Special Senses: The Eye 1/2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Photoreceptors
Cells capturing light stimuli for vision.
1. Anterior chamber
2. Posterior chamber
3. Aqueous humor
4. Pupil connects the chambers
What is contained in the anterior cavity of the eye?
Contains the vitreous body (CT)
and vitreous humor
What is contained in the posterior cavity (vitreous cavity)?
Surrounded by retina
(posterior to the lens and zonula fibers)
What is the vitreous cavity surrounded by?
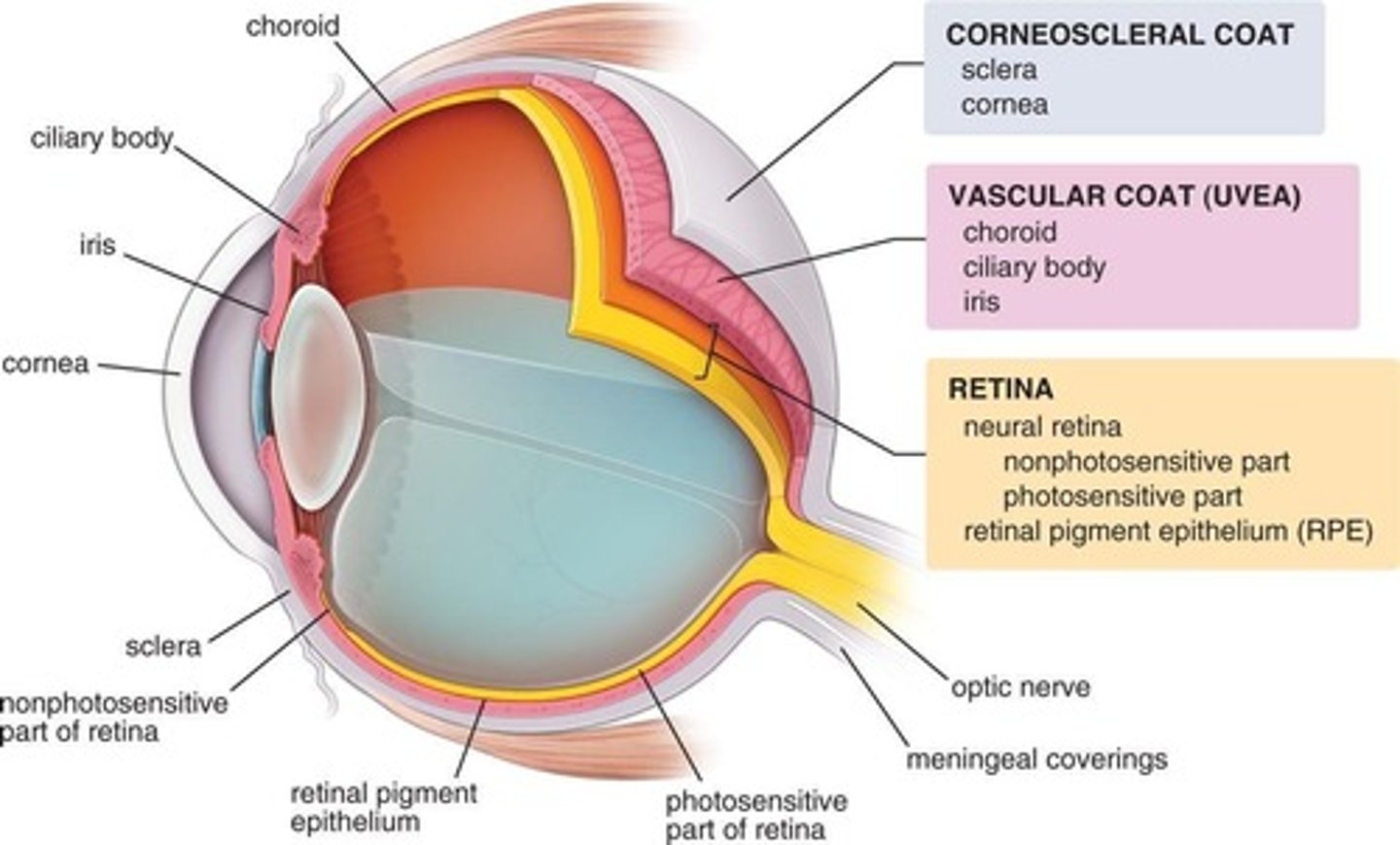
Fibrous Tunic (Corneosclera)
Outermost layer of the eyeball. Includes sclera + cornea
Episclera
Sclera proper
Suprachroid lamina (lamina fusca)
3 layers of sclera in order from outermost to innermost?
