Lecture 2: Self and Identity
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
the self
-a symbolic construct reflecting consciousness of our own identity and an awareness that we exist as a being, separate from other beings
Brewer & Gardner
-suggest there are many different forms of self and identity:
collective self
individual self
relational self
collective self (Brewer & Gardner)
-attributes shared with ingroup members and distinct from outgroup members
individual self (Brewer & Gardner)
-attributes that make us unique relative to other people
relational self (Brewer & Gardner)
-relationships one has with specific other people
Fazio
-found participants described themselves in different ways when asking them loaded questions that made them search through their self-knowledge for information that presented the self in different lights
Abrams & Hogg
-people experience different selves depending on situational factors
-yet also feel they have a coherent self-concept that integrates all their selves together
self awareness
-a psychological state in which people are aware of their traits, feelings and behaviours
Lewis & Brooks (self awareness in babies)
-put a spot of rouge on the nose of babies and put them in front of a mirror
-9-12 months treated the image as another child
-around 18 months recognised the reflection was themselves
public self-awareness
-when people are aware of how they appear to others
private self-awareness
-when people become aware of some aspects of themselves, but only in a private way
consequences of private self-awareness
intensified emotional response → focussing on the self makes us focus on our state of mind, intensifying our emotions
clarification of knowledge → focusing on internal events means we can report them with greater accuracy
adherence to personal standards of behaviour → true beliefs become emphasised and less susceptible to external forces
intensified emotional response (consequence of private self awareness)
-Scheier & Carver
-participants read aloud positive or negative statements whilst looking in a mirror or not
-participants who looked in the mirror during this task became more extreme in their emotional responses
clarification of knowledge (consequence of private self awareness)
-Gibbons
-participants were given a placebo and told it is a drug that would increase arousal
-were looking in a mirror or not
-those in front of the mirror experienced less arousal and side effects than those who could not see themselves
-mirror induced self-awareness → ignore placebo and focus on their feelings leading to more accurate knowledge
adherence to personal standards of behaviour (consequence of private self awareness)
-Scheier & Carver
-asked to write an essay that goes against their attitudes/beliefs
-were looking in a mirror or not
-induces cognitive dissonance
-writing the essay in front of the mirror → less attitude change
-private self-awareness may increase adherence to one’s true beliefs
consequences of public self awareness
evaluation apprehension
adherence to social standards of behaviour
evaluation apprehension (consequences of public self awareness)
-makes us realise we are being observed by others
-fear of negative evaluation → nervousness and reduced self esteem
-larger audiences increases anxiety during public speaking
adherence to social standards of behaviour (consequences of public self awareness)
-more likely to conform to group norms even if this goes against personal opinions
-Bateson examined the effect of an image of a pair of eyes on contributions to an honesty box
-people paid nearly three times as much when eyes were displayed rather than a control image
self-consciousness
-individual differences in chronic self-awareness is referred to as self-consciousness
-the extent to which an individual is chronically aware of their traits
privately self-consciousness
-experience more intense emotions
-greater tendency to suffer from depression and neuroticism, due to rumination on feelings of unhappiness
-act in line with personal beliefs
-less likely to suffer ill health due to noticing symptoms earlier
publicly self-consciousness
-concerned with others’ perceptions of them and so adhere to group norms
-avoid embarrassing situations
-more concerned with their appearance, and judge others according to appearance
self concept/knowledge
-the complete set of beliefs that people have about themselves, which form their understanding of who they are
-all hold a complex self-concept made up of a number of discrete self-schemas
self schemas
-how we expect ourselves to think, feel and behave in a particular situation
-consist of:
perception of ourselves
our experiences on this dimension
-self schemas vary in their importance to the self, in relation to a particular trait we may be: self-schematic, somewhat schematic or A-schematic
self-schematic (self schemas)
-traits that are highly important aspects of the self
somewhat schematic (self schemas)
-traits that describe the self to some extent
A-schematic (self schemas)
-traits which are irrelevant to the self
self schemas and well-being
-buffer against the impacts of negative self-schemas with more positive self schemas
-expands opportunities for social interaction, pleasure and personal growth
-with multiple schemas conflict can arise between self-schemas, leading to distress
theories of self
-theories of self comparison
self-discrepancy theory
-theories of social comparison
social comparison theory
-theories of group comparison
social identity theory
-inter-dependence theories
Michelangelo phenomenon
self-discrepancy theory (theory of self-comparison)
-Higgins
-the self consists of:
actual self → how we are at present
ideal self → how we would like to be
ought self → how we think we should be
-compare actual self to internalised standards of the ideal and ought self
-motivate to ensure match between actual, ideal and ought self
discrepancies (self-discrepancy theory)
-discrepancies between actual self and their ideal and ought self leads to psychological discomfort
-Higgins had participants think about the discrepancy between their actual and ideal self, vs their actual and ought self
actual-ideal discrepancy related to dejections
actual-ought discrepancy is related to agitation
Altintas - method (self-discrepancy theory)
experimental group → think of their best possible ideal self
control group → read neutral information
Altintas - results (self-discrepancy theory)
-those in the experimental group had significantly higher levels of positive affect, motivation and academic commitment compared to the control group
-discrepancies can have positive effects and motivate people to do better
