Ultrasound physics Ch 3 (Describing Sound Waves)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
The source of a sound wave is the
ultrasound system and transducer
The tissue through which sound is traveling through is also called the
medium
The following describes:
. the time it takes a wave to vibrate a single cycle
. the time from the start of one cycle to the start of the next cycle
Period
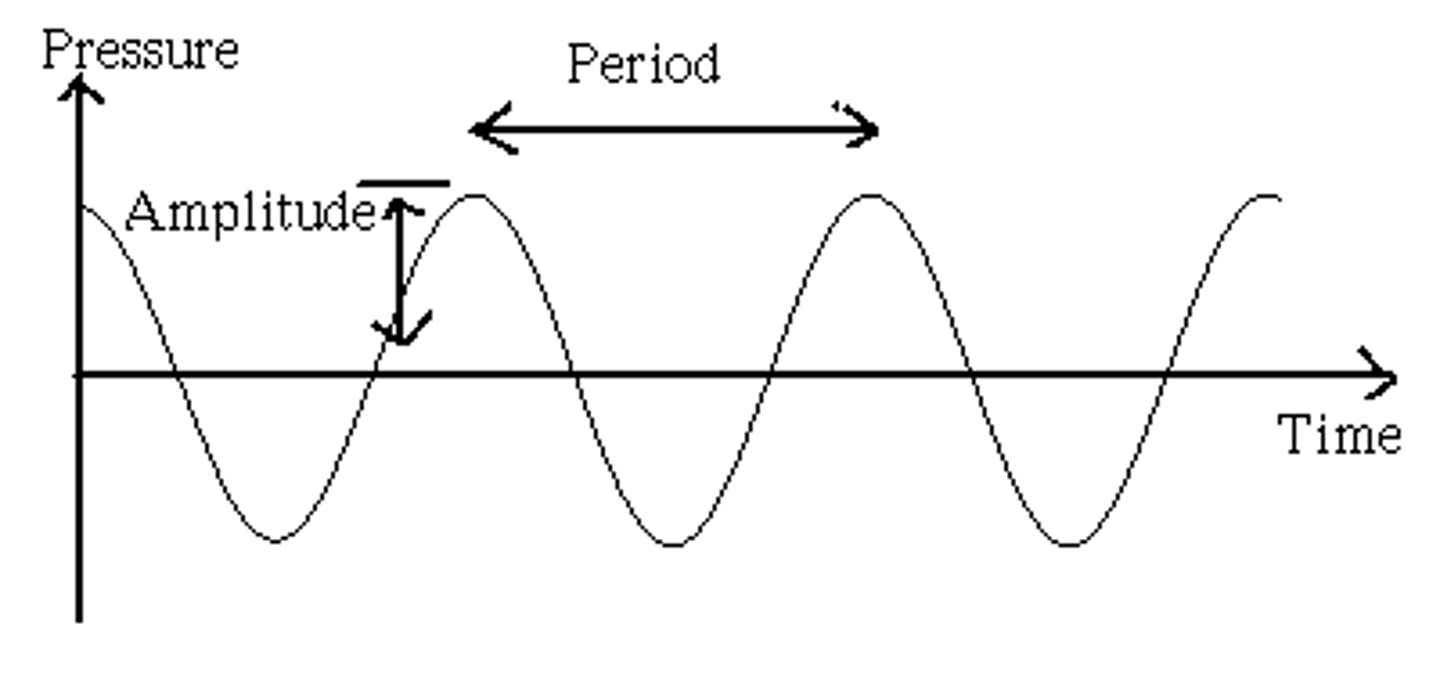
period is reported in units of
time, such as microseconds, seconds, hours, or days.
The typical value of period in diagnostic ultrasound is ________.
0.06 to 0.5 microseconds
6x10^-8 to 5x10^-7
Is period determined by the sound source or the medium?
determined by the sound source only
Can the sonographer the period?
no
The following describes:
. the number of particular events that occur in a specific duration
. the number of cycles that occurs in one second
frequency
Frequency is reported in units of
per second, 1/second, hertz, or Hz
1 cycle/second is
1 hertz
1,000 cycles/second is
1 kHz
1,000,000 cycles/second is
1 MHz
frequency ranges from approximately
2 MHz to 15 MHz (2 million to 15 million per second)
What is frequency of a sound wave determined by?