Mnoemnic for sclera layer
Every Strong Layer Forms"
Episclera – Sclerap proper – Lamina Fusca
Thin layer, abundant microvasculature, and loose CT.
Fibroblasts, macrophages, and lymphocytes.
The outermost layer of sclera (episclera) has what characteristics?
Dense connective tisssue
The episclera has loose connective tissue, while the scleara proper has ? (CT)
Sclera proper
Contains type 1 collagen and is avascular
Suprachroid lamina (lamina fusca)
Has less collagen, more fibroblasts, elastic fibers, and melanocytes
the cornea
What makes up the anterior 1/6 of the eye?
Cornea
Transparent, avascular, anterior part of the fibrous tunic.
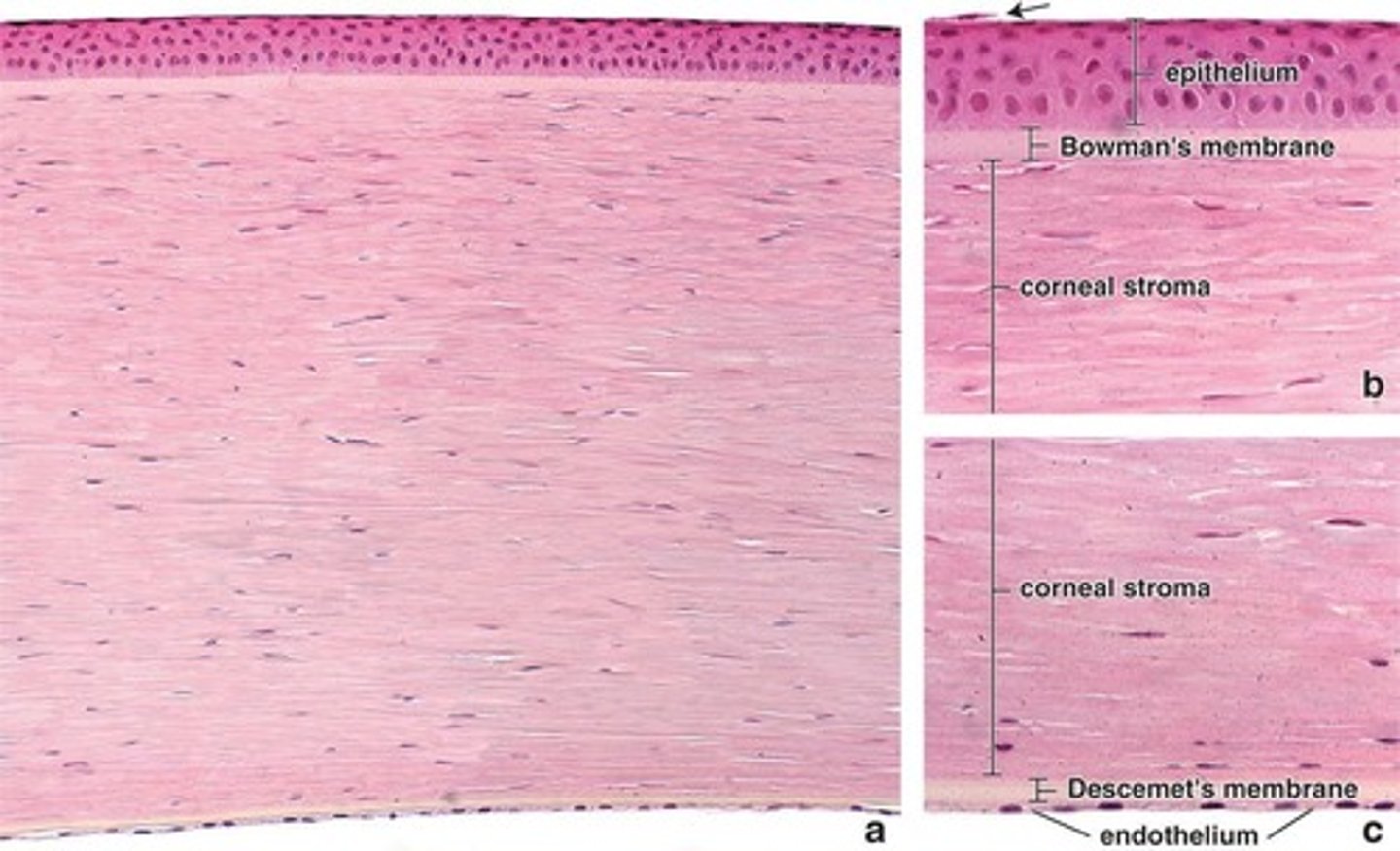
1. Corneal epithelium
2. Bowman's membrane
3. Corneal stroma
4. Descemet's membrane (posterior limiting membrane)
5. Corneal endothelium
Layers of the cornea?
