structure and bonding
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Ionic Bonding
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Giant Ionic Lattice
A continuous structure in three dimensions formed of cations and anions arranged in a regular pattern.
Electrostatic Attractions
Strong attractions between positive and negative ions present in ionic compounds.
Delocalised Electrons
Electrons that are free to move throughout a metallic structure, allowing metals to conduct electricity.
Simple Molecular Structure (simple covalent)
A 3D structure held together by weak intermolecular forces, often resulting in low melting points.
Giant Covalent Lattice
A structure where atoms are bonded together by numerous strong covalent bonds in a repeating pattern.
Electrical Conductivity
The ability of a material to conduct electricity, which depends on the presence of mobile charge carriers
Bond Strength
Refers to the strength of the attractions between particles in different types of structures, affecting melting and conductivity.
Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
can conduct electricity when molten or in solution due to the mobility of ions.
Properties of Metals
high melting points
good electrical conductivity due to strong metallic bonding and delocalised electrons.
Weak Intermolecular Forces
Forces that hold simple molecular structures together, generally resulting in lower melting points than ionic or covalent compounds.
Mobile Charge Carriers
Charged entities, such as ions in ionic compounds or delocalised electrons in metals, that enable conductivity.
Acid
A substance that donates protons (H+) in a chemical reaction.
Base
A substance that accepts protons (H+) in a chemical reaction or produces hydroxide ions (OH-).
Salt
An ionic compound formed from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base.
Metallic Bonding
A type of chemical bonding that occurs in metals, characterized by a sea of delocalized electrons.
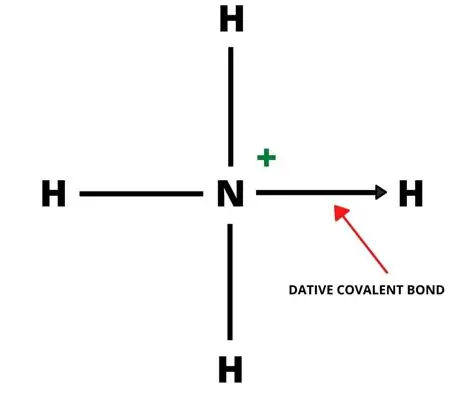