Sound source only
Can a sonographer change the frequency?
No
infrasound, which is below human hearing, is
less than 20 Hz
Audible, sound humans can hear, is
between 20 Hz and 20 kHz
Ultrasound, frequencies so high humans can't hear it, is
greater than 20 kHz (20,000 Hz)
What type of relationship do period and frequency have?
inverse relationship
These 3 parameters describe the size, magnitude, or strength of a sound wave
1. amplitude
2. power
3. intensity
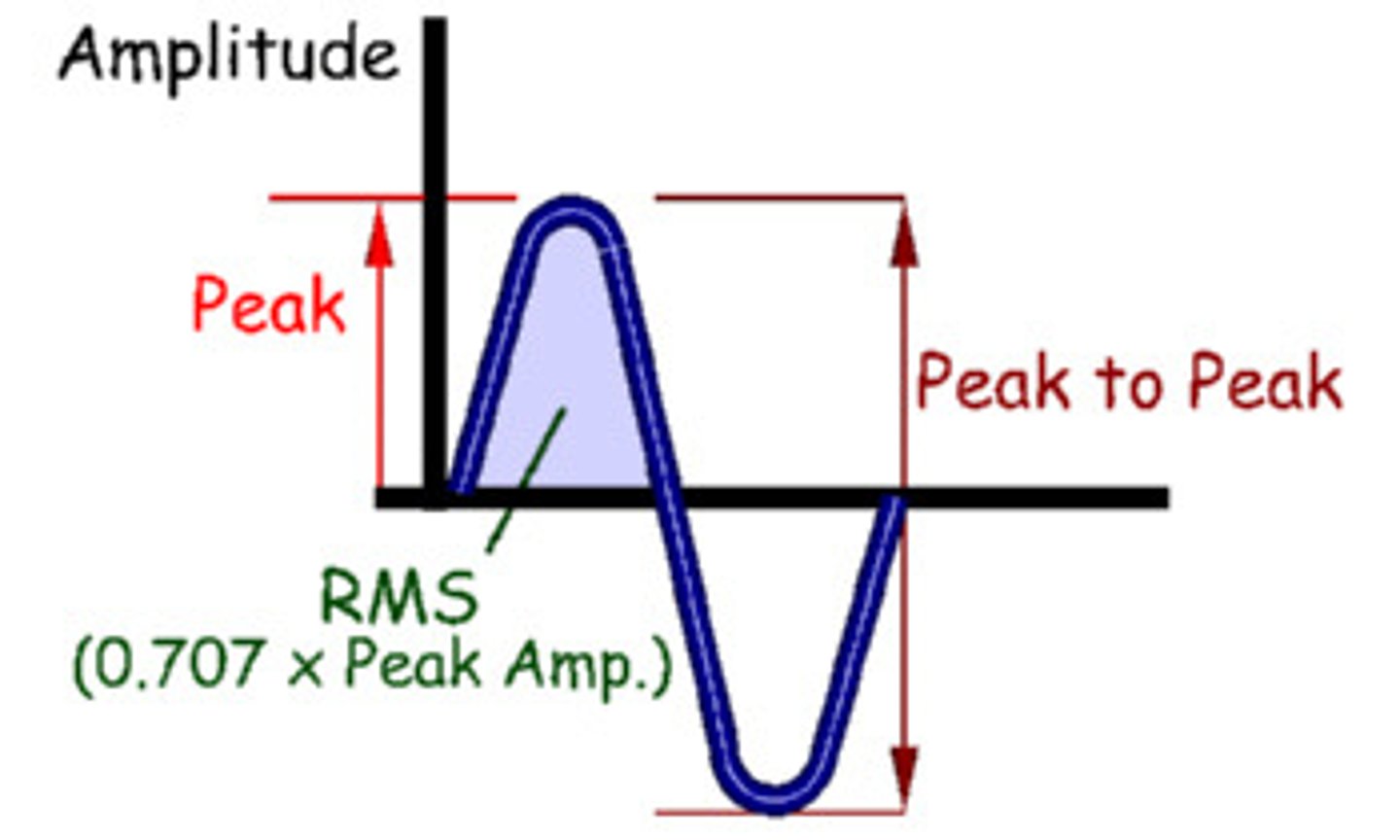
The following describes:
. difference between the maximum value and average or undisturbed value of an acoustic variable
. the difference between the minimum value and average value of the acoustic variable
amplitude
amplitude can have units of any of the acoustic variables
pressure- pascals
density- kg/cm^3
particle motion/distance- cm, inches
temperature- Fahrenheit, Celsius
decibels, dB
pressure amplitude ranges from
1 million pascals (1 MPa) to 3 million pascals (3 MPa)
Initially, amplitude is determined only by
sound source
Can the initial amplitude of a wave be changed by a sonographer?
