Chemistry - Intermolecular forces
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion
Why do electron pairs determine the shape of a covalent molecule
-Valence electron pairs in the shell of an atom will repel each other and position themselves as far as possible
-Shape is therefore determined by the number of shared/lone electron pairs
Interaction between lone pair and bonded pair
-Lone pairs repel 3x bonded pairs more than each other
Shapes
-Linear
-Trigonal planar
-Tetrahedral
-Pyramidal
-Bent/V-shape
Linear
Symmetrical molecules, all diatomic molecules
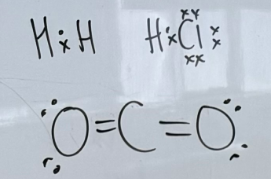
Trigonal planar
-3 bonded pairs with no free pairs
-120o Bond angle
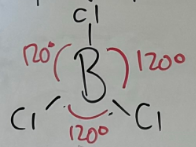
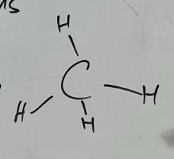
Tetrahedral
-4 bonded pairs with no free pairs
-All 4 bonds evenly spread in 3 - dimensions
-109.5o bond angle
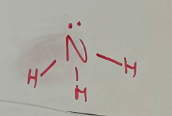
Pyramidal
-3 bonded pairs with 1 free pair
-Free pair ‘pushes’ bonded pairs away
Bent/V-shaped
2 bonded pairs and 1-2 free pairs
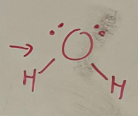
Polar and non-polar
refers to weak positive or negative charge that CAN exist for a covalent molecule only
Why do polar molecules exist
-When electrons are not shared equally between elements in the covalent molecules
-Cause by differences in electronegativity
Signs for non-polar molecules
-Made up of one element (e.g. N2, O2, Cl2)
-Molecule that only contains carbons and hydrogens
-If molecule has symmetry (e.g. CF4, CO2, BH3)
-If electronegativity difference is less than 0.5
Signs for polar molecules
-If hydrogen is bonded to NOF (N, O, F) (e.g. H20, NH3, HF, CH3OH, CH3COOH)
-If bond is asymmetrical and bond is polar
-If electronegativity difference is above 0.5
Types of IMF
-Hydrogen bonds (Only in polar)
-Dipole-Dipole bonds (Only in polar)
-Dispersion forces (In all covalent molecules (polar and non-polar)
Dipole-Dipole
-Form between polar molecules due to charged polar ends
-The + and - ends of molecules attract each other and bond
-Bonds vary in strength based on polarity of molecule
-More polar/higher EN diff → higher MP/BP

Hydrogen bonds
-Particular type of dipole-dipole bond where hydrogen is attracted to N,O,F
-Because these connections have very high electronegative difference (H-F, H-O, H-N)
-H-bonds are ~10x stronger than dipole-dipole
-Increase BP and water solubility of molecule
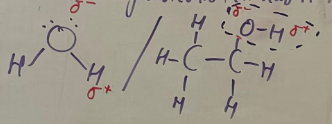
Dispersion forces
-Electrons shared in covalent molecules are in constant motion
-Will sometimes clump together temporarily and from temporary dipoles
-Thus, temp +/- areas of molecule and form attractive forces
-These temp dipoles bond non-polar molecules together
-Dispersion forces increase as molecule size/mass increases
Dispersion forces increase in strength
1.As you go down a group (number of electrons increases)
2.As molecular mass increases (i.e. methane vs ethane)
Key properties of IMF: MP/BP
-Increases with molecules size (higher dispersion forces)
-If similar mass - depends on type of IMF present
Key properties of IMF: Vapour pressure
Pressure exerted by gas particles of substance
-Low MP/BP higher vapour pressure
-Higher vapour pressure with lower IMF strength