Chemistry; Chapter 5
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Ionic Bonding
Involves a transfer of electrons. One element loses electrons and the other gains electrons
Covalent Bonding
Involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. These bonds can form between two nonmetals, resulting in molecules. It also lets Atoms reach a stable electron configuration
What is the Octet Rule?
The Octet Rule states that atoms are most stable when they have a full set of eight electrons in their outer shell, which typically occurs when they form bonds. The Atoms either gain or lose enough electrons to be isoelectronic with a noble gas
Electron Dot Structures
A way to show the number of valence electrons in an Atom

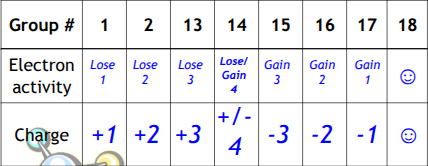
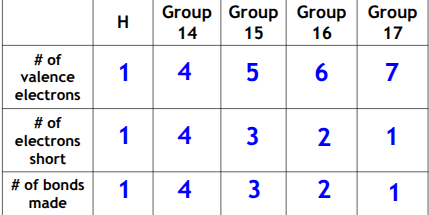
The number of valence electrons are determined by…
what group the element is in

Valence electrons determine chemical reactivity
Elements in the same group behave the same
Ionic bonds form when…
an electron is transferred from one atom to another, creating charged ions that attract each other.
What is an Ionic compound made up of?
Crystals
A crystal consists of…
A 3D repeating pattern of alternating Cations and Anions
Formula Unit
The lowest whole number ratio of Ions
Whats special about Ionic compounds
Ionic compounds have high melting points and conduct electricity when melted or dissolved
Properties of ionic bonds
Ionic bonds are very strong and are solids at room temperature. They have high melting and boiling points. Made up of metals and non-metals. Does not conduct electricity in the solid state but does in the liquid and gas
aqueous
Dissolved in water
Empirical Formulas
The chemical formula for the ionic compound is arranged in the smallest whole-number ration is known as an Empirical Formula
Covalent Bonding
A Sharing of electrons
A single covalent bond is made up of…
two electrons. None electron is donated to the bond from each atom
Covalent Bonding is made from….
Non-metals only
Atoms that are covalently bonded are called
molecules or molecular compounds
Properties of molecular compounds
Covalent bonds are weaker that ionic bonds. They have much lower melting and boiling points. Is a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature. Non-conductors in any state.
Molecular Formula
Indicates the exact makeup of one molecule
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
The electron pairs ( both shared and unshared) in the outermost energy level try to get as far apart from each other as possible (determines the shape)
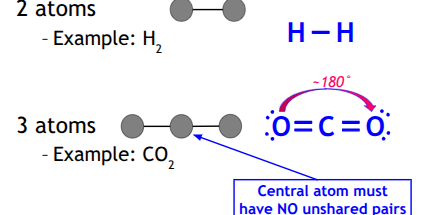
Linear
central atom must have no unshared pair
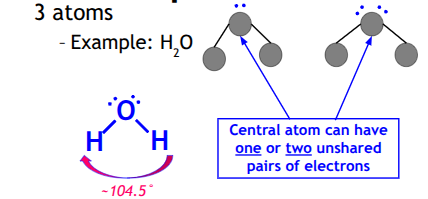
Bent
Central atom can have one or two unshared pairs of electrons
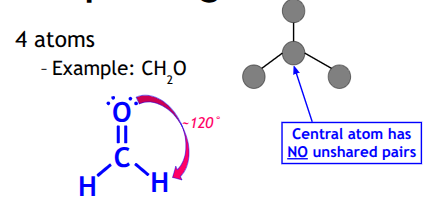
Trigonal Planar
Central atom must have no unshared pairs
pyramid
Central atom has one unshared pair

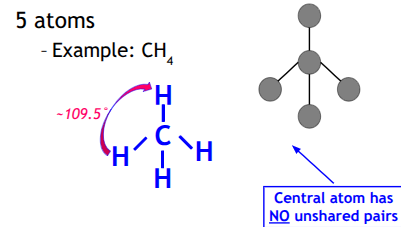
Tetrahedral
Central atom has no unshared pairs
Trigonal Bipyramidal
central atom has no unshared pairs
For elements in period 3 and higher, when bonded to Cl or F, will have an expanded octet.

polar bond
bonds where the electrons are shared unequality between atoms The atom that is more electronegative will pull the electrons closer to itself. When atoms are different, each has a different pull
Non-polar Bond
Ionic Bonding
Involves a transfer of electrons. One element loses electrons and the other gains electrons
Covalent Bonding
Involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. These bonds can form between two nonmetals, resulting in molecules. It also lets Atoms reach a stable electron configuration
What is the Octet Rule?
The Octet Rule states that atoms are most stable when they have a full set of eight electrons in their outer shell, which typically occurs when they form bonds. The Atoms either gain or lose enough electrons to be isoelectronic with a noble gas
Electron Dot Structures
A way to show the number of valence electrons in an Atom
The number of valence electrons are determined by…
what group the element is in
Valence electrons determine chemical reactivity
Elements in the same group behave the same
Ionic bonds form when…
an electron is transferred from one atom to another, creating charged ions that attract each other.
What is an Ionic compound made up of?
Crystals
A crystal consists of…
A 3D repeating pattern of alternating Cations and Anions
Formula Unit
The lowest whole number ratio of Ions
Whats special about Ionic compounds
Ionic compounds have high melting points and conduct electricity when melted or dissolved
Properties of ionic bonds
Ionic bonds are very strong and are solids at room temperature. They have high melting and boiling points. Made up of metals and non-metals. Does not conduct electricity in the solid state but does in the liquid and gas
aqueous
Dissolved in water
Empirical Formulas
The chemical formula for the ionic compound is arranged in the smallest whole-number ration is known as an Empirical Formula
Covalent Bonding
A Sharing of electrons
A single covalent bond is made up of…
two electrons. None electron is donated to the bond from each atom
Covalent Bonding is made from….
Non-metals only
Atoms that are covalently bonded are called
molecules or molecular compounds
Properties of molecular compounds
Covalent bonds are weaker that ionic bonds. They have much lower melting and boiling points. Is a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature. Non-conductors in any state.
Molecular Formula
Indicates the exact makeup of one molecule
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
The electron pairs ( both shared and unshared) in the outermost energy level try to get as far apart from each other as possible (determines the shape)
Linear
central atom must have no unshared pair
Bent
Central atom can have one or two unshared pairs of electrons
Trigonal Planar
Central atom must have no unshared pairs
pyramid
Central atom has one unshared pair
Tetrahedral
Central atom has no unshared pairs
Trigonal Bipyramidal
central atom has no unshared pairs
For elements in period 3 and higher, when bonded to Cl or F, will have an expanded octet.
polar bond
bonds where the electrons are shared unequality between atoms. The atom that is more electronegative will pull the electrons closer to itself. When atoms are different, each has a different pull
Non-polar Bond
A bond where electrons are shared equally between atoms, due to similar electronegativity.
Polar rules
1. Different atoms around a central atom will always be polar molecules.
2. Same atoms around a central atom are always nonpolar molecules.
3. Unshared electron pairs count as different atoms.