social comparison theory
-Festinger
-we define the self by comparing ourselves to others
-we make upward and downward social comparisons
Klein - method (social comparison theory)
-participants asked to select the aesthetically superior picture
-given feedback about their performance
absolute (40 or 50% correct response)
relative to other people (20% better or worse on average)
-then given a choice of two tasks: a game of skill or a game of luck to win money
Klein - results (social comparison theory)
-more likely to choose a game of luck when given relative feedback → due to leading a negative self perception
Tafjel & Turner (social identity theory)
-social identity is the part of the individual’s self concept which derives from their knowledge of their membership of a social group together with the value and emotional significance of that membership
multiple social identities (social identity theory)
-can help prevent negative psychological outcomes and promote health
-provides more ways for a person to self-protect
-linked to lower depression
context dependent social identities (social identity theory)
-active at a given time and suit the social context
-some of our social identities may be contradictory
social identity theory (theory of group comparison)
-social world is perceived in categories which are themselves socially constructed
-we each belong to some categories and not others
-we discriminate between those categories in a way which is beneficial to our self esteem and our identity
-to achieve positive self esteem related to our group membership it requires social comparison to a group of lower status
-in group favouritism increases our self-esteem
Levine - method (social identity theory)
-recruited Manchester United fans
-directed to take a short walk during which they witness an accident
-group membership manipulated → confederate was either wearing a MU, LFC or plain top
-measured rate of helping confederate
Levine - results (social identity theory)
-helping behaviour increased for in group members
-more likely to help confederate in MU top than LFC or plain top
Levine - method of second study (social identity theory)
-same method as study 1
-told they are taking part in a study about being football fans
-focussing on the positives of being a football fan
-measured helping behaviour to confederate
Levine - results of second study (social identity theory)
-equally likely to help both football fans
-those wearing a plain sports top were less likely to be helped
-helping behaviour is influenced by the most salient identity at the time
interdependence theories
-look at the role of other people and how they ‘shape’ who we are or would like to become
ideal self
-describes an individual’s dreams and aspirations, or the constellation of skills, traits and resources that an individual ideally wishes to acquire
Michelangelo phenomenon (interdependence theories)
-close partners can sculp our ideal self
-the idea of the partner as the ‘sculptor’ and the ideal self as the ‘sculpted’
-how significant others shape our pursuit of the ideal self
Rusbult (Michelangelo phenomenon)
-significant others can shape individual selves through partner affirmation which has two components:
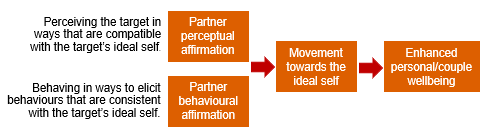
evidence for Michelangelo phenomenon
Rusbult found that partner affirmation of each other’s ideal goals is related to personal growth and movement towards the ideal self and partner well-being
Drigotas found strong associations between perceived partner affirmation and movement towards the ideal self
when the partner is affirming and the person moves closer to their ideals, this leads to improved personal wellbeing, life satisfaction and psychological health
self-esteem
-evaluative component of self-concept
-subjective appraisal of themselves as intrinsically positive or negative to some degree
-can vary depending on the context we find ourselves in
development of self esteem
-depends to some extent on parenting styles of primary caregivers
authoritative → enforce rules, disciplining but also responsive, supportive and warm → high self-esteem
authoritarian → overly strict and demanding, unresponsive to child’s needs → low self-esteem
permissive → responsive but too relaxed, no restrictions/boundaries → low self-esteem
stability of self-esteem
-Robin
-meta analysis of 50 studies
9-18 → fairly unstable self-esteem, adolescence and self-concept still developing
20-40s → greatest stability
60 → self esteem stability declines, perhaps due to later life changes
consequences of low self esteem
-mood regulation and mental health, actively dampen positive feelings
-feel worse after a negative event
-make fewer goals and plans to improve mood after failure
-associated with higher levels of depression and anxiety and lower mental wellbeing
consequences of high self-esteem
-narcissism
-unstable/fragile and reliant on validation from others
self-motives
-we are motivated to carry out
self assessment → desire to know ourselves
self-verification → verify what we already believe to be true about our self concept
self-enhancement → desire to seek information that allows us to see ourselves in the best light
self-affirmation theory (strategy to enhance the personal self)
-respond to threatened self esteem by publicly affirming positive aspects of the self
Steele - method (self-affirmation theory)
-mormons received the following messages:
threatening self-concept
irrelevant threat
no threat
Steele - results (self-affirmation theory)
-self-esteem threat → 95% agreed to help two days later to assist with a community project
-self-affirmation as a way of self-enhancement
self-serving attribution bias (strategies to enhance the self)
-we interpret events in a manner that is favourable to our view of ourselves
-success is attributed to internal characteristics
-failures attributed to external characteristics
-memory for self-enhancing information
social group membership (strategies to enhance the social self)
-self-enhancement through social group membership
-University football team winning matches → increase in students wearing clothing with university name
-people derive a positive self-concept from the achievements of other group members even if they were not personally instrumental → basking in reflected glory
negative image of social group membership (social group membership)
-social group membership can reflect a negative image and constitute a threat to social and personal identity
-to maintain a positive self-esteem can:
leave the group
remain and attempt to alter status of the group
-social creativity to find new dimensions on which the group compares more favourably