Corneal Epithelium
Non-keratinized stratified squamous cells, protective layer.
the conjuctival epithelium*
The corneal epithelium is continous with what? *
Rich sensory nerve supply
the corneal epithelium has a rich supply of?
Bowman's Membrane
Thick basement membrane, supports cornea structure.
Protects stroma against infections
The bowman's membrane protects against?
at the limbus
where does Bowman's membrane end?
Corneal Stroma
Thickest layer of cornea (90%), also known as substance proprietary.
Collagen fibrils and sheets of flattened fibroblasts in between
The corneal stroma has lamellae that contains what substance?
Descemet's Membrane
Basement membrane of endothelium. (endothelium rests on this membrane)
Corneal Endothelium
Simple squamous layer, maintains Descemet's membrane.
Corneal endothelium
Where do you find cells that are the most metabolically active cells of the cornea? *
Through Na+K+ ATPase pumps
How does the corneal endothelium regulate hydration of the corneal stroma?
A:Bowman's membrane
P: Descemet's membrane (it is thinner than Bowman's)
What is the anterior limiting membrane? posterior limiting membrane?
E – Epithelium (outermost layer)
B – Bowman's layer
S – Stroma (thickest layer)
D – Descemet’s membrane
E – Endothelium (innermost layer)
"Eager Boys Slide Down Easily"
Limbus
Transition zone between cornea and sclera. Encircles the cornea
The conjunctiva
When the surface of limbus becomes more stratified what does it form?
It becomes vascular and less well-organized
How does the stroma change in the limbus?
trabecular meshwork
In the limbus, what structure replaces the endothelium and descemet's membrane?
Trabecular meshwork
Allow slow and continuous drainage of aqueous humor
Schlemm canal (scleral venous sinus)
Channels of the meshwork convey aqueous humor to the _______ ________ ?
Uvea
What is the most vascular layer of the eye?
Choroid (posterior)
Ciliary body
Iris (anterior)
3 parts of the uvea include (vascular layer)
Choroid
Posterior 2/3 of the eye
Well vascularized, loose CT, with melanocytes
what type of tissue does the choroid have?
Choroidocapillary lamina (innermost)
Bruch membrane
What are the two layers of the choroid?