yes
Amplitude is measured from....
the middle value to the maximum value
peak to peak amplitude is
the difference between maximum and minimum values, it is twice the value of the amplitude
The following describes:
the rate of energy transfer or the rate at which work is performed
Power
The units of power is
watts
Power ranges from
0.004 to 0.090 watts
Initial power is determined by
sound source
Can the sonographer change the initial power of a wave?
yes
How is power related to amplitude?
power is proportional to amplitude squared
The following describes:
. the concentration of energy in a sound beam
. relates to power in a wave spreads or is distributed in space
. depends on both the power in a beam and the area over which the power is applied
Intensity
The units of intensity are
watts/square centimeter
The equation used to calculate intensity is
power divided by area
Power is initially determined by
sound source
Can the sonographer change the initial intensity of a wave?
yes
What is the relationship between power and intensity?
power is proportional to intensity
What is the relationship between intensity and amplitude?
Intensity is proportional to amplitude squared
The following describes:
. the distance or length of one complete cycle
wavelength
What are the units of wavelength?
mm, meters, any units of length
Wavelength in soft tissue ranges from _______.
0.1 to 0.8 mm
Is wavelength determined by the sound source or the medium?
Wavelength is determined by both the sound source and the medium
Can the sonographer change wavelength?
no
As long as a wave remains in one medium, what is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
Wavelength and frequency are inversely related
What is the wavelength of 1MHz sound in soft tissue?
Sound with a frequency of 1MHz has a wavelength of 1.54mm
What is the equation used to find wavelength?
1.54mm/ microseconds divided by frequency (MHz)
Why is wavelength important in Image quality?
Shorter wavelengths from high frequency, producing higher quality images
The following describes:
. the rate at which a sound wave travels through a medium
propagation speed
Speed is measured in units of
meters per second or any distance divided by time
Depending on the tissue it is traveling through the speed of sound ranges from ________.
500 m/s to 4000 m/s
What is speed determined by?
medium only
Regardless of frequency, does all sound travel at the same speed through any specific medium if the medium is the same?
yes
Can speed be changed by the sonographer?
no
What is the speed of sound in soft tissue?
1540 m/s or 1.54 mm/microseconds or 1.54 km/s. (A mile a second).
The speed of sound in the lung tissue is?
500 m/s
The speed of sound in fat tissue is ?
1,450 m/s
the speed of sound in soft tissue (average) is?
1,540 m/s
The speed of sound in liver tissue is?
1,560 m/s
The speed of sound in blood is
1560 m/s
The speed of sound in muscle tissue is?
1,600 m/s
The speed of sound in tendon tissue is?
1,700 m/s
The speed of sound in bone tissue is?
3,500 m/s
the speed of sound in air is?
330 m/s
the speed of sound in water is?
1,480 m/s
the speed of sound in metals is?
2,000 to 7,000
What is the equation used to find speed is?
frequency times wavelength
What 2 characteristics of a medium affect the speed of sound?
stiffness and density
The following describes:
. the ability of an object to resist compression
stiffness
How are stiffness and speed related?
directly related
increased stiffness equals increased speed
What is another term for stiffness?
bulk modulus
What terms are the opposite of stiffness?
elasticity and compressibility
The following describes:
. the relative weight of a material
Density
How are density and speed related?
inversely related
increase density equals decreased speed
Does density or stiffness have a greater influence on speed?
stiffness