Dative Covalent Bond
A bond in which both shared electrons come from the same atom, also known as a coordinate bond.
Lone Pair
A pair of valence electrons that are not involved in bonding.
Bonding Pair
A pair of electrons that are shared between two atoms in a covalent bond.
what are the names of the regular shapes of structures and the num of bonding pairs each has ?
linear - 2 bp
trigonal planar - 3 bp
tetrahedral - 4 bp
octahedral - 6 bp
what does VSEPR tell us ?
eps in the valence shell repel each other as far apart as possible
lps repel more than bps
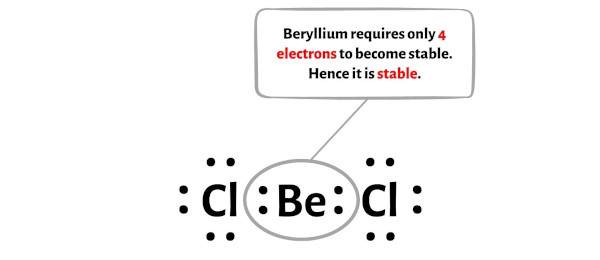
explain the shape of BeCl2
Be has 2 bps and no lps of electrons in its valence shell
eps repel each other as far apart as possible
the bond angle around Be is 180
linear shape
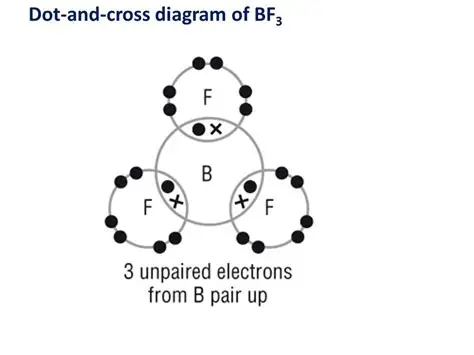
explain the shape of BF3
B has 3 bps and 0 lps of electrons in its valence shell
eps repel each other as far apart as possible
the bond angle around B is 120
trigonal planar shape
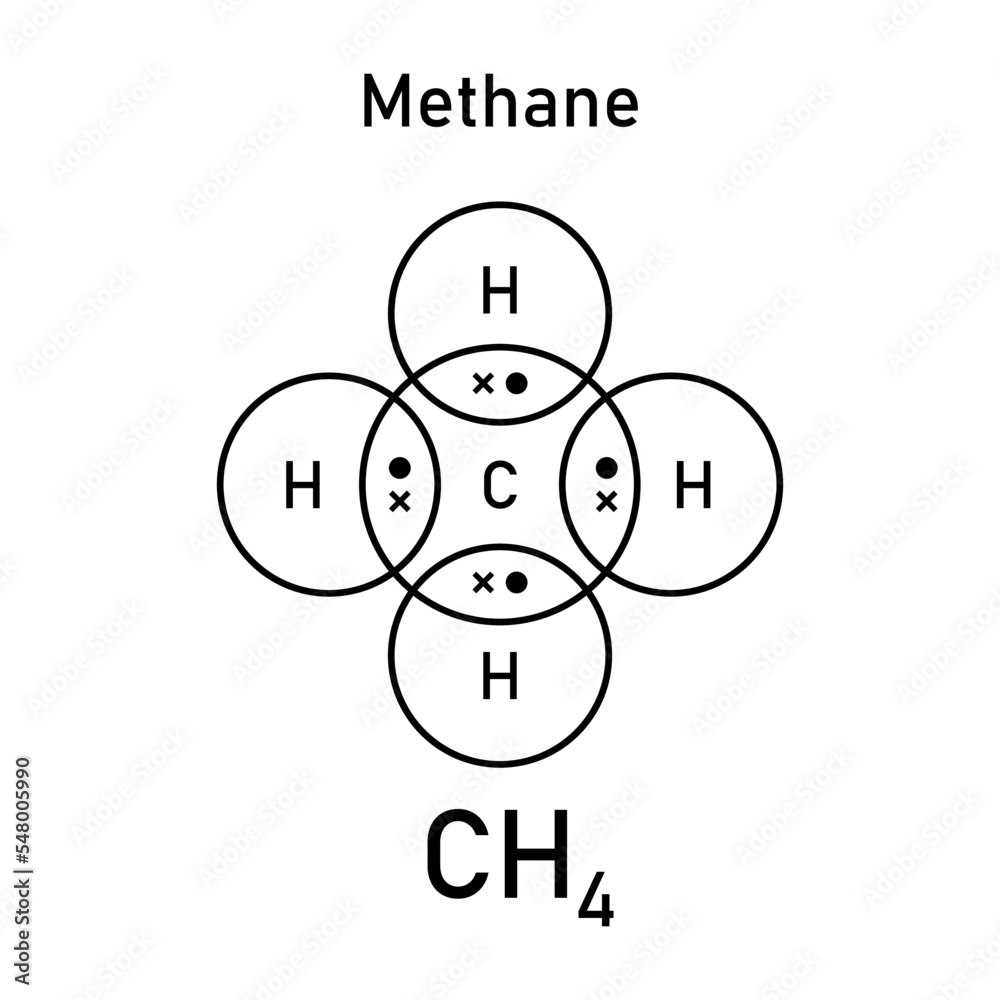
explain the shape of CH4
C has 4 bps and 0 lps of electrons in its valence shell
eps repel each other as far apart as possible
bond angle around C is 109.5
tetrahedral shape

explain the shape of SF6
S has 6 bps and o lps of electrons in its valence shell
eps repel each other as far apart as possible
bond angle around S is 90
octahedral shape
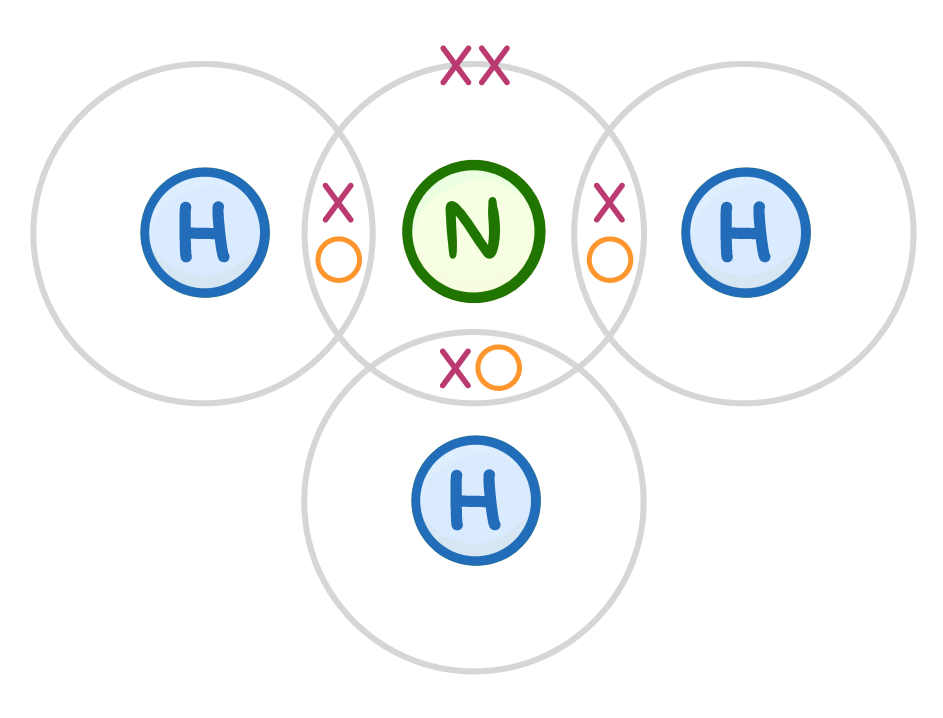
explain the shape of NH3
N has 3 bps and 1 lp of electrons in its valence shell
eps repel each other as far apart as possible but lps repel 2.5 more than bps
bond angle around N is 107 - 2.5 less than tetrahedral
pyramidal shape

explain the shape of of H2O
O has 2 bps and 2 lps of electrons in its valence shell
eps repel each other as far apart as possible but lps repel more
bond angle around O is 104.5 - 5 less than a tetrahedral
non linear shape
when trying to work out the shape of a molecule what do u do w/ double or triple bonds ?
count them as a single bonding region
electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract bps of electrons in a covalent bond
incs as u go up and across the table
in electronegativity which bond is the only exception ?
the C-H bond which is considered non polar
how is electronegativity measured ?
the pauling scale
if the difference between the electronegativity values is :
0 = non polar covalent
between 0 and or equal to 1.8 = polar covalent
>1.8= ionic
what are the factors affecting electronegativity ?
nuclear charge
atomic radius
shielding
atomic attraction
trend across a period in electronegativity ?
electronegativity incs
nuclear charge incs
atomic radius decs
so stronger attraction between nucleus and bp of electrons
is H2O a polar or no polar molecule and why ?
it has an asymmetrical structure bcs one area has more es than another
it has polar bonds
polar molecule therefore dipoles do not cancel out
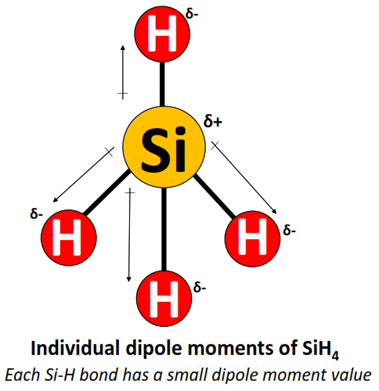
is SiH4 a polar or non polar molecule and why ?
its electrons directions are not around the central atom so its symmetrical
has polar bonds but the the dipoles cancel out so its a non polar molecule
having an asymmetrical structure makes a molecule ?
polar
having a symmetrical structure makes a molecule ?
non polar
to be polar a molecule must ….
have polar bonds and be asymmetrical
structure of diamond ?
giant covalent lattice
each c atom bonded to 4 others
high mp
tetrahedral shape
rigid and hard
not conductor
strong covalent bonds
graphite structure
giant covalent lattice
strong covalnt bonds within layers but weak ldn forces between layers
each c atom bonded to 3 others
lubricant
conductor
graphene
single 2d sheets of graphite
one atom thick
hexagonal c rings form lightweight materials
conductor
what are D block elements ?
elements w/ valence electrons in the d subshell
what are transition elements ?
elements forming one or more ions w/ incomplete d subshells
are all d block elements transition metals?
no bcs Sc and Zn form ions with empty or complete d subshells e.g. Sc3+ or Zn2+