ciliary body
anterior expansion of uvula (vascular layer) that encirlces the lens
posterior to the limbus; b/t the iris and choroid
the ciliary body is posterior to the what
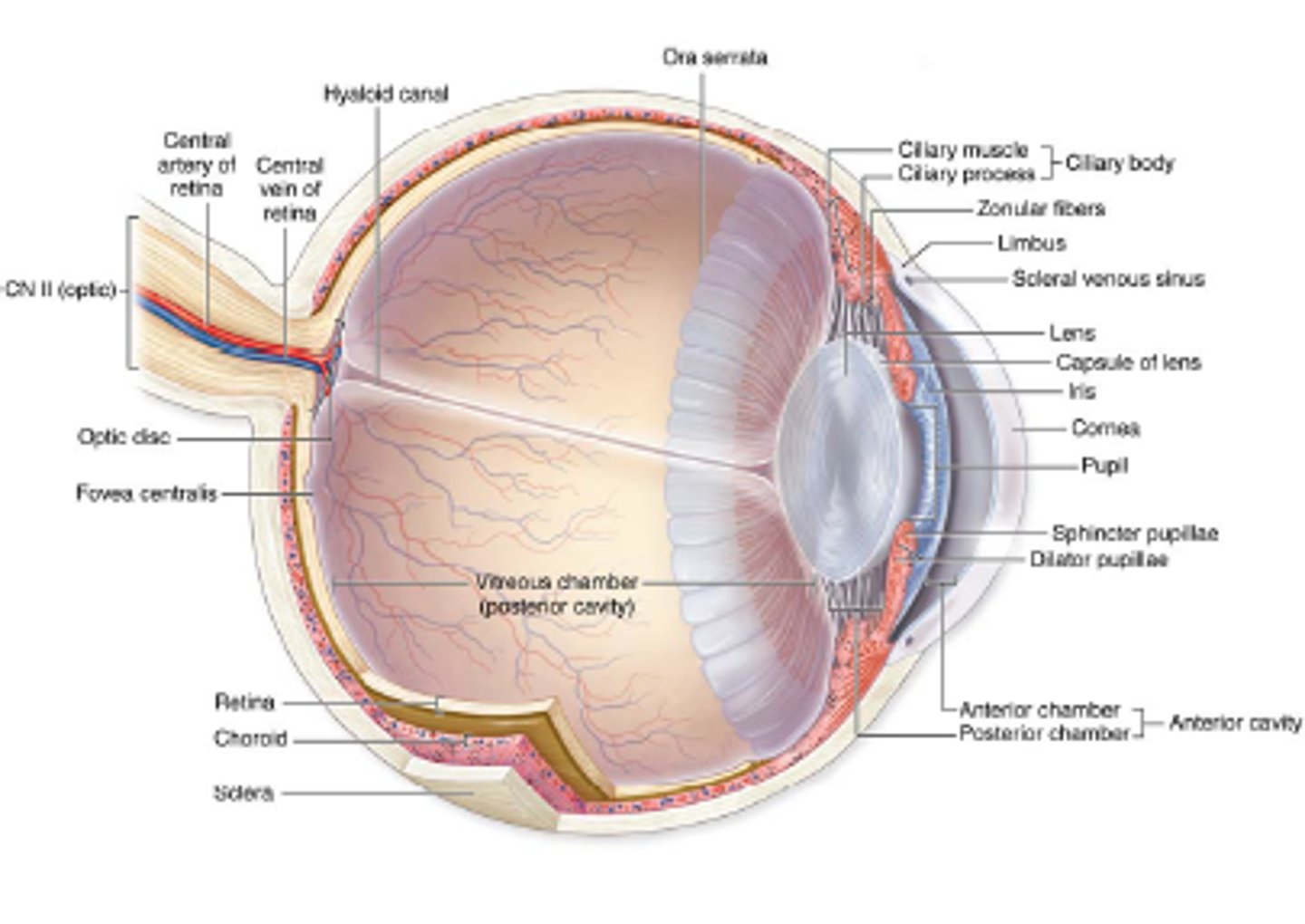
Ciliary muscle
Ciliary processes
Ciliary zonule
Three regions of the ciliary body:
Meridional or longitudinal portion
Radial or oblique portion
Circular or sphincteric portion
Three smooth muscle fibers in C. muscle:
Radial or oblique portion
Deep muscle fibers. Insert in the ciliary body
Flattening of the lens for distance vision (increases tension)
Contraction of the radial/oblique portion leads to:
Circular or sphincteric portion
Inner bundle muscle fibers, circular arrangement
Thickening of the lens for near vision (reduces tension)
Contraction of the circular portion leads to:
Ciliary processes
Radially arranged series of 75 ridges that extend from vascular region of the CB
Stratified columnar epithelium (where aqueous humor is secreted)
The ciliary processes are covered by what type of epithelia?
The pigmented epithelium of the retina
The pigmented inner layer of the ciliary processes is continuous with:
Sensory layer of the retina
The superficial layer of ciliary processes is continuous with:
Superficial layer lacks melanin
What does the superficial layer of ciliary processes NOT have?
Fibrillin 1 and 2 that holds the lens in place
what type of fibrillin does the ciliary zonule contain?