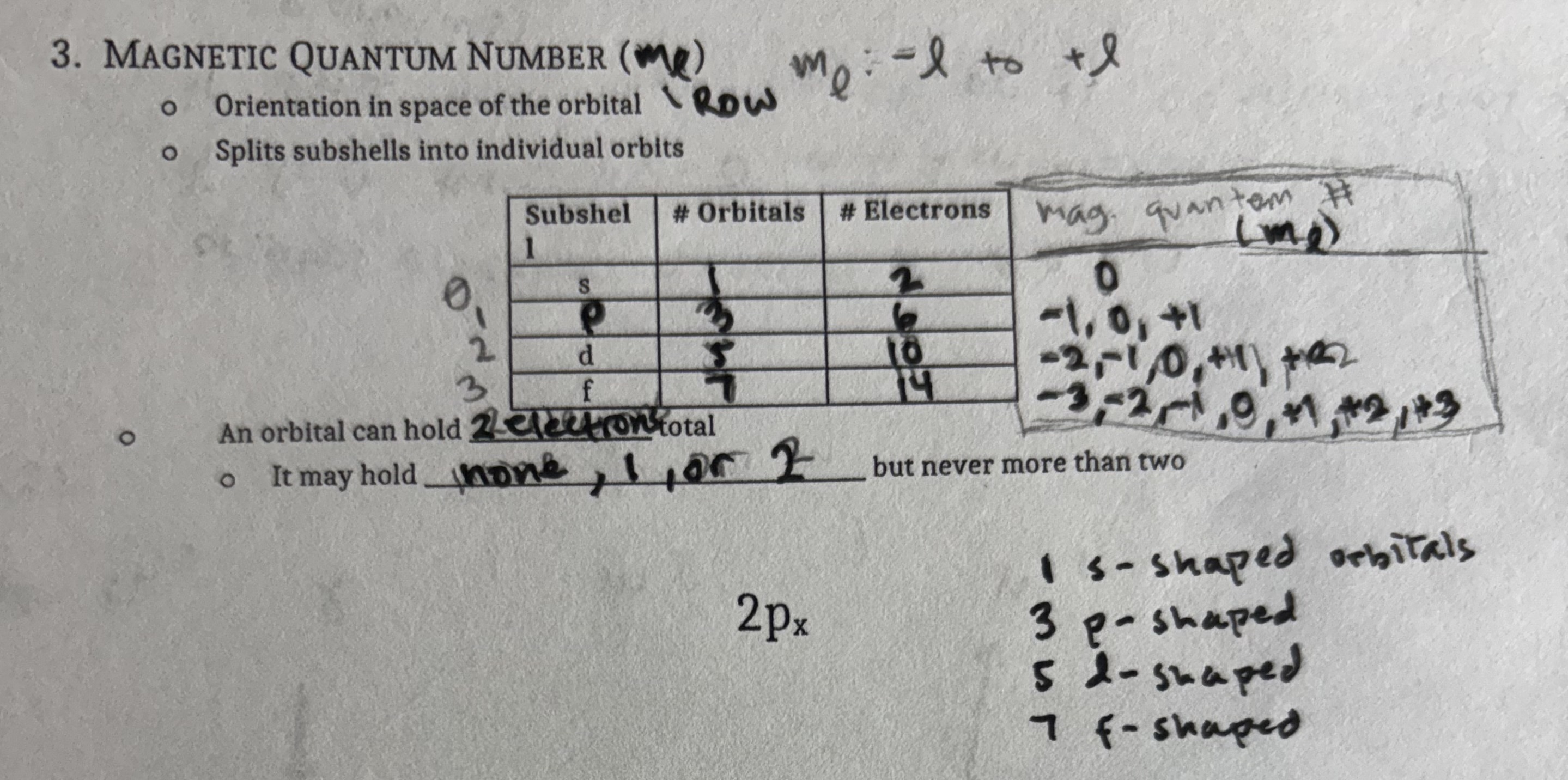
Magnetic Spin (SEAT/ms)
Indicates orientation of the electrons in each orbital
+1/2 or -1/2
Electrons can soin clockwise or counterclockwise
2 electrons in any orbital MUST have OPPOSITE spins
The number of electrons in a shell is 2n²
Aufbau principle
When adding electrons to an atom, lower energy orbits must be filled first
Pauli’s exclusion principle
Atomic orbital can ONLY have 2 electrons and they must have opposite spins
Hund’s rule
When we have degenerate orbitals (orbitals w same energy) then each orbital is filled with single electron before being doubly occupied